Zhiying Zhu
Model Discrepancy Learning: Synthetic Faces Detection Based on Multi-Reconstruction
Apr 10, 2025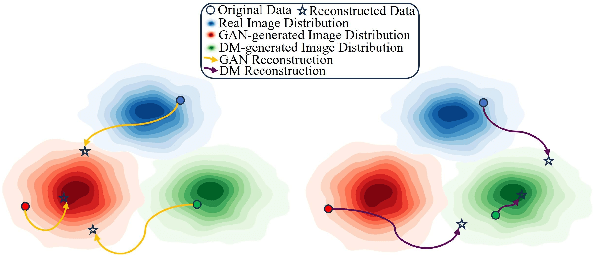
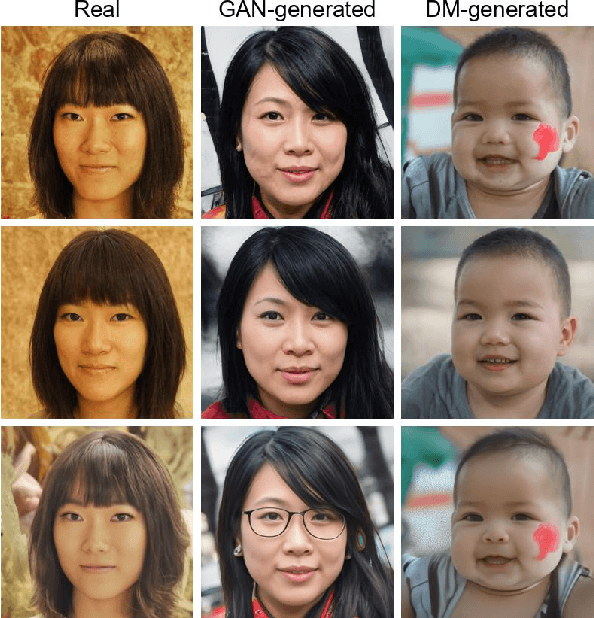

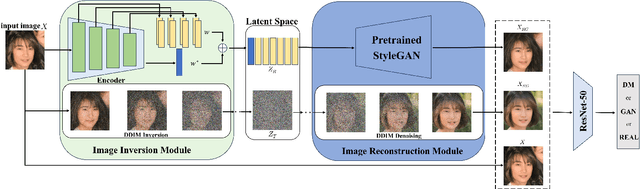

Abstract:Advances in image generation enable hyper-realistic synthetic faces but also pose risks, thus making synthetic face detection crucial. Previous research focuses on the general differences between generated images and real images, often overlooking the discrepancies among various generative techniques. In this paper, we explore the intrinsic relationship between synthetic images and their corresponding generation technologies. We find that specific images exhibit significant reconstruction discrepancies across different generative methods and that matching generation techniques provide more accurate reconstructions. Based on this insight, we propose a Multi-Reconstruction-based detector. By reversing and reconstructing images using multiple generative models, we analyze the reconstruction differences among real, GAN-generated, and DM-generated images to facilitate effective differentiation. Additionally, we introduce the Asian Synthetic Face Dataset (ASFD), containing synthetic Asian faces generated with various GANs and DMs. This dataset complements existing synthetic face datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our detector achieves exceptional performance, with strong generalization and robustness.
HaluEval-Wild: Evaluating Hallucinations of Language Models in the Wild
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Hallucinations pose a significant challenge to the reliability of large language models (LLMs) in critical domains. Recent benchmarks designed to assess LLM hallucinations within conventional NLP tasks, such as knowledge-intensive question answering (QA) and summarization, are insufficient for capturing the complexities of user-LLM interactions in dynamic, real-world settings. To address this gap, we introduce HaluEval-Wild, the first benchmark specifically designed to evaluate LLM hallucinations in the wild. We meticulously collect challenging (adversarially filtered by Alpaca) user queries from existing real-world user-LLM interaction datasets, including ShareGPT, to evaluate the hallucination rates of various LLMs. Upon analyzing the collected queries, we categorize them into five distinct types, which enables a fine-grained analysis of the types of hallucinations LLMs exhibit, and synthesize the reference answers with the powerful GPT-4 model and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Our benchmark offers a novel approach towards enhancing our comprehension and improvement of LLM reliability in scenarios reflective of real-world interactions.
GSCLIP : A Framework for Explaining Distribution Shifts in Natural Language
Jun 30, 2022


Abstract:Helping end users comprehend the abstract distribution shifts can greatly facilitate AI deployment. Motivated by this, we propose a novel task, dataset explanation. Given two image data sets, dataset explanation aims to automatically point out their dataset-level distribution shifts with natural language. Current techniques for monitoring distribution shifts provide inadequate information to understand datasets with the goal of improving data quality. Therefore, we introduce GSCLIP, a training-free framework to solve the dataset explanation task. In GSCLIP, we propose the selector as the first quantitative evaluation method to identify explanations that are proper to summarize dataset shifts. Furthermore, we leverage this selector to demonstrate the superiority of a generator based on language model generation. Systematic evaluation on natural data shift verifies that GSCLIP, a combined system of a hybrid generator group and an efficient selector is not only easy-to-use but also powerful for dataset explanation at scale.
Learning the Beauty in Songs: Neural Singing Voice Beautifier
Mar 02, 2022



Abstract:We are interested in a novel task, singing voice beautifying (SVB). Given the singing voice of an amateur singer, SVB aims to improve the intonation and vocal tone of the voice, while keeping the content and vocal timbre. Current automatic pitch correction techniques are immature, and most of them are restricted to intonation but ignore the overall aesthetic quality. Hence, we introduce Neural Singing Voice Beautifier (NSVB), the first generative model to solve the SVB task, which adopts a conditional variational autoencoder as the backbone and learns the latent representations of vocal tone. In NSVB, we propose a novel time-warping approach for pitch correction: Shape-Aware Dynamic Time Warping (SADTW), which ameliorates the robustness of existing time-warping approaches, to synchronize the amateur recording with the template pitch curve. Furthermore, we propose a latent-mapping algorithm in the latent space to convert the amateur vocal tone to the professional one. To achieve this, we also propose a new dataset containing parallel singing recordings of both amateur and professional versions. Extensive experiments on both Chinese and English songs demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods in terms of both objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available at~\url{https://neuralsvb.github.io}. Codes: \url{https://github.com/MoonInTheRiver/NeuralSVB}.
High-Speed and High-Quality Text-to-Lip Generation
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:As a key component of talking face generation, lip movements generation determines the naturalness and coherence of the generated talking face video. Prior literature mainly focuses on speech-to-lip generation while there is a paucity in text-to-lip (T2L) generation. T2L is a challenging task and existing end-to-end works depend on the attention mechanism and autoregressive (AR) decoding manner. However, the AR decoding manner generates current lip frame conditioned on frames generated previously, which inherently hinders the inference speed, and also has a detrimental effect on the quality of generated lip frames due to error propagation. This encourages the research of parallel T2L generation. In this work, we propose a novel parallel decoding model for high-speed and high-quality text-to-lip generation (HH-T2L). Specifically, we predict the duration of the encoded linguistic features and model the target lip frames conditioned on the encoded linguistic features with their duration in a non-autoregressive manner. Furthermore, we incorporate the structural similarity index loss and adversarial learning to improve perceptual quality of generated lip frames and alleviate the blurry prediction problem. Extensive experiments conducted on GRID and TCD-TIMIT datasets show that 1) HH-T2L generates lip movements with competitive quality compared with the state-of-the-art AR T2L model DualLip and exceeds the baseline AR model TransformerT2L by a notable margin benefiting from the mitigation of the error propagation problem; and 2) exhibits distinct superiority in inference speed (an average speedup of 19$\times$ than DualLip on TCD-TIMIT).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge