Ying Qin
Sparsely Shared LoRA on Whisper for Child Speech Recognition
Sep 21, 2023



Abstract:Whisper is a powerful automatic speech recognition (ASR) model. Nevertheless, its zero-shot performance on low-resource speech requires further improvement. Child speech, as a representative type of low-resource speech, is leveraged for adaptation. Recently, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) in NLP was shown to be comparable and even better than full fine-tuning, while only needing to tune a small set of trainable parameters. However, current PEFT methods have not been well examined for their effectiveness on Whisper. In this paper, only parameter composition types of PEFT approaches such as LoRA and Bitfit are investigated as they do not bring extra inference costs. Different popular PEFT methods are examined. Particularly, we compare LoRA and AdaLoRA and figure out the learnable rank coefficient is a good design. Inspired by the sparse rank distribution allocated by AdaLoRA, a novel PEFT approach Sparsely Shared LoRA (S2-LoRA) is proposed. The two low-rank decomposed matrices are globally shared. Each weight matrix only has to maintain its specific rank coefficients that are constrained to be sparse. Experiments on low-resource Chinese child speech show that with much fewer trainable parameters, S2-LoRA can achieve comparable in-domain adaptation performance to AdaLoRA and exhibit better generalization ability on out-of-domain data. In addition, the rank distribution automatically learned by S2-LoRA is found to have similar patterns to AdaLoRA's allocation.
KG-BERTScore: Incorporating Knowledge Graph into BERTScore for Reference-Free Machine Translation Evaluation
Jan 30, 2023Abstract:BERTScore is an effective and robust automatic metric for referencebased machine translation evaluation. In this paper, we incorporate multilingual knowledge graph into BERTScore and propose a metric named KG-BERTScore, which linearly combines the results of BERTScore and bilingual named entity matching for reference-free machine translation evaluation. From the experimental results on WMT19 QE as a metric without references shared tasks, our metric KG-BERTScore gets higher overall correlation with human judgements than the current state-of-the-art metrics for reference-free machine translation evaluation.1 Moreover, the pre-trained multilingual model used by KG-BERTScore and the parameter for linear combination are also studied in this paper.
Explicitly Increasing Input Information Density for Vision Transformers on Small Datasets
Oct 25, 2022Abstract:Vision Transformers have attracted a lot of attention recently since the successful implementation of Vision Transformer (ViT) on vision tasks. With vision Transformers, specifically the multi-head self-attention modules, networks can capture long-term dependencies inherently. However, these attention modules normally need to be trained on large datasets, and vision Transformers show inferior performance on small datasets when training from scratch compared with widely dominant backbones like ResNets. Note that the Transformer model was first proposed for natural language processing, which carries denser information than natural images. To boost the performance of vision Transformers on small datasets, this paper proposes to explicitly increase the input information density in the frequency domain. Specifically, we introduce selecting channels by calculating the channel-wise heatmaps in the frequency domain using Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT), reducing the size of input while keeping most information and hence increasing the information density. As a result, 25% fewer channels are kept while better performance is achieved compared with previous work. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach on five small-scale datasets, including CIFAR-10/100, SVHN, Flowers-102, and Tiny ImageNet. The accuracy has been boosted up to 17.05% with Swin and Focal Transformers. Codes are available at https://github.com/xiangyu8/DenseVT.
iEmoTTS: Toward Robust Cross-Speaker Emotion Transfer and Control for Speech Synthesis based on Disentanglement between Prosody and Timbre
Jun 29, 2022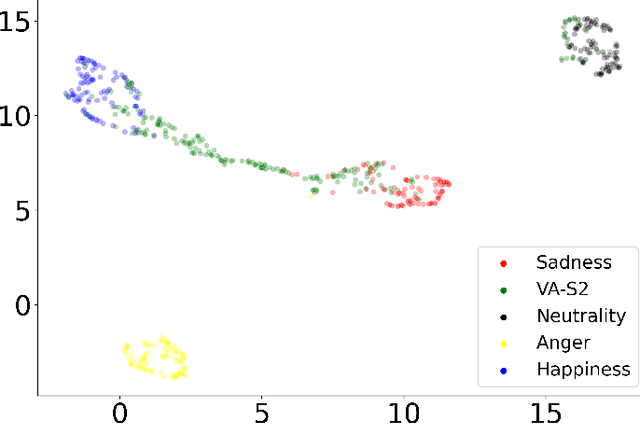
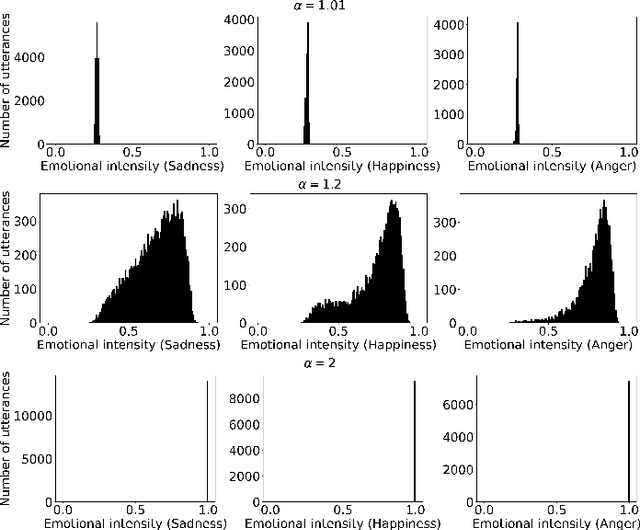
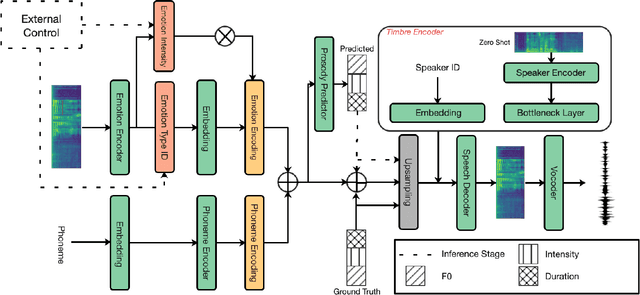
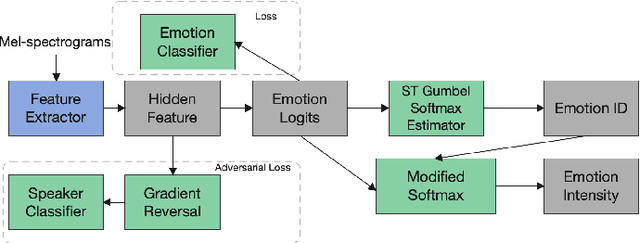
Abstract:The capability of generating speech with specific type of emotion is desired for many applications of human-computer interaction. Cross-speaker emotion transfer is a common approach to generating emotional speech when speech with emotion labels from target speakers is not available for model training. This paper presents a novel cross-speaker emotion transfer system, named iEmoTTS. The system is composed of an emotion encoder, a prosody predictor, and a timbre encoder. The emotion encoder extracts the identity of emotion type as well as the respective emotion intensity from the mel-spectrogram of input speech. The emotion intensity is measured by the posterior probability that the input utterance carries that emotion. The prosody predictor is used to provide prosodic features for emotion transfer. The timber encoder provides timbre-related information for the system. Unlike many other studies which focus on disentangling speaker and style factors of speech, the iEmoTTS is designed to achieve cross-speaker emotion transfer via disentanglement between prosody and timbre. Prosody is considered as the main carrier of emotion-related speech characteristics and timbre accounts for the essential characteristics for speaker identification. Zero-shot emotion transfer, meaning that speech of target speakers are not seen in model training, is also realized with iEmoTTS. Extensive experiments of subjective evaluation have been carried out. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of iEmoTTS as compared with other recently proposed systems of cross-speaker emotion transfer. It is shown that iEmoTTS can produce speech with designated emotion type and controllable emotion intensity. With appropriate information bottleneck capacity, iEmoTTS is able to effectively transfer emotion information to a new speaker. Audio samples are publicly available\footnote{https://patrick-g-zhang.github.io/iemotts/}.
Neighbors Are Not Strangers: Improving Non-Autoregressive Translation under Low-Frequency Lexical Constraints
Apr 28, 2022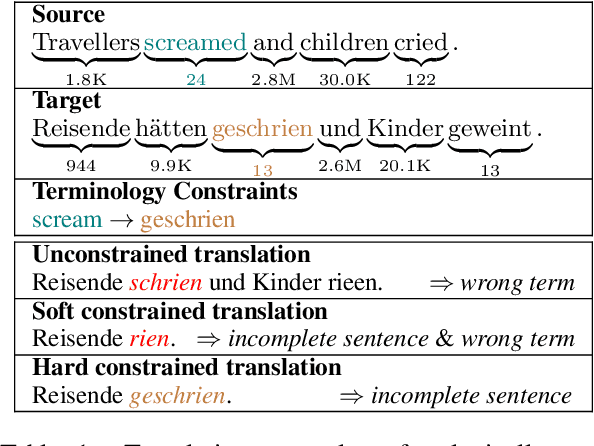
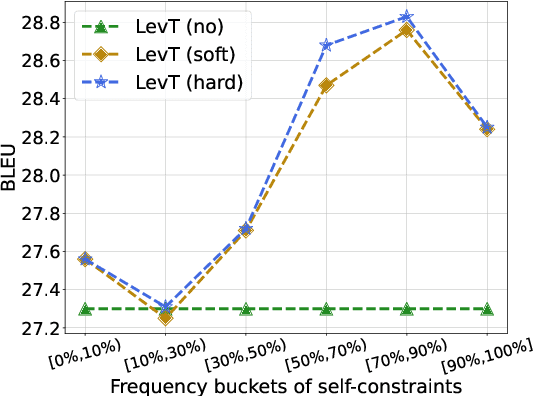
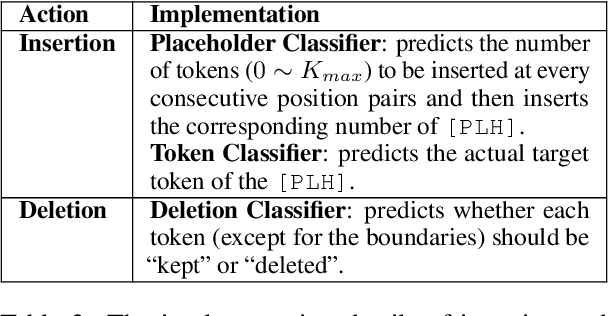
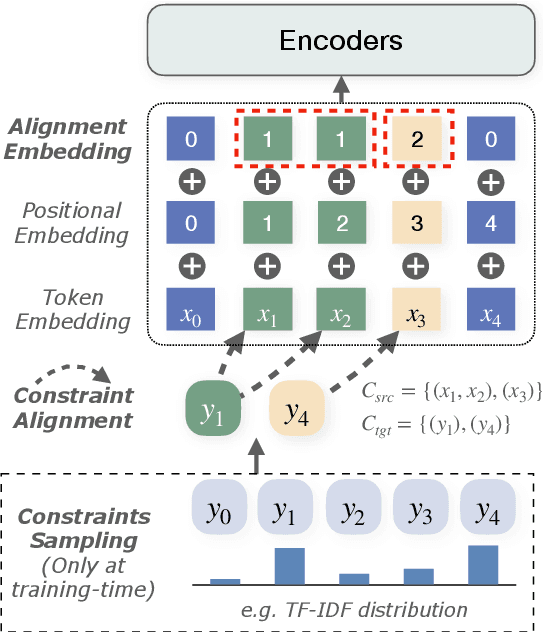
Abstract:However, current autoregressive approaches suffer from high latency. In this paper, we focus on non-autoregressive translation (NAT) for this problem for its efficiency advantage. We identify that current constrained NAT models, which are based on iterative editing, do not handle low-frequency constraints well. To this end, we propose a plug-in algorithm for this line of work, i.e., Aligned Constrained Training (ACT), which alleviates this problem by familiarizing the model with the source-side context of the constraints. Experiments on the general and domain datasets show that our model improves over the backbone constrained NAT model in constraint preservation and translation quality, especially for rare constraints.
A study on the efficacy of model pre-training in developing neural text-to-speech system
Oct 08, 2021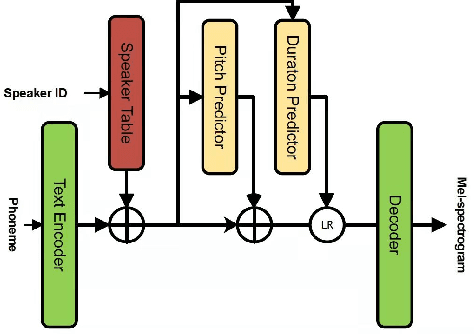
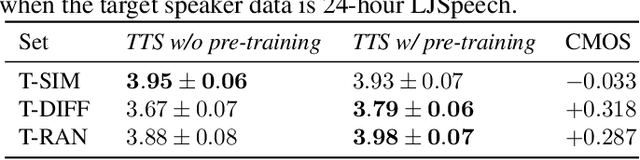
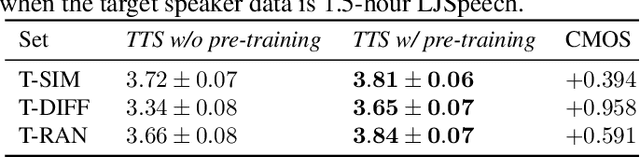
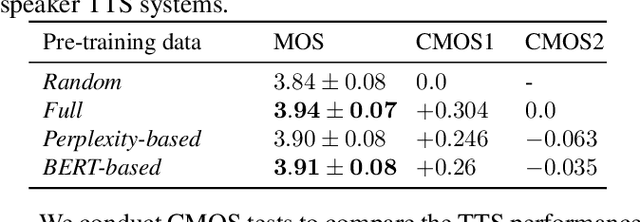
Abstract:In the development of neural text-to-speech systems, model pre-training with a large amount of non-target speakers' data is a common approach. However, in terms of ultimately achieved system performance for target speaker(s), the actual benefits of model pre-training are uncertain and unstable, depending very much on the quantity and text content of training data. This study aims to understand better why and how model pre-training can positively contribute to TTS system performance. It is postulated that the pre-training process plays a critical role in learning text-related variation in speech, while further training with the target speaker's data aims to capture the speaker-related variation. Different test sets are created with varying degrees of similarity to target speaker data in terms of text content. Experiments show that leveraging a speaker-independent TTS trained on speech data with diverse text content can improve the target speaker TTS on domain-mismatched text. We also attempt to reduce the amount of pre-training data for a new text domain and improve the data and computational efficiency. It is found that the TTS system could achieve comparable performance when the pre-training data is reduced to 1/8 of its original size.
Exploiting Pre-Trained ASR Models for Alzheimer's Disease Recognition Through Spontaneous Speech
Oct 04, 2021



Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease and recently attracts extensive attention worldwide. Speech technology is considered a promising solution for the early diagnosis of AD and has been enthusiastically studied. Most recent works concentrate on the use of advanced BERT-like classifiers for AD detection. Input to these classifiers are speech transcripts produced by automatic speech recognition (ASR) models. The major challenge is that the quality of transcription could degrade significantly under complex acoustic conditions in the real world. The detection performance, in consequence, is largely limited. This paper tackles the problem via tailoring and adapting pre-trained neural-network based ASR model for the downstream AD recognition task. Only bottom layers of the ASR model are retained. A simple fully-connected neural network is added on top of the tailored ASR model for classification. The heavy BERT classifier is discarded. The resulting model is light-weight and can be fine-tuned in an end-to-end manner for AD recognition. Our proposed approach takes only raw speech as input, and no extra transcription process is required. The linguistic information of speech is implicitly encoded in the tailored ASR model and contributes to boosting the performance. Experiments show that our proposed approach outperforms the best manual transcript-based RoBERTa by an absolute margin of 4.6% in terms of accuracy. Our best-performing models achieve the accuracy of 83.2% and 78.0% in the long-audio and short-audio competition tracks of the 2021 NCMMSC Alzheimer's Disease Recognition Challenge, respectively.
The HW-TSC's Offline Speech Translation Systems for IWSLT 2021 Evaluation
Aug 09, 2021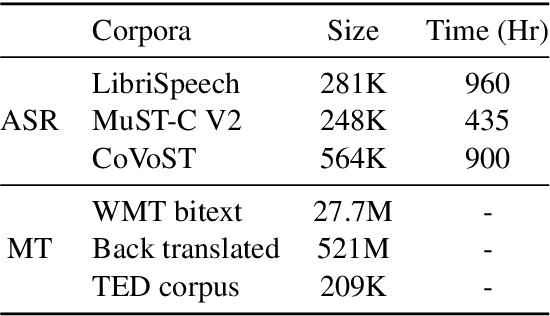
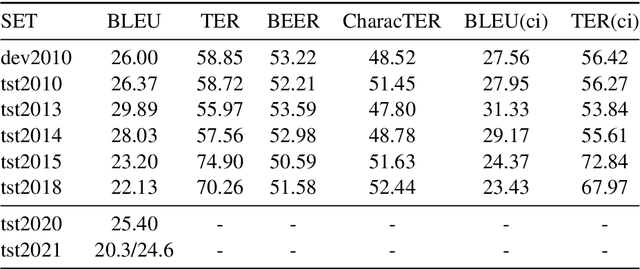
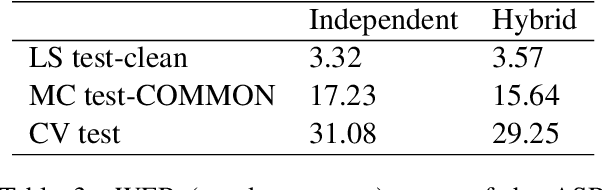
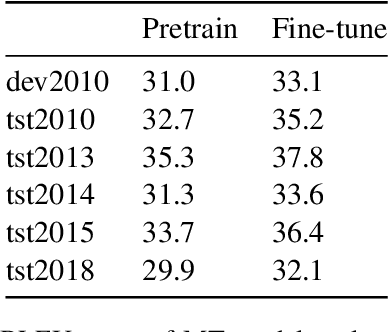
Abstract:This paper describes our work in participation of the IWSLT-2021 offline speech translation task. Our system was built in a cascade form, including a speaker diarization module, an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) module and a Machine Translation (MT) module. We directly use the LIUM SpkDiarization tool as the diarization module. The ASR module is trained with three ASR datasets from different sources, by multi-source training, using a modified Transformer encoder. The MT module is pretrained on the large-scale WMT news translation dataset and fine-tuned on the TED corpus. Our method achieves 24.6 BLEU score on the 2021 test set.
Applying the Information Bottleneck Principle to Prosodic Representation Learning
Aug 05, 2021


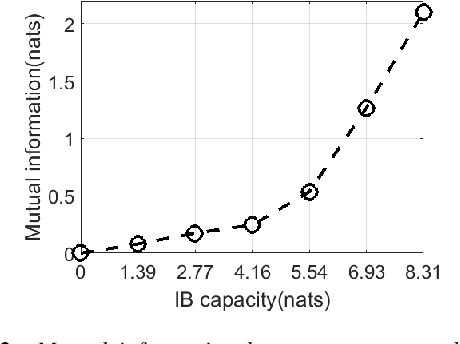
Abstract:This paper describes a novel design of a neural network-based speech generation model for learning prosodic representation.The problem of representation learning is formulated according to the information bottleneck (IB) principle. A modified VQ-VAE quantized layer is incorporated in the speech generation model to control the IB capacity and adjust the balance between reconstruction power and disentangle capability of the learned representation. The proposed model is able to learn word-level prosodic representations from speech data. With an optimized IB capacity, the learned representations not only are adequate to reconstruct the original speech but also can be used to transfer the prosody onto different textual content. Extensive results of the objective and subjective evaluation are presented to demonstrate the effect of IB capacity control, the effectiveness, and potential usage of the learned prosodic representation in controllable neural speech generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge