Yuan Liang
O-Mem: Omni Memory System for Personalized, Long Horizon, Self-Evolving Agents
Nov 18, 2025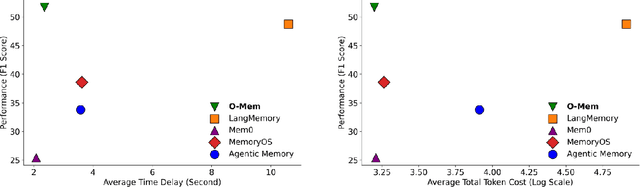
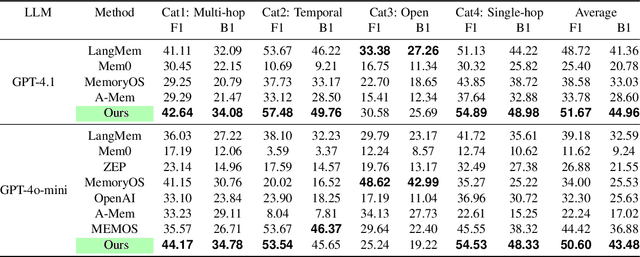
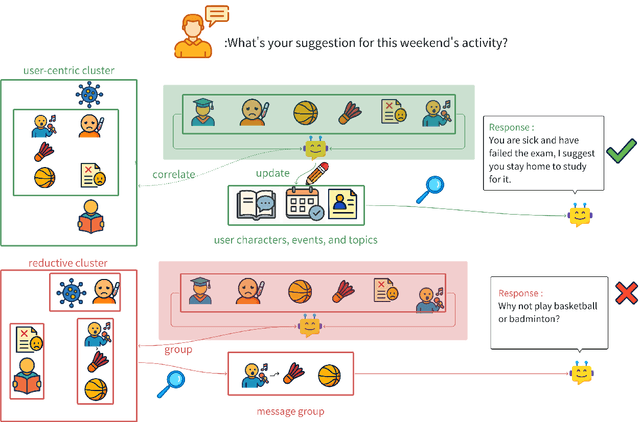
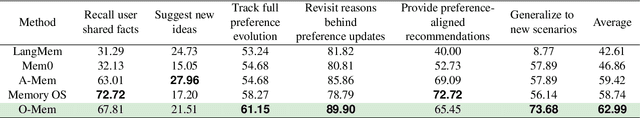
Abstract:Recent advancements in LLM-powered agents have demonstrated significant potential in generating human-like responses; however, they continue to face challenges in maintaining long-term interactions within complex environments, primarily due to limitations in contextual consistency and dynamic personalization. Existing memory systems often depend on semantic grouping prior to retrieval, which can overlook semantically irrelevant yet critical user information and introduce retrieval noise. In this report, we propose the initial design of O-Mem, a novel memory framework based on active user profiling that dynamically extracts and updates user characteristics and event records from their proactive interactions with agents. O-Mem supports hierarchical retrieval of persona attributes and topic-related context, enabling more adaptive and coherent personalized responses. O-Mem achieves 51.67% on the public LoCoMo benchmark, a nearly 3% improvement upon LangMem,the previous state-of-the-art, and it achieves 62.99% on PERSONAMEM, a 3.5% improvement upon A-Mem,the previous state-of-the-art. O-Mem also boosts token and interaction response time efficiency compared to previous memory frameworks. Our work opens up promising directions for developing efficient and human-like personalized AI assistants in the future.
NeuroDx-LM: A Clinical Large-Scale Model for EEG-based Neurological Disorder Detection
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Large-scale models pre-trained on Electroencephalography (EEG) have shown promise in clinical applications such as neurological disorder detection. However, the practical deployment of EEG-based large-scale models faces critical challenges such as limited labeled EEG data and suboptimal performance in clinical scenarios. To address these issues, we propose NeuroDx-LM, a novel large-scale model specifically designed for detecting EEG-based neurological disorders. Our key contributions include (i) a Selective Temporal-Frequency Embedding mechanism that adaptively captures complex temporal and spectral patterns in EEG signals; and (ii) a Progressive Feature-Aware Training strategy that refines feature representation in a two-stage process. In the first stage, our model learns the fundamental discriminative features of EEG activities; in the second stage, the model further extracts more specialized fine-grained features for accurate diagnostic performance. We evaluated NeuroDx-LM on the CHB-MIT and Schizophrenia datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in EEG-based seizure and schizophrenia detection, respectively. These results demonstrate the great potential of EEG-based large-scale models to advance clinical applicability. Our code is available at https://github.com/LetItBe12345/NeuroDx-LM.
Memp: Exploring Agent Procedural Memory
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) based agents excel at diverse tasks, yet they suffer from brittle procedural memory that is manually engineered or entangled in static parameters. In this work, we investigate strategies to endow agents with a learnable, updatable, and lifelong procedural memory. We propose Memp that distills past agent trajectories into both fine-grained, step-by-step instructions and higher-level, script-like abstractions, and explore the impact of different strategies for Build, Retrieval, and Update of procedural memory. Coupled with a dynamic regimen that continuously updates, corrects, and deprecates its contents, this repository evolves in lockstep with new experience. Empirical evaluation on TravelPlanner and ALFWorld shows that as the memory repository is refined, agents achieve steadily higher success rates and greater efficiency on analogous tasks. Moreover, procedural memory built from a stronger model retains its value: migrating the procedural memory to a weaker model yields substantial performance gains.
SynWorld: Virtual Scenario Synthesis for Agentic Action Knowledge Refinement
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:In the interaction between agents and their environments, agents expand their capabilities by planning and executing actions. However, LLM-based agents face substantial challenges when deployed in novel environments or required to navigate unconventional action spaces. To empower agents to autonomously explore environments, optimize workflows, and enhance their understanding of actions, we propose SynWorld, a framework that allows agents to synthesize possible scenarios with multi-step action invocation within the action space and perform Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) exploration to effectively refine their action knowledge in the current environment. Our experiments demonstrate that SynWorld is an effective and general approach to learning action knowledge in new environments. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/SynWorld.
TripoSG: High-Fidelity 3D Shape Synthesis using Large-Scale Rectified Flow Models
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in diffusion techniques have propelled image and video generation to unprece- dented levels of quality, significantly accelerating the deployment and application of generative AI. However, 3D shape generation technology has so far lagged behind, constrained by limitations in 3D data scale, complexity of 3D data process- ing, and insufficient exploration of advanced tech- niques in the 3D domain. Current approaches to 3D shape generation face substantial challenges in terms of output quality, generalization capa- bility, and alignment with input conditions. We present TripoSG, a new streamlined shape diffu- sion paradigm capable of generating high-fidelity 3D meshes with precise correspondence to input images. Specifically, we propose: 1) A large-scale rectified flow transformer for 3D shape generation, achieving state-of-the-art fidelity through training on extensive, high-quality data. 2) A hybrid supervised training strategy combining SDF, normal, and eikonal losses for 3D VAE, achieving high- quality 3D reconstruction performance. 3) A data processing pipeline to generate 2 million high- quality 3D samples, highlighting the crucial rules for data quality and quantity in training 3D gen- erative models. Through comprehensive experi- ments, we have validated the effectiveness of each component in our new framework. The seamless integration of these parts has enabled TripoSG to achieve state-of-the-art performance in 3D shape generation. The resulting 3D shapes exhibit en- hanced detail due to high-resolution capabilities and demonstrate exceptional fidelity to input im- ages. Moreover, TripoSG demonstrates improved versatility in generating 3D models from diverse image styles and contents, showcasing strong gen- eralization capabilities. To foster progress and innovation in the field of 3D generation, we will make our model publicly available.
ConCL: Concept Contrastive Learning for Dense Prediction Pre-training in Pathology Images
Jul 14, 2022



Abstract:Detectingandsegmentingobjectswithinwholeslideimagesis essential in computational pathology workflow. Self-supervised learning (SSL) is appealing to such annotation-heavy tasks. Despite the extensive benchmarks in natural images for dense tasks, such studies are, unfortunately, absent in current works for pathology. Our paper intends to narrow this gap. We first benchmark representative SSL methods for dense prediction tasks in pathology images. Then, we propose concept contrastive learning (ConCL), an SSL framework for dense pre-training. We explore how ConCL performs with concepts provided by different sources and end up with proposing a simple dependency-free concept generating method that does not rely on external segmentation algorithms or saliency detection models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of ConCL over previous state-of-the-art SSL methods across different settings. Along our exploration, we distll several important and intriguing components contributing to the success of dense pre-training for pathology images. We hope this work could provide useful data points and encourage the community to conduct ConCL pre-training for problems of interest. Code is available.
RAAT: Relation-Augmented Attention Transformer for Relation Modeling in Document-Level Event Extraction
Jun 07, 2022


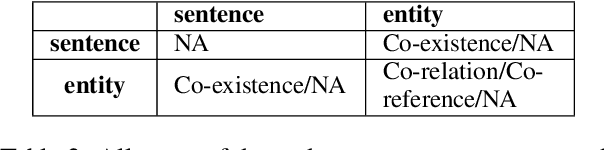
Abstract:In document-level event extraction (DEE) task, event arguments always scatter across sentences (across-sentence issue) and multiple events may lie in one document (multi-event issue). In this paper, we argue that the relation information of event arguments is of great significance for addressing the above two issues, and propose a new DEE framework which can model the relation dependencies, called Relation-augmented Document-level Event Extraction (ReDEE). More specifically, this framework features a novel and tailored transformer, named as Relation-augmented Attention Transformer (RAAT). RAAT is scalable to capture multi-scale and multi-amount argument relations. To further leverage relation information, we introduce a separate event relation prediction task and adopt multi-task learning method to explicitly enhance event extraction performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which can achieve state-of-the-art performance on two public datasets. Our code is available at https://github. com/TencentYoutuResearch/RAAT.
LW-GCN: A Lightweight FPGA-based Graph Convolutional Network Accelerator
Nov 04, 2021

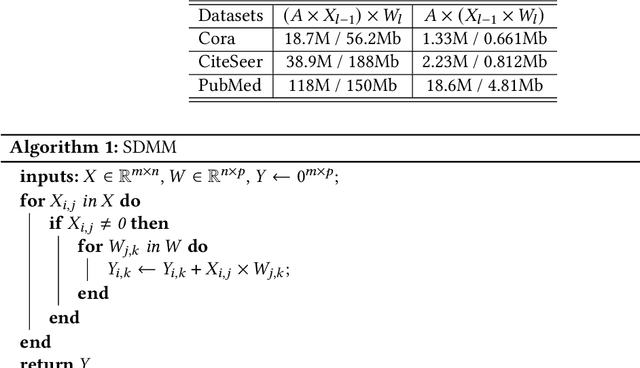

Abstract:Graph convolutional networks (GCNs) have been introduced to effectively process non-euclidean graph data. However, GCNs incur large amounts of irregularity in computation and memory access, which prevents efficient use of traditional neural network accelerators. Moreover, existing dedicated GCN accelerators demand high memory volumes and are difficult to implement onto resource limited edge devices. In this work, we propose LW-GCN, a lightweight FPGA-based accelerator with a software-hardware co-designed process to tackle irregularity in computation and memory access in GCN inference. LW-GCN decomposes the main GCN operations into sparse-dense matrix multiplication (SDMM) and dense matrix multiplication (DMM). We propose a novel compression format to balance workload across PEs and prevent data hazards. Moreover, we apply data quantization and workload tiling, and map both SDMM and DMM of GCN inference onto a uniform architecture on resource limited hardware. Evaluation on GCN and GraphSAGE are performed on Xilinx Kintex-7 FPGA with three popular datasets. Compared to existing CPU, GPU, and state-of-the-art FPGA-based accelerator, LW-GCN reduces latency by up to 60x, 12x and 1.7x and increases power efficiency by up to 912x., 511x and 3.87x, respectively. Furthermore, compared with NVIDIA's latest edge GPU Jetson Xavier NX, LW-GCN achieves speedup and energy savings of 32x and 84x, respectively.
X2Teeth: 3D Teeth Reconstruction from a Single Panoramic Radiograph
Aug 30, 2021
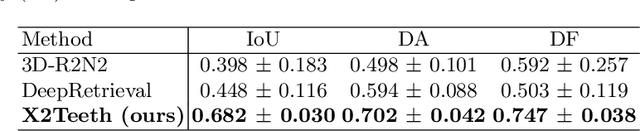


Abstract:3D teeth reconstruction from X-ray is important for dental diagnosis and many clinical operations. However, no existing work has explored the reconstruction of teeth for a whole cavity from a single panoramic radiograph. Different from single object reconstruction from photos, this task has the unique challenge of constructing multiple objects at high resolutions. To conquer this task, we develop a novel ConvNet X2Teeth that decomposes the task into teeth localization and single-shape estimation. We also introduce a patch-based training strategy, such that X2Teeth can be end-to-end trained for optimal performance. Extensive experiments show that our method can successfully estimate the 3D structure of the cavity and reflect the details for each tooth. Moreover, X2Teeth achieves a reconstruction IoU of 0.681, which significantly outperforms the encoder-decoder method by $1.71X and the retrieval-based method by $1.52X. Our method can also be promising for other multi-anatomy 3D reconstruction tasks.
TumorCP: A Simple but Effective Object-Level Data Augmentation for Tumor Segmentation
Jul 21, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning models are notoriously data-hungry. Thus, there is an urging need for data-efficient techniques in medical image analysis, where well-annotated data are costly and time consuming to collect. Motivated by the recently revived "Copy-Paste" augmentation, we propose TumorCP, a simple but effective object-level data augmentation method tailored for tumor segmentation. TumorCP is online and stochastic, providing unlimited augmentation possibilities for tumors' subjects, locations, appearances, as well as morphologies. Experiments on kidney tumor segmentation task demonstrate that TumorCP surpasses the strong baseline by a remarkable margin of 7.12% on tumor Dice. Moreover, together with image-level data augmentation, it beats the current state-of-the-art by 2.32% on tumor Dice. Comprehensive ablation studies are performed to validate the effectiveness of TumorCP. Meanwhile, we show that TumorCP can lead to striking improvements in extremely low-data regimes. Evaluated with only 10% labeled data, TumorCP significantly boosts tumor Dice by 21.87%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the very first work exploring and extending the "Copy-Paste" design in medical imaging domain. Code is available at: https://github.com/YaoZhang93/TumorCP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge