Shouyue Liu
Beyond the Eye: A Relational Model for Early Dementia Detection Using Retinal OCTA Images
Aug 09, 2024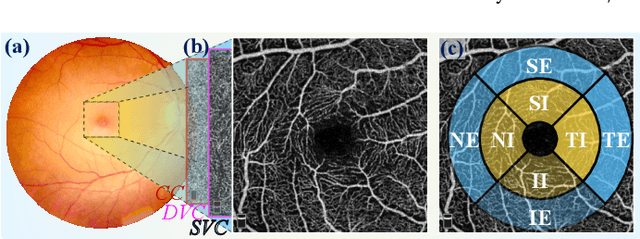
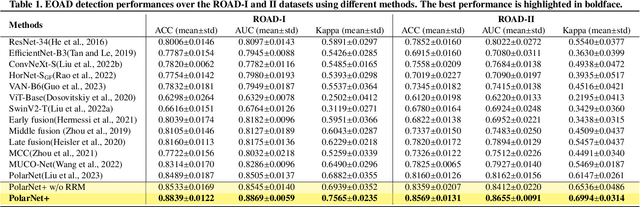
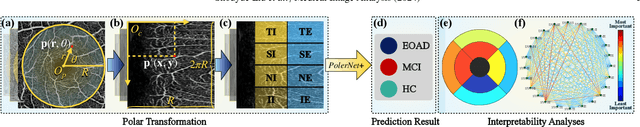
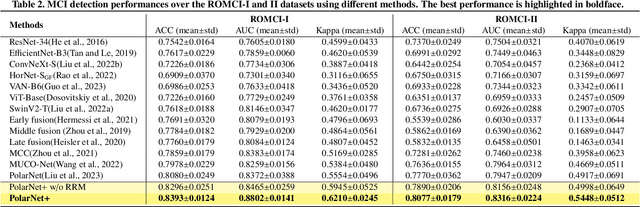
Abstract:Early detection of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) or mild cognitive impairment (MCI), is essential to enable timely intervention and potential treatment. Accurate detection of AD/MCI is challenging due to the high complexity, cost, and often invasive nature of current diagnostic techniques, which limit their suitability for large-scale population screening. Given the shared embryological origins and physiological characteristics of the retina and brain, retinal imaging is emerging as a potentially rapid and cost-effective alternative for the identification of individuals with or at high risk of AD. In this paper, we present a novel PolarNet+ that uses retinal optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) to discriminate early-onset AD (EOAD) and MCI subjects from controls. Our method first maps OCTA images from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates, allowing approximate sub-region calculation to implement the clinician-friendly early treatment of diabetic retinopathy study (ETDRS) grid analysis. We then introduce a multi-view module to serialize and analyze the images along three dimensions for comprehensive, clinically useful information extraction. Finally, we abstract the sequence embedding into a graph, transforming the detection task into a general graph classification problem. A regional relationship module is applied after the multi-view module to excavate the relationship between the sub-regions. Such regional relationship analyses validate known eye-brain links and reveal new discriminative patterns.
Polar-Net: A Clinical-Friendly Model for Alzheimer's Disease Detection in OCTA Images
Nov 10, 2023Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) is a promising tool for detecting Alzheimer's disease (AD) by imaging the retinal microvasculature. Ophthalmologists commonly use region-based analysis, such as the ETDRS grid, to study OCTA image biomarkers and understand the correlation with AD. However, existing studies have used general deep computer vision methods, which present challenges in providing interpretable results and leveraging clinical prior knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose a novel deep-learning framework called Polar-Net. Our approach involves mapping OCTA images from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates, which allows for the use of approximate sector convolution and enables the implementation of the ETDRS grid-based regional analysis method commonly used in clinical practice. Furthermore, Polar-Net incorporates clinical prior information of each sector region into the training process, which further enhances its performance. Additionally, our framework adapts to acquire the importance of the corresponding retinal region, which helps researchers and clinicians understand the model's decision-making process in detecting AD and assess its conformity to clinical observations. Through evaluations on private and public datasets, we have demonstrated that Polar-Net outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods and provides more valuable pathological evidence for the association between retinal vascular changes and AD. In addition, we also show that the two innovative modules introduced in our framework have a significant impact on improving overall performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge