Li Lu
HyperPotter: Spell the Charm of High-Order Interactions in Audio Deepfake Detection
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Advances in AIGC technologies have enabled the synthesis of highly realistic audio deepfakes capable of deceiving human auditory perception. Although numerous audio deepfake detection (ADD) methods have been developed, most rely on local temporal/spectral features or pairwise relations, overlooking high-order interactions (HOIs). HOIs capture discriminative patterns that emerge from multiple feature components beyond their individual contributions. We propose HyperPotter, a hypergraph-based framework that explicitly models these synergistic HOIs through clustering-based hyperedges with class-aware prototype initialization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperPotter surpasses its baseline by an average relative gain of 22.15% across 11 datasets and outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 13.96% on 4 challenging cross-domain datasets, demonstrating superior generalization to diverse attacks and speakers.
Neural Collapse in Test-Time Adaptation
Dec 11, 2025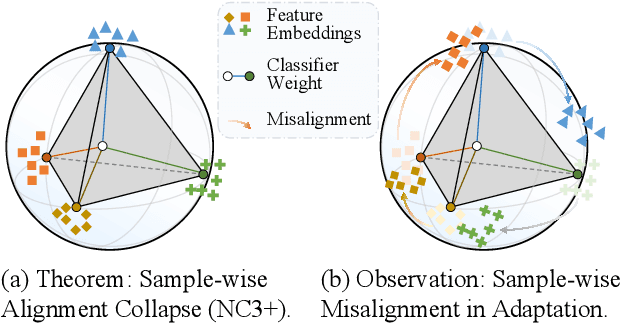
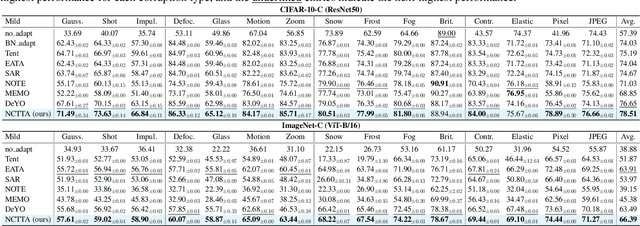
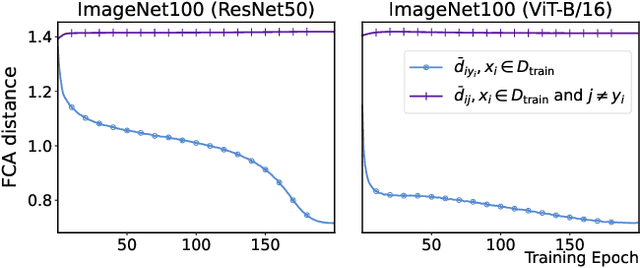
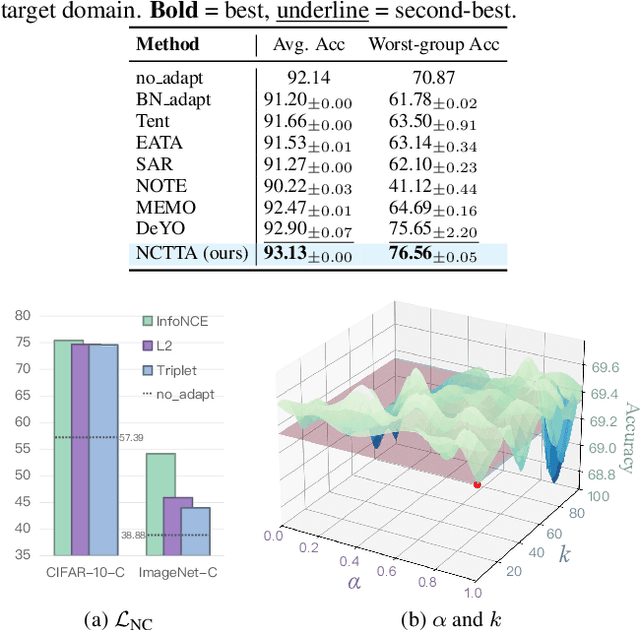
Abstract:Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) enhances model robustness to out-of-distribution (OOD) data by updating the model online during inference, yet existing methods lack theoretical insights into the fundamental causes of performance degradation under domain shifts. Recently, Neural Collapse (NC) has been proposed as an emergent geometric property of deep neural networks (DNNs), providing valuable insights for TTA. In this work, we extend NC to the sample-wise level and discover a novel phenomenon termed Sample-wise Alignment Collapse (NC3+), demonstrating that a sample's feature embedding, obtained by a trained model, aligns closely with the corresponding classifier weight. Building on NC3+, we identify that the performance degradation stems from sample-wise misalignment in adaptation which exacerbates under larger distribution shifts. This indicates the necessity of realigning the feature embeddings with their corresponding classifier weights. However, the misalignment makes pseudo-labels unreliable under domain shifts. To address this challenge, we propose NCTTA, a novel feature-classifier alignment method with hybrid targets to mitigate the impact of unreliable pseudo-labels, which blends geometric proximity with predictive confidence. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of NCTTA in enhancing robustness to domain shifts. For example, NCTTA outperforms Tent by 14.52% on ImageNet-C.
REACT-LLM: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Integration with Causal Features in Clinical Prognostic Tasks
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) and causal learning each hold strong potential for clinical decision making (CDM). However, their synergy remains poorly understood, largely due to the lack of systematic benchmarks evaluating their integration in clinical risk prediction. In real-world healthcare, identifying features with causal influence on outcomes is crucial for actionable and trustworthy predictions. While recent work highlights LLMs' emerging causal reasoning abilities, there lacks comprehensive benchmarks to assess their causal learning and performance informed by causal features in clinical risk prediction. To address this, we introduce REACT-LLM, a benchmark designed to evaluate whether combining LLMs with causal features can enhance clinical prognostic performance and potentially outperform traditional machine learning (ML) methods. Unlike existing LLM-clinical benchmarks that often focus on a limited set of outcomes, REACT-LLM evaluates 7 clinical outcomes across 2 real-world datasets, comparing 15 prominent LLMs, 6 traditional ML models, and 3 causal discovery (CD) algorithms. Our findings indicate that while LLMs perform reasonably in clinical prognostics, they have not yet outperformed traditional ML models. Integrating causal features derived from CD algorithms into LLMs offers limited performance gains, primarily due to the strict assumptions of many CD methods, which are often violated in complex clinical data. While the direct integration yields limited improvement, our benchmark reveals a more promising synergy.
Imagine with the Teacher: Complete Shape in a Multi-View Distillation Way
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Point cloud completion aims to recover the completed 3D shape of an object from its partial observation caused by occlusion, sensor's limitation, noise, etc. When some key semantic information is lost in the incomplete point cloud, the neural network needs to infer the missing part based on the input information. Intuitively we would apply an autoencoder architecture to solve this kind of problem, which take the incomplete point cloud as input and is supervised by the ground truth. This process that develops model's imagination from incomplete shape to complete shape is done automatically in the latent space. But the knowledge for mapping from incomplete to complete still remains dark and could be further explored. Motivated by the knowledge distillation's teacher-student learning strategy, we design a knowledge transfer way for completing 3d shape. In this work, we propose a novel View Distillation Point Completion Network (VD-PCN), which solve the completion problem by a multi-view distillation way. The design methodology fully leverages the orderliness of 2d pixels, flexibleness of 2d processing and powerfulness of 2d network. Extensive evaluations on PCN, ShapeNet55/34, and MVP datasets confirm the effectiveness of our design and knowledge transfer strategy, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Committed to facilitate ongoing research, we will make our code publicly available.
Towards Lightweight and Stable Zero-shot TTS with Self-distilled Representation Disentanglement
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot Text-To-Speech (TTS) synthesis shows great promise for personalized voice customization through voice cloning. However, current methods for achieving zero-shot TTS heavily rely on large model scales and extensive training datasets to ensure satisfactory performance and generalizability across various speakers. This raises concerns regarding both deployment costs and data security. In this paper, we present a lightweight and stable zero-shot TTS system. We introduce a novel TTS architecture designed to effectively model linguistic content and various speaker attributes from source speech and prompt speech, respectively. Furthermore, we present a two-stage self-distillation framework that constructs parallel data pairs for effectively disentangling linguistic content and speakers from the perspective of training data. Extensive experiments show that our system exhibits excellent performance and superior stability on the zero-shot TTS tasks. Moreover, it shows markedly superior computational efficiency, with RTFs of 0.13 and 0.012 on the CPU and GPU, respectively.
ALIF: Low-Cost Adversarial Audio Attacks on Black-Box Speech Platforms using Linguistic Features
Aug 03, 2024Abstract:Extensive research has revealed that adversarial examples (AE) pose a significant threat to voice-controllable smart devices. Recent studies have proposed black-box adversarial attacks that require only the final transcription from an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system. However, these attacks typically involve many queries to the ASR, resulting in substantial costs. Moreover, AE-based adversarial audio samples are susceptible to ASR updates. In this paper, we identify the root cause of these limitations, namely the inability to construct AE attack samples directly around the decision boundary of deep learning (DL) models. Building on this observation, we propose ALIF, the first black-box adversarial linguistic feature-based attack pipeline. We leverage the reciprocal process of text-to-speech (TTS) and ASR models to generate perturbations in the linguistic embedding space where the decision boundary resides. Based on the ALIF pipeline, we present the ALIF-OTL and ALIF-OTA schemes for launching attacks in both the digital domain and the physical playback environment on four commercial ASRs and voice assistants. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that ALIF-OTL and -OTA significantly improve query efficiency by 97.7% and 73.3%, respectively, while achieving competitive performance compared to existing methods. Notably, ALIF-OTL can generate an attack sample with only one query. Furthermore, our test-of-time experiment validates the robustness of our approach against ASR updates.
Exposing the Deception: Uncovering More Forgery Clues for Deepfake Detection
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Deepfake technology has given rise to a spectrum of novel and compelling applications. Unfortunately, the widespread proliferation of high-fidelity fake videos has led to pervasive confusion and deception, shattering our faith that seeing is believing. One aspect that has been overlooked so far is that current deepfake detection approaches may easily fall into the trap of overfitting, focusing only on forgery clues within one or a few local regions. Moreover, existing works heavily rely on neural networks to extract forgery features, lacking theoretical constraints guaranteeing that sufficient forgery clues are extracted and superfluous features are eliminated. These deficiencies culminate in unsatisfactory accuracy and limited generalizability in real-life scenarios. In this paper, we try to tackle these challenges through three designs: (1) We present a novel framework to capture broader forgery clues by extracting multiple non-overlapping local representations and fusing them into a global semantic-rich feature. (2) Based on the information bottleneck theory, we derive Local Information Loss to guarantee the orthogonality of local representations while preserving comprehensive task-relevant information. (3) Further, to fuse the local representations and remove task-irrelevant information, we arrive at a Global Information Loss through the theoretical analysis of mutual information. Empirically, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on five benchmark datasets.Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/QingyuLiu/Exposing-the-Deception}, hoping to inspire researchers.
Phoneme-Based Proactive Anti-Eavesdropping with Controlled Recording Privilege
Jan 28, 2024



Abstract:The widespread smart devices raise people's concerns of being eavesdropped on. To enhance voice privacy, recent studies exploit the nonlinearity in microphone to jam audio recorders with inaudible ultrasound. However, existing solutions solely rely on energetic masking. Their simple-form noise leads to several problems, such as high energy requirements and being easily removed by speech enhancement techniques. Besides, most of these solutions do not support authorized recording, which restricts their usage scenarios. In this paper, we design an efficient yet robust system that can jam microphones while preserving authorized recording. Specifically, we propose a novel phoneme-based noise with the idea of informational masking, which can distract both machines and humans and is resistant to denoising techniques. Besides, we optimize the noise transmission strategy for broader coverage and implement a hardware prototype of our system. Experimental results show that our system can reduce the recognition accuracy of recordings to below 50\% under all tested speech recognition systems, which is much better than existing solutions.
FLTracer: Accurate Poisoning Attack Provenance in Federated Learning
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a promising distributed learning approach that enables multiple clients to collaboratively train a shared global model. However, recent studies show that FL is vulnerable to various poisoning attacks, which can degrade the performance of global models or introduce backdoors into them. In this paper, we first conduct a comprehensive study on prior FL attacks and detection methods. The results show that all existing detection methods are only effective against limited and specific attacks. Most detection methods suffer from high false positives, which lead to significant performance degradation, especially in not independent and identically distributed (non-IID) settings. To address these issues, we propose FLTracer, the first FL attack provenance framework to accurately detect various attacks and trace the attack time, objective, type, and poisoned location of updates. Different from existing methodologies that rely solely on cross-client anomaly detection, we propose a Kalman filter-based cross-round detection to identify adversaries by seeking the behavior changes before and after the attack. Thus, this makes it resilient to data heterogeneity and is effective even in non-IID settings. To further improve the accuracy of our detection method, we employ four novel features and capture their anomalies with the joint decisions. Extensive evaluations show that FLTracer achieves an average true positive rate of over $96.88\%$ at an average false positive rate of less than $2.67\%$, significantly outperforming SOTA detection methods. \footnote{Code is available at \url{https://github.com/Eyr3/FLTracer}.}
Privacy-Utility Balanced Voice De-Identification Using Adversarial Examples
Nov 10, 2022



Abstract:Faced with the threat of identity leakage during voice data publishing, users are engaged in a privacy-utility dilemma when enjoying convenient voice services. Existing studies employ direct modification or text-based re-synthesis to de-identify users' voices, but resulting in inconsistent audibility in the presence of human participants. In this paper, we propose a voice de-identification system, which uses adversarial examples to balance the privacy and utility of voice services. Instead of typical additive examples inducing perceivable distortions, we design a novel convolutional adversarial example that modulates perturbations into real-world room impulse responses. Benefit from this, our system could preserve user identity from exposure by Automatic Speaker Identification (ASI) while remaining the voice perceptual quality for non-intrusive de-identification. Moreover, our system learns a compact speaker distribution through a conditional variational auto-encoder to sample diverse target embeddings on demand. Combining diverse target generation and input-specific perturbation construction, our system enables any-to-any identify transformation for adaptive de-identification. Experimental results show that our system could achieve 98% and 79% successful de-identification on mainstream ASIs and commercial systems with an objective Mel cepstral distortion of 4.31dB and a subjective mean opinion score of 4.48.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge