Nikolaos Malandrakis
Multi-User MultiWOZ: Task-Oriented Dialogues among Multiple Users
Oct 31, 2023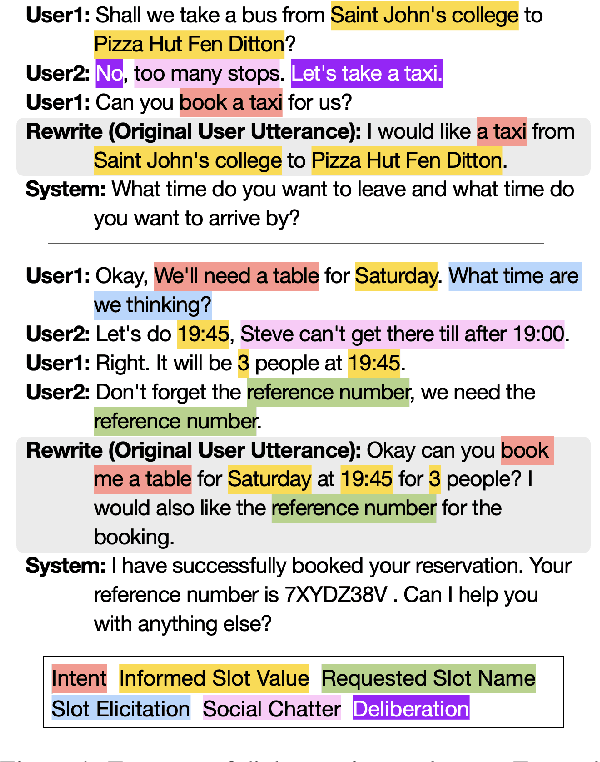
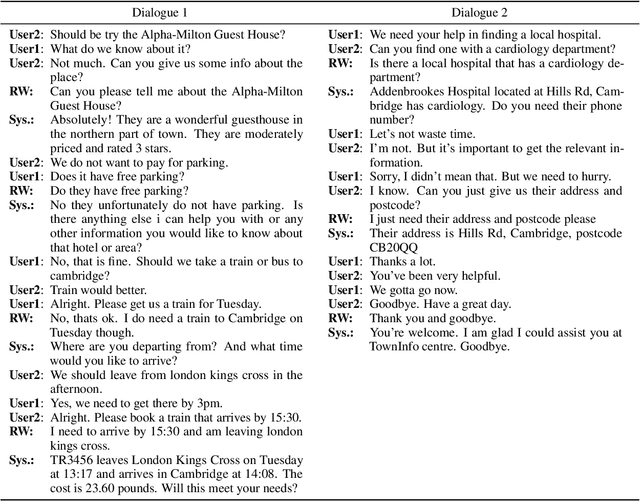
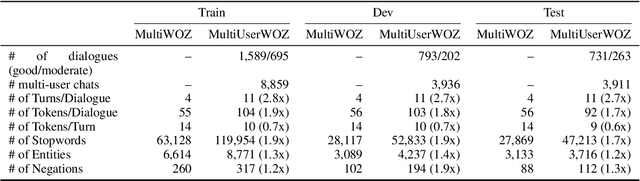
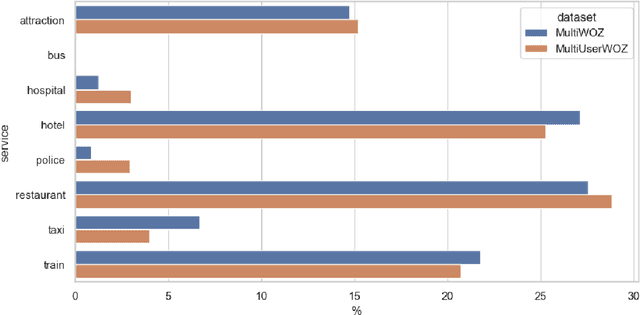
Abstract:While most task-oriented dialogues assume conversations between the agent and one user at a time, dialogue systems are increasingly expected to communicate with multiple users simultaneously who make decisions collaboratively. To facilitate development of such systems, we release the Multi-User MultiWOZ dataset: task-oriented dialogues among two users and one agent. To collect this dataset, each user utterance from MultiWOZ 2.2 was replaced with a small chat between two users that is semantically and pragmatically consistent with the original user utterance, thus resulting in the same dialogue state and system response. These dialogues reflect interesting dynamics of collaborative decision-making in task-oriented scenarios, e.g., social chatter and deliberation. Supported by this data, we propose the novel task of multi-user contextual query rewriting: to rewrite a task-oriented chat between two users as a concise task-oriented query that retains only task-relevant information and that is directly consumable by the dialogue system. We demonstrate that in multi-user dialogues, using predicted rewrites substantially improves dialogue state tracking without modifying existing dialogue systems that are trained for single-user dialogues. Further, this method surpasses training a medium-sized model directly on multi-user dialogues and generalizes to unseen domains.
Controlled Text Generation for Data Augmentation in Intelligent Artificial Agents
Oct 04, 2019
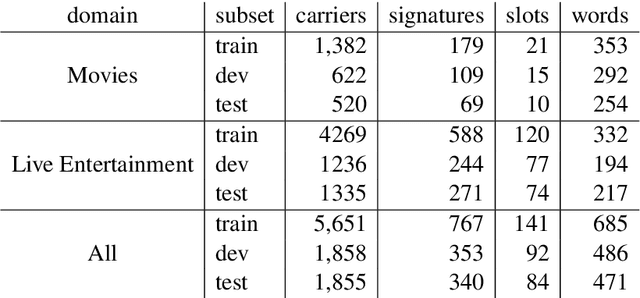
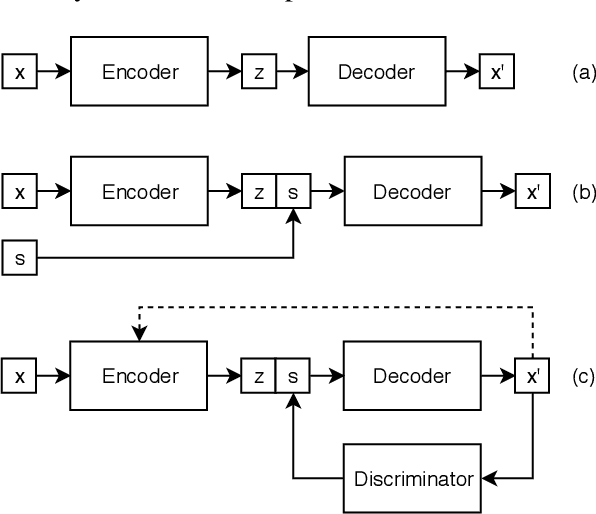
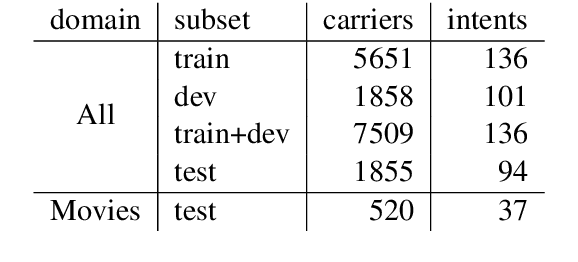
Abstract:Data availability is a bottleneck during early stages of development of new capabilities for intelligent artificial agents. We investigate the use of text generation techniques to augment the training data of a popular commercial artificial agent across categories of functionality, with the goal of faster development of new functionality. We explore a variety of encoder-decoder generative models for synthetic training data generation and propose using conditional variational auto-encoders. Our approach requires only direct optimization, works well with limited data and significantly outperforms the previous controlled text generation techniques. Further, the generated data are used as additional training samples in an extrinsic intent classification task, leading to improved performance by up to 5\% absolute f-score in low-resource cases, validating the usefulness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge