Stereo InSE-NET: Stereo Audio Quality Predictor Transfer Learned from Mono InSE-NET
Paper and Code
Sep 23, 2022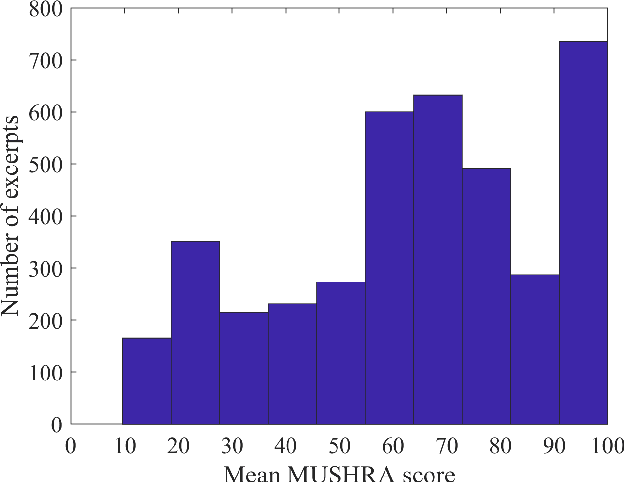
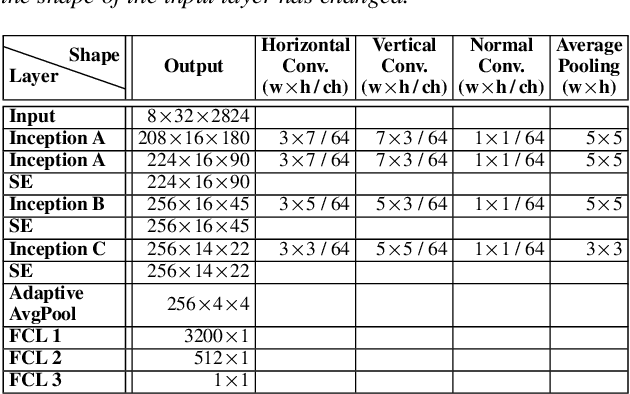
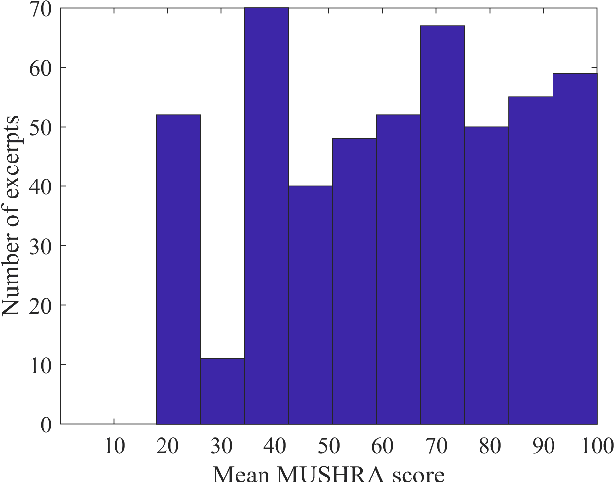
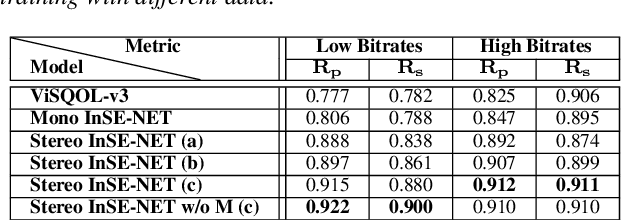
Automatic coded audio quality predictors are typically designed for evaluating single channels without considering any spatial aspects. With InSE-NET [1], we demonstrated mimicking a state-of-the-art coded audio quality metric (ViSQOL-v3 [2]) with deep neural networks (DNN) and subsequently improving it - completely with programmatically generated data. In this study, we take steps towards building a DNN-based coded stereo audio quality predictor and we propose an extension of the InSE-NET for handling stereo signals. The design considers stereo/spatial aspects by conditioning the model with left, right, mid, and side channels; and we name our model Stereo InSE-NET. By transferring selected weights from the pre-trained mono InSE-NET and retraining with both real and synthetically augmented listening tests, we demonstrate a significant improvement of 12% and 6% of Pearson and Spearman Rank correlation coefficient, respectively, over the latest ViSQOL-v3 [3].
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge