Arijit Biswas
DISPO: Enhancing Training Efficiency and Stability in Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Model Mathematical Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards has emerged as a promising paradigm for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models particularly in mathematics. Current approaches in this domain present a clear trade-off: PPO-style methods (e.g., GRPO/DAPO) offer training stability but exhibit slow learning trajectories due to their trust-region constraints on policy updates, while REINFORCE-style approaches (e.g., CISPO) demonstrate improved learning efficiency but suffer from performance instability as they clip importance sampling weights while still permitting non-zero gradients outside the trust-region. To address these limitations, we introduce DISPO, a simple yet effective REINFORCE-style algorithm that decouples the up-clipping and down-clipping of importance sampling weights for correct and incorrect responses, yielding four controllable policy update regimes. Through targeted ablations, we uncover how each regime impacts training: for correct responses, weights >1 increase the average token entropy (i.e., exploration) while weights <1 decrease it (i.e., distillation) -- both beneficial but causing gradual performance degradation when excessive. For incorrect responses, overly restrictive clipping triggers sudden performance collapse through repetitive outputs (when weights >1) or vanishing response lengths (when weights <1). By separately tuning these four clipping parameters, DISPO maintains the exploration-distillation balance while preventing catastrophic failures, achieving 61.04% on AIME'24 (vs. 55.42% CISPO and 50.21% DAPO) with similar gains across various benchmarks and models.
RF-GML: Reference-Free Generative Machine Listener
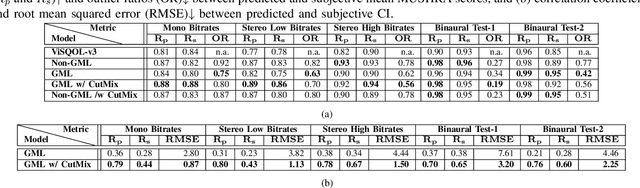
Sep 16, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel reference-free (RF) audio quality metric called the RF-Generative Machine Listener (RF-GML), designed to evaluate coded mono, stereo, and binaural audio at a 48 kHz sample rate. RF-GML leverages transfer learning from a state-of-the-art full-reference (FR) Generative Machine Listener (GML) with minimal architectural modifications. The term "generative" refers to the model's ability to generate an arbitrary number of simulated listening scores. Unlike existing RF models, RF-GML accurately predicts subjective quality scores across diverse content types and codecs. Extensive evaluations demonstrate its superiority in rating unencoded audio and distinguishing different levels of coding artifacts. RF-GML's performance and versatility make it a valuable tool for coded audio quality assessment and monitoring in various applications, all without the need for a reference signal.
FANTAstic SEquences and Where to Find Them: Faithful and Efficient API Call Generation through State-tracked Constrained Decoding and Reranking
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:API call generation is the cornerstone of large language models' tool-using ability that provides access to the larger world. However, existing supervised and in-context learning approaches suffer from high training costs, poor data efficiency, and generated API calls that can be unfaithful to the API documentation and the user's request. To address these limitations, we propose an output-side optimization approach called FANTASE. Two of the unique contributions of FANTASE are its State-Tracked Constrained Decoding (SCD) and Reranking components. SCD dynamically incorporates appropriate API constraints in the form of Token Search Trie for efficient and guaranteed generation faithfulness with respect to the API documentation. The Reranking component efficiently brings in the supervised signal by leveraging a lightweight model as the discriminator to rerank the beam-searched candidate generations of the large language model. We demonstrate the superior performance of FANTASE in API call generation accuracy, inference efficiency, and context efficiency with DSTC8 and API Bank datasets.
Multi-User MultiWOZ: Task-Oriented Dialogues among Multiple Users
Oct 31, 2023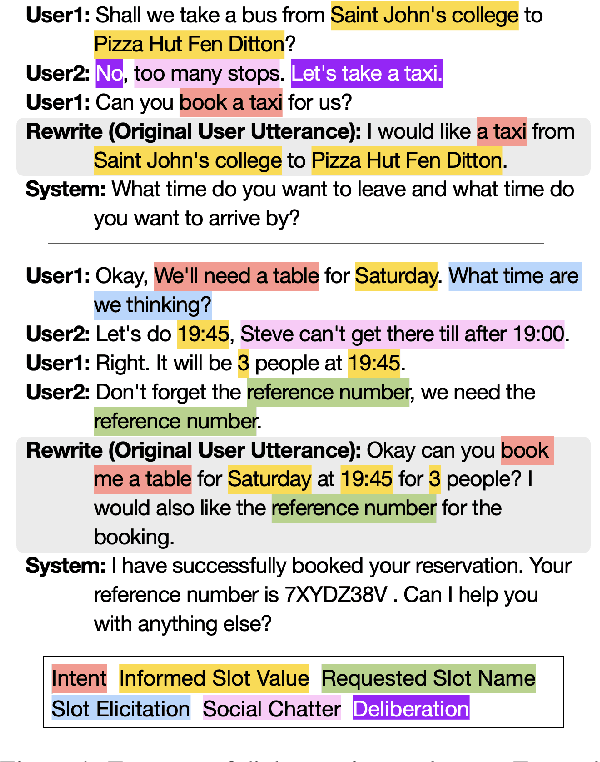
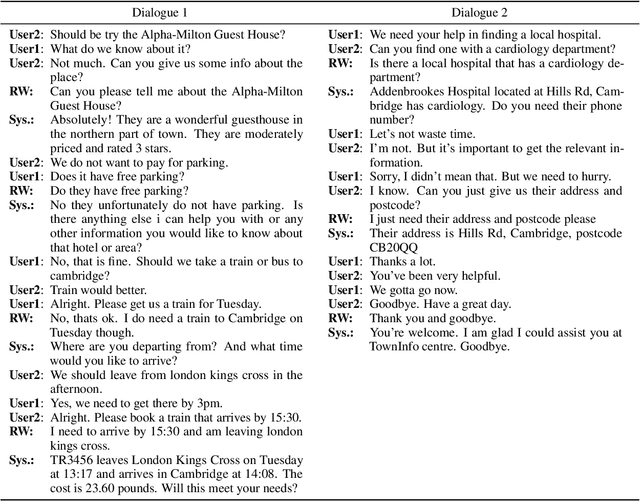
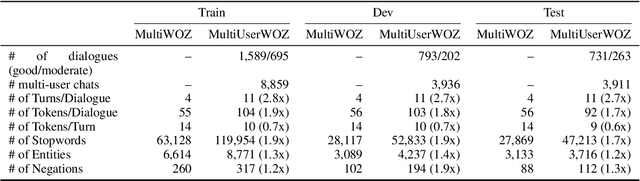
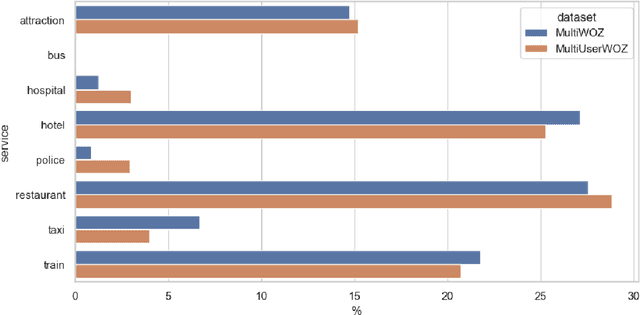
Abstract:While most task-oriented dialogues assume conversations between the agent and one user at a time, dialogue systems are increasingly expected to communicate with multiple users simultaneously who make decisions collaboratively. To facilitate development of such systems, we release the Multi-User MultiWOZ dataset: task-oriented dialogues among two users and one agent. To collect this dataset, each user utterance from MultiWOZ 2.2 was replaced with a small chat between two users that is semantically and pragmatically consistent with the original user utterance, thus resulting in the same dialogue state and system response. These dialogues reflect interesting dynamics of collaborative decision-making in task-oriented scenarios, e.g., social chatter and deliberation. Supported by this data, we propose the novel task of multi-user contextual query rewriting: to rewrite a task-oriented chat between two users as a concise task-oriented query that retains only task-relevant information and that is directly consumable by the dialogue system. We demonstrate that in multi-user dialogues, using predicted rewrites substantially improves dialogue state tracking without modifying existing dialogue systems that are trained for single-user dialogues. Further, this method surpasses training a medium-sized model directly on multi-user dialogues and generalizes to unseen domains.
Generative Machine Listener
Aug 18, 2023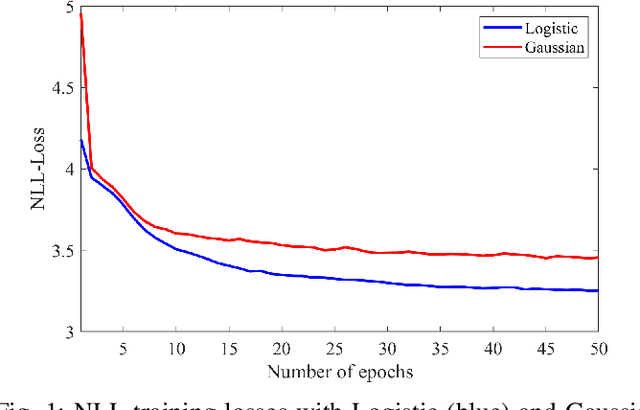
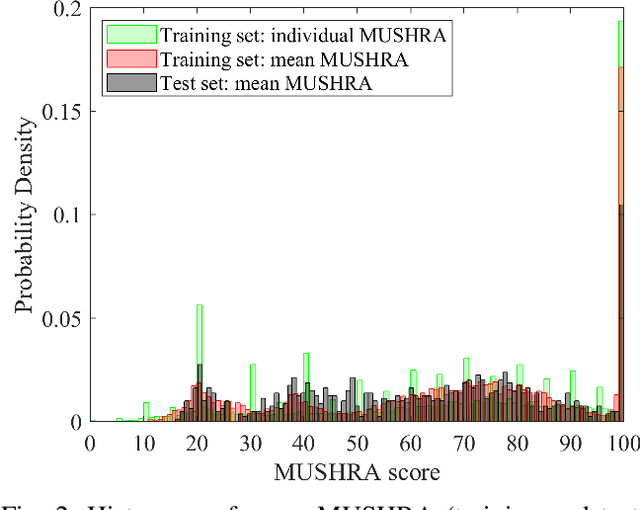
Abstract:We show how a neural network can be trained on individual intrusive listening test scores to predict a distribution of scores for each pair of reference and coded input stereo or binaural signals. We nickname this method the Generative Machine Listener (GML), as it is capable of generating an arbitrary amount of simulated listening test data. Compared to a baseline system using regression over mean scores, we observe lower outlier ratios (OR) for the mean score predictions, and obtain easy access to the prediction of confidence intervals (CI). The introduction of data augmentation techniques from the image domain results in a significant increase in CI prediction accuracy as well as Pearson and Spearman rank correlation of mean scores.
AudioVMAF: Audio Quality Prediction with VMAF
Aug 07, 2023Abstract:Video Multimethod Assessment Fusion (VMAF) [1], [2], [3] is a popular tool in the industry for measuring coded video quality. In this study, we propose an auditory-inspired frontend in existing VMAF for creating videos of reference and coded spectrograms, and extended VMAF for measuring coded audio quality. We name our system AudioVMAF. We demonstrate that image replication is capable of further enhancing prediction accuracy, especially when band-limited anchors are present. The proposed method significantly outperforms all existing visual quality features repurposed for audio, and even demonstrates a significant overall improvement of 7.8% and 2.0% of Pearson and Spearman rank correlation coefficient, respectively, over a dedicated audio quality metric (ViSQOL-v3 [4]) also inspired from the image domain.
Stereo InSE-NET: Stereo Audio Quality Predictor Transfer Learned from Mono InSE-NET
Sep 23, 2022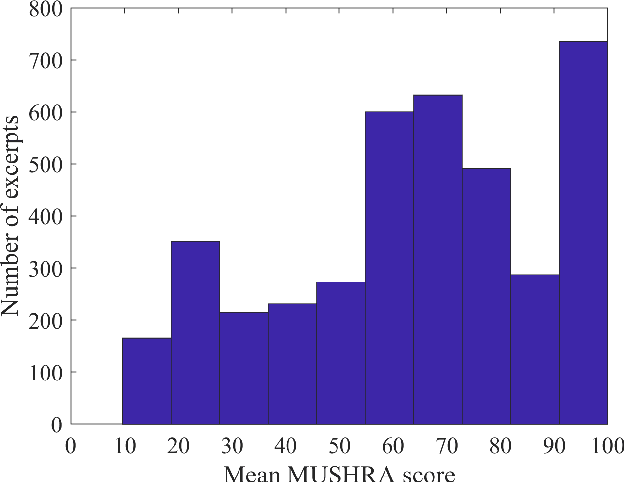
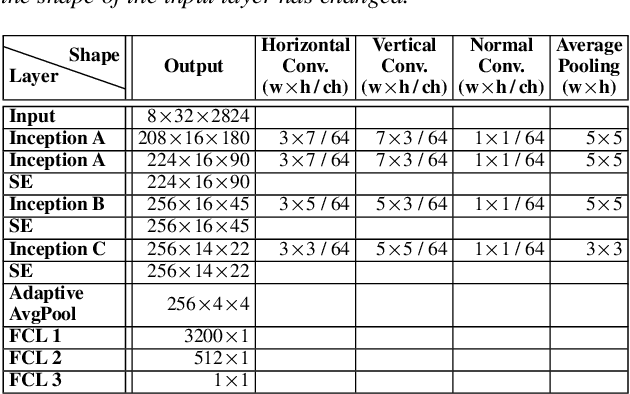
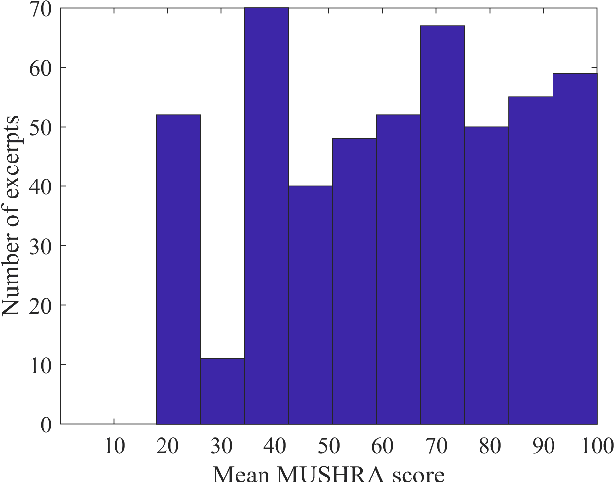
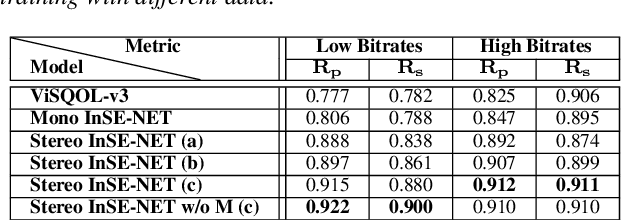
Abstract:Automatic coded audio quality predictors are typically designed for evaluating single channels without considering any spatial aspects. With InSE-NET [1], we demonstrated mimicking a state-of-the-art coded audio quality metric (ViSQOL-v3 [2]) with deep neural networks (DNN) and subsequently improving it - completely with programmatically generated data. In this study, we take steps towards building a DNN-based coded stereo audio quality predictor and we propose an extension of the InSE-NET for handling stereo signals. The design considers stereo/spatial aspects by conditioning the model with left, right, mid, and side channels; and we name our model Stereo InSE-NET. By transferring selected weights from the pre-trained mono InSE-NET and retraining with both real and synthetically augmented listening tests, we demonstrate a significant improvement of 12% and 6% of Pearson and Spearman Rank correlation coefficient, respectively, over the latest ViSQOL-v3 [3].
Building Goal-Oriented Dialogue Systems with Situated Visual Context
Nov 22, 2021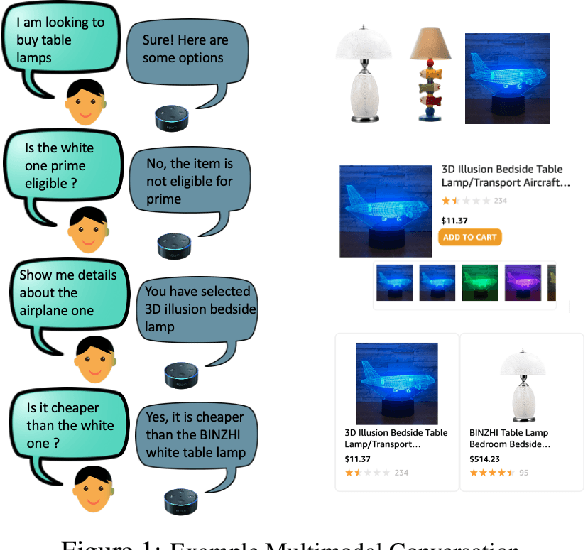
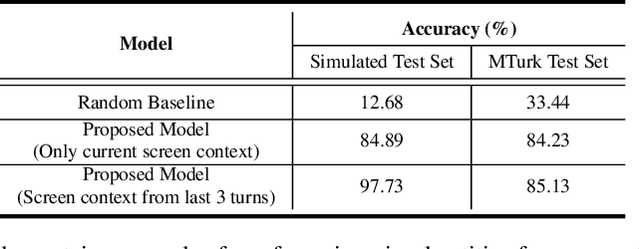
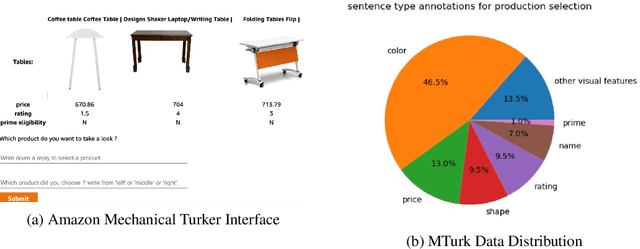
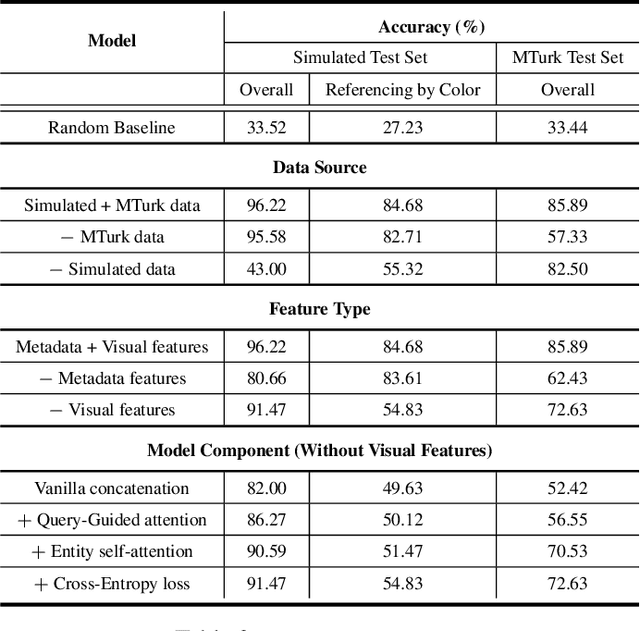
Abstract:Most popular goal-oriented dialogue agents are capable of understanding the conversational context. However, with the surge of virtual assistants with screen, the next generation of agents are required to also understand screen context in order to provide a proper interactive experience, and better understand users' goals. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal conversational framework, where the dialogue agent's next action and their arguments are derived jointly conditioned both on the conversational and the visual context. Specifically, we propose a new model, that can reason over the visual context within a conversation and populate API arguments with visual entities given the user query. Our model can recognize visual features such as color and shape as well as the metadata based features such as price or star rating associated with a visual entity. In order to train our model, due to a lack of suitable multimodal conversational datasets, we also propose a novel multimodal dialog simulator to generate synthetic data and also collect realistic user data from MTurk to improve model robustness. The proposed model achieves a reasonable 85% model accuracy, without high inference latency. We also demonstrate the proposed approach in a prototypical furniture shopping experience for a multimodal virtual assistant.
InSE-NET: A Perceptually Coded Audio Quality Model based on CNN
Aug 30, 2021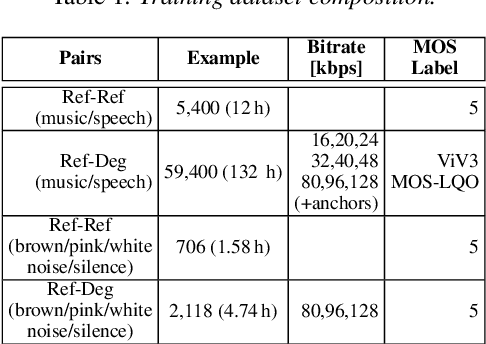
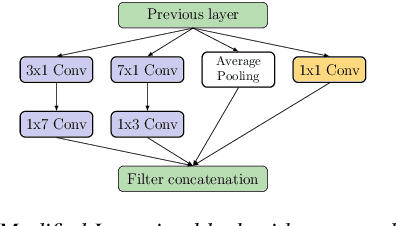
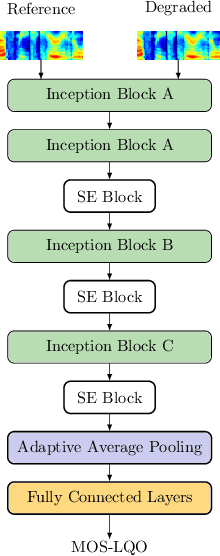
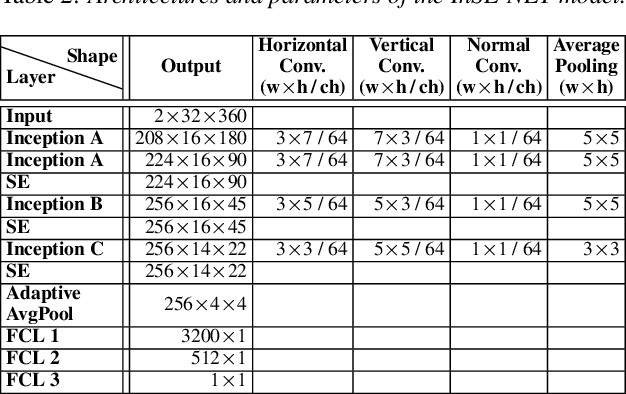
Abstract:Automatic coded audio quality assessment is an important task whose progress is hampered by the scarcity of human annotations, poor generalization to unseen codecs, bitrates, content-types, and a lack of flexibility of existing approaches. One of the typical human-perception-related metrics, ViSQOL v3 (ViV3), has been proven to provide a high correlation to the quality scores rated by humans. In this study, we take steps to tackle problems of predicting coded audio quality by completely utilizing programmatically generated data that is informed with expert domain knowledge. We propose a learnable neural network, entitled InSE-NET, with a backbone of Inception and Squeeze-and-Excitation modules to assess the perceived quality of coded audio at a 48kHz sample rate. We demonstrate that synthetic data augmentation is capable of enhancing the prediction. Our proposed method is intrusive, i.e. it requires Gammatone spectrograms of unencoded reference signals. Besides a comparable performance to ViV3, our approach provides a more robust prediction towards higher bitrates.
Alexa Conversations: An Extensible Data-driven Approach for Building Task-oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 19, 2021
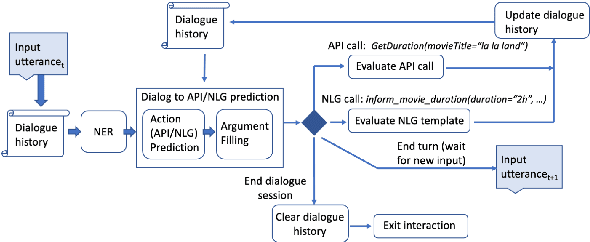
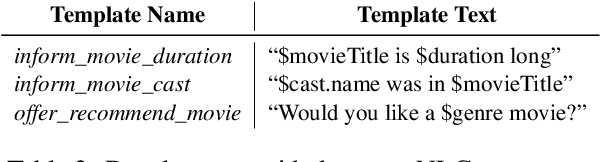
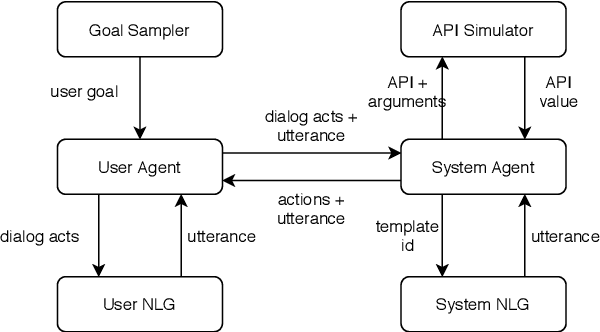
Abstract:Traditional goal-oriented dialogue systems rely on various components such as natural language understanding, dialogue state tracking, policy learning and response generation. Training each component requires annotations which are hard to obtain for every new domain, limiting scalability of such systems. Similarly, rule-based dialogue systems require extensive writing and maintenance of rules and do not scale either. End-to-End dialogue systems, on the other hand, do not require module-specific annotations but need a large amount of data for training. To overcome these problems, in this demo, we present Alexa Conversations, a new approach for building goal-oriented dialogue systems that is scalable, extensible as well as data efficient. The components of this system are trained in a data-driven manner, but instead of collecting annotated conversations for training, we generate them using a novel dialogue simulator based on a few seed dialogues and specifications of APIs and entities provided by the developer. Our approach provides out-of-the-box support for natural conversational phenomena like entity sharing across turns or users changing their mind during conversation without requiring developers to provide any such dialogue flows. We exemplify our approach using a simple pizza ordering task and showcase its value in reducing the developer burden for creating a robust experience. Finally, we evaluate our system using a typical movie ticket booking task and show that the dialogue simulator is an essential component of the system that leads to over $50\%$ improvement in turn-level action signature prediction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge