Yitian Zhao
Leveraging Persistence Image to Enhance Robustness and Performance in Curvilinear Structure Segmentation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Segmenting curvilinear structures in medical images is essential for analyzing morphological patterns in clinical applications. Integrating topological properties, such as connectivity, improves segmentation accuracy and consistency. However, extracting and embedding such properties - especially from Persistence Diagrams (PD) - is challenging due to their non-differentiability and computational cost. Existing approaches mostly encode topology through handcrafted loss functions, which generalize poorly across tasks. In this paper, we propose PIs-Regressor, a simple yet effective module that learns persistence image (PI) - finite, differentiable representations of topological features - directly from data. Together with Topology SegNet, which fuses these features in both downsampling and upsampling stages, our framework integrates topology into the network architecture itself rather than auxiliary losses. Unlike existing methods that depend heavily on handcrafted loss functions, our approach directly incorporates topological information into the network structure, leading to more robust segmentation. Our design is flexible and can be seamlessly combined with other topology-based methods to further enhance segmentation performance. Experimental results show that integrating topological features enhances model robustness, effectively handling challenges like overexposure and blurring in medical imaging. Our approach on three curvilinear benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in both pixel-level accuracy and topological fidelity.
StealthMark: Harmless and Stealthy Ownership Verification for Medical Segmentation via Uncertainty-Guided Backdoors
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Annotating medical data for training AI models is often costly and limited due to the shortage of specialists with relevant clinical expertise. This challenge is further compounded by privacy and ethical concerns associated with sensitive patient information. As a result, well-trained medical segmentation models on private datasets constitute valuable intellectual property requiring robust protection mechanisms. Existing model protection techniques primarily focus on classification and generative tasks, while segmentation models-crucial to medical image analysis-remain largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel, stealthy, and harmless method, StealthMark, for verifying the ownership of medical segmentation models under black-box conditions. Our approach subtly modulates model uncertainty without altering the final segmentation outputs, thereby preserving the model's performance. To enable ownership verification, we incorporate model-agnostic explanation methods, e.g. LIME, to extract feature attributions from the model outputs. Under specific triggering conditions, these explanations reveal a distinct and verifiable watermark. We further design the watermark as a QR code to facilitate robust and recognizable ownership claims. We conducted extensive experiments across four medical imaging datasets and five mainstream segmentation models. The results demonstrate the effectiveness, stealthiness, and harmlessness of our method on the original model's segmentation performance. For example, when applied to the SAM model, StealthMark consistently achieved ASR above 95% across various datasets while maintaining less than a 1% drop in Dice and AUC scores, significantly outperforming backdoor-based watermarking methods and highlighting its strong potential for practical deployment. Our implementation code is made available at: https://github.com/Qinkaiyu/StealthMark.
A Frequency-Aware Self-Supervised Learning for Ultra-Wide-Field Image Enhancement
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Ultra-Wide-Field (UWF) retinal imaging has revolutionized retinal diagnostics by providing a comprehensive view of the retina. However, it often suffers from quality-degrading factors such as blurring and uneven illumination, which obscure fine details and mask pathological information. While numerous retinal image enhancement methods have been proposed for other fundus imageries, they often fail to address the unique requirements in UWF, particularly the need to preserve pathological details. In this paper, we propose a novel frequency-aware self-supervised learning method for UWF image enhancement. It incorporates frequency-decoupled image deblurring and Retinex-guided illumination compensation modules. An asymmetric channel integration operation is introduced in the former module, so as to combine global and local views by leveraging high- and low-frequency information, ensuring the preservation of fine and broader structural details. In addition, a color preservation unit is proposed in the latter Retinex-based module, to provide multi-scale spatial and frequency information, enabling accurate illumination estimation and correction. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed work not only enhances visualization quality but also improves disease diagnosis performance by restoring and correcting fine local details and uneven intensity. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt for UWF image enhancement, offering a robust and clinically valuable tool for improving retinal disease management.
Are Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolution Networks for Human Action Recognition Over-Parameterized?
May 15, 2025Abstract:Spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCNs) showcase impressive performance in skeleton-based human action recognition (HAR). However, despite the development of numerous models, their recognition performance does not differ significantly after aligning the input settings. With this observation, we hypothesize that ST-GCNs are over-parameterized for HAR, a conjecture subsequently confirmed through experiments employing the lottery ticket hypothesis. Additionally, a novel sparse ST-GCNs generator is proposed, which trains a sparse architecture from a randomly initialized dense network while maintaining comparable performance levels to the dense components. Moreover, we generate multi-level sparsity ST-GCNs by integrating sparse structures at various sparsity levels and demonstrate that the assembled model yields a significant enhancement in HAR performance. Thorough experiments on four datasets, including NTU-RGB+D 60(120), Kinetics-400, and FineGYM, demonstrate that the proposed sparse ST-GCNs can achieve comparable performance to their dense components. Even with 95% fewer parameters, the sparse ST-GCNs exhibit a degradation of <1% in top-1 accuracy. Meanwhile, the multi-level sparsity ST-GCNs, which require only 66% of the parameters of the dense ST-GCNs, demonstrate an improvement of >1% in top-1 accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/davelailai/Sparse-ST-GCN.
A Clinician-Friendly Platform for Ophthalmic Image Analysis Without Technical Barriers
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) shows remarkable potential in medical imaging diagnostics, but current models typically require retraining when deployed across different clinical centers, limiting their widespread adoption. We introduce GlobeReady, a clinician-friendly AI platform that enables ocular disease diagnosis without retraining/fine-tuning or technical expertise. GlobeReady achieves high accuracy across imaging modalities: 93.9-98.5% for an 11-category fundus photo dataset and 87.2-92.7% for a 15-category OCT dataset. Through training-free local feature augmentation, it addresses domain shifts across centers and populations, reaching an average accuracy of 88.9% across five centers in China, 86.3% in Vietnam, and 90.2% in the UK. The built-in confidence-quantifiable diagnostic approach further boosted accuracy to 94.9-99.4% (fundus) and 88.2-96.2% (OCT), while identifying out-of-distribution cases at 86.3% (49 CFP categories) and 90.6% (13 OCT categories). Clinicians from multiple countries rated GlobeReady highly (average 4.6 out of 5) for its usability and clinical relevance. These results demonstrate GlobeReady's robust, scalable diagnostic capability and potential to support ophthalmic care without technical barriers.
MIFNet: Learning Modality-Invariant Features for Generalizable Multimodal Image Matching
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:Many keypoint detection and description methods have been proposed for image matching or registration. While these methods demonstrate promising performance for single-modality image matching, they often struggle with multimodal data because the descriptors trained on single-modality data tend to lack robustness against the non-linear variations present in multimodal data. Extending such methods to multimodal image matching often requires well-aligned multimodal data to learn modality-invariant descriptors. However, acquiring such data is often costly and impractical in many real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a modality-invariant feature learning network (MIFNet) to compute modality-invariant features for keypoint descriptions in multimodal image matching using only single-modality training data. Specifically, we propose a novel latent feature aggregation module and a cumulative hybrid aggregation module to enhance the base keypoint descriptors trained on single-modality data by leveraging pre-trained features from Stable Diffusion models. We validate our method with recent keypoint detection and description methods in three multimodal retinal image datasets (CF-FA, CF-OCT, EMA-OCTA) and two remote sensing datasets (Optical-SAR and Optical-NIR). Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed MIFNet is able to learn modality-invariant feature for multimodal image matching without accessing the targeted modality and has good zero-shot generalization ability. The source code will be made publicly available.
Beyond the Eye: A Relational Model for Early Dementia Detection Using Retinal OCTA Images
Aug 09, 2024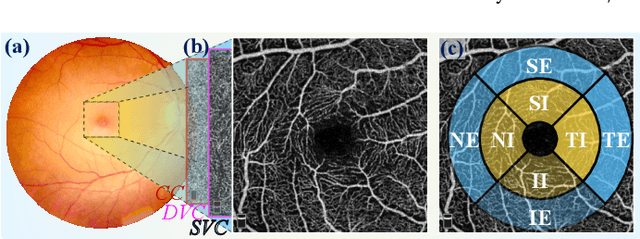
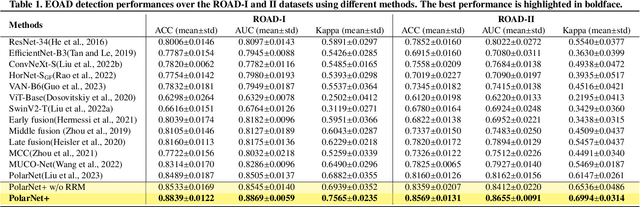
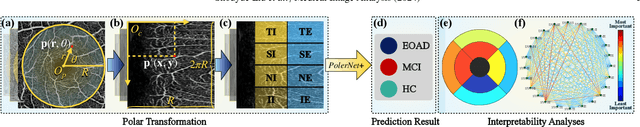
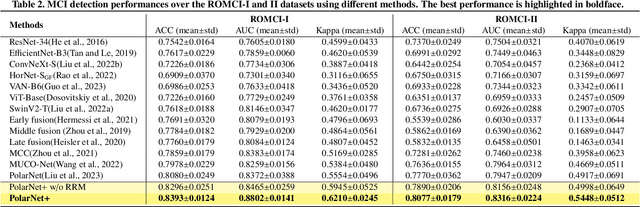
Abstract:Early detection of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) or mild cognitive impairment (MCI), is essential to enable timely intervention and potential treatment. Accurate detection of AD/MCI is challenging due to the high complexity, cost, and often invasive nature of current diagnostic techniques, which limit their suitability for large-scale population screening. Given the shared embryological origins and physiological characteristics of the retina and brain, retinal imaging is emerging as a potentially rapid and cost-effective alternative for the identification of individuals with or at high risk of AD. In this paper, we present a novel PolarNet+ that uses retinal optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) to discriminate early-onset AD (EOAD) and MCI subjects from controls. Our method first maps OCTA images from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates, allowing approximate sub-region calculation to implement the clinician-friendly early treatment of diabetic retinopathy study (ETDRS) grid analysis. We then introduce a multi-view module to serialize and analyze the images along three dimensions for comprehensive, clinically useful information extraction. Finally, we abstract the sequence embedding into a graph, transforming the detection task into a general graph classification problem. A regional relationship module is applied after the multi-view module to excavate the relationship between the sub-regions. Such regional relationship analyses validate known eye-brain links and reveal new discriminative patterns.
CLIP-DR: Textual Knowledge-Guided Diabetic Retinopathy Grading with Ranking-aware Prompting
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a complication of diabetes and usually takes decades to reach sight-threatening levels. Accurate and robust detection of DR severity is critical for the timely management and treatment of diabetes. However, most current DR grading methods suffer from insufficient robustness to data variability (\textit{e.g.} colour fundus images), posing a significant difficulty for accurate and robust grading. In this work, we propose a novel DR grading framework CLIP-DR based on three observations: 1) Recent pre-trained visual language models, such as CLIP, showcase a notable capacity for generalisation across various downstream tasks, serving as effective baseline models. 2) The grading of image-text pairs for DR often adheres to a discernible natural sequence, yet most existing DR grading methods have primarily overlooked this aspect. 3) A long-tailed distribution among DR severity levels complicates the grading process. This work proposes a novel ranking-aware prompting strategy to help the CLIP model exploit the ordinal information. Specifically, we sequentially design learnable prompts between neighbouring text-image pairs in two different ranking directions. Additionally, we introduce a Similarity Matrix Smooth module into the structure of CLIP to balance the class distribution. Finally, we perform extensive comparisons with several state-of-the-art methods on the GDRBench benchmark, demonstrating our CLIP-DR's robustness and superior performance. The implementation code is available \footnote{\url{https://github.com/Qinkaiyu/CLIP-DR}
DSCA: A Digital Subtraction Angiography Sequence Dataset and Spatio-Temporal Model for Cerebral Artery Segmentation
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:Cerebrovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading cause of global disability and mortality. Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) sequences, recognized as the golden standard for diagnosing CVDs, can clearly visualize the dynamic flow and reveal pathological conditions within the cerebrovasculature. Therefore, precise segmentation of cerebral arteries (CAs) and classification between their main trunks and branches are crucial for physicians to accurately quantify diseases. However, achieving accurate CA segmentation in DSA sequences remains a challenging task due to small vessels with low contrast, and ambiguity between vessels and residual skull structures. Moreover, the lack of publicly available datasets limits exploration in the field. In this paper, we introduce a DSA Sequence-based Cerebral Artery segmentation dataset (DSCA), the first publicly accessible dataset designed specifically for pixel-level semantic segmentation of CAs. Additionally, we propose DSANet, a spatio-temporal network for CA segmentation in DSA sequences. Unlike existing DSA segmentation methods that focus only on a single frame, the proposed DSANet introduces a separate temporal encoding branch to capture dynamic vessel details across multiple frames. To enhance small vessel segmentation and improve vessel connectivity, we design a novel TemporalFormer module to capture global context and correlations among sequential frames. Furthermore, we develop a Spatio-Temporal Fusion (STF) module to effectively integrate spatial and temporal features from the encoder. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DSANet outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in CA segmentation, achieving a Dice of 0.9033.
Polar-Net: A Clinical-Friendly Model for Alzheimer's Disease Detection in OCTA Images
Nov 10, 2023Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) is a promising tool for detecting Alzheimer's disease (AD) by imaging the retinal microvasculature. Ophthalmologists commonly use region-based analysis, such as the ETDRS grid, to study OCTA image biomarkers and understand the correlation with AD. However, existing studies have used general deep computer vision methods, which present challenges in providing interpretable results and leveraging clinical prior knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose a novel deep-learning framework called Polar-Net. Our approach involves mapping OCTA images from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates, which allows for the use of approximate sector convolution and enables the implementation of the ETDRS grid-based regional analysis method commonly used in clinical practice. Furthermore, Polar-Net incorporates clinical prior information of each sector region into the training process, which further enhances its performance. Additionally, our framework adapts to acquire the importance of the corresponding retinal region, which helps researchers and clinicians understand the model's decision-making process in detecting AD and assess its conformity to clinical observations. Through evaluations on private and public datasets, we have demonstrated that Polar-Net outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods and provides more valuable pathological evidence for the association between retinal vascular changes and AD. In addition, we also show that the two innovative modules introduced in our framework have a significant impact on improving overall performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge