Xiaoyan Zhu
Making Every Head Count: Sparse Attention Without the Speed-Performance Trade-off
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:The design of Large Language Models (LLMs) has long been hampered by a fundamental conflict within their core attention mechanism: its remarkable expressivity is built upon a computational complexity of $O(H \cdot N^2)$ that grows quadratically with the context size ($N$) and linearly with the number of heads ($H$). This standard implementation harbors significant computational redundancy, as all heads independently compute attention over the same sequence space. Existing sparse methods, meanwhile, often trade information integrity for computational efficiency. To resolve this efficiency-performance trade-off, we propose SPAttention, whose core contribution is the introduction of a new paradigm we term Principled Structural Sparsity. SPAttention does not merely drop connections but instead reorganizes the computational task by partitioning the total attention workload into balanced, non-overlapping distance bands, assigning each head a unique segment. This approach transforms the multi-head attention mechanism from $H$ independent $O(N^2)$ computations into a single, collaborative $O(N^2)$ computation, fundamentally reducing complexity by a factor of $H$. The structured inductive bias compels functional specialization among heads, enabling a more efficient allocation of computational resources from redundant modeling to distinct dependencies across the entire sequence span. Extensive empirical validation on the OLMoE-1B-7B and 0.25B-1.75B model series demonstrates that while delivering an approximately two-fold increase in training throughput, its performance is on par with standard dense attention, even surpassing it on select key metrics, while consistently outperforming representative sparse attention methods including Longformer, Reformer, and BigBird across all evaluation metrics.
DecompEval: Evaluating Generated Texts as Unsupervised Decomposed Question Answering
Jul 13, 2023



Abstract:Existing evaluation metrics for natural language generation (NLG) tasks face the challenges on generalization ability and interpretability. Specifically, most of the well-performed metrics are required to train on evaluation datasets of specific NLG tasks and evaluation dimensions, which may cause over-fitting to task-specific datasets. Furthermore, existing metrics only provide an evaluation score for each dimension without revealing the evidence to interpret how this score is obtained. To deal with these challenges, we propose a simple yet effective metric called DecompEval. This metric formulates NLG evaluation as an instruction-style question answering task and utilizes instruction-tuned pre-trained language models (PLMs) without training on evaluation datasets, aiming to enhance the generalization ability. To make the evaluation process more interpretable, we decompose our devised instruction-style question about the quality of generated texts into the subquestions that measure the quality of each sentence. The subquestions with their answers generated by PLMs are then recomposed as evidence to obtain the evaluation result. Experimental results show that DecompEval achieves state-of-the-art performance in untrained metrics for evaluating text summarization and dialogue generation, which also exhibits strong dimension-level / task-level generalization ability and interpretability.
SoK: Comparing Different Membership Inference Attacks with a Comprehensive Benchmark
Jul 12, 2023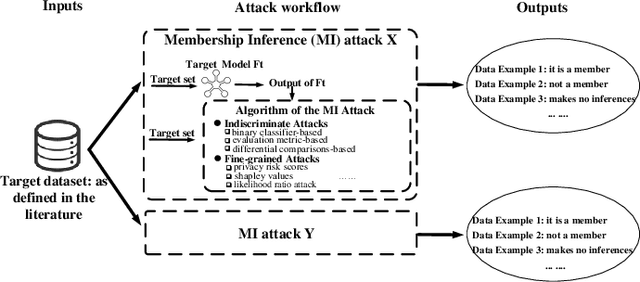
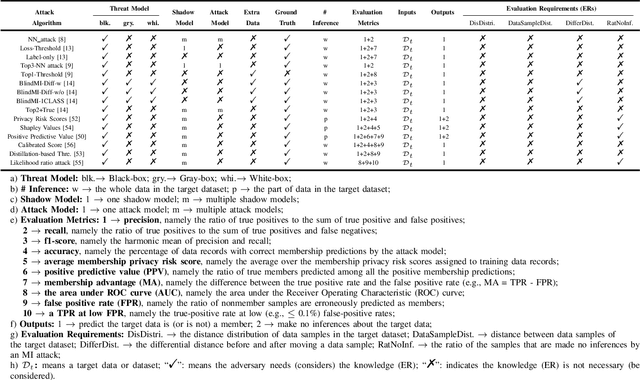
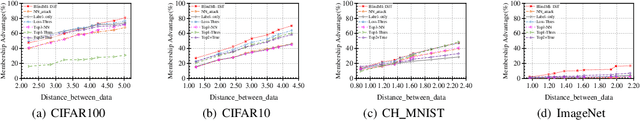
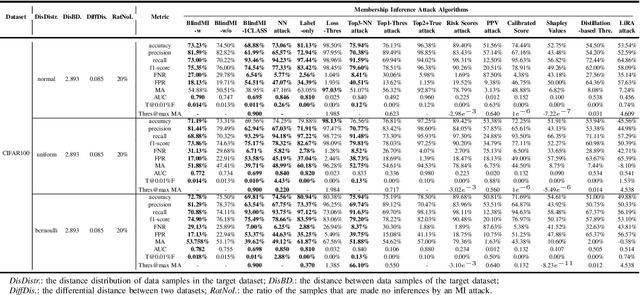
Abstract:Membership inference (MI) attacks threaten user privacy through determining if a given data example has been used to train a target model. However, it has been increasingly recognized that the "comparing different MI attacks" methodology used in the existing works has serious limitations. Due to these limitations, we found (through the experiments in this work) that some comparison results reported in the literature are quite misleading. In this paper, we seek to develop a comprehensive benchmark for comparing different MI attacks, called MIBench, which consists not only the evaluation metrics, but also the evaluation scenarios. And we design the evaluation scenarios from four perspectives: the distance distribution of data samples in the target dataset, the distance between data samples of the target dataset, the differential distance between two datasets (i.e., the target dataset and a generated dataset with only nonmembers), and the ratio of the samples that are made no inferences by an MI attack. The evaluation metrics consist of ten typical evaluation metrics. We have identified three principles for the proposed "comparing different MI attacks" methodology, and we have designed and implemented the MIBench benchmark with 84 evaluation scenarios for each dataset. In total, we have used our benchmark to fairly and systematically compare 15 state-of-the-art MI attack algorithms across 588 evaluation scenarios, and these evaluation scenarios cover 7 widely used datasets and 7 representative types of models. All codes and evaluations of MIBench are publicly available at https://github.com/MIBench/MIBench.github.io/blob/main/README.md.
KPT: Keyword-guided Pre-training for Grounded Dialog Generation
Dec 04, 2022Abstract:Incorporating external knowledge into the response generation process is essential to building more helpful and reliable dialog agents. However, collecting knowledge-grounded conversations is often costly, calling for a better pre-trained model for grounded dialog generation that generalizes well w.r.t. different types of knowledge. In this work, we propose KPT (Keyword-guided Pre-Training), a novel self-supervised pre-training method for grounded dialog generation without relying on extra knowledge annotation. Specifically, we use a pre-trained language model to extract the most uncertain tokens in the dialog as keywords. With these keywords, we construct two kinds of knowledge and pre-train a knowledge-grounded response generation model, aiming at handling two different scenarios: (1) the knowledge should be faithfully grounded; (2) it can be selectively used. For the former, the grounding knowledge consists of keywords extracted from the response. For the latter, the grounding knowledge is additionally augmented with keywords extracted from other utterances in the same dialog. Since the knowledge is extracted from the dialog itself, KPT can be easily performed on a large volume and variety of dialogue data. We considered three data sources (open-domain, task-oriented, conversational QA) with a total of 2.5M dialogues. We conduct extensive experiments on various few-shot knowledge-grounded generation tasks, including grounding on dialog acts, knowledge graphs, persona descriptions, and Wikipedia passages. Our comprehensive experiments and analyses demonstrate that KPT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on these tasks with diverse grounding knowledge.
Learning Instructions with Unlabeled Data for Zero-Shot Cross-Task Generalization
Oct 17, 2022



Abstract:Training language models to learn from human instructions for zero-shot cross-task generalization has attracted much attention in NLP communities. Recently, instruction tuning (IT), which fine-tunes a pre-trained language model on a massive collection of tasks described via human-craft instructions, has been shown effective in instruction learning for unseen tasks. However, IT relies on a large amount of human-annotated samples, which restricts its generalization. Unlike labeled data, unlabeled data are often massive and cheap to obtain. In this work, we study how IT can be improved with unlabeled data. We first empirically explore the IT performance trends versus the number of labeled data, instructions, and training tasks. We find it critical to enlarge the number of training instructions, and the instructions can be underutilized due to the scarcity of labeled data. Then, we propose Unlabeled Data Augmented Instruction Tuning (UDIT) to take better advantage of the instructions during IT by constructing pseudo-labeled data from unlabeled plain texts. We conduct extensive experiments to show UDIT's effectiveness in various scenarios of tasks and datasets. We also comprehensively analyze the key factors of UDIT to investigate how to better improve IT with unlabeled data. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/thu-coai/UDIT.
Curriculum-Based Self-Training Makes Better Few-Shot Learners for Data-to-Text Generation
Jun 06, 2022



Abstract:Despite the success of text-to-text pre-trained models in various natural language generation (NLG) tasks, the generation performance is largely restricted by the number of labeled data in downstream tasks, particularly in data-to-text generation tasks. Existing works mostly utilize abundant unlabeled structured data to conduct unsupervised pre-training for task adaption, which fail to model the complex relationship between source structured data and target texts. Thus, we introduce self-training as a better few-shot learner than task-adaptive pre-training, which explicitly captures this relationship via pseudo-labeled data generated by the pre-trained model. To alleviate the side-effect of low-quality pseudo-labeled data during self-training, we propose a novel method called Curriculum-Based Self-Training (CBST) to effectively leverage unlabeled data in a rearranged order determined by the difficulty of text generation. Experimental results show that our method can outperform fine-tuning and task-adaptive pre-training methods, and achieve state-of-the-art performance in the few-shot setting of data-to-text generation.
Rethinking and Refining the Distinct Metric
Apr 03, 2022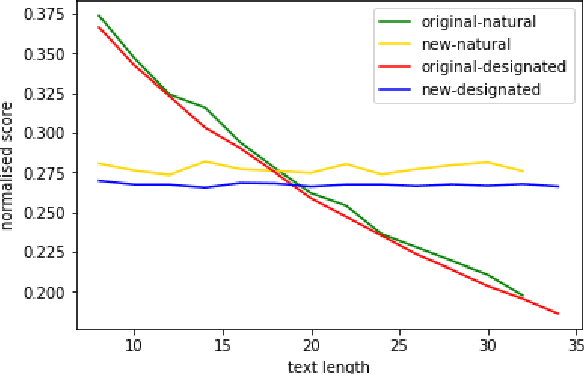
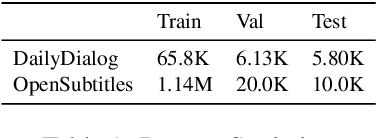
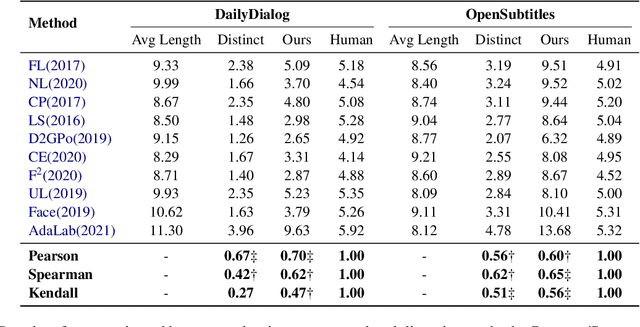
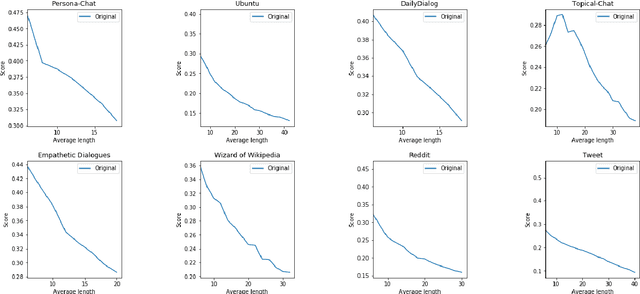
Abstract:Distinct-$n$ score\cite{Li2016} is a widely used automatic metric for evaluating diversity in language generation tasks. However, we observed that the original approach for calculating distinct scores has evident biases that tend to assign higher penalties to longer sequences. We refine the calculation of distinct scores by scaling the number of distinct tokens based on their expectations. We provide both empirical and theoretical evidence to show that our method effectively removes the biases existing in the original distinct score. Our experiments show that our proposed metric, \textit{Expectation-Adjusted Distinct (EAD)}, correlates better with human judgment in evaluating response diversity. To foster future research, we provide an example implementation at \url{https://github.com/lsy641/Expectation-Adjusted-Distinct}.
CTRLEval: An Unsupervised Reference-Free Metric for Evaluating Controlled Text Generation
Apr 02, 2022



Abstract:Existing reference-free metrics have obvious limitations for evaluating controlled text generation models. Unsupervised metrics can only provide a task-agnostic evaluation result which correlates weakly with human judgments, whereas supervised ones may overfit task-specific data with poor generalization ability to other datasets. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised reference-free metric called CTRLEval, which evaluates controlled text generation from different aspects by formulating each aspect into multiple text infilling tasks. On top of these tasks, the metric assembles the generation probabilities from a pre-trained language model without any model training. Experimental results show that our metric has higher correlations with human judgments than other baselines, while obtaining better generalization of evaluating generated texts from different models and with different qualities.
EVA2.0: Investigating Open-Domain Chinese Dialogue Systems with Large-Scale Pre-Training
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Large-scale pre-training has shown remarkable performance in building open-domain dialogue systems. However, previous works mainly focus on showing and evaluating the conversational performance of the released dialogue model, ignoring the discussion of some key factors towards a powerful human-like chatbot, especially in Chinese scenarios. In this paper, we conduct extensive experiments to investigate these under-explored factors, including data quality control, model architecture designs, training approaches, and decoding strategies. We propose EVA2.0, a large-scale pre-trained open-domain Chinese dialogue model with 2.8 billion parameters, and make our models and code publicly available. To our knowledge, EVA2.0 is the largest open-source Chinese dialogue model. Automatic and human evaluations show that our model significantly outperforms other open-source counterparts. We also discuss the limitations of this work by presenting some failure cases and pose some future directions.
Continual Prompt Tuning for Dialog State Tracking
Mar 13, 2022



Abstract:A desirable dialog system should be able to continually learn new skills without forgetting old ones, and thereby adapt to new domains or tasks in its life cycle. However, continually training a model often leads to a well-known catastrophic forgetting issue. In this paper, we present Continual Prompt Tuning, a parameter-efficient framework that not only avoids forgetting but also enables knowledge transfer between tasks. To avoid forgetting, we only learn and store a few prompt tokens' embeddings for each task while freezing the backbone pre-trained model. To achieve bi-directional knowledge transfer among tasks, we propose several techniques (continual prompt initialization, query fusion, and memory replay) to transfer knowledge from preceding tasks and a memory-guided technique to transfer knowledge from subsequent tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed method on continual learning for dialog state tracking, compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge