Xinyan Zhao
Towards Safety Reasoning in LLMs: AI-agentic Deliberation for Policy-embedded CoT Data Creation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Safety reasoning is a recent paradigm where LLMs reason over safety policies before generating responses, thereby mitigating limitations in existing safety measures such as over-refusal and jailbreak vulnerabilities. However, implementing this paradigm is challenging due to the resource-intensive process of creating high-quality policy-embedded chain-of-thought (CoT) datasets while ensuring reasoning remains accurate and free from hallucinations or policy conflicts. To tackle this, we propose AIDSAFE: Agentic Iterative Deliberation for Safety Reasoning, a novel data generation recipe that leverages multi-agent deliberation to iteratively expand reasoning on safety policies. A data refiner stage in AIDSAFE ensures high-quality outputs by eliminating repetitive, redundant, and deceptive thoughts. AIDSAFE-generated CoTs provide a strong foundation for supervised fine-tuning (SFT)-based safety training. Additionally, to address the need of preference data in alignment stages, such as DPO training, we introduce a supplemental recipe that uses belief augmentation to create distinct selected and rejected CoT samples. Our evaluations demonstrate that AIDSAFE-generated CoTs achieve superior policy adherence and reasoning quality. Consequently, we show that fine-tuning open-source LLMs on these CoTs can significantly improve safety generalization and jailbreak robustness while maintaining acceptable utility and over-refusal accuracy. AIDSAFE-generated CoT datasets can be found here: https://huggingface.co/datasets/AmazonScience/AIDSAFE
FANTAstic SEquences and Where to Find Them: Faithful and Efficient API Call Generation through State-tracked Constrained Decoding and Reranking
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:API call generation is the cornerstone of large language models' tool-using ability that provides access to the larger world. However, existing supervised and in-context learning approaches suffer from high training costs, poor data efficiency, and generated API calls that can be unfaithful to the API documentation and the user's request. To address these limitations, we propose an output-side optimization approach called FANTASE. Two of the unique contributions of FANTASE are its State-Tracked Constrained Decoding (SCD) and Reranking components. SCD dynamically incorporates appropriate API constraints in the form of Token Search Trie for efficient and guaranteed generation faithfulness with respect to the API documentation. The Reranking component efficiently brings in the supervised signal by leveraging a lightweight model as the discriminator to rerank the beam-searched candidate generations of the large language model. We demonstrate the superior performance of FANTASE in API call generation accuracy, inference efficiency, and context efficiency with DSTC8 and API Bank datasets.
Tailoring Generative AI Chatbots for Multiethnic Communities in Disaster Preparedness Communication: Extending the CASA Paradigm
Jun 12, 2024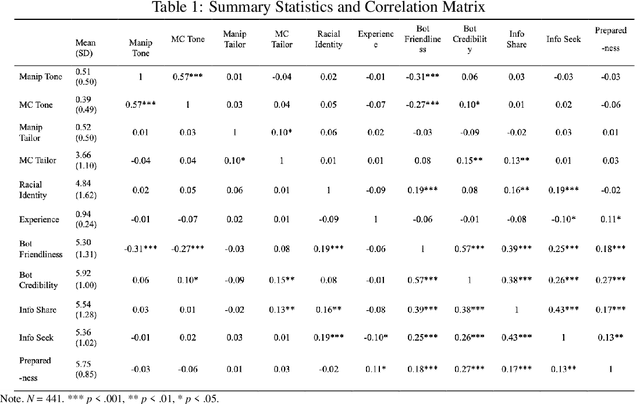
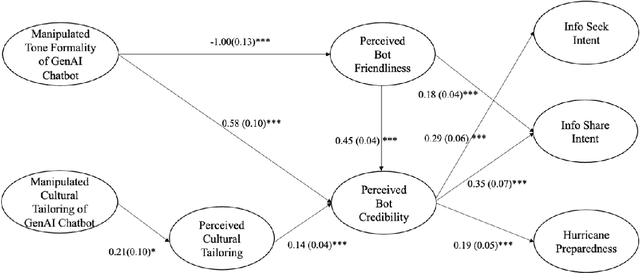
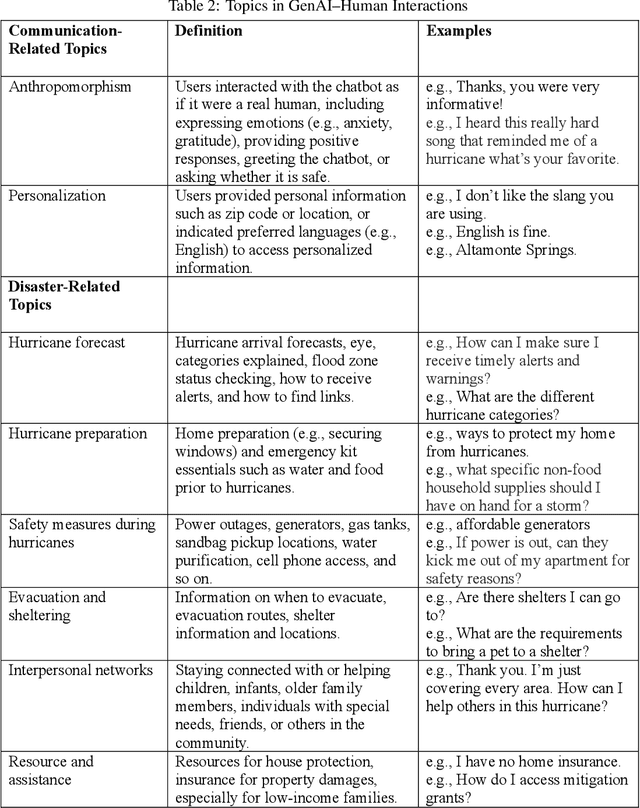
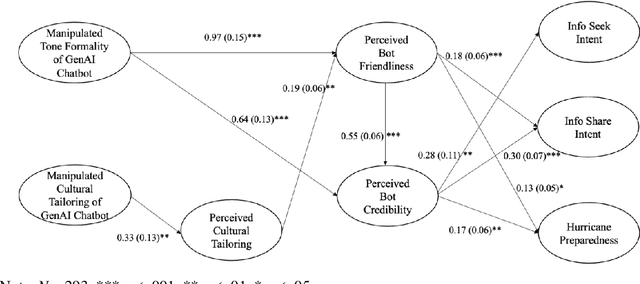
Abstract:This study is among the first to develop different prototypes of generative AI (GenAI) chatbots powered by GPT 4 to communicate hurricane preparedness information to diverse residents. Drawing from the Computers Are Social Actors (CASA) paradigm and the literature on disaster vulnerability and cultural tailoring, this study conducted a between-subjects experiment with 441 Black, Hispanic, and Caucasian residents of Florida. A computational analysis of chat logs (N = 7,848) shows that anthropomorphism and personalization are key communication topics in GenAI chatbot-user interactions. SEM results (N = 441) suggest that GenAI chatbots varying in tone formality and cultural tailoring significantly predict bot perceptions and, subsequently, hurricane preparedness outcomes. These results highlight the potential of using GenAI chatbots to improve diverse communities' disaster preparedness.
Multi-User MultiWOZ: Task-Oriented Dialogues among Multiple Users
Oct 31, 2023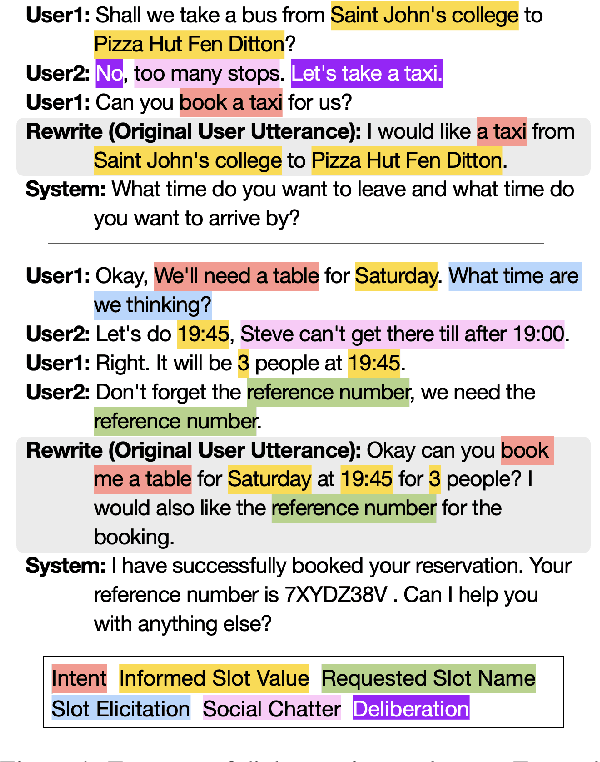
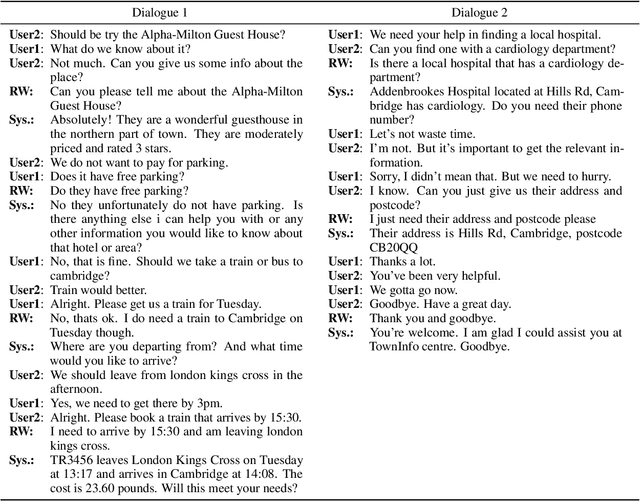
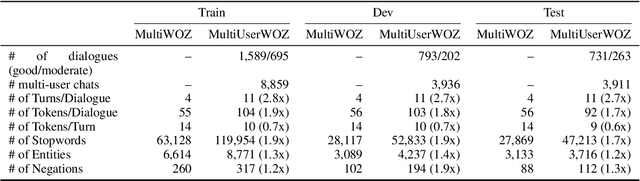
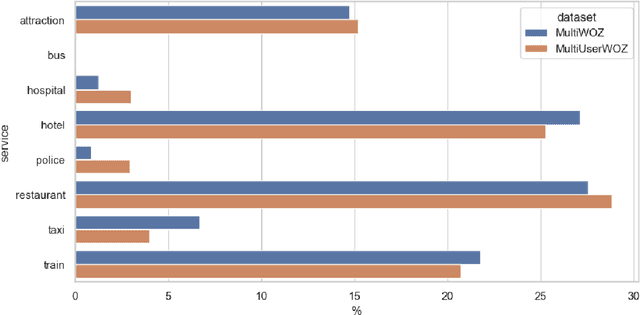
Abstract:While most task-oriented dialogues assume conversations between the agent and one user at a time, dialogue systems are increasingly expected to communicate with multiple users simultaneously who make decisions collaboratively. To facilitate development of such systems, we release the Multi-User MultiWOZ dataset: task-oriented dialogues among two users and one agent. To collect this dataset, each user utterance from MultiWOZ 2.2 was replaced with a small chat between two users that is semantically and pragmatically consistent with the original user utterance, thus resulting in the same dialogue state and system response. These dialogues reflect interesting dynamics of collaborative decision-making in task-oriented scenarios, e.g., social chatter and deliberation. Supported by this data, we propose the novel task of multi-user contextual query rewriting: to rewrite a task-oriented chat between two users as a concise task-oriented query that retains only task-relevant information and that is directly consumable by the dialogue system. We demonstrate that in multi-user dialogues, using predicted rewrites substantially improves dialogue state tracking without modifying existing dialogue systems that are trained for single-user dialogues. Further, this method surpasses training a medium-sized model directly on multi-user dialogues and generalizes to unseen domains.
PharmMT: A Neural Machine Translation Approach to Simplify Prescription Directions
Apr 08, 2022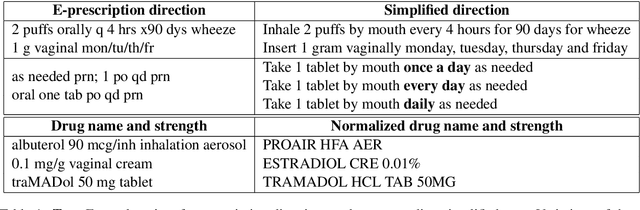
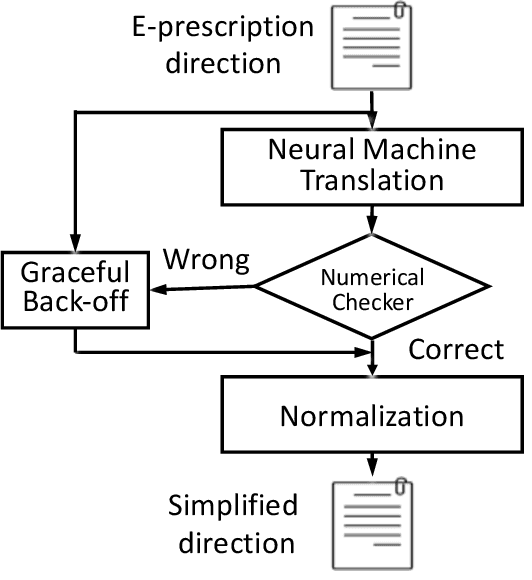
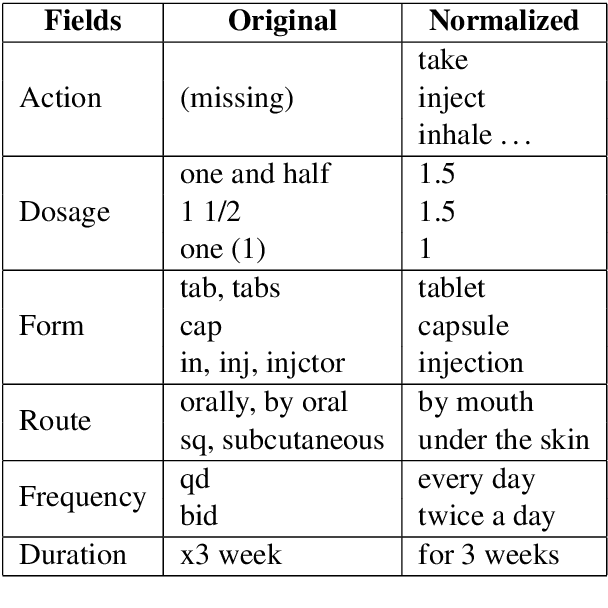
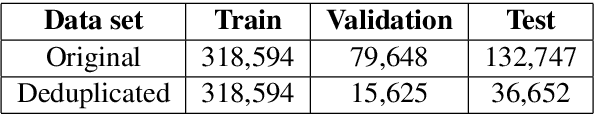
Abstract:The language used by physicians and health professionals in prescription directions includes medical jargon and implicit directives and causes much confusion among patients. Human intervention to simplify the language at the pharmacies may introduce additional errors that can lead to potentially severe health outcomes. We propose a novel machine translation-based approach, PharmMT, to automatically and reliably simplify prescription directions into patient-friendly language, thereby significantly reducing pharmacist workload. We evaluate the proposed approach over a dataset consisting of over 530K prescriptions obtained from a large mail-order pharmacy. The end-to-end system achieves a BLEU score of 60.27 against the reference directions generated by pharmacists, a 39.6% relative improvement over the rule-based normalization. Pharmacists judged 94.3% of the simplified directions as usable as-is or with minimal changes. This work demonstrates the feasibility of a machine translation-based tool for simplifying prescription directions in real-life.
* Findings of EMNLP '20 Camera Ready
UniDS: A Unified Dialogue System for Chit-Chat and Task-oriented Dialogues
Oct 15, 2021



Abstract:With the advances in deep learning, tremendous progress has been made with chit-chat dialogue systems and task-oriented dialogue systems. However, these two systems are often tackled separately in current methods. To achieve more natural interaction with humans, a dialogue agent needs to be capable of both chatting and accomplishing tasks. To this end, we propose a unified dialogue system (UniDS) with the two aforementioned skills. In particular, we design a unified dialogue data schema, compatible for both chit-chat and task-oriented dialogues, and we train UniDS with mixed dialogue data from a pretrained chit-chat dialogue model. Without adding extra parameters to SOTA baselines, UniDS can alternatively handle chit-chat and task-oriented dialogues in a unified framework. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed UniDS works comparably well as the pure chit-chat system, and it outperforms state-of-the-art task-oriented dialogue systems. More importantly, UniDS achieves better robustness as it is able to smoothly switch between two types of dialogues. These results demonstrate the feasibility and potential of building an one-for-all dialogue system.
GLaRA: Graph-based Labeling Rule Augmentation for Weakly Supervised Named Entity Recognition
Apr 13, 2021



Abstract:Instead of using expensive manual annotations, researchers have proposed to train named entity recognition (NER) systems using heuristic labeling rules. However, devising labeling rules is challenging because it often requires a considerable amount of manual effort and domain expertise. To alleviate this problem, we propose \textsc{GLaRA}, a graph-based labeling rule augmentation framework, to learn new labeling rules from unlabeled data. We first create a graph with nodes representing candidate rules extracted from unlabeled data. Then, we design a new graph neural network to augment labeling rules by exploring the semantic relations between rules. We finally apply the augmented rules on unlabeled data to generate weak labels and train a NER model using the weakly labeled data. We evaluate our method on three NER datasets and find that we can achieve an average improvement of +20\% F1 score over the best baseline when given a small set of seed rules.
Toward Effective Automated Content Analysis via Crowdsourcing
Jan 12, 2021
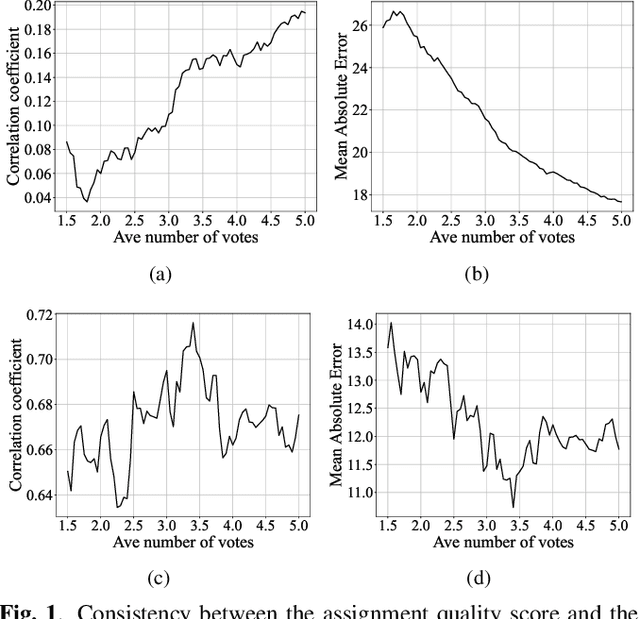


Abstract:Many computer scientists use the aggregated answers of online workers to represent ground truth. Prior work has shown that aggregation methods such as majority voting are effective for measuring relatively objective features. For subjective features such as semantic connotation, online workers, known for optimizing their hourly earnings, tend to deteriorate in the quality of their responses as they work longer. In this paper, we aim to address this issue by proposing a quality-aware semantic data annotation system. We observe that with timely feedback on workers' performance quantified by quality scores, better informed online workers can maintain the quality of their labeling throughout an extended period of time. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed annotation system through i) evaluating performance based on an expert-labeled dataset, and ii) demonstrating machine learning tasks that can lead to consistent learning behavior with 70%-80% accuracy. Our results suggest that with our system, researchers can collect high-quality answers of subjective semantic features at a large scale.
LIREx: Augmenting Language Inference with Relevant Explanation
Dec 16, 2020



Abstract:Natural language explanations (NLEs) are a special form of data annotation in which annotators identify rationales (most significant text tokens) when assigning labels to data instances, and write out explanations for the labels in natural language based on the rationales. NLEs have been shown to capture human reasoning better, but not as beneficial for natural language inference (NLI). In this paper, we analyze two primary flaws in the way NLEs are currently used to train explanation generators for language inference tasks. We find that the explanation generators do not take into account the variability inherent in human explanation of labels, and that the current explanation generation models generate spurious explanations. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel framework, LIREx, that incorporates both a rationale-enabled explanation generator and an instance selector to select only relevant, plausible NLEs to augment NLI models. When evaluated on the standardized SNLI data set, LIREx achieved an accuracy of 91.87%, an improvement of 0.32 over the baseline and matching the best-reported performance on the data set. It also achieves significantly better performance than previous studies when transferred to the out-of-domain MultiNLI data set. Qualitative analysis shows that LIREx generates flexible, faithful, and relevant NLEs that allow the model to be more robust to spurious explanations. The code is available at https://github.com/zhaoxy92/LIREx.
A Graph Based and Patient Demographics Aware Dialogue System for Disease Diagnosis
Oct 21, 2020



Abstract:A dialogue system for disease diagnosis aims at making a diagnosis by conversing with patients. Existing disease diagnosis dialogue systems highly rely on data-driven methods and statistical features, lacking profound comprehension of medical knowledge, such as symptom-disease relations. In addition, previous work pays less attention to demographic attributes of a patient, which are important factors in clinical diagnoses. To tackle these issues, this work presents a graph based and demographic attributes aware dialogue system for disease diagnosis. Specifically, we first build a weighted bidirectional graph based on clinical dialogues to depict the relationship between symptoms and diseases and then present a bidirectional graph based deep Q-network (BG-DQN) for dialogue management. By extending Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) to learn the embeddings of diseases and symptoms from both the structural and attribute information in the graph, BG-DQN could capture the relations between diseases and symptoms better. Moreover, BG-DQN also encodes the demographic attributes of a patient to assist the disease diagnosis process. Experimental results show that the proposed dialogue system outperforms several competitive methods in terms of diagnostic accuracy. More importantly, our method can complete the task with less dialogue turns and possesses better distinguishing capability on diseases with similar symptoms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge