Richard Zemel
Let the Experts Speak: Improving Survival Prediction & Calibration via Mixture-of-Experts Heads
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Deep mixture-of-experts models have attracted a lot of attention for survival analysis problems, particularly for their ability to cluster similar patients together. In practice, grouping often comes at the expense of key metrics such calibration error and predictive accuracy. This is due to the restrictive inductive bias that mixture-of-experts imposes, that predictions for individual patients must look like predictions for the group they're assigned to. Might we be able to discover patient group structure, where it exists, while improving calibration and predictive accuracy? In this work, we introduce several discrete-time deep mixture-of-experts (MoE) based architectures for survival analysis problems, one of which achieves all desiderata: clustering, calibration, and predictive accuracy. We show that a key differentiator between this array of MoEs is how expressive their experts are. We find that more expressive experts that tailor predictions per patient outperform experts that rely on fixed group prototypes.
Confidence Calibration in Vision-Language-Action Models
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Trustworthy robot behavior requires not only high levels of task success but also that the robot can reliably quantify how likely it is to succeed. To this end, we present the first systematic study of confidence calibration in vision-language-action (VLA) foundation models, which map visual observations and natural-language instructions to low-level robot motor commands. We begin with extensive benchmarking to understand the critical relationship between task success and calibration error across multiple datasets and VLA variants, finding that task performance and calibration are not in tension. Next, we introduce prompt ensembles for VLAs, a lightweight, Bayesian-inspired algorithm that averages confidence across paraphrased instructions and consistently improves calibration. We further analyze calibration over the task time horizon, showing that confidence is often most reliable after making some progress, suggesting natural points for risk-aware intervention. Finally, we reveal differential miscalibration across action dimensions and propose action-wise Platt scaling, a method to recalibrate each action dimension independently to produce better confidence estimates. Our aim in this study is to begin to develop the tools and conceptual understanding necessary to render VLAs both highly performant and highly trustworthy via reliable uncertainty quantification.
Guiding LLM Decision-Making with Fairness Reward Models
Jul 15, 2025



Abstract:Large language models are increasingly used to support high-stakes decisions, potentially influencing who is granted bail or receives a loan. Naive chain-of-thought sampling can improve average decision accuracy, but has also been shown to amplify unfair bias. To address this challenge and enable the trustworthy use of reasoning models in high-stakes decision-making, we propose a framework for training a generalizable Fairness Reward Model (FRM). Our model assigns a fairness score to LLM reasoning, enabling the system to down-weight biased trajectories and favor equitable ones when aggregating decisions across reasoning chains. We show that a single Fairness Reward Model, trained on weakly supervised, LLM-annotated examples of biased versus unbiased reasoning, transfers across tasks, domains, and model families without additional fine-tuning. Applied to real-world decision-making tasks including recidivism prediction and social media moderation, we show that our approach consistently improves fairness while matching, or even surpassing, baseline accuracy.
Replay Can Provably Increase Forgetting
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Continual learning seeks to enable machine learning systems to solve an increasing corpus of tasks sequentially. A critical challenge for continual learning is forgetting, where the performance on previously learned tasks decreases as new tasks are introduced. One of the commonly used techniques to mitigate forgetting, sample replay, has been shown empirically to reduce forgetting by retaining some examples from old tasks and including them in new training episodes. In this work, we provide a theoretical analysis of sample replay in an over-parameterized continual linear regression setting, where each task is given by a linear subspace and with enough replay samples, one would be able to eliminate forgetting. Our analysis focuses on sample replay and highlights the role of the replayed samples and the relationship between task subspaces. Surprisingly, we find that, even in a noiseless setting, forgetting can be non-monotonic with respect to the number of replay samples. We present tasks where replay can be harmful with respect to worst-case settings, and also in distributional settings where replay of randomly selected samples increases forgetting in expectation. We also give empirical evidence that harmful replay is not limited to training with linear models by showing similar behavior for a neural networks equipped with SGD. Through experiments on a commonly used benchmark, we provide additional evidence that, even in seemingly benign scenarios, performance of the replay heavily depends on the choice of replay samples and the relationship between tasks.
Towards Safety Reasoning in LLMs: AI-agentic Deliberation for Policy-embedded CoT Data Creation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Safety reasoning is a recent paradigm where LLMs reason over safety policies before generating responses, thereby mitigating limitations in existing safety measures such as over-refusal and jailbreak vulnerabilities. However, implementing this paradigm is challenging due to the resource-intensive process of creating high-quality policy-embedded chain-of-thought (CoT) datasets while ensuring reasoning remains accurate and free from hallucinations or policy conflicts. To tackle this, we propose AIDSAFE: Agentic Iterative Deliberation for Safety Reasoning, a novel data generation recipe that leverages multi-agent deliberation to iteratively expand reasoning on safety policies. A data refiner stage in AIDSAFE ensures high-quality outputs by eliminating repetitive, redundant, and deceptive thoughts. AIDSAFE-generated CoTs provide a strong foundation for supervised fine-tuning (SFT)-based safety training. Additionally, to address the need of preference data in alignment stages, such as DPO training, we introduce a supplemental recipe that uses belief augmentation to create distinct selected and rejected CoT samples. Our evaluations demonstrate that AIDSAFE-generated CoTs achieve superior policy adherence and reasoning quality. Consequently, we show that fine-tuning open-source LLMs on these CoTs can significantly improve safety generalization and jailbreak robustness while maintaining acceptable utility and over-refusal accuracy. AIDSAFE-generated CoT datasets can be found here: https://huggingface.co/datasets/AmazonScience/AIDSAFE
Adaptive Elicitation of Latent Information Using Natural Language
Apr 05, 2025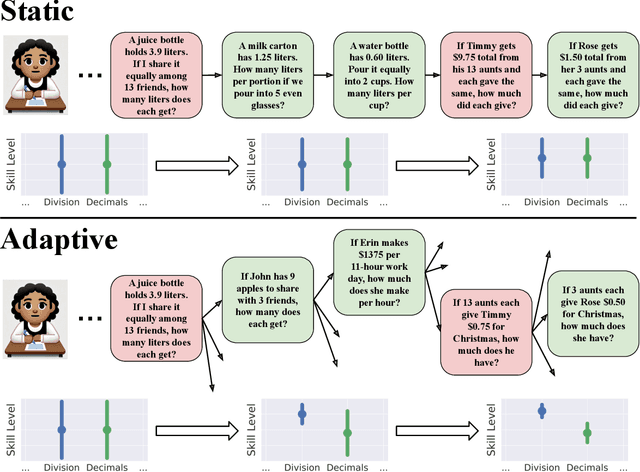
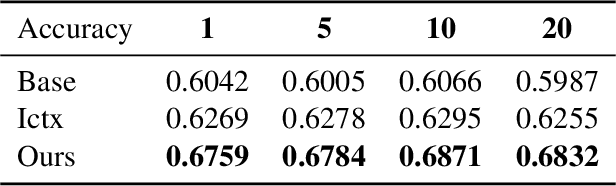
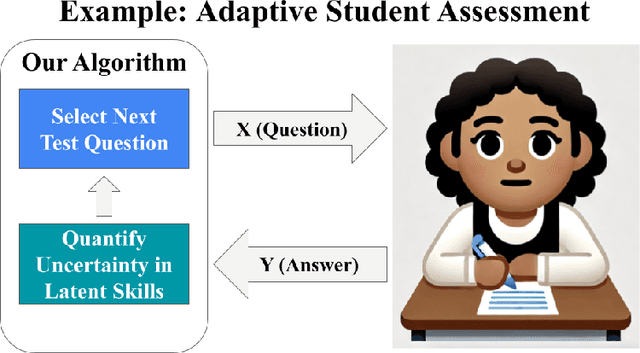

Abstract:Eliciting information to reduce uncertainty about a latent entity is a critical task in many application domains, e.g., assessing individual student learning outcomes, diagnosing underlying diseases, or learning user preferences. Though natural language is a powerful medium for this purpose, large language models (LLMs) and existing fine-tuning algorithms lack mechanisms for strategically gathering information to refine their own understanding of the latent entity. To harness the generalization power and world knowledge of LLMs in developing effective information-gathering strategies, we propose an adaptive elicitation framework that actively reduces uncertainty on the latent entity. Since probabilistic modeling of an abstract latent entity is difficult, our framework adopts a predictive view of uncertainty, using a meta-learned language model to simulate future observations and enable scalable uncertainty quantification over complex natural language. Through autoregressive forward simulation, our model quantifies how new questions reduce epistemic uncertainty, enabling the development of sophisticated information-gathering strategies to choose the most informative next queries. In experiments on the 20 questions game, dynamic opinion polling, and adaptive student assessment, our method consistently outperforms baselines in identifying critical unknowns and improving downstream predictions, illustrating the promise of strategic information gathering in natural language settings.
Towards Effective Discrimination Testing for Generative AI
Dec 30, 2024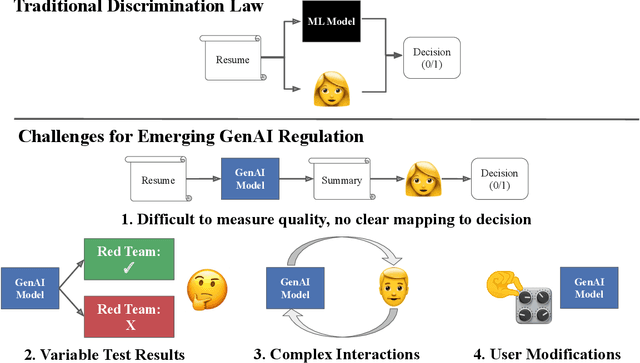

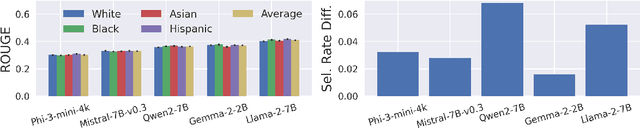
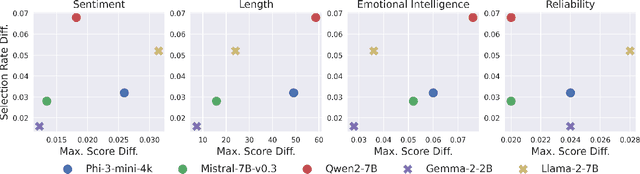
Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) models present new challenges in regulating against discriminatory behavior. In this paper, we argue that GenAI fairness research still has not met these challenges; instead, a significant gap remains between existing bias assessment methods and regulatory goals. This leads to ineffective regulation that can allow deployment of reportedly fair, yet actually discriminatory, GenAI systems. Towards remedying this problem, we connect the legal and technical literature around GenAI bias evaluation and identify areas of misalignment. Through four case studies, we demonstrate how this misalignment between fairness testing techniques and regulatory goals can result in discriminatory outcomes in real-world deployments, especially in adaptive or complex environments. We offer practical recommendations for improving discrimination testing to better align with regulatory goals and enhance the reliability of fairness assessments in future deployments.
Improving Predictor Reliability with Selective Recalibration
Oct 07, 2024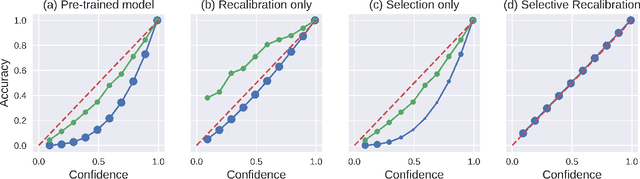
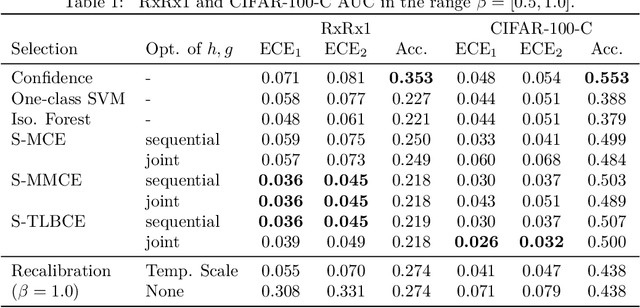
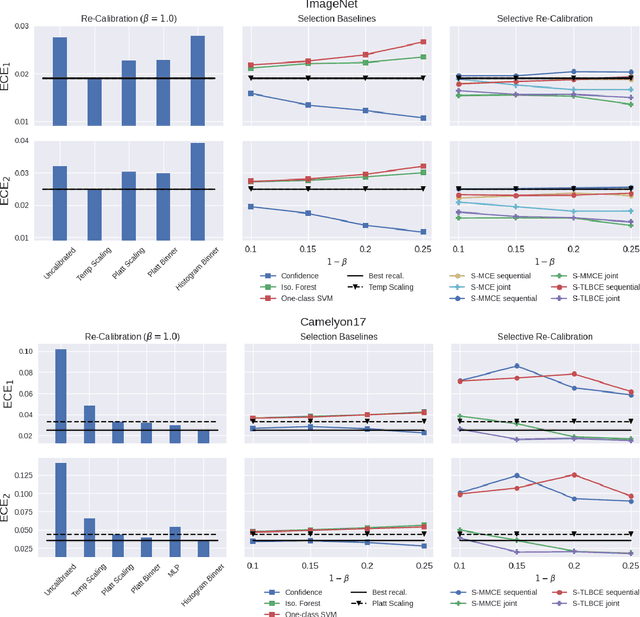
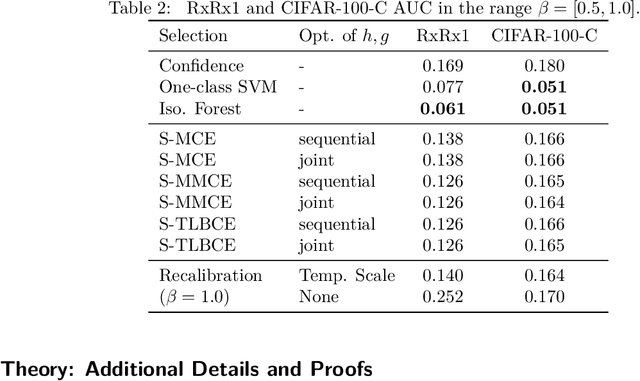
Abstract:A reliable deep learning system should be able to accurately express its confidence with respect to its predictions, a quality known as calibration. One of the most effective ways to produce reliable confidence estimates with a pre-trained model is by applying a post-hoc recalibration method. Popular recalibration methods like temperature scaling are typically fit on a small amount of data and work in the model's output space, as opposed to the more expressive feature embedding space, and thus usually have only one or a handful of parameters. However, the target distribution to which they are applied is often complex and difficult to fit well with such a function. To this end we propose \textit{selective recalibration}, where a selection model learns to reject some user-chosen proportion of the data in order to allow the recalibrator to focus on regions of the input space that can be well-captured by such a model. We provide theoretical analysis to motivate our algorithm, and test our method through comprehensive experiments on difficult medical imaging and zero-shot classification tasks. Our results show that selective recalibration consistently leads to significantly lower calibration error than a wide range of selection and recalibration baselines.
Attribute Controlled Fine-tuning for Large Language Models: A Case Study on Detoxification
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:We propose a constraint learning schema for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with attribute control. Given a training corpus and control criteria formulated as a sequence-level constraint on model outputs, our method fine-tunes the LLM on the training corpus while enhancing constraint satisfaction with minimal impact on its utility and generation quality. Specifically, our approach regularizes the LLM training by penalizing the KL divergence between the desired output distribution, which satisfies the constraints, and the LLM's posterior. This regularization term can be approximated by an auxiliary model trained to decompose the sequence-level constraints into token-level guidance, allowing the term to be measured by a closed-form formulation. To further improve efficiency, we design a parallel scheme for concurrently updating both the LLM and the auxiliary model. We evaluate the empirical performance of our approach by controlling the toxicity when training an LLM. We show that our approach leads to an LLM that produces fewer inappropriate responses while achieving competitive performance on benchmarks and a toxicity detection task.
Controlling the World by Sleight of Hand
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Humans naturally build mental models of object interactions and dynamics, allowing them to imagine how their surroundings will change if they take a certain action. While generative models today have shown impressive results on generating/editing images unconditionally or conditioned on text, current methods do not provide the ability to perform object manipulation conditioned on actions, an important tool for world modeling and action planning. Therefore, we propose to learn an action-conditional generative models by learning from unlabeled videos of human hands interacting with objects. The vast quantity of such data on the internet allows for efficient scaling which can enable high-performing action-conditional models. Given an image, and the shape/location of a desired hand interaction, CosHand, synthesizes an image of a future after the interaction has occurred. Experiments show that the resulting model can predict the effects of hand-object interactions well, with strong generalization particularly to translation, stretching, and squeezing interactions of unseen objects in unseen environments. Further, CosHand can be sampled many times to predict multiple possible effects, modeling the uncertainty of forces in the interaction/environment. Finally, method generalizes to different embodiments, including non-human hands, i.e. robot hands, suggesting that generative video models can be powerful models for robotics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge