Zhonghua Zhai
Composable Visual Tokenizers with Generator-Free Diagnostics of Learnability
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We introduce CompTok, a training framework for learning visual tokenizers whose tokens are enhanced for compositionality. CompTok uses a token-conditioned diffusion decoder. By employing an InfoGAN-style objective, where we train a recognition model to predict the tokens used to condition the diffusion decoder using the decoded images, we enforce the decoder to not ignore any of the tokens. To promote compositional control, besides the original images, CompTok also trains on tokens formed by swapping token subsets between images, enabling more compositional control of the token over the decoder. As the swapped tokens between images do not have ground truth image targets, we apply a manifold constraint via an adversarial flow regularizer to keep unpaired swap generations on the natural-image distribution. The resulting tokenizer not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on image class-conditioned generation, but also demonstrates properties such as swapping tokens between images to achieve high level semantic editing of an image. Additionally, we propose two metrics that measures the landscape of the token space that can be useful to describe not only the compositionality of the tokens, but also how easy to learn the landscape is for a generator to be trained on this space. We show in experiments that CompTok can improve on both of the metrics as well as supporting state-of-the-art generators for class conditioned generation.
Revisiting Multi-Task Visual Representation Learning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Current visual representation learning remains bifurcated: vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) excel at global semantic alignment but lack spatial precision, while self-supervised methods (e.g., MAE, DINO) capture intricate local structures yet struggle with high-level semantic context. We argue that these paradigms are fundamentally complementary and can be integrated into a principled multi-task framework, further enhanced by dense spatial supervision. We introduce MTV, a multi-task visual pretraining framework that jointly optimizes a shared backbone across vision-language contrastive, self-supervised, and dense spatial objectives. To mitigate the need for manual annotations, we leverage high-capacity "expert" models -- such as Depth Anything V2 and OWLv2 -- to synthesize dense, structured pseudo-labels at scale. Beyond the framework, we provide a systematic investigation into the mechanics of multi-task visual learning, analyzing: (i) the marginal gain of each objective, (ii) task synergies versus interference, and (iii) scaling behavior across varying data and model scales. Our results demonstrate that MTV achieves "best-of-both-worlds" performance, significantly enhancing fine-grained spatial reasoning without compromising global semantic understanding. Our findings suggest that multi-task learning, fueled by high-quality pseudo-supervision, is a scalable path toward more general visual encoders.
Universal Video Temporal Grounding with Generative Multi-modal Large Language Models
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a computational model for universal video temporal grounding, which accurately localizes temporal moments in videos based on natural language queries (e.g., questions or descriptions). Unlike existing methods that are often limited to specific video domains or durations, we propose UniTime, a robust and universal video grounding model leveraging the strong vision-language understanding capabilities of generative Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Our model effectively handles videos of diverse views, genres, and lengths while comprehending complex language queries. The key contributions include: (i) We consider steering strong MLLMs for temporal grounding in videos. To enable precise timestamp outputs, we incorporate temporal information by interleaving timestamp tokens with video tokens. (ii) By training the model to handle videos with different input granularities through adaptive frame scaling, our approach achieves robust temporal grounding for both short and long videos. (iii) Comprehensive experiments show that UniTime outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both zero-shot and dataset-specific finetuned settings across five public temporal grounding benchmarks. (iv) When employed as a preliminary moment retriever for long-form video question-answering (VideoQA), UniTime significantly improves VideoQA accuracy, highlighting its value for complex video understanding tasks.
SeedEdit 3.0: Fast and High-Quality Generative Image Editing
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce SeedEdit 3.0, in companion with our T2I model Seedream 3.0, which significantly improves over our previous SeedEdit versions in both aspects of edit instruction following and image content (e.g., ID/IP) preservation on real image inputs. Additional to model upgrading with T2I, in this report, we present several key improvements. First, we develop an enhanced data curation pipeline with a meta-info paradigm and meta-info embedding strategy that help mix images from multiple data sources. This allows us to scale editing data effectively, and meta information is helpfult to connect VLM with diffusion model more closely. Second, we introduce a joint learning pipeline for computing a diffusion loss and reward losses. Finally, we evaluate SeedEdit 3.0 on our testing benchmarks, for real/synthetic image editing, where it achieves a best trade-off between multiple aspects, yielding a high usability rate of 56.1%, compared to SeedEdit 1.6 (38.4%), GPT4o (37.1%) and Gemini 2.0 (30.3%).
Seedream 3.0 Technical Report
Apr 16, 2025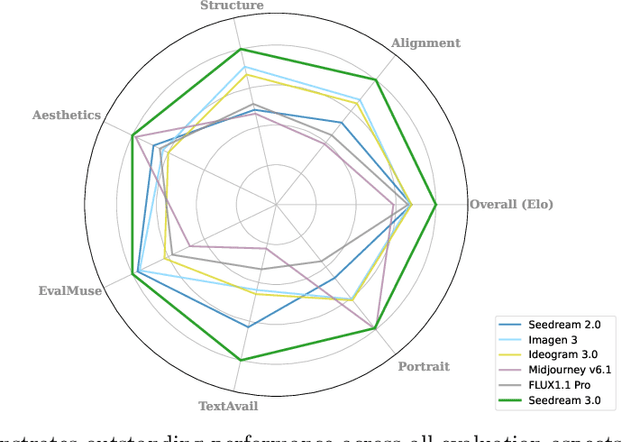
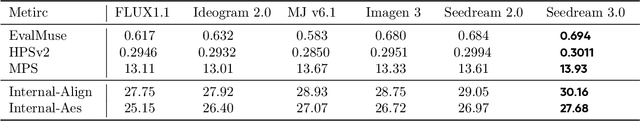

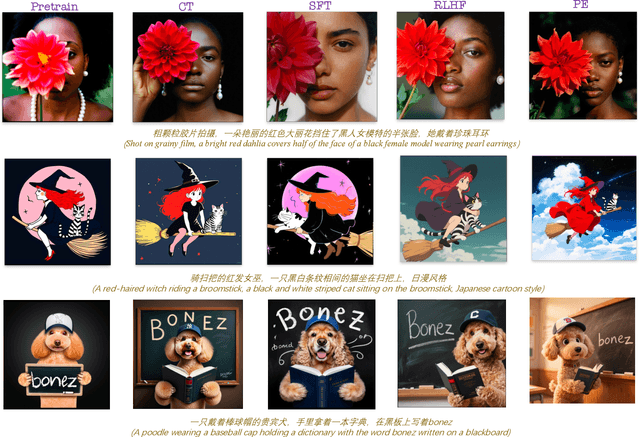
Abstract:We present Seedream 3.0, a high-performance Chinese-English bilingual image generation foundation model. We develop several technical improvements to address existing challenges in Seedream 2.0, including alignment with complicated prompts, fine-grained typography generation, suboptimal visual aesthetics and fidelity, and limited image resolutions. Specifically, the advancements of Seedream 3.0 stem from improvements across the entire pipeline, from data construction to model deployment. At the data stratum, we double the dataset using a defect-aware training paradigm and a dual-axis collaborative data-sampling framework. Furthermore, we adopt several effective techniques such as mixed-resolution training, cross-modality RoPE, representation alignment loss, and resolution-aware timestep sampling in the pre-training phase. During the post-training stage, we utilize diversified aesthetic captions in SFT, and a VLM-based reward model with scaling, thereby achieving outputs that well align with human preferences. Furthermore, Seedream 3.0 pioneers a novel acceleration paradigm. By employing consistent noise expectation and importance-aware timestep sampling, we achieve a 4 to 8 times speedup while maintaining image quality. Seedream 3.0 demonstrates significant improvements over Seedream 2.0: it enhances overall capabilities, in particular for text-rendering in complicated Chinese characters which is important to professional typography generation. In addition, it provides native high-resolution output (up to 2K), allowing it to generate images with high visual quality.
Seedream 2.0: A Native Chinese-English Bilingual Image Generation Foundation Model
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Rapid advancement of diffusion models has catalyzed remarkable progress in the field of image generation. However, prevalent models such as Flux, SD3.5 and Midjourney, still grapple with issues like model bias, limited text rendering capabilities, and insufficient understanding of Chinese cultural nuances. To address these limitations, we present Seedream 2.0, a native Chinese-English bilingual image generation foundation model that excels across diverse dimensions, which adeptly manages text prompt in both Chinese and English, supporting bilingual image generation and text rendering. We develop a powerful data system that facilitates knowledge integration, and a caption system that balances the accuracy and richness for image description. Particularly, Seedream is integrated with a self-developed bilingual large language model as a text encoder, allowing it to learn native knowledge directly from massive data. This enable it to generate high-fidelity images with accurate cultural nuances and aesthetic expressions described in either Chinese or English. Beside, Glyph-Aligned ByT5 is applied for flexible character-level text rendering, while a Scaled ROPE generalizes well to untrained resolutions. Multi-phase post-training optimizations, including SFT and RLHF iterations, further improve the overall capability. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that Seedream 2.0 achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple aspects, including prompt-following, aesthetics, text rendering, and structural correctness. Furthermore, Seedream 2.0 has been optimized through multiple RLHF iterations to closely align its output with human preferences, as revealed by its outstanding ELO score. In addition, it can be readily adapted to an instruction-based image editing model, such as SeedEdit, with strong editing capability that balances instruction-following and image consistency.
Tunnel Try-on: Excavating Spatial-temporal Tunnels for High-quality Virtual Try-on in Videos
Apr 26, 2024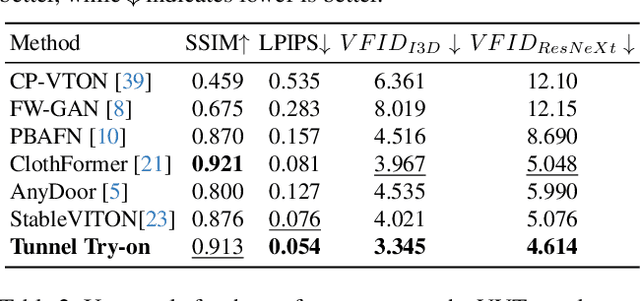
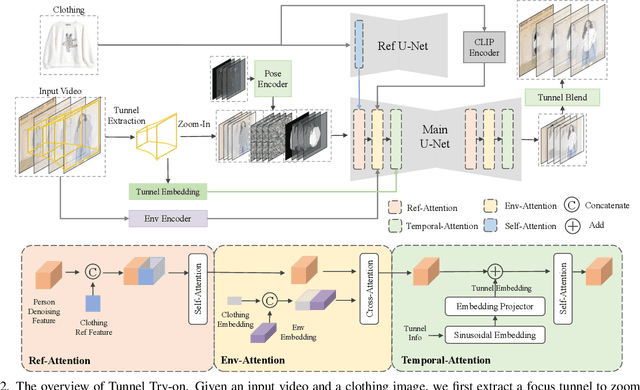
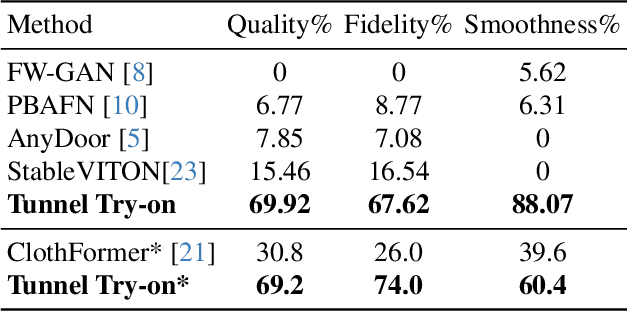

Abstract:Video try-on is a challenging task and has not been well tackled in previous works. The main obstacle lies in preserving the details of the clothing and modeling the coherent motions simultaneously. Faced with those difficulties, we address video try-on by proposing a diffusion-based framework named "Tunnel Try-on." The core idea is excavating a "focus tunnel" in the input video that gives close-up shots around the clothing regions. We zoom in on the region in the tunnel to better preserve the fine details of the clothing. To generate coherent motions, we first leverage the Kalman filter to construct smooth crops in the focus tunnel and inject the position embedding of the tunnel into attention layers to improve the continuity of the generated videos. In addition, we develop an environment encoder to extract the context information outside the tunnels as supplementary cues. Equipped with these techniques, Tunnel Try-on keeps the fine details of the clothing and synthesizes stable and smooth videos. Demonstrating significant advancements, Tunnel Try-on could be regarded as the first attempt toward the commercial-level application of virtual try-on in videos.
Cell Variational Information Bottleneck Network
Mar 29, 2024
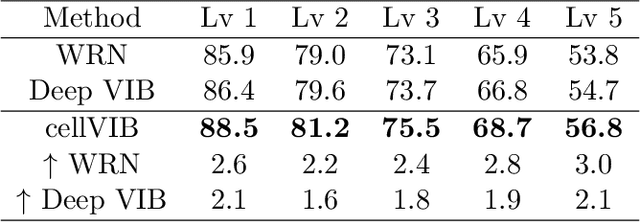

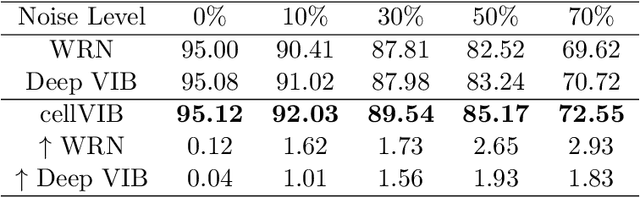
Abstract:In this work, we propose Cell Variational Information Bottleneck Network (cellVIB), a convolutional neural network using information bottleneck mechanism, which can be combined with the latest feedforward network architecture in an end-to-end training method. Our Cell Variational Information Bottleneck Network is constructed by stacking VIB cells, which generate feature maps with uncertainty. As layers going deeper, the regularization effect will gradually increase, instead of directly adding excessive regular constraints to the output layer of the model as in Deep VIB. Under each VIB cell, the feedforward process learns an independent mean term and an standard deviation term, and predicts the Gaussian distribution based on them. The feedback process is based on reparameterization trick for effective training. This work performs an extensive analysis on MNIST dataset to verify the effectiveness of each VIB cells, and provides an insightful analysis on how the VIB cells affect mutual information. Experiments conducted on CIFAR-10 also prove that our cellVIB is robust against noisy labels during training and against corrupted images during testing. Then, we validate our method on PACS dataset, whose results show that the VIB cells can significantly improve the generalization performance of the basic model. Finally, in a more complex representation learning task, face recognition, our network structure has also achieved very competitive results.
Wear-Any-Way: Manipulable Virtual Try-on via Sparse Correspondence Alignment
Mar 19, 2024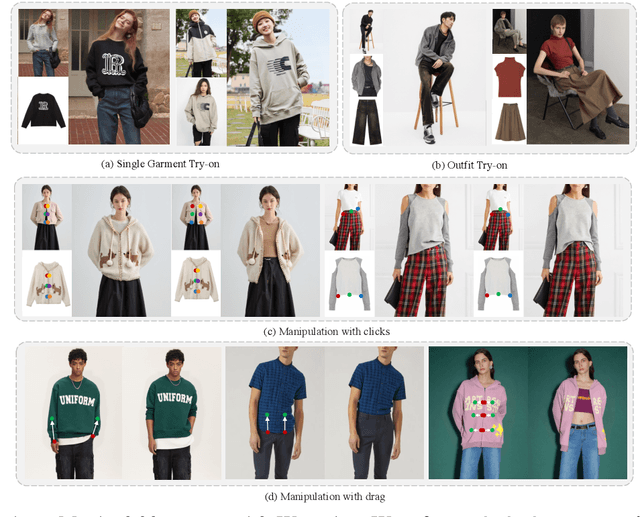

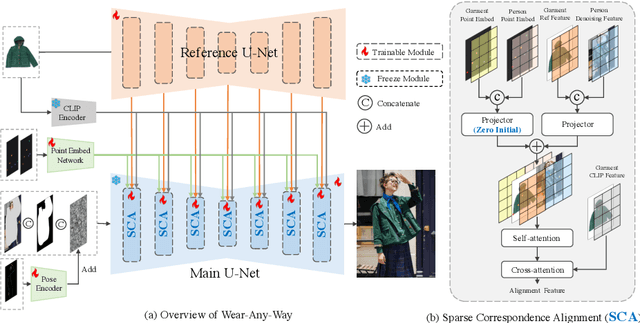
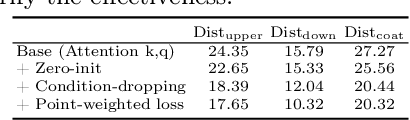
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel framework for virtual try-on, termed Wear-Any-Way. Different from previous methods, Wear-Any-Way is a customizable solution. Besides generating high-fidelity results, our method supports users to precisely manipulate the wearing style. To achieve this goal, we first construct a strong pipeline for standard virtual try-on, supporting single/multiple garment try-on and model-to-model settings in complicated scenarios. To make it manipulable, we propose sparse correspondence alignment which involves point-based control to guide the generation for specific locations. With this design, Wear-Any-Way gets state-of-the-art performance for the standard setting and provides a novel interaction form for customizing the wearing style. For instance, it supports users to drag the sleeve to make it rolled up, drag the coat to make it open, and utilize clicks to control the style of tuck, etc. Wear-Any-Way enables more liberated and flexible expressions of the attires, holding profound implications in the fashion industry.
Turbo: Informativity-Driven Acceleration Plug-In for Vision-Language Models
Dec 12, 2023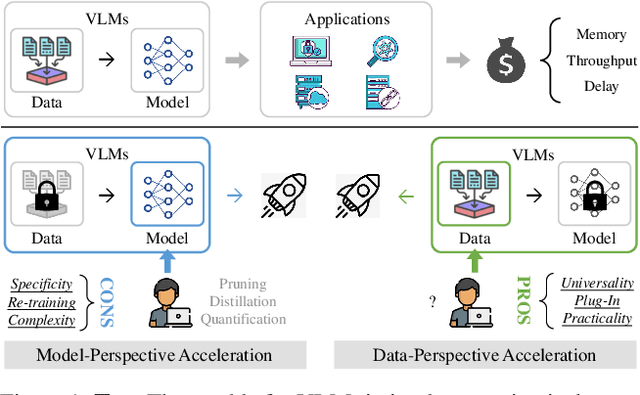
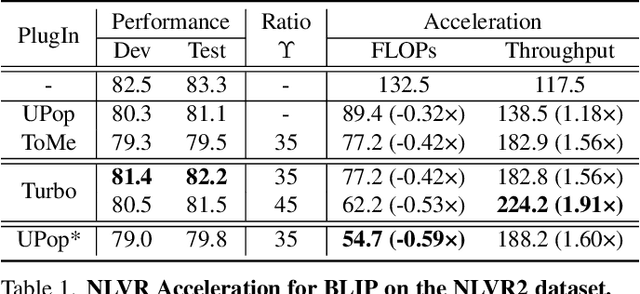
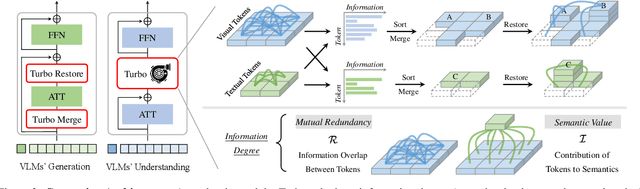
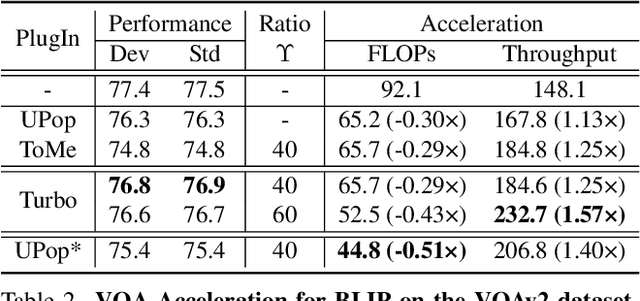
Abstract:Vision-Language Large Models (VLMs) have become primary backbone of AI, due to the impressive performance. However, their expensive computation costs, i.e., throughput and delay, impede potentials in real-world scenarios. To achieve acceleration for VLMs, most existing methods focus on the model perspective: pruning, distillation, quantification, but completely overlook the data-perspective redundancy. To fill the overlook, this paper pioneers the severity of data redundancy, and designs one plug-and-play Turbo module guided by information degree to prune inefficient tokens from visual or textual data. In pursuit of efficiency-performance trade-offs, information degree takes two key factors into consideration: mutual redundancy and semantic value. Concretely, the former evaluates the data duplication between sequential tokens; while the latter evaluates each token by its contribution to the overall semantics. As a result, tokens with high information degree carry less redundancy and stronger semantics. For VLMs' calculation, Turbo works as a user-friendly plug-in that sorts data referring to information degree, utilizing only top-level ones to save costs. Its advantages are multifaceted, e.g., being generally compatible to various VLMs across understanding and generation, simple use without retraining and trivial engineering efforts. On multiple public VLMs benchmarks, we conduct extensive experiments to reveal the gratifying acceleration of Turbo, under negligible performance drop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge