Yao Wei
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
SWE-Dev: Building Software Engineering Agents with Training and Inference Scaling
Jun 09, 2025
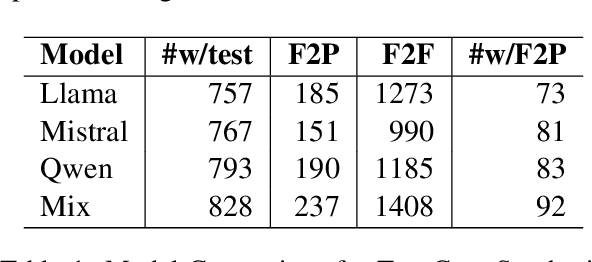
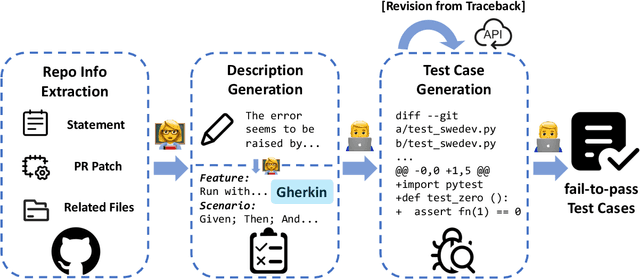
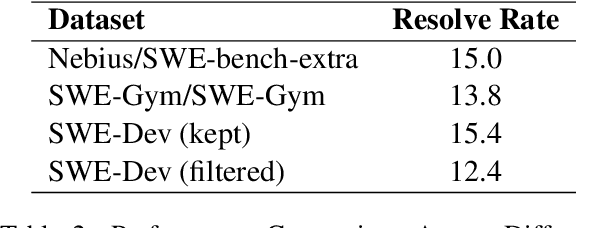
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have advanced rapidly from conversational problem solving to addressing real-world tasks involving tool use, such as software engineering (SWE). Recent LLM-powered toolkits, such as OpenAI Codex and Cursor, have offered end-to-end automation of the software development process. However, building effective SWE agents remains challenging due to the lack of high-quality training data and effective test cases. To address this issue, we present SWE-Dev, an SWE agent built upon open-source LLMs. First, we develop a robust pipeline to synthesize test cases for patch evaluation. Second, we scale up agent trajectories to construct the training data for building SWE-Dev. Experiments on the SWE-bench-Verified benchmark show that the SWE-Dev models can achieve top performance among all open SWE agents. Specifically, the success rates of the SWE-Dev 7B and 32B parameter models reach 23.4% and 36.6%, respectively, outperforming state-of-the-art open-source models. All code, models, and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/THUDM/SWE-Dev.
InspectionV3: Enhancing Tobacco Quality Assessment with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Automated Workshop Management
May 22, 2025Abstract:The problems that tobacco workshops encounter include poor curing, inconsistencies in supplies, irregular scheduling, and a lack of oversight, all of which drive up expenses and worse quality. Large quantities make manual examination costly, sluggish, and unreliable. Deep convolutional neural networks have recently made strides in capabilities that transcend those of conventional methods. To effectively enhance them, nevertheless, extensive customization is needed to account for subtle variations in tobacco grade. This study introduces InspectionV3, an integrated solution for automated flue-cured tobacco grading that makes use of a customized deep convolutional neural network architecture. A scope that covers color, maturity, and curing subtleties is established via a labelled dataset consisting of 21,113 images spanning 20 quality classes. Expert annotators performed preprocessing on the tobacco leaf images, including cleaning, labelling, and augmentation. Multi-layer CNN factors use batch normalization to describe domain properties like as permeability and moisture spots, and so account for the subtleties of the workshop. Its expertise lies in converting visual patterns into useful information for enhancing workflow. Fast notifications are made possible by real-time, on-the-spot grading that matches human expertise. Images-powered analytics dashboards facilitate the tracking of yield projections, inventories, bottlenecks, and the optimization of data-driven choices. More labelled images are assimilated after further retraining, improving representational capacities and enabling adaptations for seasonal variability. Metrics demonstrate 97% accuracy, 95% precision and recall, 96% F1-score and AUC, 95% specificity; validating real-world viability.
Compositional 3D Scene Synthesis with Scene Graph Guided Layout-Shape Generation
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:Compositional 3D scene synthesis has diverse applications across a spectrum of industries such as robotics, films, and video games, as it closely mirrors the complexity of real-world multi-object environments. Early works typically employ shape retrieval based frameworks which naturally suffer from limited shape diversity. Recent progresses have been made in shape generation with powerful generative models, such as diffusion models, which increases the shape fidelity. However, these approaches separately treat 3D shape generation and layout generation. The synthesized scenes are usually hampered by layout collision, which implies that the scene-level fidelity is still under-explored. In this paper, we aim at generating realistic and reasonable 3D scenes from scene graph. To enrich the representation capability of the given scene graph inputs, large language model is utilized to explicitly aggregate the global graph features with local relationship features. With a unified graph convolution network (GCN), graph features are extracted from scene graphs updated via joint layout-shape distribution. During scene generation, an IoU-based regularization loss is introduced to constrain the predicted 3D layouts. Benchmarked on the SG-FRONT dataset, our method achieves better 3D scene synthesis, especially in terms of scene-level fidelity. The source code will be released after publication.
Phoneme-Based Proactive Anti-Eavesdropping with Controlled Recording Privilege
Jan 28, 2024



Abstract:The widespread smart devices raise people's concerns of being eavesdropped on. To enhance voice privacy, recent studies exploit the nonlinearity in microphone to jam audio recorders with inaudible ultrasound. However, existing solutions solely rely on energetic masking. Their simple-form noise leads to several problems, such as high energy requirements and being easily removed by speech enhancement techniques. Besides, most of these solutions do not support authorized recording, which restricts their usage scenarios. In this paper, we design an efficient yet robust system that can jam microphones while preserving authorized recording. Specifically, we propose a novel phoneme-based noise with the idea of informational masking, which can distract both machines and humans and is resistant to denoising techniques. Besides, we optimize the noise transmission strategy for broader coverage and implement a hardware prototype of our system. Experimental results show that our system can reduce the recognition accuracy of recordings to below 50\% under all tested speech recognition systems, which is much better than existing solutions.
DFIL: Deepfake Incremental Learning by Exploiting Domain-invariant Forgery Clues
Sep 18, 2023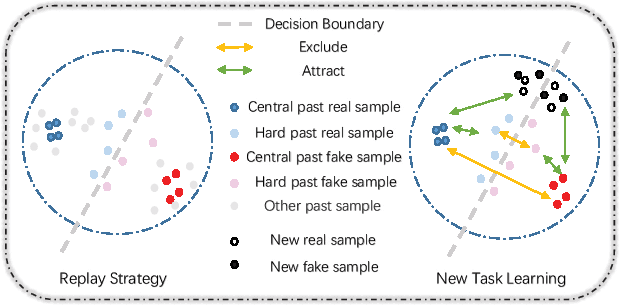

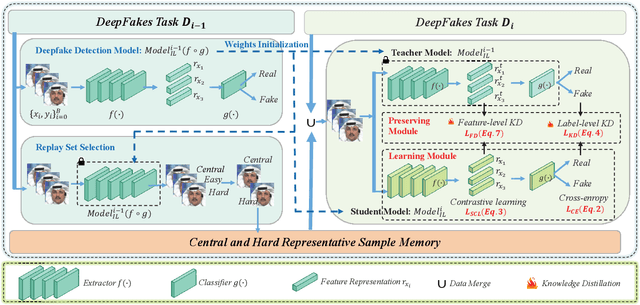

Abstract:The malicious use and widespread dissemination of deepfake pose a significant crisis of trust. Current deepfake detection models can generally recognize forgery images by training on a large dataset. However, the accuracy of detection models degrades significantly on images generated by new deepfake methods due to the difference in data distribution. To tackle this issue, we present a novel incremental learning framework that improves the generalization of deepfake detection models by continual learning from a small number of new samples. To cope with different data distributions, we propose to learn a domain-invariant representation based on supervised contrastive learning, preventing overfit to the insufficient new data. To mitigate catastrophic forgetting, we regularize our model in both feature-level and label-level based on a multi-perspective knowledge distillation approach. Finally, we propose to select both central and hard representative samples to update the replay set, which is beneficial for both domain-invariant representation learning and rehearsal-based knowledge preserving. We conduct extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets, obtaining the new state-of-the-art average forgetting rate of 7.01 and average accuracy of 85.49 on FF++, DFDC-P, DFD, and CDF2. Our code is released at https://github.com/DeepFakeIL/DFIL.
BuilDiff: 3D Building Shape Generation using Single-Image Conditional Point Cloud Diffusion Models
Aug 31, 2023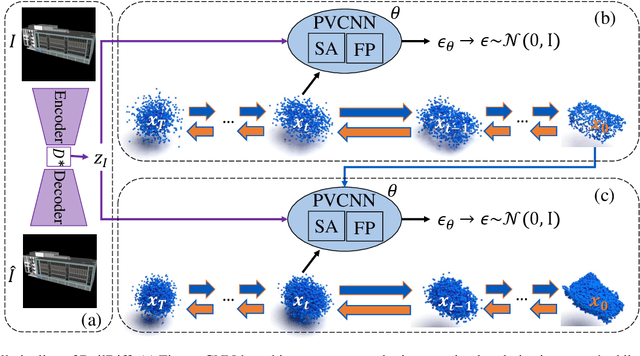
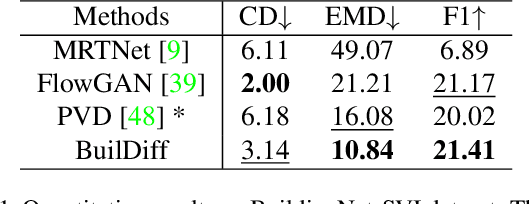
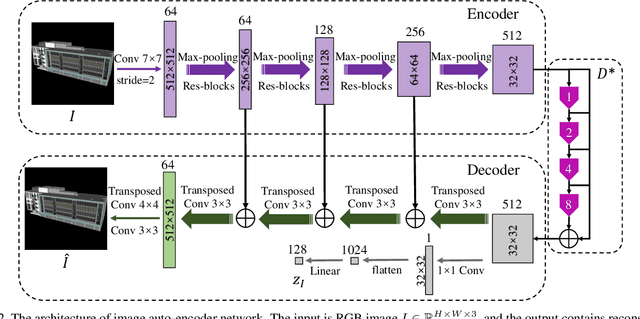
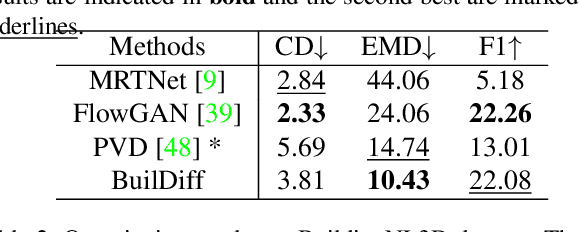
Abstract:3D building generation with low data acquisition costs, such as single image-to-3D, becomes increasingly important. However, most of the existing single image-to-3D building creation works are restricted to those images with specific viewing angles, hence they are difficult to scale to general-view images that commonly appear in practical cases. To fill this gap, we propose a novel 3D building shape generation method exploiting point cloud diffusion models with image conditioning schemes, which demonstrates flexibility to the input images. By cooperating two conditional diffusion models and introducing a regularization strategy during denoising process, our method is able to synthesize building roofs while maintaining the overall structures. We validate our framework on two newly built datasets and extensive experiments show that our method outperforms previous works in terms of building generation quality.
Is Imitation All You Need? Generalized Decision-Making with Dual-Phase Training
Jul 18, 2023



Abstract:We introduce DualMind, a generalist agent designed to tackle various decision-making tasks that addresses challenges posed by current methods, such as overfitting behaviors and dependence on task-specific fine-tuning. DualMind uses a novel "Dual-phase" training strategy that emulates how humans learn to act in the world. The model first learns fundamental common knowledge through a self-supervised objective tailored for control tasks and then learns how to make decisions based on different contexts through imitating behaviors conditioned on given prompts. DualMind can handle tasks across domains, scenes, and embodiments using just a single set of model weights and can execute zero-shot prompting without requiring task-specific fine-tuning. We evaluate DualMind on MetaWorld and Habitat through extensive experiments and demonstrate its superior generalizability compared to previous techniques, outperforming other generalist agents by over 50$\%$ and 70$\%$ on Habitat and MetaWorld, respectively. On the 45 tasks in MetaWorld, DualMind achieves over 30 tasks at a 90$\%$ success rate.
Attention Based Relation Network for Facial Action Units Recognition
Oct 23, 2022



Abstract:Facial action unit (AU) recognition is essential to facial expression analysis. Since there are highly positive or negative correlations between AUs, some existing AU recognition works have focused on modeling AU relations. However, previous relationship-based approaches typically embed predefined rules into their models and ignore the impact of various AU relations in different crowds. In this paper, we propose a novel Attention Based Relation Network (ABRNet) for AU recognition, which can automatically capture AU relations without unnecessary or even disturbing predefined rules. ABRNet uses several relation learning layers to automatically capture different AU relations. The learned AU relation features are then fed into a self-attention fusion module, which aims to refine individual AU features with attention weights to enhance the feature robustness. Furthermore, we propose an AU relation dropout strategy and AU relation loss (AUR-Loss) to better model AU relations, which can further improve AU recognition. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the DISFA and DISFA+ datasets.
Flow-based GAN for 3D Point Cloud Generation from a Single Image
Oct 08, 2022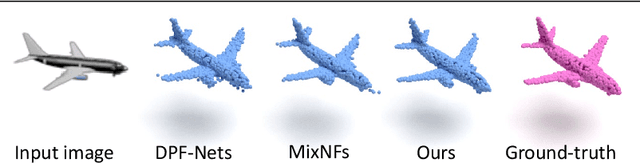
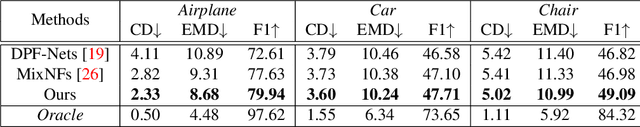
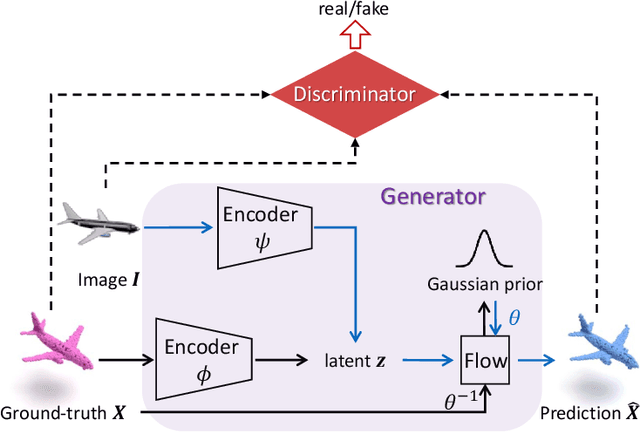
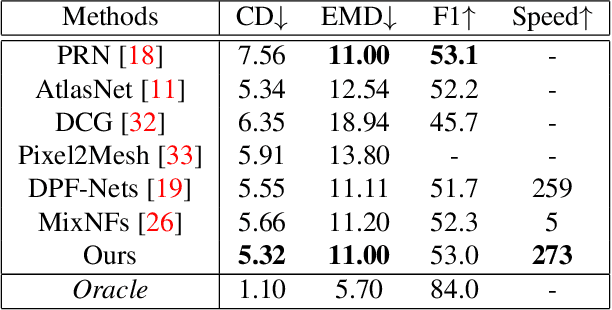
Abstract:Generating a 3D point cloud from a single 2D image is of great importance for 3D scene understanding applications. To reconstruct the whole 3D shape of the object shown in the image, the existing deep learning based approaches use either explicit or implicit generative modeling of point clouds, which, however, suffer from limited quality. In this work, we aim to alleviate this issue by introducing a hybrid explicit-implicit generative modeling scheme, which inherits the flow-based explicit generative models for sampling point clouds with arbitrary resolutions while improving the detailed 3D structures of point clouds by leveraging the implicit generative adversarial networks (GANs). We evaluate on the large-scale synthetic dataset ShapeNet, with the experimental results demonstrating the superior performance of the proposed method. In addition, the generalization ability of our method is demonstrated by performing on cross-category synthetic images as well as by testing on real images from PASCAL3D+ dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge