Jianyang Xie
A Frequency-Aware Self-Supervised Learning for Ultra-Wide-Field Image Enhancement
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Ultra-Wide-Field (UWF) retinal imaging has revolutionized retinal diagnostics by providing a comprehensive view of the retina. However, it often suffers from quality-degrading factors such as blurring and uneven illumination, which obscure fine details and mask pathological information. While numerous retinal image enhancement methods have been proposed for other fundus imageries, they often fail to address the unique requirements in UWF, particularly the need to preserve pathological details. In this paper, we propose a novel frequency-aware self-supervised learning method for UWF image enhancement. It incorporates frequency-decoupled image deblurring and Retinex-guided illumination compensation modules. An asymmetric channel integration operation is introduced in the former module, so as to combine global and local views by leveraging high- and low-frequency information, ensuring the preservation of fine and broader structural details. In addition, a color preservation unit is proposed in the latter Retinex-based module, to provide multi-scale spatial and frequency information, enabling accurate illumination estimation and correction. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed work not only enhances visualization quality but also improves disease diagnosis performance by restoring and correcting fine local details and uneven intensity. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt for UWF image enhancement, offering a robust and clinically valuable tool for improving retinal disease management.
Are Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolution Networks for Human Action Recognition Over-Parameterized?
May 15, 2025Abstract:Spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCNs) showcase impressive performance in skeleton-based human action recognition (HAR). However, despite the development of numerous models, their recognition performance does not differ significantly after aligning the input settings. With this observation, we hypothesize that ST-GCNs are over-parameterized for HAR, a conjecture subsequently confirmed through experiments employing the lottery ticket hypothesis. Additionally, a novel sparse ST-GCNs generator is proposed, which trains a sparse architecture from a randomly initialized dense network while maintaining comparable performance levels to the dense components. Moreover, we generate multi-level sparsity ST-GCNs by integrating sparse structures at various sparsity levels and demonstrate that the assembled model yields a significant enhancement in HAR performance. Thorough experiments on four datasets, including NTU-RGB+D 60(120), Kinetics-400, and FineGYM, demonstrate that the proposed sparse ST-GCNs can achieve comparable performance to their dense components. Even with 95% fewer parameters, the sparse ST-GCNs exhibit a degradation of <1% in top-1 accuracy. Meanwhile, the multi-level sparsity ST-GCNs, which require only 66% of the parameters of the dense ST-GCNs, demonstrate an improvement of >1% in top-1 accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/davelailai/Sparse-ST-GCN.
CathAction: A Benchmark for Endovascular Intervention Understanding
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:Real-time visual feedback from catheterization analysis is crucial for enhancing surgical safety and efficiency during endovascular interventions. However, existing datasets are often limited to specific tasks, small scale, and lack the comprehensive annotations necessary for broader endovascular intervention understanding. To tackle these limitations, we introduce CathAction, a large-scale dataset for catheterization understanding. Our CathAction dataset encompasses approximately 500,000 annotated frames for catheterization action understanding and collision detection, and 25,000 ground truth masks for catheter and guidewire segmentation. For each task, we benchmark recent related works in the field. We further discuss the challenges of endovascular intentions compared to traditional computer vision tasks and point out open research questions. We hope that CathAction will facilitate the development of endovascular intervention understanding methods that can be applied to real-world applications. The dataset is available at https://airvlab.github.io/cathdata/.
CLIP-DR: Textual Knowledge-Guided Diabetic Retinopathy Grading with Ranking-aware Prompting
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a complication of diabetes and usually takes decades to reach sight-threatening levels. Accurate and robust detection of DR severity is critical for the timely management and treatment of diabetes. However, most current DR grading methods suffer from insufficient robustness to data variability (\textit{e.g.} colour fundus images), posing a significant difficulty for accurate and robust grading. In this work, we propose a novel DR grading framework CLIP-DR based on three observations: 1) Recent pre-trained visual language models, such as CLIP, showcase a notable capacity for generalisation across various downstream tasks, serving as effective baseline models. 2) The grading of image-text pairs for DR often adheres to a discernible natural sequence, yet most existing DR grading methods have primarily overlooked this aspect. 3) A long-tailed distribution among DR severity levels complicates the grading process. This work proposes a novel ranking-aware prompting strategy to help the CLIP model exploit the ordinal information. Specifically, we sequentially design learnable prompts between neighbouring text-image pairs in two different ranking directions. Additionally, we introduce a Similarity Matrix Smooth module into the structure of CLIP to balance the class distribution. Finally, we perform extensive comparisons with several state-of-the-art methods on the GDRBench benchmark, demonstrating our CLIP-DR's robustness and superior performance. The implementation code is available \footnote{\url{https://github.com/Qinkaiyu/CLIP-DR}
3D Vessel Reconstruction in OCT-Angiography via Depth Map Estimation
Feb 26, 2021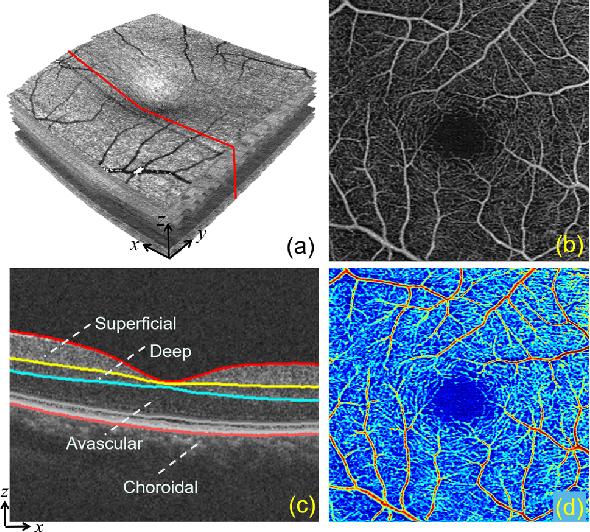
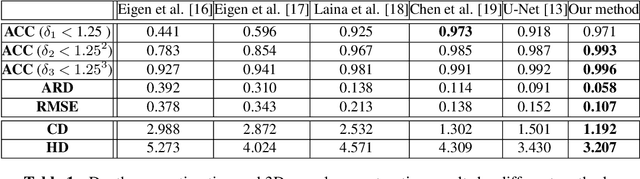
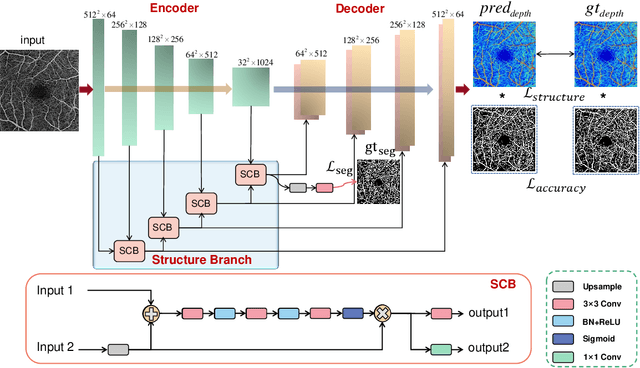
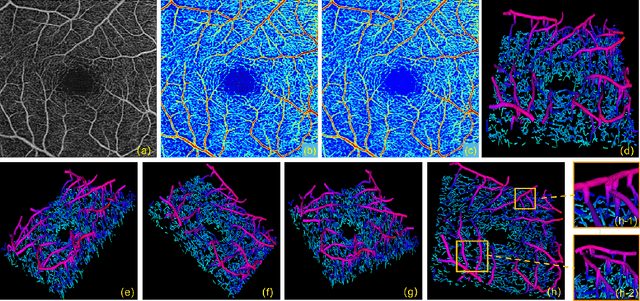
Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) has been increasingly used in the management of eye and systemic diseases in recent years. Manual or automatic analysis of blood vessel in 2D OCTA images (en face angiograms) is commonly used in clinical practice, however it may lose rich 3D spatial distribution information of blood vessels or capillaries that are useful for clinical decision-making. In this paper, we introduce a novel 3D vessel reconstruction framework based on the estimation of vessel depth maps from OCTA images. First, we design a network with structural constraints to predict the depth of blood vessels in OCTA images. In order to promote the accuracy of the predicted depth map at both the overall structure- and pixel- level, we combine MSE and SSIM loss as the training loss function. Finally, the 3D vessel reconstruction is achieved by utilizing the estimated depth map and 2D vessel segmentation results. Experimental results demonstrate that our method is effective in the depth prediction and 3D vessel reconstruction for OCTA images.% results may be used to guide subsequent vascular analysis
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge