Zhongjie Ba
HyperPotter: Spell the Charm of High-Order Interactions in Audio Deepfake Detection
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Advances in AIGC technologies have enabled the synthesis of highly realistic audio deepfakes capable of deceiving human auditory perception. Although numerous audio deepfake detection (ADD) methods have been developed, most rely on local temporal/spectral features or pairwise relations, overlooking high-order interactions (HOIs). HOIs capture discriminative patterns that emerge from multiple feature components beyond their individual contributions. We propose HyperPotter, a hypergraph-based framework that explicitly models these synergistic HOIs through clustering-based hyperedges with class-aware prototype initialization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperPotter surpasses its baseline by an average relative gain of 22.15% across 11 datasets and outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 13.96% on 4 challenging cross-domain datasets, demonstrating superior generalization to diverse attacks and speakers.
AgentDoG: A Diagnostic Guardrail Framework for AI Agent Safety and Security
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The rise of AI agents introduces complex safety and security challenges arising from autonomous tool use and environmental interactions. Current guardrail models lack agentic risk awareness and transparency in risk diagnosis. To introduce an agentic guardrail that covers complex and numerous risky behaviors, we first propose a unified three-dimensional taxonomy that orthogonally categorizes agentic risks by their source (where), failure mode (how), and consequence (what). Guided by this structured and hierarchical taxonomy, we introduce a new fine-grained agentic safety benchmark (ATBench) and a Diagnostic Guardrail framework for agent safety and security (AgentDoG). AgentDoG provides fine-grained and contextual monitoring across agent trajectories. More Crucially, AgentDoG can diagnose the root causes of unsafe actions and seemingly safe but unreasonable actions, offering provenance and transparency beyond binary labels to facilitate effective agent alignment. AgentDoG variants are available in three sizes (4B, 7B, and 8B parameters) across Qwen and Llama model families. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that AgentDoG achieves state-of-the-art performance in agentic safety moderation in diverse and complex interactive scenarios. All models and datasets are openly released.
Attack-Resistant Watermarking for AIGC Image Forensics via Diffusion-based Semantic Deflection
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Protecting the copyright of user-generated AI images is an emerging challenge as AIGC becomes pervasive in creative workflows. Existing watermarking methods (1) remain vulnerable to real-world adversarial threats, often forced to trade off between defenses against spoofing and removal attacks; and (2) cannot support semantic-level tamper localization. We introduce PAI, a training-free inherent watermarking framework for AIGC copyright protection, plug-and-play with diffusion-based AIGC services. PAI simultaneously provides three key functionalities: robust ownership verification, attack detection, and semantic-level tampering localization. Unlike existing inherent watermark methods that only embed watermarks at noise initialization of diffusion models, we design a novel key-conditioned deflection mechanism that subtly steers the denoising trajectory according to the user key. Such trajectory-level coupling further strengthens the semantic entanglement of identity and content, thereby further enhancing robustness against real-world threats. Moreover, we also provide a theoretical analysis proving that only the valid key can pass verification. Experiments across 12 attack methods show that PAI achieves 98.43\% verification accuracy, improving over SOTA methods by 37.25\% on average, and retains strong tampering localization performance even against advanced AIGC edits. Our code is available at https://github.com/QingyuLiu/PAI.
FBA$^2$D: Frequency-based Black-box Attack for AI-generated Image Detection
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:The prosperous development of Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC) has brought people's anxiety about the spread of false information on social media. Designing detectors for filtering is an effective defense method, but most detectors will be compromised by adversarial samples. Currently, most studies exposing AIGC security issues assume information on model structure and data distribution. In real applications, attackers query and interfere with models that provide services in the form of application programming interfaces (APIs), which constitutes the black-box decision-based attack paradigm. However, to the best of our knowledge, decision-based attacks on AIGC detectors remain unexplored. In this study, we propose \textbf{FBA$^2$D}: a frequency-based black-box attack method for AIGC detection to fill the research gap. Motivated by frequency-domain discrepancies between generated and real images, we develop a decision-based attack that leverages the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) for fine-grained spectral partitioning and selects frequency bands as query subspaces, improving both query efficiency and image quality. Moreover, attacks on AIGC detectors should mitigate initialization failures, preserve image quality, and operate under strict query budgets. To address these issues, we adopt an ``adversarial example soup'' method, averaging candidates from successive surrogate iterations and using the result as the initialization to accelerate the query-based attack. The empirical study on the Synthetic LSUN dataset and GenImage dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our prosed method. This study shows the urgency of addressing practical AIGC security problems.
Model Discrepancy Learning: Synthetic Faces Detection Based on Multi-Reconstruction
Apr 10, 2025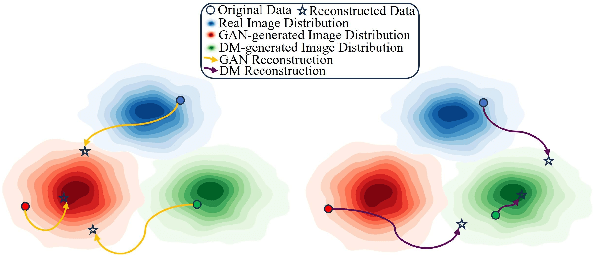
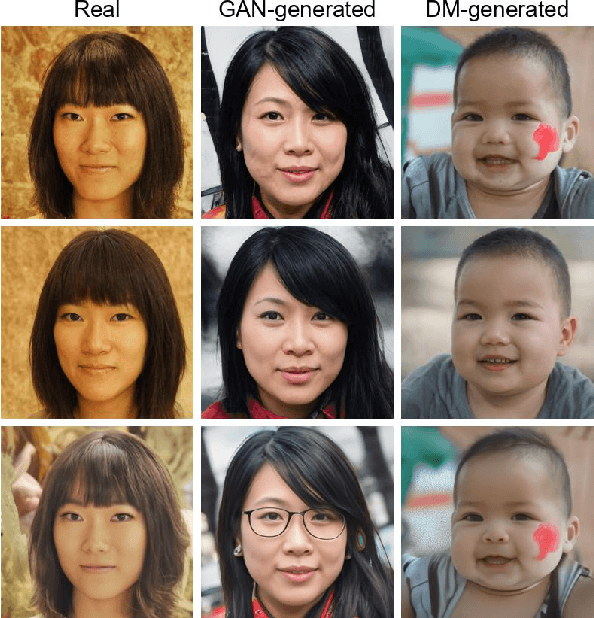

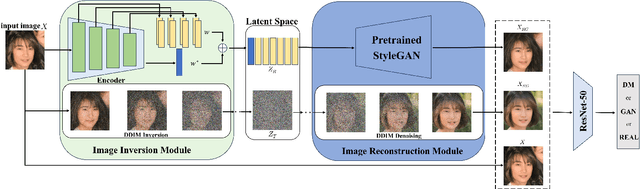

Abstract:Advances in image generation enable hyper-realistic synthetic faces but also pose risks, thus making synthetic face detection crucial. Previous research focuses on the general differences between generated images and real images, often overlooking the discrepancies among various generative techniques. In this paper, we explore the intrinsic relationship between synthetic images and their corresponding generation technologies. We find that specific images exhibit significant reconstruction discrepancies across different generative methods and that matching generation techniques provide more accurate reconstructions. Based on this insight, we propose a Multi-Reconstruction-based detector. By reversing and reconstructing images using multiple generative models, we analyze the reconstruction differences among real, GAN-generated, and DM-generated images to facilitate effective differentiation. Additionally, we introduce the Asian Synthetic Face Dataset (ASFD), containing synthetic Asian faces generated with various GANs and DMs. This dataset complements existing synthetic face datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our detector achieves exceptional performance, with strong generalization and robustness.
Imperceptible but Forgeable: Practical Invisible Watermark Forgery via Diffusion Models
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Invisible watermarking is critical for content provenance and accountability in Generative AI. Although commercial companies have increasingly committed to using watermarks, the robustness of existing watermarking schemes against forgery attacks is understudied. This paper proposes DiffForge, the first watermark forgery framework capable of forging imperceptible watermarks under a no-box setting. We estimate the watermark distribution using an unconditional diffusion model and introduce shallow inversion to inject the watermark into a non-watermarked image seamlessly. This approach facilitates watermark injection while preserving image quality by adaptively selecting the depth of inversion steps, leveraging our key insight that watermarks degrade with added noise during the early diffusion phases. Comprehensive evaluations show that DiffForge deceives open-source watermark detectors with a 96.38% success rate and misleads a commercial watermark system with over 97% success rate, achieving high confidence.1 This work reveals fundamental security limitations in current watermarking paradigms.
Harnessing Frequency Spectrum Insights for Image Copyright Protection Against Diffusion Models
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in novel view synthesis, but their reliance on large, diverse, and often untraceable Web datasets has raised pressing concerns about image copyright protection. Current methods fall short in reliably identifying unauthorized image use, as they struggle to generalize across varied generation tasks and fail when the training dataset includes images from multiple sources with few identifiable (watermarked or poisoned) samples. In this paper, we present novel evidence that diffusion-generated images faithfully preserve the statistical properties of their training data, particularly reflected in their spectral features. Leveraging this insight, we introduce \emph{CoprGuard}, a robust frequency domain watermarking framework to safeguard against unauthorized image usage in diffusion model training and fine-tuning. CoprGuard demonstrates remarkable effectiveness against a wide range of models, from naive diffusion models to sophisticated text-to-image models, and is robust even when watermarked images comprise a mere 1\% of the training dataset. This robust and versatile approach empowers content owners to protect their intellectual property in the era of AI-driven image generation.
Towards Label-Only Membership Inference Attack against Pre-trained Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Membership Inference Attacks (MIAs) aim to predict whether a data sample belongs to the model's training set or not. Although prior research has extensively explored MIAs in Large Language Models (LLMs), they typically require accessing to complete output logits (\ie, \textit{logits-based attacks}), which are usually not available in practice. In this paper, we study the vulnerability of pre-trained LLMs to MIAs in the \textit{label-only setting}, where the adversary can only access generated tokens (text). We first reveal that existing label-only MIAs have minor effects in attacking pre-trained LLMs, although they are highly effective in inferring fine-tuning datasets used for personalized LLMs. We find that their failure stems from two main reasons, including better generalization and overly coarse perturbation. Specifically, due to the extensive pre-training corpora and exposing each sample only a few times, LLMs exhibit minimal robustness differences between members and non-members. This makes token-level perturbations too coarse to capture such differences. To alleviate these problems, we propose \textbf{PETAL}: a label-only membership inference attack based on \textbf{PE}r-\textbf{T}oken sem\textbf{A}ntic simi\textbf{L}arity. Specifically, PETAL leverages token-level semantic similarity to approximate output probabilities and subsequently calculate the perplexity. It finally exposes membership based on the common assumption that members are `better' memorized and have smaller perplexity. We conduct extensive experiments on the WikiMIA benchmark and the more challenging MIMIR benchmark. Empirically, our PETAL performs better than the extensions of existing label-only attacks against personalized LLMs and even on par with other advanced logit-based attacks across all metrics on five prevalent open-source LLMs.
Robust Watermarks Leak: Channel-Aware Feature Extraction Enables Adversarial Watermark Manipulation
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Watermarking plays a key role in the provenance and detection of AI-generated content. While existing methods prioritize robustness against real-world distortions (e.g., JPEG compression and noise addition), we reveal a fundamental tradeoff: such robust watermarks inherently improve the redundancy of detectable patterns encoded into images, creating exploitable information leakage. To leverage this, we propose an attack framework that extracts leakage of watermark patterns through multi-channel feature learning using a pre-trained vision model. Unlike prior works requiring massive data or detector access, our method achieves both forgery and detection evasion with a single watermarked image. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves a 60\% success rate gain in detection evasion and 51\% improvement in forgery accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods while maintaining visual fidelity. Our work exposes the robustness-stealthiness paradox: current "robust" watermarks sacrifice security for distortion resistance, providing insights for future watermark design.
FSFM: A Generalizable Face Security Foundation Model via Self-Supervised Facial Representation Learning
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:This work asks: with abundant, unlabeled real faces, how to learn a robust and transferable facial representation that boosts various face security tasks with respect to generalization performance? We make the first attempt and propose a self-supervised pretraining framework to learn fundamental representations of real face images, FSFM, that leverages the synergy between masked image modeling (MIM) and instance discrimination (ID). We explore various facial masking strategies for MIM and present a simple yet powerful CRFR-P masking, which explicitly forces the model to capture meaningful intra-region consistency and challenging inter-region coherency. Furthermore, we devise the ID network that naturally couples with MIM to establish underlying local-to-global correspondence via tailored self-distillation. These three learning objectives, namely 3C, empower encoding both local features and global semantics of real faces. After pretraining, a vanilla ViT serves as a universal vision foundation model for downstream face security tasks: cross-dataset deepfake detection, cross-domain face anti-spoofing, and unseen diffusion facial forgery detection. Extensive experiments on 10 public datasets demonstrate that our model transfers better than supervised pretraining, visual and facial self-supervised learning arts, and even outperforms task-specialized SOTA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge