Xingzhi Sun
Dispersion Loss Counteracts Embedding Condensation and Improves Generalization in Small Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable performance through ever-increasing parameter counts, but scaling incurs steep computational costs. To better understand LLM scaling, we study representational differences between LLMs and their smaller counterparts, with the goal of replicating the representational qualities of larger models in the smaller models. We observe a geometric phenomenon which we term $\textbf{embedding condensation}$, where token embeddings collapse into a narrow cone-like subspace in some language models. Through systematic analyses across multiple Transformer families, we show that small models such as $\texttt{GPT2}$ and $\texttt{Qwen3-0.6B}$ exhibit severe condensation, whereas the larger models such as $\texttt{GPT2-xl}$ and $\texttt{Qwen3-32B}$ are more resistant to this phenomenon. Additional observations show that embedding condensation is not reliably mitigated by knowledge distillation from larger models. To fight against it, we formulate a dispersion loss that explicitly encourages embedding dispersion during training. Experiments demonstrate that it mitigates condensation, recovers dispersion patterns seen in larger models, and yields performance gains across 10 benchmarks. We believe this work offers a principled path toward improving smaller Transformers without additional parameters.
STAGED: A Multi-Agent Neural Network for Learning Cellular Interaction Dynamics
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:The advent of single-cell technology has significantly improved our understanding of cellular states and subpopulations in various tissues under normal and diseased conditions by employing data-driven approaches such as clustering and trajectory inference. However, these methods consider cells as independent data points of population distributions. With spatial transcriptomics, we can represent cellular organization, along with dynamic cell-cell interactions that lead to changes in cell state. Still, key computational advances are necessary to enable the data-driven learning of such complex interactive cellular dynamics. While agent-based modeling (ABM) provides a powerful framework, traditional approaches rely on handcrafted rules derived from domain knowledge rather than data-driven approaches. To address this, we introduce Spatio Temporal Agent-Based Graph Evolution Dynamics(STAGED) integrating ABM with deep learning to model intercellular communication, and its effect on the intracellular gene regulatory network. Using graph ODE networks (GDEs) with shared weights per cell type, our approach represents genes as vertices and interactions as directed edges, dynamically learning their strengths through a designed attention mechanism. Trained to match continuous trajectories of simulated as well as inferred trajectories from spatial transcriptomics data, the model captures both intercellular and intracellular interactions, enabling a more adaptive and accurate representation of cellular dynamics.
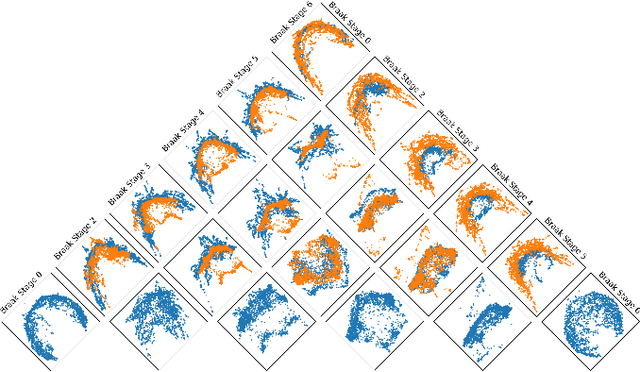
Principal Curvatures Estimation with Applications to Single Cell Data
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:The rapidly growing field of single-cell transcriptomic sequencing (scRNAseq) presents challenges for data analysis due to its massive datasets. A common method in manifold learning consists in hypothesizing that datasets lie on a lower dimensional manifold. This allows to study the geometry of point clouds by extracting meaningful descriptors like curvature. In this work, we will present Adaptive Local PCA (AdaL-PCA), a data-driven method for accurately estimating various notions of intrinsic curvature on data manifolds, in particular principal curvatures for surfaces. The model relies on local PCA to estimate the tangent spaces. The evaluation of AdaL-PCA on sampled surfaces shows state-of-the-art results. Combined with a PHATE embedding, the model applied to single-cell RNA sequencing data allows us to identify key variations in the cellular differentiation.
Geometry-Aware Generative Autoencoders for Warped Riemannian Metric Learning and Generative Modeling on Data Manifolds
Oct 16, 2024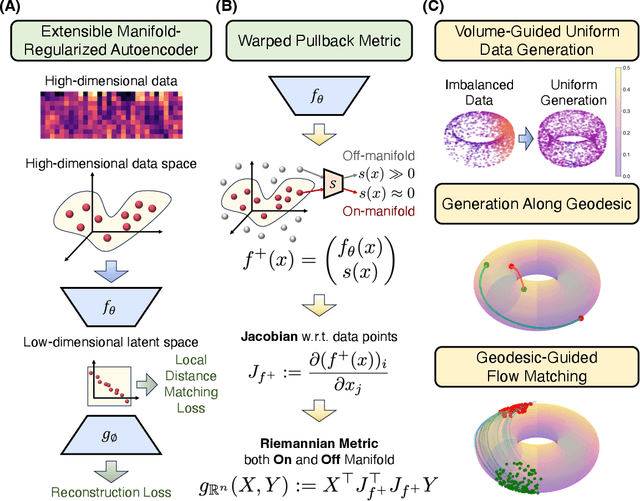
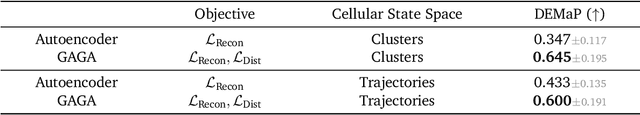
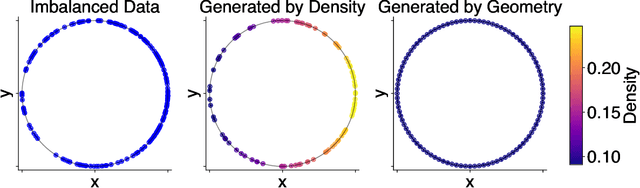

Abstract:Rapid growth of high-dimensional datasets in fields such as single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial genomics has led to unprecedented opportunities for scientific discovery, but it also presents unique computational and statistical challenges. Traditional methods struggle with geometry-aware data generation, interpolation along meaningful trajectories, and transporting populations via feasible paths. To address these issues, we introduce Geometry-Aware Generative Autoencoder (GAGA), a novel framework that combines extensible manifold learning with generative modeling. GAGA constructs a neural network embedding space that respects the intrinsic geometries discovered by manifold learning and learns a novel warped Riemannian metric on the data space. This warped metric is derived from both the points on the data manifold and negative samples off the manifold, allowing it to characterize a meaningful geometry across the entire latent space. Using this metric, GAGA can uniformly sample points on the manifold, generate points along geodesics, and interpolate between populations across the learned manifold. GAGA shows competitive performance in simulated and real world datasets, including a 30% improvement over the state-of-the-art methods in single-cell population-level trajectory inference.
ZALM3: Zero-Shot Enhancement of Vision-Language Alignment via In-Context Information in Multi-Turn Multimodal Medical Dialogue
Sep 26, 2024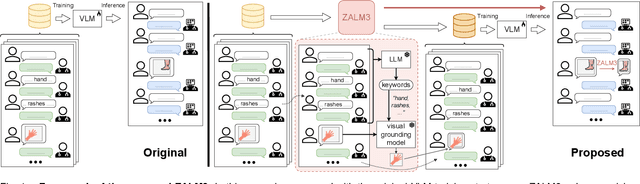
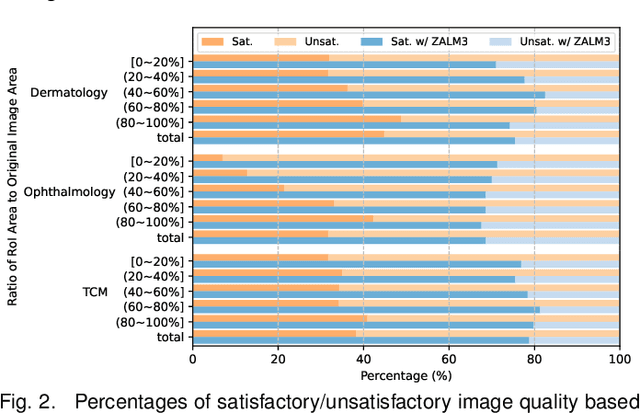
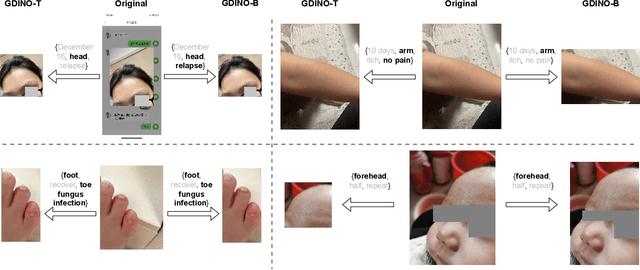
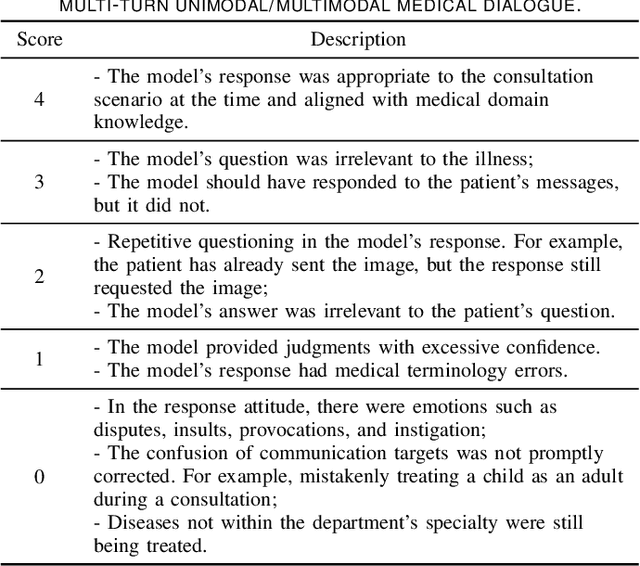
Abstract:The rocketing prosperity of large language models (LLMs) in recent years has boosted the prevalence of vision-language models (VLMs) in the medical sector. In our online medical consultation scenario, a doctor responds to the texts and images provided by a patient in multiple rounds to diagnose her/his health condition, forming a multi-turn multimodal medical dialogue format. Unlike high-quality images captured by professional equipment in traditional medical visual question answering (Med-VQA), the images in our case are taken by patients' mobile phones. These images have poor quality control, with issues such as excessive background elements and the lesion area being significantly off-center, leading to degradation of vision-language alignment in the model training phase. In this paper, we propose ZALM3, a Zero-shot strategy to improve vision-language ALignment in Multi-turn Multimodal Medical dialogue. Since we observe that the preceding text conversations before an image can infer the regions of interest (RoIs) in the image, ZALM3 employs an LLM to summarize the keywords from the preceding context and a visual grounding model to extract the RoIs. The updated images eliminate unnecessary background noise and provide more effective vision-language alignment. To better evaluate our proposed method, we design a new subjective assessment metric for multi-turn unimodal/multimodal medical dialogue to provide a fine-grained performance comparison. Our experiments across three different clinical departments remarkably demonstrate the efficacy of ZALM3 with statistical significance.
Hyperedge Representations with Hypergraph Wavelets: Applications to Spatial Transcriptomics
Sep 14, 2024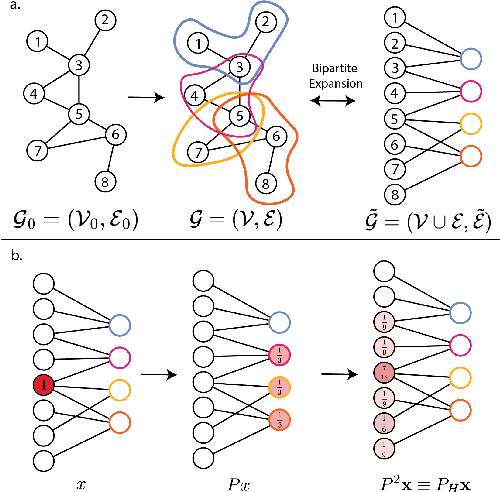
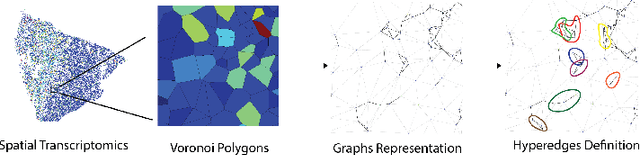
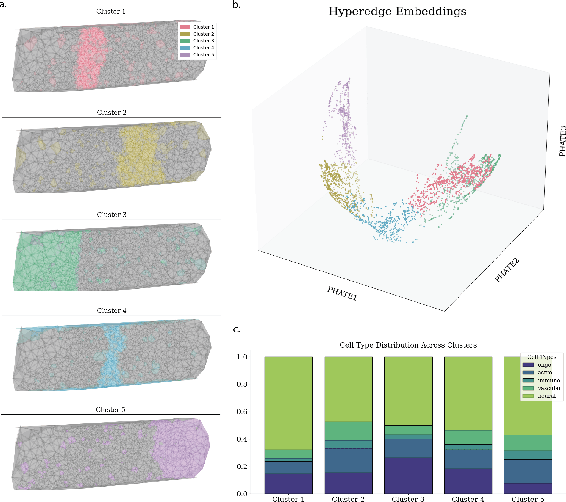
Abstract:In many data-driven applications, higher-order relationships among multiple objects are essential in capturing complex interactions. Hypergraphs, which generalize graphs by allowing edges to connect any number of nodes, provide a flexible and powerful framework for modeling such higher-order relationships. In this work, we introduce hypergraph diffusion wavelets and describe their favorable spectral and spatial properties. We demonstrate their utility for biomedical discovery in spatially resolved transcriptomics by applying the method to represent disease-relevant cellular niches for Alzheimer's disease.
Bayesian Formulations for Graph Spectral Denoising
Nov 27, 2023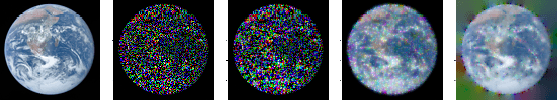



Abstract:We consider noisy signals which are defined on the vertices of a graph and present smoothing algorithms for the cases of Gaussian, dropout, and uniformly distributed noise. The signals are assumed to follow a prior distribution defined in the frequency domain which favors signals which are smooth across the edges of the graph. By pairing this prior distribution with our three models of noise generation, we propose \textit{Maximum A Posteriori} (M.A.P.) estimates of the true signal in the presence of noisy data and provide algorithms for computing the M.A.P. Finally, we demonstrate the algorithms' ability to effectively restore white noise on image data, and from severe dropout in toy \& EHR data.
Graph topological property recovery with heat and wave dynamics-based features on graphs
Sep 19, 2023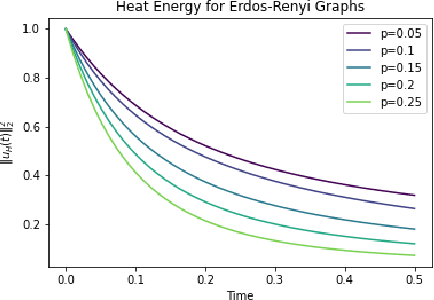
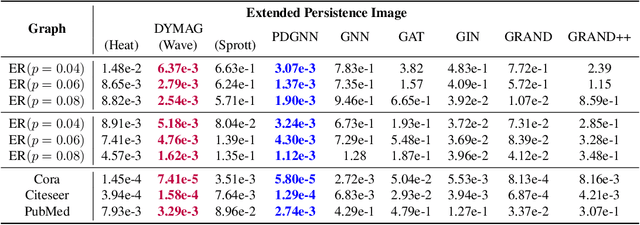
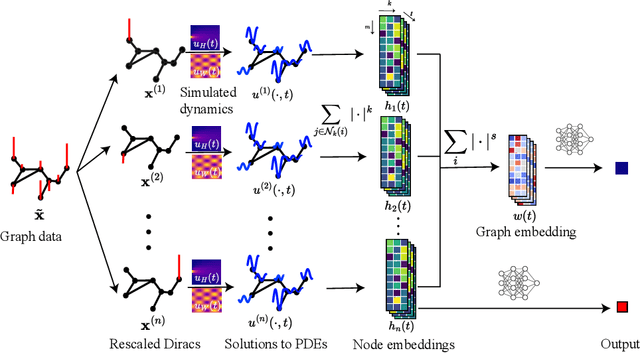
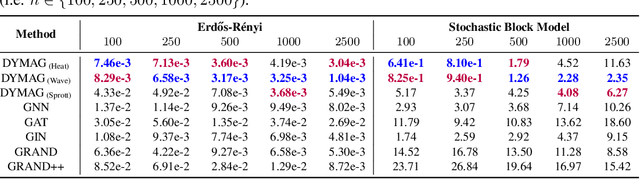
Abstract:In this paper, we propose Graph Differential Equation Network (GDeNet), an approach that harnesses the expressive power of solutions to PDEs on a graph to obtain continuous node- and graph-level representations for various downstream tasks. We derive theoretical results connecting the dynamics of heat and wave equations to the spectral properties of the graph and to the behavior of continuous-time random walks on graphs. We demonstrate experimentally that these dynamics are able to capture salient aspects of graph geometry and topology by recovering generating parameters of random graphs, Ricci curvature, and persistent homology. Furthermore, we demonstrate the superior performance of GDeNet on real-world datasets including citation graphs, drug-like molecules, and proteins.
Interactive Molecular Discovery with Natural Language
Jun 21, 2023Abstract:Natural language is expected to be a key medium for various human-machine interactions in the era of large language models. When it comes to the biochemistry field, a series of tasks around molecules (e.g., property prediction, molecule mining, etc.) are of great significance while having a high technical threshold. Bridging the molecule expressions in natural language and chemical language can not only hugely improve the interpretability and reduce the operation difficulty of these tasks, but also fuse the chemical knowledge scattered in complementary materials for a deeper comprehension of molecules. Based on these benefits, we propose the conversational molecular design, a novel task adopting natural language for describing and editing target molecules. To better accomplish this task, we design ChatMol, a knowledgeable and versatile generative pre-trained model, enhanced by injecting experimental property information, molecular spatial knowledge, and the associations between natural and chemical languages into it. Several typical solutions including large language models (e.g., ChatGPT) are evaluated, proving the challenge of conversational molecular design and the effectiveness of our knowledge enhancement method. Case observations and analysis are conducted to provide directions for further exploration of natural-language interaction in molecular discovery.
Identification of 27 abnormalities from multi-lead ECG signals: An ensembled Se-ResNet framework with Sign Loss function
Jan 12, 2021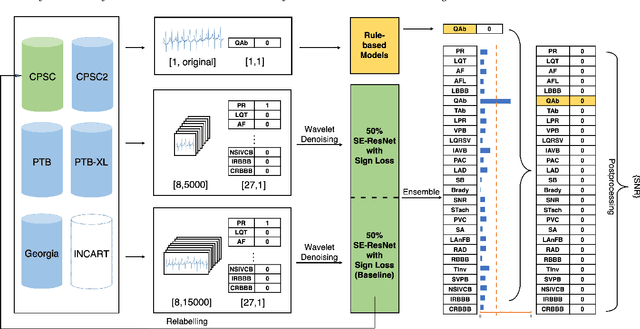
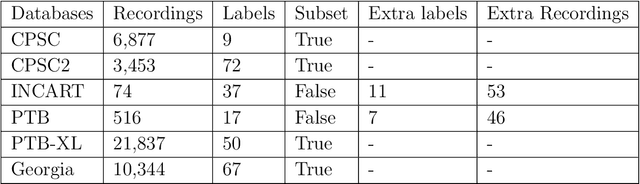
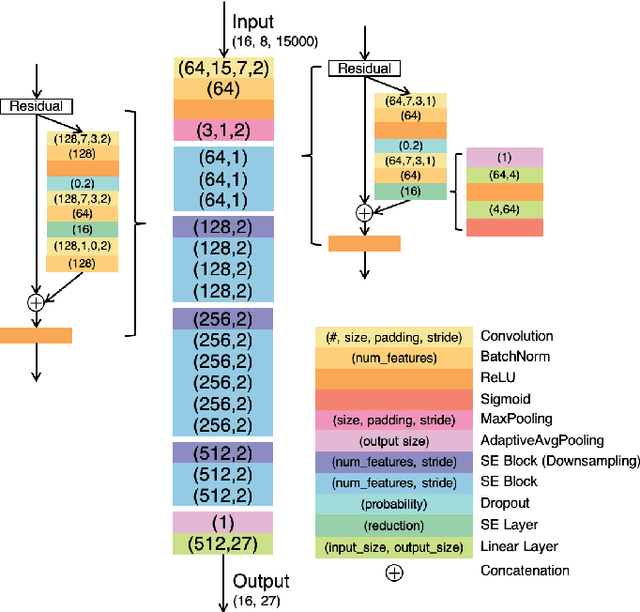
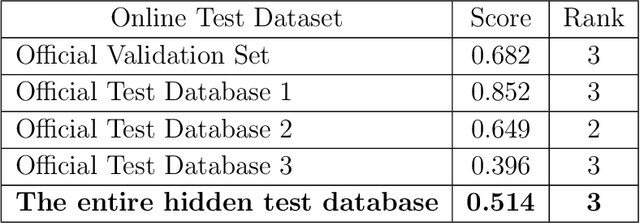
Abstract:Cardiovascular disease is a major threat to health and one of the primary causes of death globally. The 12-lead ECG is a cheap and commonly accessible tool to identify cardiac abnormalities. Early and accurate diagnosis will allow early treatment and intervention to prevent severe complications of cardiovascular disease. In the PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge 2020, our objective is to develop an algorithm that automatically identifies 27 ECG abnormalities from 12-lead ECG recordings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge