Michael Perlmutter
InfoGain Wavelets: Furthering the Design of Diffusion Wavelets for Graph-Structured Data
Apr 08, 2025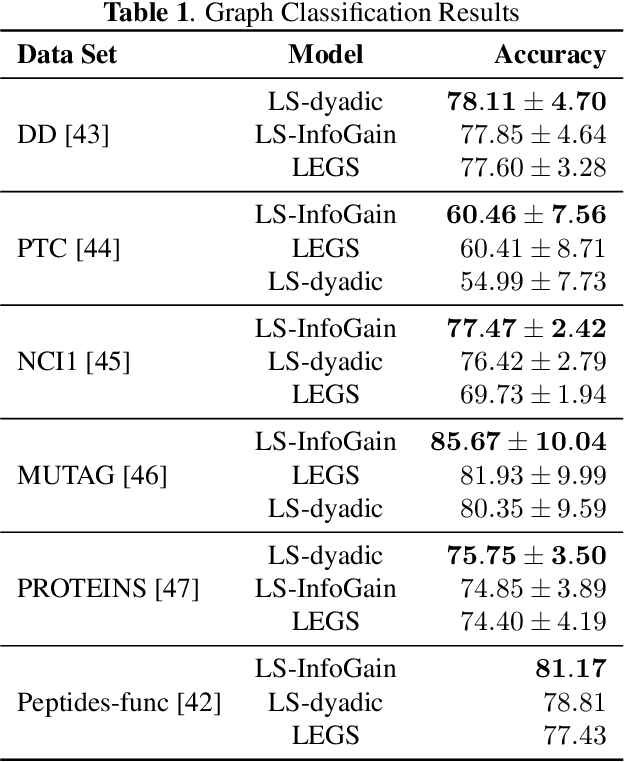
Abstract:Diffusion wavelets extract information from graph signals at different scales of resolution by utilizing graph diffusion operators raised to various powers, known as diffusion scales. Traditionally, the diffusion scales are chosen to be dyadic integers, $\mathbf{2^j}$. Here, we propose a novel, unsupervised method for selecting the diffusion scales based on ideas from information theory. We then show that our method can be incorporated into wavelet-based GNNs via graph classification experiments.
HiPoNet: A Topology-Preserving Multi-View Neural Network For High Dimensional Point Cloud and Single-Cell Data
Feb 11, 2025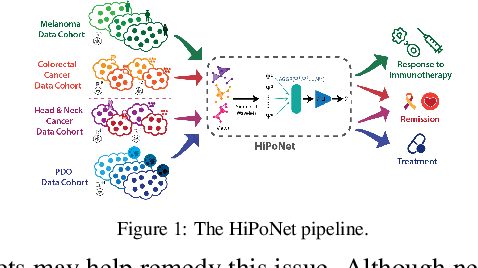
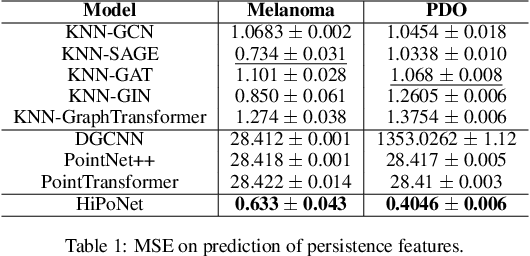
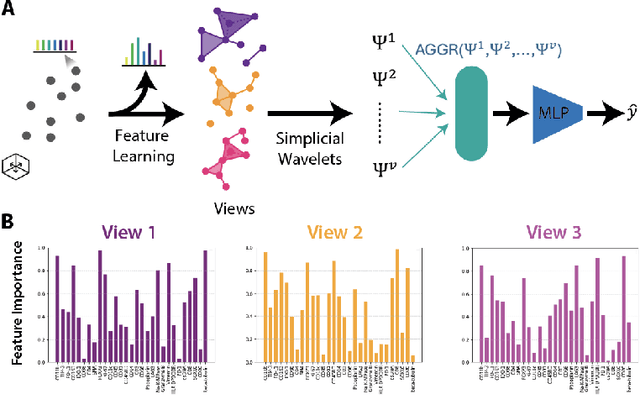
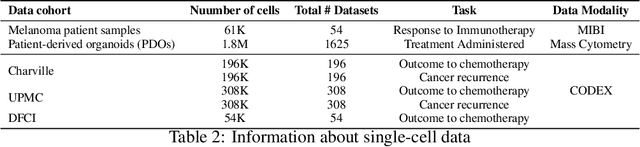
Abstract:In this paper, we propose HiPoNet, an end-to-end differentiable neural network for regression, classification, and representation learning on high-dimensional point clouds. Single-cell data can have high dimensionality exceeding the capabilities of existing methods point cloud tailored for 3D data. Moreover, modern single-cell and spatial experiments now yield entire cohorts of datasets (i.e. one on every patient), necessitating models that can process large, high-dimensional point clouds at scale. Most current approaches build a single nearest-neighbor graph, discarding important geometric information. In contrast, HiPoNet forms higher-order simplicial complexes through learnable feature reweighting, generating multiple data views that disentangle distinct biological processes. It then employs simplicial wavelet transforms to extract multi-scale features - capturing both local and global topology. We empirically show that these components preserve topological information in the learned representations, and that HiPoNet significantly outperforms state-of-the-art point-cloud and graph-based models on single cell. We also show an application of HiPoNet on spatial transcriptomics datasets using spatial co-ordinates as one of the views. Overall, HiPoNet offers a robust and scalable solution for high-dimensional data analysis.
Convergence of Manifold Filter-Combine Networks
Oct 18, 2024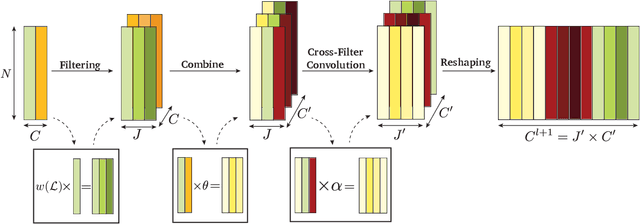
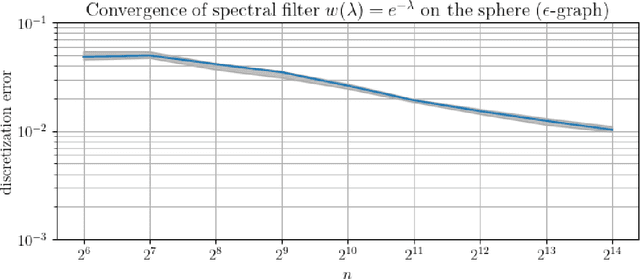
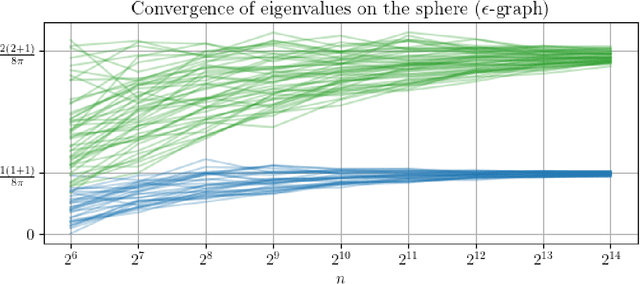
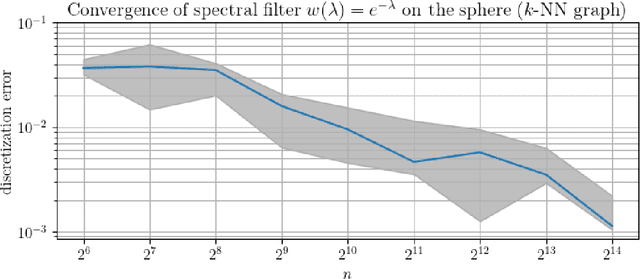
Abstract:In order to better understand manifold neural networks (MNNs), we introduce Manifold Filter-Combine Networks (MFCNs). The filter-combine framework parallels the popular aggregate-combine paradigm for graph neural networks (GNNs) and naturally suggests many interesting families of MNNs which can be interpreted as the manifold analog of various popular GNNs. We then propose a method for implementing MFCNs on high-dimensional point clouds that relies on approximating the manifold by a sparse graph. We prove that our method is consistent in the sense that it converges to a continuum limit as the number of data points tends to infinity.
Hyperedge Representations with Hypergraph Wavelets: Applications to Spatial Transcriptomics
Sep 14, 2024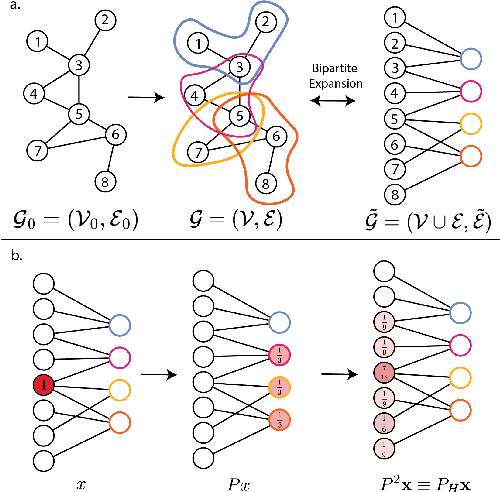
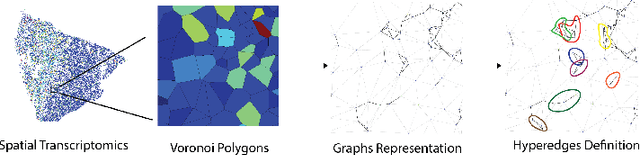
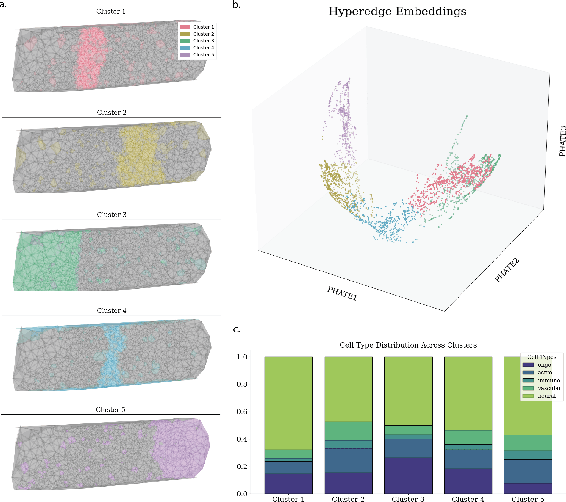
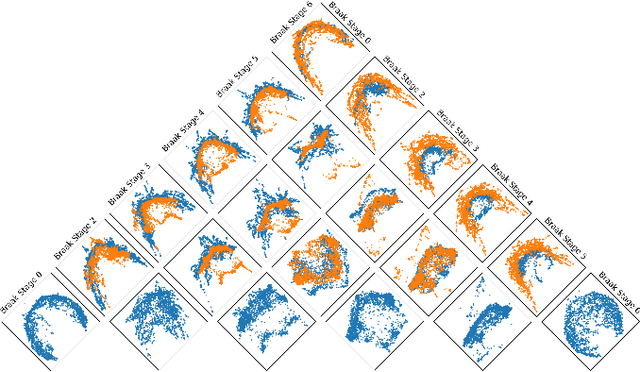
Abstract:In many data-driven applications, higher-order relationships among multiple objects are essential in capturing complex interactions. Hypergraphs, which generalize graphs by allowing edges to connect any number of nodes, provide a flexible and powerful framework for modeling such higher-order relationships. In this work, we introduce hypergraph diffusion wavelets and describe their favorable spectral and spatial properties. We demonstrate their utility for biomedical discovery in spatially resolved transcriptomics by applying the method to represent disease-relevant cellular niches for Alzheimer's disease.
Towards a General GNN Framework for Combinatorial Optimization
May 31, 2024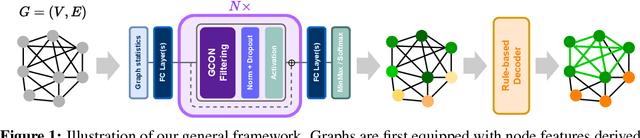
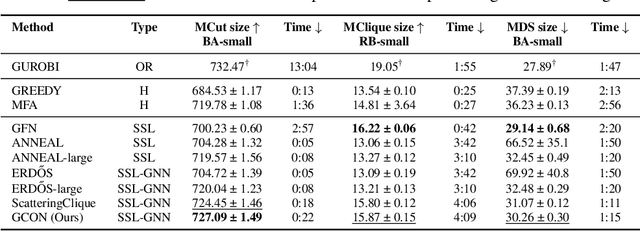
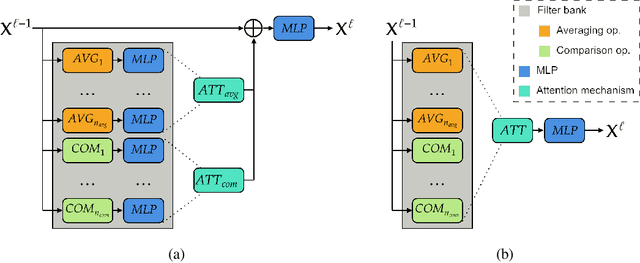
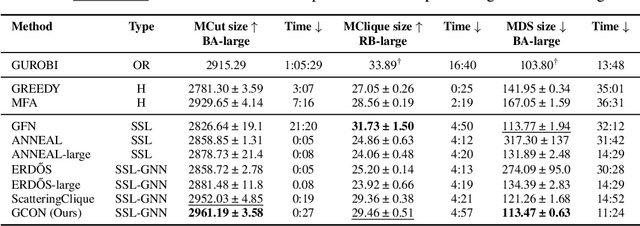
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have achieved great success for a variety of tasks such as node classification, graph classification, and link prediction. However, the use of GNNs (and machine learning more generally) to solve combinatorial optimization (CO) problems is much less explored. Here, we introduce a novel GNN architecture which leverages a complex filter bank and localized attention mechanisms designed to solve CO problems on graphs. We show how our method differentiates itself from prior GNN-based CO solvers and how it can be effectively applied to the maximum clique, minimum dominating set, and maximum cut problems in a self-supervised learning setting. In addition to demonstrating competitive overall performance across all tasks, we establish state-of-the-art results for the max cut problem.
Bayesian Formulations for Graph Spectral Denoising
Nov 27, 2023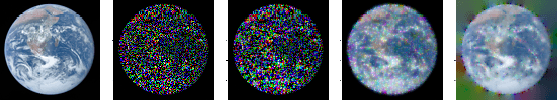



Abstract:We consider noisy signals which are defined on the vertices of a graph and present smoothing algorithms for the cases of Gaussian, dropout, and uniformly distributed noise. The signals are assumed to follow a prior distribution defined in the frequency domain which favors signals which are smooth across the edges of the graph. By pairing this prior distribution with our three models of noise generation, we propose \textit{Maximum A Posteriori} (M.A.P.) estimates of the true signal in the presence of noisy data and provide algorithms for computing the M.A.P. Finally, we demonstrate the algorithms' ability to effectively restore white noise on image data, and from severe dropout in toy \& EHR data.
BLIS-Net: Classifying and Analyzing Signals on Graphs
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for tasks such as node classification and graph classification. However, much less work has been done on signal classification, where the data consists of many functions (referred to as signals) defined on the vertices of a single graph. These tasks require networks designed differently from those designed for traditional GNN tasks. Indeed, traditional GNNs rely on localized low-pass filters, and signals of interest may have intricate multi-frequency behavior and exhibit long range interactions. This motivates us to introduce the BLIS-Net (Bi-Lipschitz Scattering Net), a novel GNN that builds on the previously introduced geometric scattering transform. Our network is able to capture both local and global signal structure and is able to capture both low-frequency and high-frequency information. We make several crucial changes to the original geometric scattering architecture which we prove increase the ability of our network to capture information about the input signal and show that BLIS-Net achieves superior performance on both synthetic and real-world data sets based on traffic flow and fMRI data.
Graph topological property recovery with heat and wave dynamics-based features on graphs
Sep 19, 2023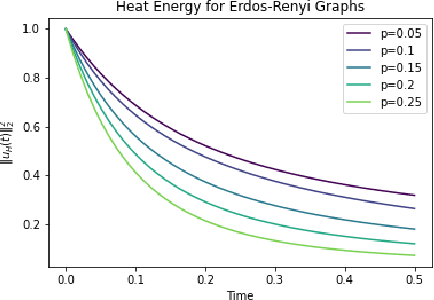
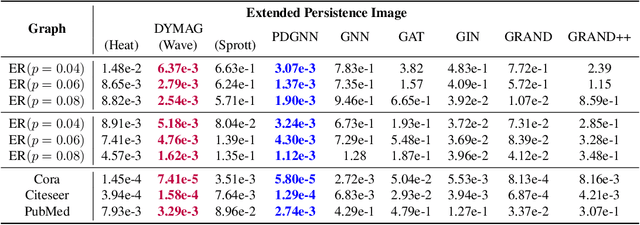
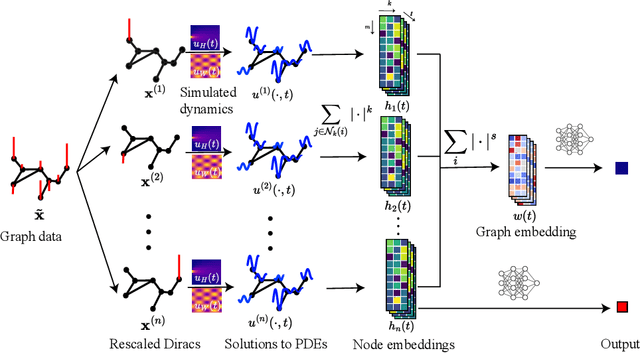
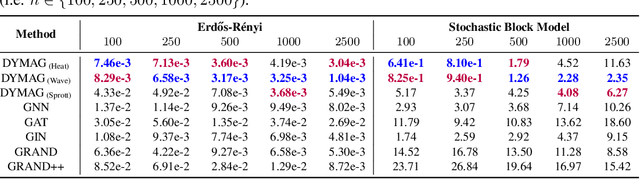
Abstract:In this paper, we propose Graph Differential Equation Network (GDeNet), an approach that harnesses the expressive power of solutions to PDEs on a graph to obtain continuous node- and graph-level representations for various downstream tasks. We derive theoretical results connecting the dynamics of heat and wave equations to the spectral properties of the graph and to the behavior of continuous-time random walks on graphs. We demonstrate experimentally that these dynamics are able to capture salient aspects of graph geometry and topology by recovering generating parameters of random graphs, Ricci curvature, and persistent homology. Furthermore, we demonstrate the superior performance of GDeNet on real-world datasets including citation graphs, drug-like molecules, and proteins.
Directed Scattering for Knowledge Graph-based Cellular Signaling Analysis
Sep 14, 2023Abstract:Directed graphs are a natural model for many phenomena, in particular scientific knowledge graphs such as molecular interaction or chemical reaction networks that define cellular signaling relationships. In these situations, source nodes typically have distinct biophysical properties from sinks. Due to their ordered and unidirectional relationships, many such networks also have hierarchical and multiscale structure. However, the majority of methods performing node- and edge-level tasks in machine learning do not take these properties into account, and thus have not been leveraged effectively for scientific tasks such as cellular signaling network inference. We propose a new framework called Directed Scattering Autoencoder (DSAE) which uses a directed version of a geometric scattering transform, combined with the non-linear dimensionality reduction properties of an autoencoder and the geometric properties of the hyperbolic space to learn latent hierarchies. We show this method outperforms numerous others on tasks such as embedding directed graphs and learning cellular signaling networks.
A Flow Artist for High-Dimensional Cellular Data
Jul 31, 2023Abstract:We consider the problem of embedding point cloud data sampled from an underlying manifold with an associated flow or velocity. Such data arises in many contexts where static snapshots of dynamic entities are measured, including in high-throughput biology such as single-cell transcriptomics. Existing embedding techniques either do not utilize velocity information or embed the coordinates and velocities independently, i.e., they either impose velocities on top of an existing point embedding or embed points within a prescribed vector field. Here we present FlowArtist, a neural network that embeds points while jointly learning a vector field around the points. The combination allows FlowArtist to better separate and visualize velocity-informed structures. Our results, on toy datasets and single-cell RNA velocity data, illustrate the value of utilizing coordinate and velocity information in tandem for embedding and visualizing high-dimensional data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge