Yiding Wang
Knowledge is Not Enough: Injecting RL Skills for Continual Adaptation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) face the "knowledge cutoff" challenge, where their frozen parametric memory prevents direct internalization of new information. While Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) is commonly used to update model knowledge, it often updates factual content without reliably improving the model's ability to use the newly incorporated information for question answering or decision-making. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is essential for acquiring reasoning skills; however, its high computational cost makes it impractical for efficient online adaptation. We empirically observe that the parameter updates induced by SFT and RL are nearly orthogonal. Based on this observation, we propose Parametric Skill Transfer (PaST), a framework that supports modular skill transfer for efficient and effective knowledge adaptation. By extracting a domain-agnostic Skill Vector from a source domain, we can linearly inject knowledge manipulation skills into a target model after it has undergone lightweight SFT on new data. Experiments on knowledge-incorporation QA (SQuAD, LooGLE) and agentic tool-use benchmarks (ToolBench) demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. On SQuAD, PaST outperforms the state-of-the-art self-editing SFT baseline by up to 9.9 points. PaST further scales to long-context QA on LooGLE with an 8.0-point absolute accuracy gain, and improves zero-shot ToolBench success rates by +10.3 points on average with consistent gains across tool categories, indicating strong scalability and cross-domain transferability of the Skill Vector.
Beyond Outcome Reward: Decoupling Search and Answering Improves LLM Agents
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Enabling large language models (LLMs) to utilize search tools offers a promising path to overcoming fundamental limitations such as knowledge cutoffs and hallucinations. Recent work has explored reinforcement learning (RL) for training search-augmented agents that interleave reasoning and retrieval before answering. These approaches usually rely on outcome-based rewards (e.g., exact match), implicitly assuming that optimizing for final answers will also yield effective intermediate search behaviors. Our analysis challenges this assumption: we uncover multiple systematic deficiencies in search that arise under outcome-only training and ultimately degrade final answer quality, including failure to invoke tools, invalid queries, and redundant searches. To address these shortcomings, we introduce DeSA (Decoupling Search-and-Answering), a simple two-stage training framework that explicitly separates search optimization from answer generation. In Stage 1, agents are trained to improve search effectiveness with retrieval recall-based rewards. In Stage 2, outcome rewards are employed to optimize final answer generation. Across seven QA benchmarks, DeSA-trained agents consistently improve search behaviors, delivering substantially higher search recall and answer accuracy than outcome-only baselines. Notably, DeSA outperforms single-stage training approaches that simultaneously optimize recall and outcome rewards, underscoring the necessity of explicitly decoupling the two objectives.
HD-PiSSA: High-Rank Distributed Orthogonal Adaptation
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Existing parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods for large language models (LLMs), such as LoRA and PiSSA, constrain model updates to low-rank subspaces, limiting their expressiveness and leading to suboptimal performance on complex tasks. To address this, we introduce High-rank Distributed PiSSA (HD-PiSSA), a distributed PEFT approach that initializes orthogonal adapters across different devices and aggregates their delta updates collectively on W for fine-tuning. Unlike Data Parallel LoRA or PiSSA, which maintain identical adapters across all devices, HD-PiSSA assigns different principal components of the pre-trained weights to each GPU, significantly expanding the range of update directions. This results in over 16x higher effective updated ranks than data-parallel LoRA or PiSSA when fine-tuning on 8 GPUs with the same per-device adapter rank. Empirically, we evaluate HD-PiSSA across various challenging downstream tasks, including mathematics, code generation, and multi-task learning. In the multi-task setting, HD-PiSSA achieves average gains of 10.0 absolute points (14.63%) over LoRA and 4.98 points (6.60%) over PiSSA across 12 benchmarks, demonstrating its benefits from the extra optimization flexibility.
A Deep Spatio-Temporal Architecture for Dynamic Effective Connectivity Network Analysis Based on Dynamic Causal Discovery
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Dynamic effective connectivity networks (dECNs) reveal the changing directed brain activity and the dynamic causal influences among brain regions, which facilitate the identification of individual differences and enhance the understanding of human brain. Although the existing causal discovery methods have shown promising results in effective connectivity network analysis, they often overlook the dynamics of causality, in addition to the incorporation of spatio-temporal information in brain activity data. To address these issues, we propose a deep spatio-temporal fusion architecture, which employs a dynamic causal deep encoder to incorporate spatio-temporal information into dynamic causality modeling, and a dynamic causal deep decoder to verify the discovered causality. The effectiveness of the proposed method is first illustrated with simulated data. Then, experimental results from Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort (PNC) demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in inferring dECNs, which reveal the dynamic evolution of directed flow between brain regions. The analysis shows the difference of dECNs between young adults and children. Specifically, the directed brain functional networks transit from fluctuating undifferentiated systems to more stable specialized networks as one grows. This observation provides further evidence on the modularization and adaptation of brain networks during development, leading to higher cognitive abilities observed in young adults.
Simulating Human-like Daily Activities with Desire-driven Autonomy
Dec 09, 2024
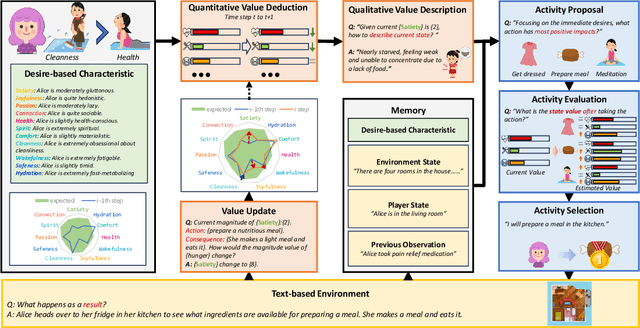
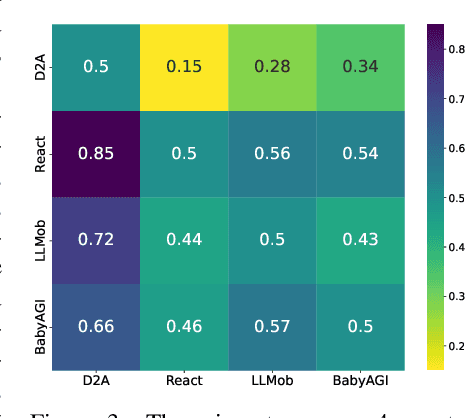
Abstract:Existing task-oriented AI agents often depend on explicit instructions or external rewards, limiting their ability to be driven by intrinsic motivations like humans. In this paper, we present a desire-driven autonomy framework to guide a Large Language Model-based (LLM-based) agent to simulate human-like daily activities. In contrast to previous agents, our Desire-driven Autonomous Agent (D2A) operates on the principle of intrinsic desire, allowing it to propose and select tasks that fulfill its motivational framework autonomously. Inspired by the Theory of Needs, the motivational framework incorporates an understanding of human-like desires, such as the need for social interaction, personal fulfillment, and self-care. Utilizing a desire-driven task generation mechanism, the agent evaluates its current state and takes a sequence of activities aligned with its intrinsic motivations. Through simulations, we demonstrate that our Desire-driven Autonomous Agent (D2A) generates coherent, contextually relevant daily activities while exhibiting variability and adaptability similar to human behavior. A comparative analysis with other LLM-based frameworks demonstrates that our approach significantly enhances the rationality of the simulated activities.
Scaling Law for Language Models Training Considering Batch Size
Dec 02, 2024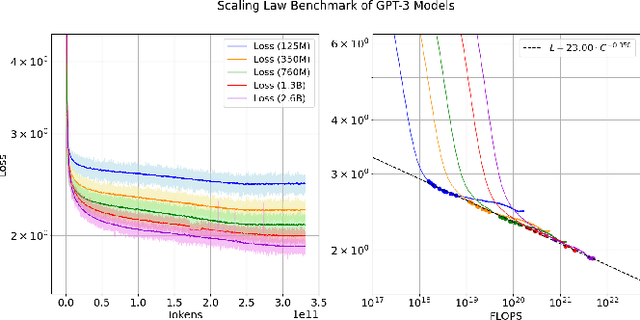
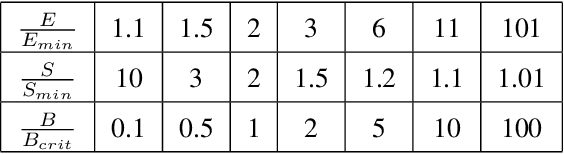
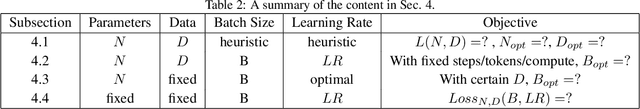
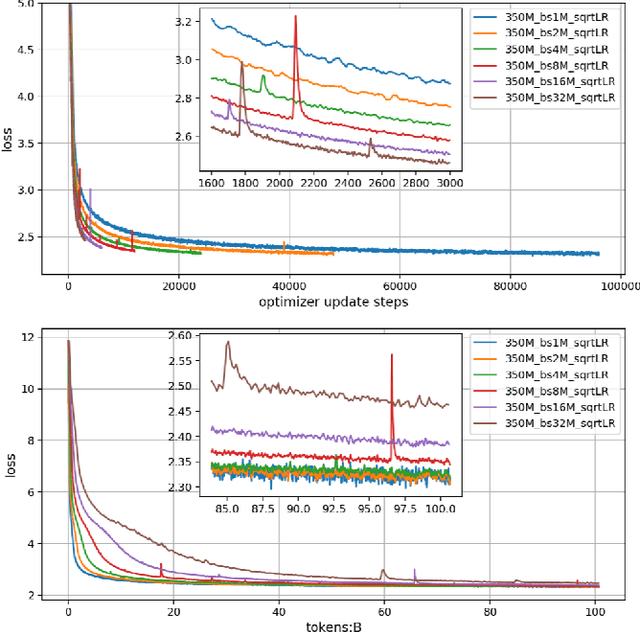
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have made remarkable advances in recent years, with scaling laws playing a critical role in this rapid progress. In this paper, we empirically investigate how a critical hyper-parameter, i.e., the global batch size, influences the LLM training prdocess. We begin by training language models ranging from 125 million to 2.6 billion parameters, using up to 300 billion high-quality tokens. Through these experiments, we establish a basic scaling law on model size and training data amount. We then examine how varying batch sizes and learning rates affect the convergence and generalization of these models. Our analysis yields batch size scaling laws under two different cases: with a fixed compute budget, and with a fixed amount of training data. Extrapolation experiments on models of increasing sizes validate our predicted laws, which provides guidance for optimizing LLM training strategies under specific resource constraints.
Chain of Images for Intuitively Reasoning
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:The human brain is naturally equipped to comprehend and interpret visual information rapidly. When confronted with complex problems or concepts, we use flowcharts, sketches, and diagrams to aid our thought process. Leveraging this inherent ability can significantly enhance logical reasoning. However, current Large Language Models (LLMs) do not utilize such visual intuition to help their thinking. Even the most advanced version language models (e.g., GPT-4V and LLaVA) merely align images into textual space, which means their reasoning processes remain purely verbal. To mitigate such limitations, we present a Chain of Images (CoI) approach, which can convert complex language reasoning problems to simple pattern recognition by generating a series of images as intermediate representations. Furthermore, we have developed a CoI evaluation dataset encompassing 15 distinct domains where images can intuitively aid problem-solving. Based on this dataset, we aim to construct a benchmark to assess the capability of future multimodal large-scale models to leverage images for reasoning. In supporting our CoI reasoning, we introduce a symbolic multimodal large language model (SyMLLM) that generates images strictly based on language instructions and accepts both text and image as input. Experiments on Geometry, Chess and Common Sense tasks sourced from the CoI evaluation dataset show that CoI improves performance significantly over the pure-language Chain of Thoughts (CoT) baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/GraphPKU/CoI.
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering. However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan 2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens. Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan 2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH: A Novel Approach for Support Vector Classifier Training and Parameter Selection
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:The selection of Gaussian kernel parameters plays an important role in the applications of support vector classification (SVC). A commonly used method is the k-fold cross validation with grid search (CV), which is extremely time-consuming because it needs to train a large number of SVC models. In this paper, a new approach is proposed to train SVC and optimize the selection of Gaussian kernel parameters. We first formulate the training and parameter selection of SVC as a minimax optimization problem named as MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH, in which the minimization problem is an optimization problem of finding the closest points between two normal convex hulls (L2-SVC-NCH) while the maximization problem is an optimization problem of finding the optimal Gaussian kernel parameters. A lower time complexity can be expected in MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH because CV is not needed. We then propose a projected gradient algorithm (PGA) for training L2-SVC-NCH. The famous sequential minimal optimization (SMO) algorithm is a special case of the PGA. Thus, the PGA can provide more flexibility than the SMO. Furthermore, the solution of the maximization problem is done by a gradient ascent algorithm with dynamic learning rate. The comparative experiments between MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH and the previous best approaches on public datasets show that MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH greatly reduces the number of models to be trained while maintaining competitive test accuracy. These findings indicate that MaxMin-L2-SVC-NCH is a better choice for SVC tasks.
Efficient DNN Training with Knowledge-Guided Layer Freezing
Jan 17, 2022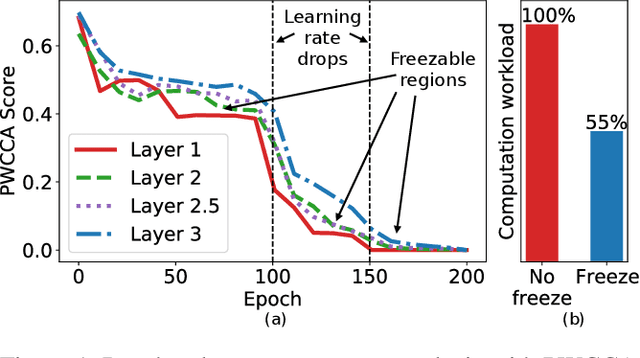
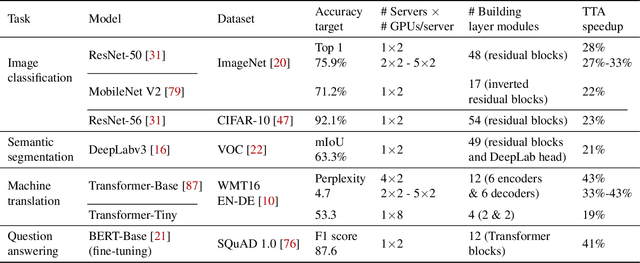
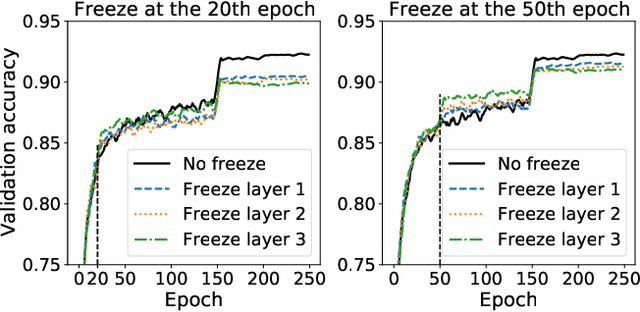
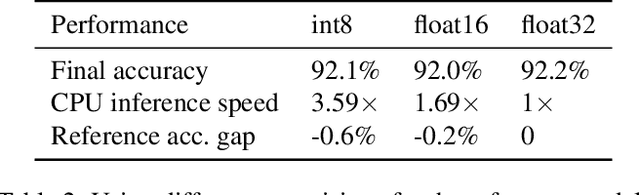
Abstract:Training deep neural networks (DNNs) is time-consuming. While most existing solutions try to overlap/schedule computation and communication for efficient training, this paper goes one step further by skipping computing and communication through DNN layer freezing. Our key insight is that the training progress of internal DNN layers differs significantly, and front layers often become well-trained much earlier than deep layers. To explore this, we first introduce the notion of training plasticity to quantify the training progress of internal DNN layers. Then we design KGT, a knowledge-guided DNN training system that employs semantic knowledge from a reference model to accurately evaluate individual layers' training plasticity and safely freeze the converged ones, saving their corresponding backward computation and communication. Our reference model is generated on the fly using quantization techniques and runs forward operations asynchronously on available CPUs to minimize the overhead. In addition, KGT caches the intermediate outputs of the frozen layers with prefetching to further skip the forward computation. Our implementation and testbed experiments with popular vision and language models show that KGT achieves 19%-43% training speedup w.r.t. the state-of-the-art without sacrificing accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge