Sanchit Agarwal
Building Goal-Oriented Dialogue Systems with Situated Visual Context
Nov 22, 2021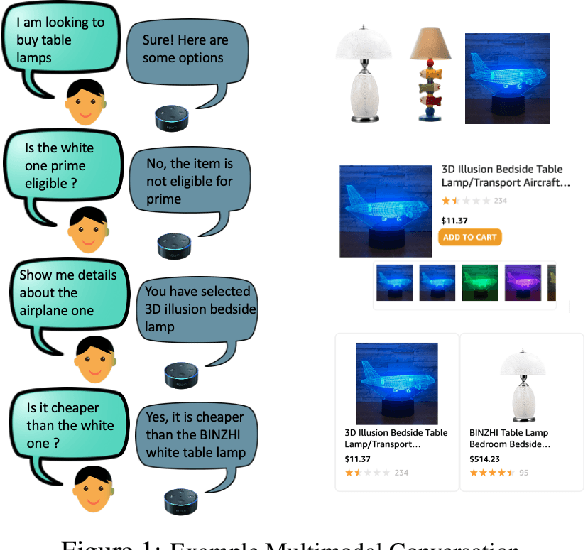
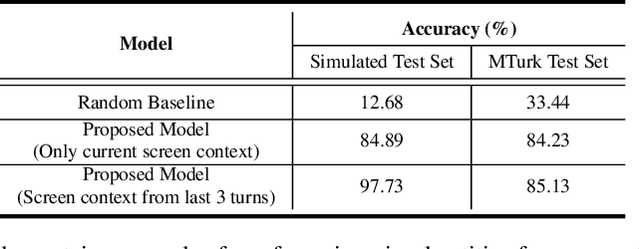
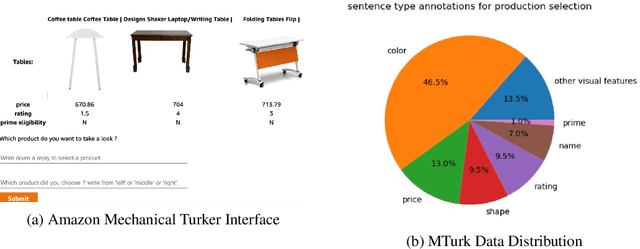
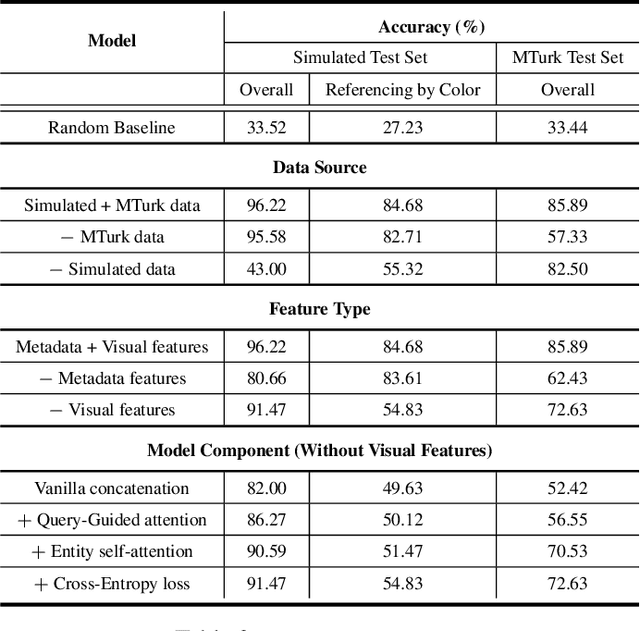
Abstract:Most popular goal-oriented dialogue agents are capable of understanding the conversational context. However, with the surge of virtual assistants with screen, the next generation of agents are required to also understand screen context in order to provide a proper interactive experience, and better understand users' goals. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal conversational framework, where the dialogue agent's next action and their arguments are derived jointly conditioned both on the conversational and the visual context. Specifically, we propose a new model, that can reason over the visual context within a conversation and populate API arguments with visual entities given the user query. Our model can recognize visual features such as color and shape as well as the metadata based features such as price or star rating associated with a visual entity. In order to train our model, due to a lack of suitable multimodal conversational datasets, we also propose a novel multimodal dialog simulator to generate synthetic data and also collect realistic user data from MTurk to improve model robustness. The proposed model achieves a reasonable 85% model accuracy, without high inference latency. We also demonstrate the proposed approach in a prototypical furniture shopping experience for a multimodal virtual assistant.
Alexa Conversations: An Extensible Data-driven Approach for Building Task-oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 19, 2021
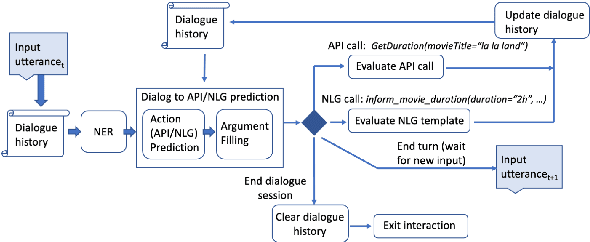
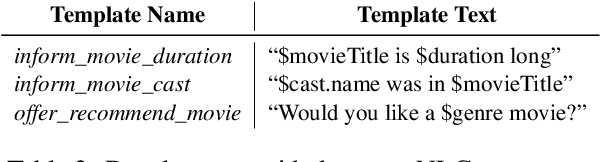
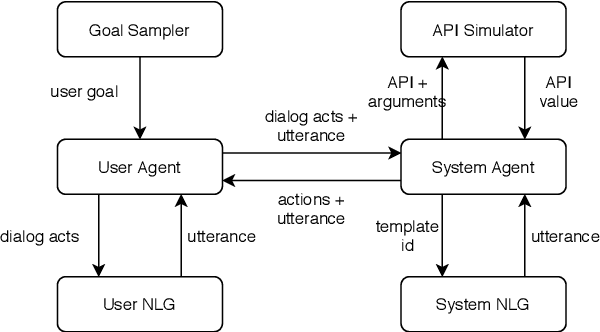
Abstract:Traditional goal-oriented dialogue systems rely on various components such as natural language understanding, dialogue state tracking, policy learning and response generation. Training each component requires annotations which are hard to obtain for every new domain, limiting scalability of such systems. Similarly, rule-based dialogue systems require extensive writing and maintenance of rules and do not scale either. End-to-End dialogue systems, on the other hand, do not require module-specific annotations but need a large amount of data for training. To overcome these problems, in this demo, we present Alexa Conversations, a new approach for building goal-oriented dialogue systems that is scalable, extensible as well as data efficient. The components of this system are trained in a data-driven manner, but instead of collecting annotated conversations for training, we generate them using a novel dialogue simulator based on a few seed dialogues and specifications of APIs and entities provided by the developer. Our approach provides out-of-the-box support for natural conversational phenomena like entity sharing across turns or users changing their mind during conversation without requiring developers to provide any such dialogue flows. We exemplify our approach using a simple pizza ordering task and showcase its value in reducing the developer burden for creating a robust experience. Finally, we evaluate our system using a typical movie ticket booking task and show that the dialogue simulator is an essential component of the system that leads to over $50\%$ improvement in turn-level action signature prediction accuracy.
Few Shot Dialogue State Tracking using Meta-learning
Jan 23, 2021



Abstract:Dialogue State Tracking (DST) forms a core component of automated chatbot based systems designed for specific goals like hotel, taxi reservation, tourist information, etc. With the increasing need to deploy such systems in new domains, solving the problem of zero/few-shot DST has become necessary. There has been a rising trend for learning to transfer knowledge from resource-rich domains to unknown domains with minimal need for additional data. In this work, we explore the merits of meta-learning algorithms for this transfer and hence, propose a meta-learner D-REPTILE specific to the DST problem. With extensive experimentation, we provide clear evidence of benefits over conventional approaches across different domains, methods, base models, and datasets with significant (5-25%) improvement over the baseline in a low-data setting. Our proposed meta-learner is agnostic of the underlying model and hence any existing state-of-the-art DST system can improve its performance on unknown domains using our training strategy.
From Machine Reading Comprehension to Dialogue State Tracking: Bridging the Gap
Apr 13, 2020



Abstract:Dialogue state tracking (DST) is at the heart of task-oriented dialogue systems. However, the scarcity of labeled data is an obstacle to building accurate and robust state tracking systems that work across a variety of domains. Existing approaches generally require some dialogue data with state information and their ability to generalize to unknown domains is limited. In this paper, we propose using machine reading comprehension (RC) in state tracking from two perspectives: model architectures and datasets. We divide the slot types in dialogue state into categorical or extractive to borrow the advantages from both multiple-choice and span-based reading comprehension models. Our method achieves near the current state-of-the-art in joint goal accuracy on MultiWOZ 2.1 given full training data. More importantly, by leveraging machine reading comprehension datasets, our method outperforms the existing approaches by many a large margin in few-shot scenarios when the availability of in-domain data is limited. Lastly, even without any state tracking data, i.e., zero-shot scenario, our proposed approach achieves greater than 90% average slot accuracy in 12 out of 30 slots in MultiWOZ 2.1.
Dialog State Tracking: A Neural Reading Comprehension Approach
Aug 15, 2019



Abstract:Dialog state tracking is used to estimate the current belief state of a dialog given all the preceding conversation. Machine reading comprehension, on the other hand, focuses on building systems that read passages of text and answer questions that require some understanding of passages. We formulate dialog state tracking as a reading comprehension task to answer the question $what\ is\ the\ state\ of\ the\ current\ dialog?$ after reading conversational context. In contrast to traditional state tracking methods where the dialog state is often predicted as a distribution over a closed set of all the possible slot values within an ontology, our method uses a simple attention-based neural network to point to the slot values within the conversation. Experiments on MultiWOZ-2.0 cross-domain dialog dataset show that our simple system can obtain similar accuracies compared to the previous more complex methods. By exploiting recent advances in contextual word embeddings, adding a model that explicitly tracks whether a slot value should be carried over to the next turn, and combining our method with a traditional joint state tracking method that relies on closed set vocabulary, we can obtain a joint-goal accuracy of $47.33\%$ on the standard test split, exceeding current state-of-the-art by $11.75\%$**.
MultiWOZ 2.1: Multi-Domain Dialogue State Corrections and State Tracking Baselines
Jul 02, 2019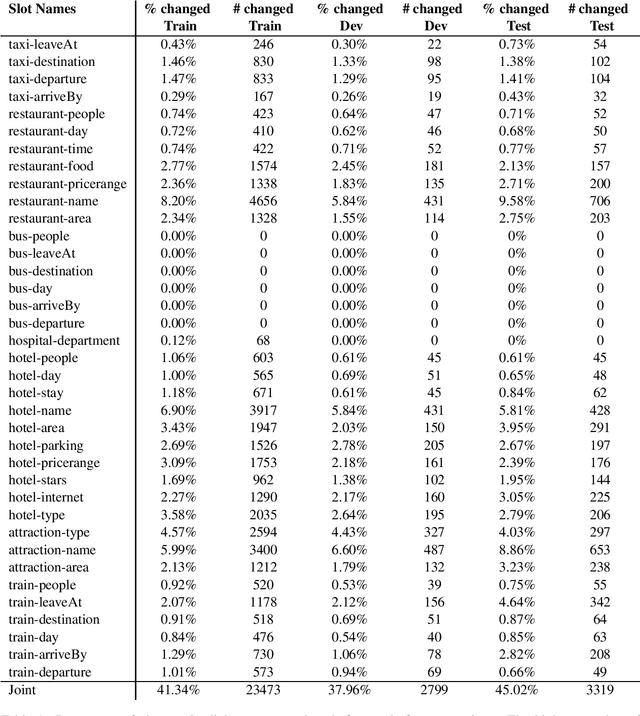
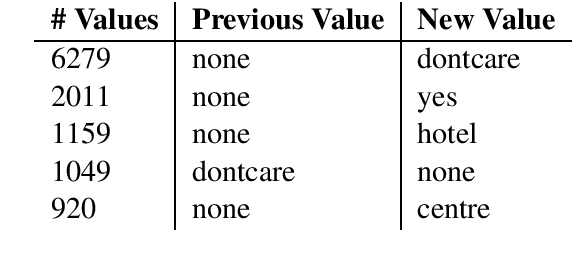
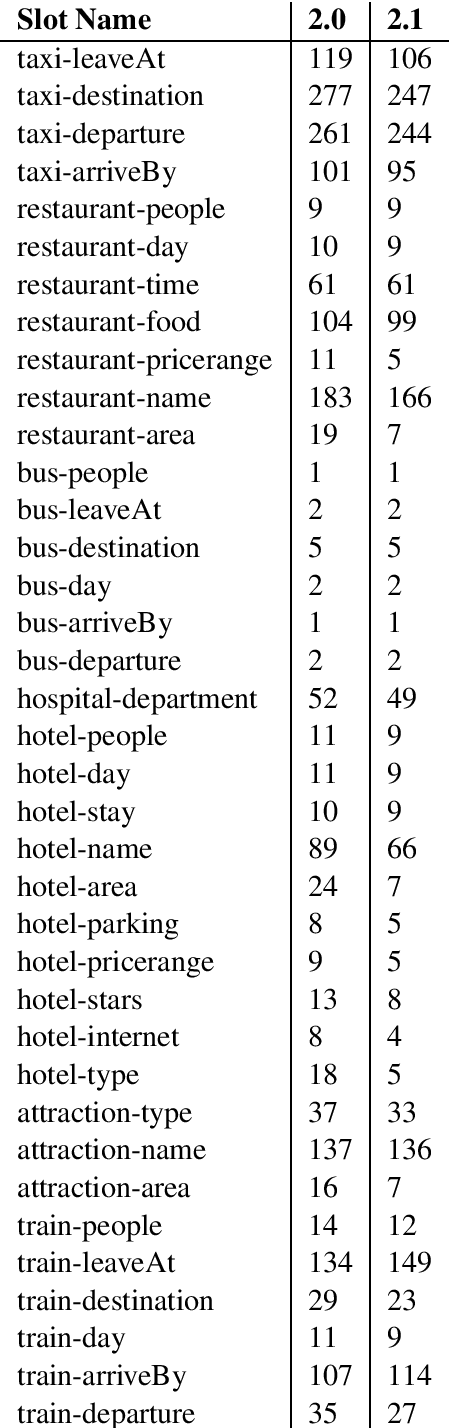
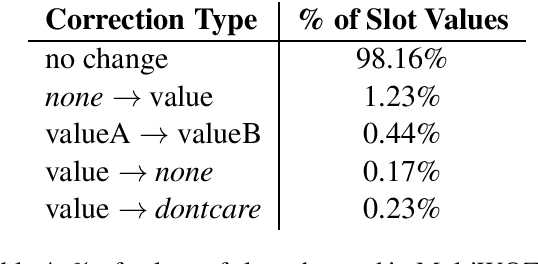
Abstract:MultiWOZ is a recently-released multidomain dialogue dataset spanning 7 distinct domains and containing over 10000 dialogues, one of the largest resources of its kind to-date. Though an immensely useful resource, while building different classes of dialogue state tracking models using MultiWOZ, we detected substantial errors in the state annotations and dialogue utterances which negatively impacted the performance of our models. In order to alleviate this problem, we use crowdsourced workers to fix the state annotations and utterances in the original version of the data. Our correction process results in changes to over 32% of state annotations across 40% of the dialogue turns. In addition, we fix 146 dialogue utterances throughout the dataset focusing in particular on addressing slot value errors represented within the conversations. We then benchmark a number of state-of-the-art dialogue state tracking models on this new MultiWOZ 2.1 dataset and show joint state tracking performance on the corrected state annotations. We are publicly releasing MultiWOZ 2.1 to the community, hoping that this dataset resource will allow for more effective dialogue state tracking models to be built in the future.
Parsing Coordination for Spoken Language Understanding
Oct 26, 2018
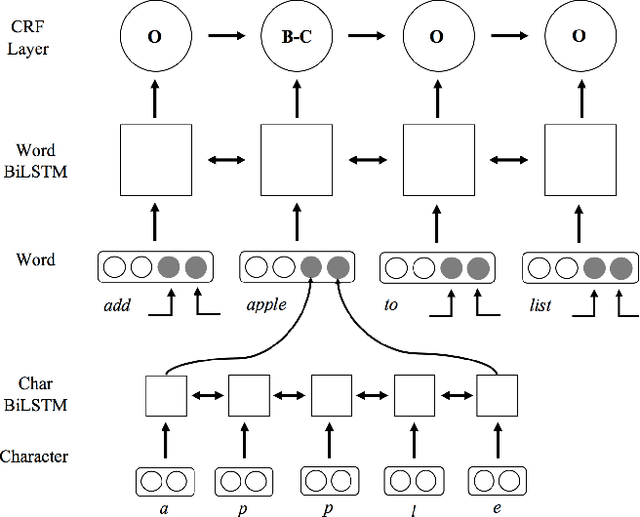

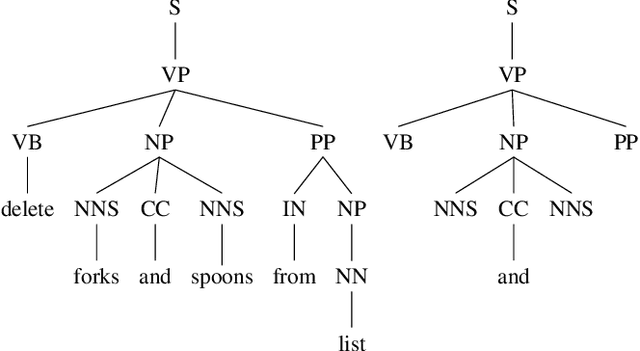
Abstract:Typical spoken language understanding systems provide narrow semantic parses using a domain-specific ontology. The parses contain intents and slots that are directly consumed by downstream domain applications. In this work we discuss expanding such systems to handle compound entities and intents by introducing a domain-agnostic shallow parser that handles linguistic coordination. We show that our model for parsing coordination learns domain-independent and slot-independent features and is able to segment conjunct boundaries of many different phrasal categories. We also show that using adversarial training can be effective for improving generalization across different slot types for coordination parsing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge