Xiaoyang Wu
Any3D-VLA: Enhancing VLA Robustness via Diverse Point Clouds
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Existing Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models typically take 2D images as visual input, which limits their spatial understanding in complex scenes. How can we incorporate 3D information to enhance VLA capabilities? We conduct a pilot study across different observation spaces and visual representations. The results show that explicitly lifting visual input into point clouds yields representations that better complement their corresponding 2D representations. To address the challenges of (1) scarce 3D data and (2) the domain gap induced by cross-environment differences and depth-scale biases, we propose Any3D-VLA. It unifies the simulator, sensor, and model-estimated point clouds within a training pipeline, constructs diverse inputs, and learns domain-agnostic 3D representations that are fused with the corresponding 2D representations. Simulation and real-world experiments demonstrate Any3D-VLA's advantages in improving performance and mitigating the domain gap. Our project homepage is available at https://xianzhefan.github.io/Any3D-VLA.github.io.
Train Once, Deploy Anywhere: Realize Data-Efficient Dynamic Object Manipulation
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Realizing generalizable dynamic object manipulation is important for enhancing manufacturing efficiency, as it eliminates specialized engineering for various scenarios. To this end, imitation learning emerges as a promising paradigm, leveraging expert demonstrations to teach a policy manipulation skills. Although the generalization of an imitation learning policy can be improved by increasing demonstrations, demonstration collection is labor-intensive. To address this problem, this paper investigates whether strong generalization in dynamic object manipulation is achievable with only a few demonstrations. Specifically, we develop an entropy-based theoretical framework to quantify the optimization of imitation learning. Based on this framework, we propose a system named Generalizable Entropy-based Manipulation (GEM). Extensive experiments in simulated and real tasks demonstrate that GEM can generalize across diverse environment backgrounds, robot embodiments, motion dynamics, and object geometries. Notably, GEM has been deployed in a real canteen for tableware collection. Without any in-scene demonstration, it achieves a success rate of over 97% across more than 10,000 operations.
LiteReality: Graphics-Ready 3D Scene Reconstruction from RGB-D Scans
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:We propose LiteReality, a novel pipeline that converts RGB-D scans of indoor environments into compact, realistic, and interactive 3D virtual replicas. LiteReality not only reconstructs scenes that visually resemble reality but also supports key features essential for graphics pipelines -- such as object individuality, articulation, high-quality physically based rendering materials, and physically based interaction. At its core, LiteReality first performs scene understanding and parses the results into a coherent 3D layout and objects with the help of a structured scene graph. It then reconstructs the scene by retrieving the most visually similar 3D artist-crafted models from a curated asset database. Next, the Material Painting module enhances realism by recovering high-quality, spatially varying materials. Finally, the reconstructed scene is integrated into a simulation engine with basic physical properties to enable interactive behavior. The resulting scenes are compact, editable, and fully compatible with standard graphics pipelines, making them suitable for applications in AR/VR, gaming, robotics, and digital twins. In addition, LiteReality introduces a training-free object retrieval module that achieves state-of-the-art similarity performance on the Scan2CAD benchmark, along with a robust material painting module capable of transferring appearances from images of any style to 3D assets -- even under severe misalignment, occlusion, and poor lighting. We demonstrate the effectiveness of LiteReality on both real-life scans and public datasets. Project page: https://litereality.github.io; Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ecK9m3LXg2c
DreamComposer++: Empowering Diffusion Models with Multi-View Conditions for 3D Content Generation
Jul 03, 2025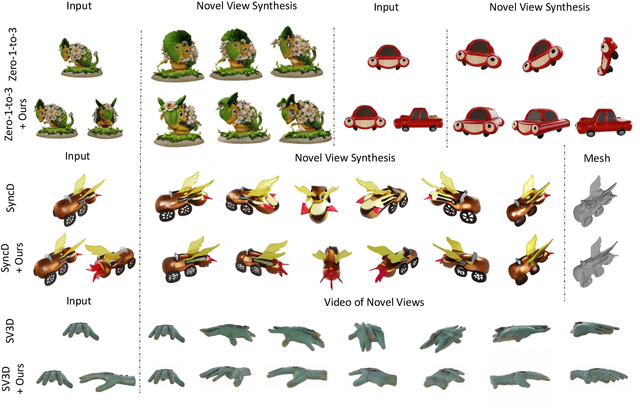
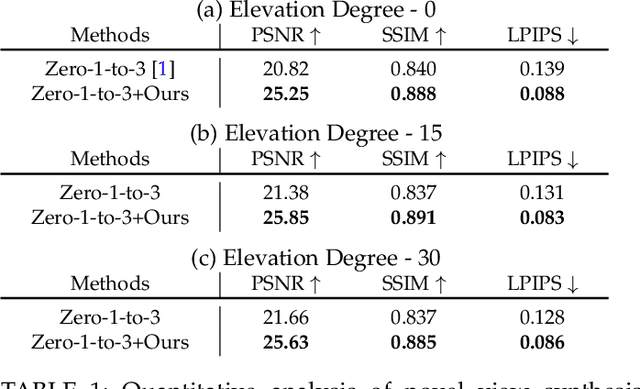
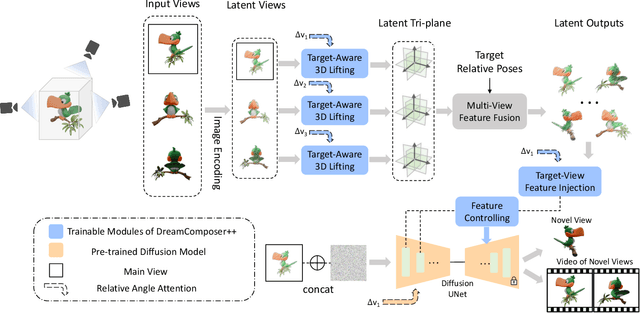
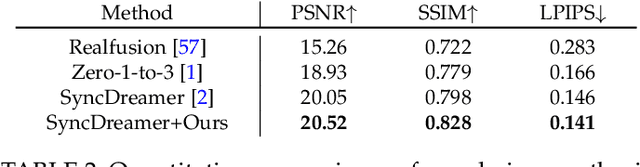
Abstract:Recent advancements in leveraging pre-trained 2D diffusion models achieve the generation of high-quality novel views from a single in-the-wild image. However, existing works face challenges in producing controllable novel views due to the lack of information from multiple views. In this paper, we present DreamComposer++, a flexible and scalable framework designed to improve current view-aware diffusion models by incorporating multi-view conditions. Specifically, DreamComposer++ utilizes a view-aware 3D lifting module to extract 3D representations of an object from various views. These representations are then aggregated and rendered into the latent features of target view through the multi-view feature fusion module. Finally, the obtained features of target view are integrated into pre-trained image or video diffusion models for novel view synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that DreamComposer++ seamlessly integrates with cutting-edge view-aware diffusion models and enhances their abilities to generate controllable novel views from multi-view conditions. This advancement facilitates controllable 3D object reconstruction and enables a wide range of applications.
Sonata: Self-Supervised Learning of Reliable Point Representations
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we question whether we have a reliable self-supervised point cloud model that can be used for diverse 3D tasks via simple linear probing, even with limited data and minimal computation. We find that existing 3D self-supervised learning approaches fall short when evaluated on representation quality through linear probing. We hypothesize that this is due to what we term the "geometric shortcut", which causes representations to collapse to low-level spatial features. This challenge is unique to 3D and arises from the sparse nature of point cloud data. We address it through two key strategies: obscuring spatial information and enhancing the reliance on input features, ultimately composing a Sonata of 140k point clouds through self-distillation. Sonata is simple and intuitive, yet its learned representations are strong and reliable: zero-shot visualizations demonstrate semantic grouping, alongside strong spatial reasoning through nearest-neighbor relationships. Sonata demonstrates exceptional parameter and data efficiency, tripling linear probing accuracy (from 21.8% to 72.5%) on ScanNet and nearly doubling performance with only 1% of the data compared to previous approaches. Full fine-tuning further advances SOTA across both 3D indoor and outdoor perception tasks.
SAMPart3D: Segment Any Part in 3D Objects
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:3D part segmentation is a crucial and challenging task in 3D perception, playing a vital role in applications such as robotics, 3D generation, and 3D editing. Recent methods harness the powerful Vision Language Models (VLMs) for 2D-to-3D knowledge distillation, achieving zero-shot 3D part segmentation. However, these methods are limited by their reliance on text prompts, which restricts the scalability to large-scale unlabeled datasets and the flexibility in handling part ambiguities. In this work, we introduce SAMPart3D, a scalable zero-shot 3D part segmentation framework that segments any 3D object into semantic parts at multiple granularities, without requiring predefined part label sets as text prompts. For scalability, we use text-agnostic vision foundation models to distill a 3D feature extraction backbone, allowing scaling to large unlabeled 3D datasets to learn rich 3D priors. For flexibility, we distill scale-conditioned part-aware 3D features for 3D part segmentation at multiple granularities. Once the segmented parts are obtained from the scale-conditioned part-aware 3D features, we use VLMs to assign semantic labels to each part based on the multi-view renderings. Compared to previous methods, our SAMPart3D can scale to the recent large-scale 3D object dataset Objaverse and handle complex, non-ordinary objects. Additionally, we contribute a new 3D part segmentation benchmark to address the lack of diversity and complexity of objects and parts in existing benchmarks. Experiments show that our SAMPart3D significantly outperforms existing zero-shot 3D part segmentation methods, and can facilitate various applications such as part-level editing and interactive segmentation.
VIRT: Vision Instructed Transformer for Robotic Manipulation
Oct 09, 2024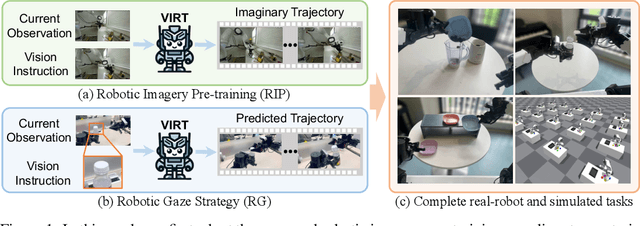
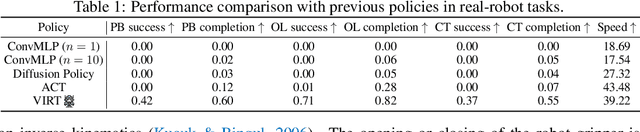
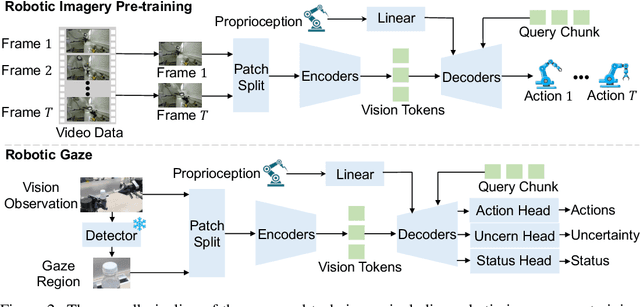
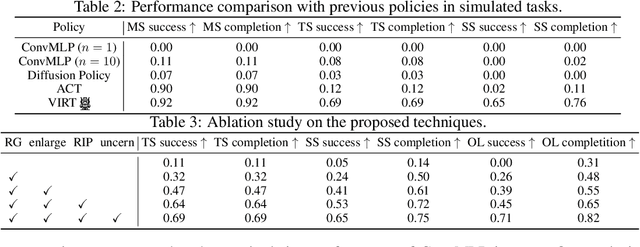
Abstract:Robotic manipulation, owing to its multi-modal nature, often faces significant training ambiguity, necessitating explicit instructions to clearly delineate the manipulation details in tasks. In this work, we highlight that vision instruction is naturally more comprehensible to recent robotic policies than the commonly adopted text instruction, as these policies are born with some vision understanding ability like human infants. Building on this premise and drawing inspiration from cognitive science, we introduce the robotic imagery paradigm, which realizes large-scale robotic data pre-training without text annotations. Additionally, we propose the robotic gaze strategy that emulates the human eye gaze mechanism, thereby guiding subsequent actions and focusing the attention of the policy on the manipulated object. Leveraging these innovations, we develop VIRT, a fully Transformer-based policy. We design comprehensive tasks using both a physical robot and simulated environments to assess the efficacy of VIRT. The results indicate that VIRT can complete very competitive tasks like ``opening the lid of a tightly sealed bottle'', and the proposed techniques boost the success rates of the baseline policy on diverse challenging tasks from nearly 0% to more than 65%.
Conditional Testing based on Localized Conformal p-values
Sep 25, 2024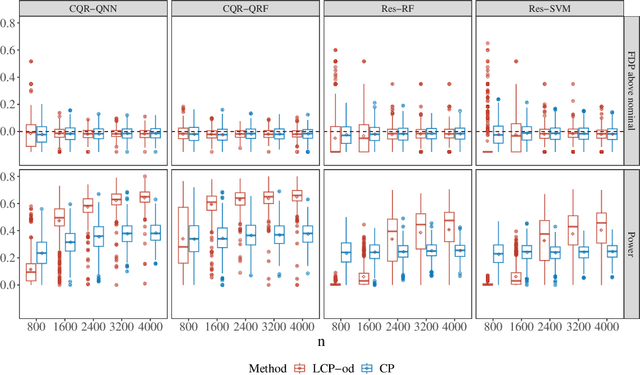
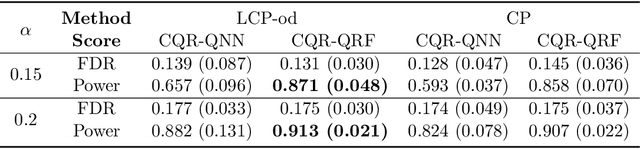
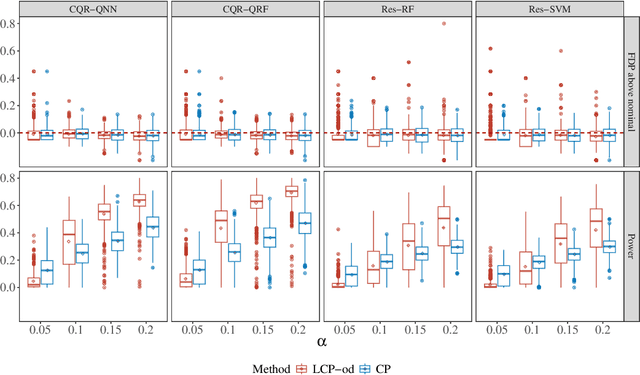
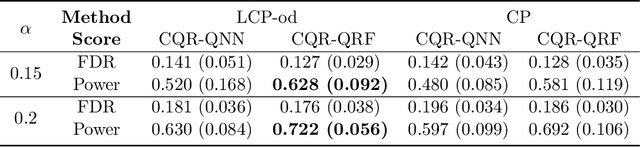
Abstract:In this paper, we address conditional testing problems through the conformal inference framework. We define the localized conformal p-values by inverting prediction intervals and prove their theoretical properties. These defined p-values are then applied to several conditional testing problems to illustrate their practicality. Firstly, we propose a conditional outlier detection procedure to test for outliers in the conditional distribution with finite-sample false discovery rate (FDR) control. We also introduce a novel conditional label screening problem with the goal of screening multivariate response variables and propose a screening procedure to control the family-wise error rate (FWER). Finally, we consider the two-sample conditional distribution test and define a weighted U-statistic through the aggregation of localized p-values. Numerical simulations and real-data examples validate the superior performance of our proposed strategies.
Point Transformer V3 Extreme: 1st Place Solution for 2024 Waymo Open Dataset Challenge in Semantic Segmentation
Jul 21, 2024



Abstract:In this technical report, we detail our first-place solution for the 2024 Waymo Open Dataset Challenge's semantic segmentation track. We significantly enhanced the performance of Point Transformer V3 on the Waymo benchmark by implementing cutting-edge, plug-and-play training and inference technologies. Notably, our advanced version, Point Transformer V3 Extreme, leverages multi-frame training and a no-clipping-point policy, achieving substantial gains over the original PTv3 performance. Additionally, employing a straightforward model ensemble strategy further boosted our results. This approach secured us the top position on the Waymo Open Dataset semantic segmentation leaderboard, markedly outperforming other entries.
Tailor3D: Customized 3D Assets Editing and Generation with Dual-Side Images
Jul 08, 2024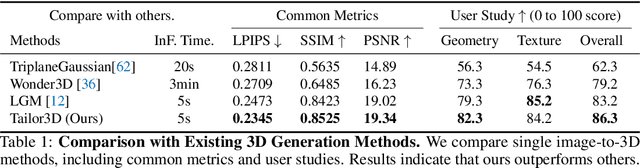
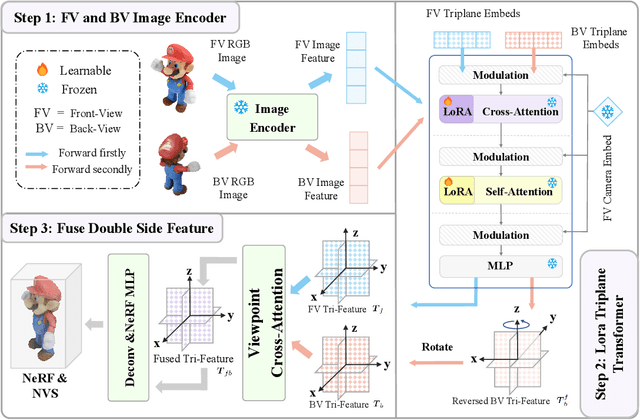
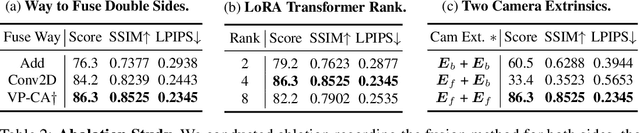
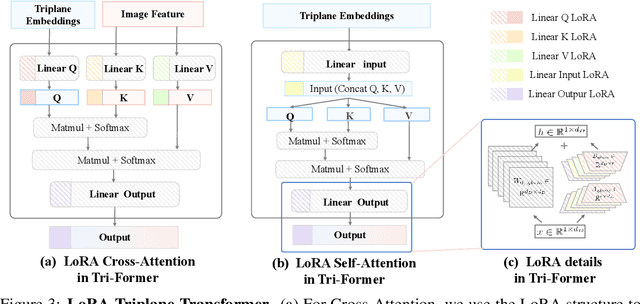
Abstract:Recent advances in 3D AIGC have shown promise in directly creating 3D objects from text and images, offering significant cost savings in animation and product design. However, detailed edit and customization of 3D assets remains a long-standing challenge. Specifically, 3D Generation methods lack the ability to follow finely detailed instructions as precisely as their 2D image creation counterparts. Imagine you can get a toy through 3D AIGC but with undesired accessories and dressing. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel pipeline called Tailor3D, which swiftly creates customized 3D assets from editable dual-side images. We aim to emulate a tailor's ability to locally change objects or perform overall style transfer. Unlike creating 3D assets from multiple views, using dual-side images eliminates conflicts on overlapping areas that occur when editing individual views. Specifically, it begins by editing the front view, then generates the back view of the object through multi-view diffusion. Afterward, it proceeds to edit the back views. Finally, a Dual-sided LRM is proposed to seamlessly stitch together the front and back 3D features, akin to a tailor sewing together the front and back of a garment. The Dual-sided LRM rectifies imperfect consistencies between the front and back views, enhancing editing capabilities and reducing memory burdens while seamlessly integrating them into a unified 3D representation with the LoRA Triplane Transformer. Experimental results demonstrate Tailor3D's effectiveness across various 3D generation and editing tasks, including 3D generative fill and style transfer. It provides a user-friendly, efficient solution for editing 3D assets, with each editing step taking only seconds to complete.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge