Yuan-Chen Guo
OmniPart: Part-Aware 3D Generation with Semantic Decoupling and Structural Cohesion
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:The creation of 3D assets with explicit, editable part structures is crucial for advancing interactive applications, yet most generative methods produce only monolithic shapes, limiting their utility. We introduce OmniPart, a novel framework for part-aware 3D object generation designed to achieve high semantic decoupling among components while maintaining robust structural cohesion. OmniPart uniquely decouples this complex task into two synergistic stages: (1) an autoregressive structure planning module generates a controllable, variable-length sequence of 3D part bounding boxes, critically guided by flexible 2D part masks that allow for intuitive control over part decomposition without requiring direct correspondences or semantic labels; and (2) a spatially-conditioned rectified flow model, efficiently adapted from a pre-trained holistic 3D generator, synthesizes all 3D parts simultaneously and consistently within the planned layout. Our approach supports user-defined part granularity, precise localization, and enables diverse downstream applications. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OmniPart achieves state-of-the-art performance, paving the way for more interpretable, editable, and versatile 3D content.
DreamComposer++: Empowering Diffusion Models with Multi-View Conditions for 3D Content Generation
Jul 03, 2025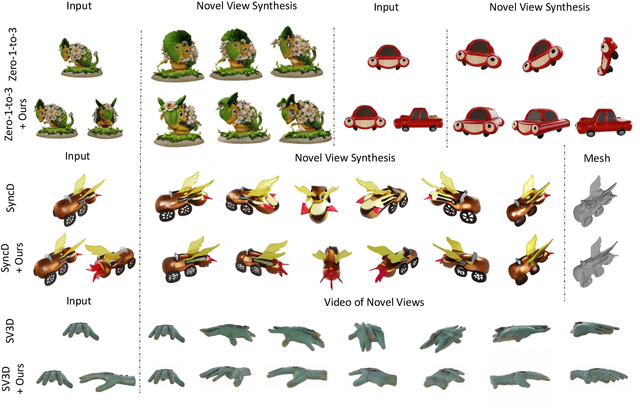
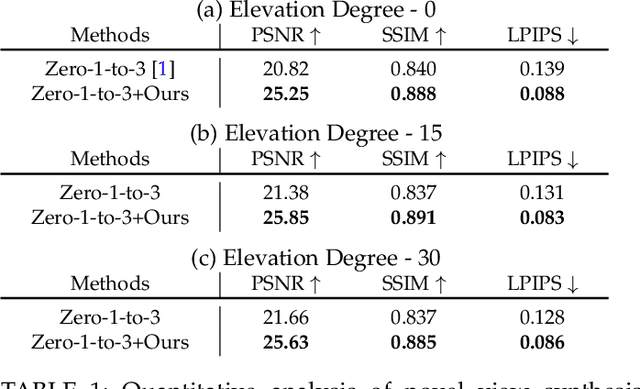
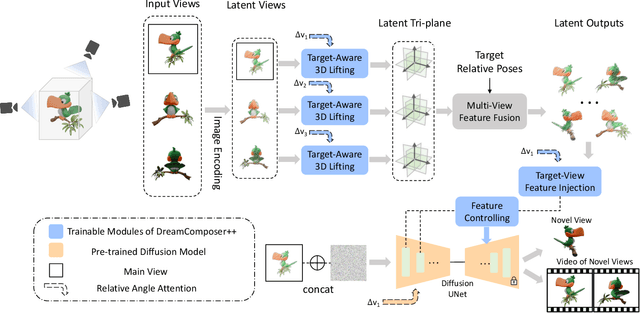
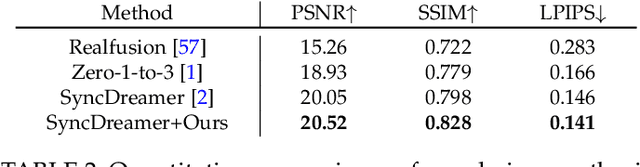
Abstract:Recent advancements in leveraging pre-trained 2D diffusion models achieve the generation of high-quality novel views from a single in-the-wild image. However, existing works face challenges in producing controllable novel views due to the lack of information from multiple views. In this paper, we present DreamComposer++, a flexible and scalable framework designed to improve current view-aware diffusion models by incorporating multi-view conditions. Specifically, DreamComposer++ utilizes a view-aware 3D lifting module to extract 3D representations of an object from various views. These representations are then aggregated and rendered into the latent features of target view through the multi-view feature fusion module. Finally, the obtained features of target view are integrated into pre-trained image or video diffusion models for novel view synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that DreamComposer++ seamlessly integrates with cutting-edge view-aware diffusion models and enhances their abilities to generate controllable novel views from multi-view conditions. This advancement facilitates controllable 3D object reconstruction and enables a wide range of applications.
UniGeo: Taming Video Diffusion for Unified Consistent Geometry Estimation
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recently, methods leveraging diffusion model priors to assist monocular geometric estimation (e.g., depth and normal) have gained significant attention due to their strong generalization ability. However, most existing works focus on estimating geometric properties within the camera coordinate system of individual video frames, neglecting the inherent ability of diffusion models to determine inter-frame correspondence. In this work, we demonstrate that, through appropriate design and fine-tuning, the intrinsic consistency of video generation models can be effectively harnessed for consistent geometric estimation. Specifically, we 1) select geometric attributes in the global coordinate system that share the same correspondence with video frames as the prediction targets, 2) introduce a novel and efficient conditioning method by reusing positional encodings, and 3) enhance performance through joint training on multiple geometric attributes that share the same correspondence. Our results achieve superior performance in predicting global geometric attributes in videos and can be directly applied to reconstruction tasks. Even when trained solely on static video data, our approach exhibits the potential to generalize to dynamic video scenes.
HoloPart: Generative 3D Part Amodal Segmentation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:3D part amodal segmentation--decomposing a 3D shape into complete, semantically meaningful parts, even when occluded--is a challenging but crucial task for 3D content creation and understanding. Existing 3D part segmentation methods only identify visible surface patches, limiting their utility. Inspired by 2D amodal segmentation, we introduce this novel task to the 3D domain and propose a practical, two-stage approach, addressing the key challenges of inferring occluded 3D geometry, maintaining global shape consistency, and handling diverse shapes with limited training data. First, we leverage existing 3D part segmentation to obtain initial, incomplete part segments. Second, we introduce HoloPart, a novel diffusion-based model, to complete these segments into full 3D parts. HoloPart utilizes a specialized architecture with local attention to capture fine-grained part geometry and global shape context attention to ensure overall shape consistency. We introduce new benchmarks based on the ABO and PartObjaverse-Tiny datasets and demonstrate that HoloPart significantly outperforms state-of-the-art shape completion methods. By incorporating HoloPart with existing segmentation techniques, we achieve promising results on 3D part amodal segmentation, opening new avenues for applications in geometry editing, animation, and material assignment.
SparseFlex: High-Resolution and Arbitrary-Topology 3D Shape Modeling
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Creating high-fidelity 3D meshes with arbitrary topology, including open surfaces and complex interiors, remains a significant challenge. Existing implicit field methods often require costly and detail-degrading watertight conversion, while other approaches struggle with high resolutions. This paper introduces SparseFlex, a novel sparse-structured isosurface representation that enables differentiable mesh reconstruction at resolutions up to $1024^3$ directly from rendering losses. SparseFlex combines the accuracy of Flexicubes with a sparse voxel structure, focusing computation on surface-adjacent regions and efficiently handling open surfaces. Crucially, we introduce a frustum-aware sectional voxel training strategy that activates only relevant voxels during rendering, dramatically reducing memory consumption and enabling high-resolution training. This also allows, for the first time, the reconstruction of mesh interiors using only rendering supervision. Building upon this, we demonstrate a complete shape modeling pipeline by training a variational autoencoder (VAE) and a rectified flow transformer for high-quality 3D shape generation. Our experiments show state-of-the-art reconstruction accuracy, with a ~82% reduction in Chamfer Distance and a ~88% increase in F-score compared to previous methods, and demonstrate the generation of high-resolution, detailed 3D shapes with arbitrary topology. By enabling high-resolution, differentiable mesh reconstruction and generation with rendering losses, SparseFlex significantly advances the state-of-the-art in 3D shape representation and modeling.
TripoSG: High-Fidelity 3D Shape Synthesis using Large-Scale Rectified Flow Models
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in diffusion techniques have propelled image and video generation to unprece- dented levels of quality, significantly accelerating the deployment and application of generative AI. However, 3D shape generation technology has so far lagged behind, constrained by limitations in 3D data scale, complexity of 3D data process- ing, and insufficient exploration of advanced tech- niques in the 3D domain. Current approaches to 3D shape generation face substantial challenges in terms of output quality, generalization capa- bility, and alignment with input conditions. We present TripoSG, a new streamlined shape diffu- sion paradigm capable of generating high-fidelity 3D meshes with precise correspondence to input images. Specifically, we propose: 1) A large-scale rectified flow transformer for 3D shape generation, achieving state-of-the-art fidelity through training on extensive, high-quality data. 2) A hybrid supervised training strategy combining SDF, normal, and eikonal losses for 3D VAE, achieving high- quality 3D reconstruction performance. 3) A data processing pipeline to generate 2 million high- quality 3D samples, highlighting the crucial rules for data quality and quantity in training 3D gen- erative models. Through comprehensive experi- ments, we have validated the effectiveness of each component in our new framework. The seamless integration of these parts has enabled TripoSG to achieve state-of-the-art performance in 3D shape generation. The resulting 3D shapes exhibit en- hanced detail due to high-resolution capabilities and demonstrate exceptional fidelity to input im- ages. Moreover, TripoSG demonstrates improved versatility in generating 3D models from diverse image styles and contents, showcasing strong gen- eralization capabilities. To foster progress and innovation in the field of 3D generation, we will make our model publicly available.
MIDI: Multi-Instance Diffusion for Single Image to 3D Scene Generation
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces MIDI, a novel paradigm for compositional 3D scene generation from a single image. Unlike existing methods that rely on reconstruction or retrieval techniques or recent approaches that employ multi-stage object-by-object generation, MIDI extends pre-trained image-to-3D object generation models to multi-instance diffusion models, enabling the simultaneous generation of multiple 3D instances with accurate spatial relationships and high generalizability. At its core, MIDI incorporates a novel multi-instance attention mechanism, that effectively captures inter-object interactions and spatial coherence directly within the generation process, without the need for complex multi-step processes. The method utilizes partial object images and global scene context as inputs, directly modeling object completion during 3D generation. During training, we effectively supervise the interactions between 3D instances using a limited amount of scene-level data, while incorporating single-object data for regularization, thereby maintaining the pre-trained generalization ability. MIDI demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in image-to-scene generation, validated through evaluations on synthetic data, real-world scene data, and stylized scene images generated by text-to-image diffusion models.
MV-Adapter: Multi-view Consistent Image Generation Made Easy
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Existing multi-view image generation methods often make invasive modifications to pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) models and require full fine-tuning, leading to (1) high computational costs, especially with large base models and high-resolution images, and (2) degradation in image quality due to optimization difficulties and scarce high-quality 3D data. In this paper, we propose the first adapter-based solution for multi-view image generation, and introduce MV-Adapter, a versatile plug-and-play adapter that enhances T2I models and their derivatives without altering the original network structure or feature space. By updating fewer parameters, MV-Adapter enables efficient training and preserves the prior knowledge embedded in pre-trained models, mitigating overfitting risks. To efficiently model the 3D geometric knowledge within the adapter, we introduce innovative designs that include duplicated self-attention layers and parallel attention architecture, enabling the adapter to inherit the powerful priors of the pre-trained models to model the novel 3D knowledge. Moreover, we present a unified condition encoder that seamlessly integrates camera parameters and geometric information, facilitating applications such as text- and image-based 3D generation and texturing. MV-Adapter achieves multi-view generation at 768 resolution on Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL), and demonstrates adaptability and versatility. It can also be extended to arbitrary view generation, enabling broader applications. We demonstrate that MV-Adapter sets a new quality standard for multi-view image generation, and opens up new possibilities due to its efficiency, adaptability and versatility.
SuperMat: Physically Consistent PBR Material Estimation at Interactive Rates
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Decomposing physically-based materials from images into their constituent properties remains challenging, particularly when maintaining both computational efficiency and physical consistency. While recent diffusion-based approaches have shown promise, they face substantial computational overhead due to multiple denoising steps and separate models for different material properties. We present SuperMat, a single-step framework that achieves high-quality material decomposition with one-step inference. This enables end-to-end training with perceptual and re-render losses while decomposing albedo, metallic, and roughness maps at millisecond-scale speeds. We further extend our framework to 3D objects through a UV refinement network, enabling consistent material estimation across viewpoints while maintaining efficiency. Experiments demonstrate that SuperMat achieves state-of-the-art PBR material decomposition quality while reducing inference time from seconds to milliseconds per image, and completes PBR material estimation for 3D objects in approximately 3 seconds.
TEXGen: a Generative Diffusion Model for Mesh Textures
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:While high-quality texture maps are essential for realistic 3D asset rendering, few studies have explored learning directly in the texture space, especially on large-scale datasets. In this work, we depart from the conventional approach of relying on pre-trained 2D diffusion models for test-time optimization of 3D textures. Instead, we focus on the fundamental problem of learning in the UV texture space itself. For the first time, we train a large diffusion model capable of directly generating high-resolution texture maps in a feed-forward manner. To facilitate efficient learning in high-resolution UV spaces, we propose a scalable network architecture that interleaves convolutions on UV maps with attention layers on point clouds. Leveraging this architectural design, we train a 700 million parameter diffusion model that can generate UV texture maps guided by text prompts and single-view images. Once trained, our model naturally supports various extended applications, including text-guided texture inpainting, sparse-view texture completion, and text-driven texture synthesis. Project page is at http://cvmi-lab.github.io/TEXGen/.
* Accepted to SIGGRAPH Asia Journal Article (TOG 2024)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge