Weikang Wan
LodeStar: Long-horizon Dexterity via Synthetic Data Augmentation from Human Demonstrations
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Developing robotic systems capable of robustly executing long-horizon manipulation tasks with human-level dexterity is challenging, as such tasks require both physical dexterity and seamless sequencing of manipulation skills while robustly handling environment variations. While imitation learning offers a promising approach, acquiring comprehensive datasets is resource-intensive. In this work, we propose a learning framework and system LodeStar that automatically decomposes task demonstrations into semantically meaningful skills using off-the-shelf foundation models, and generates diverse synthetic demonstration datasets from a few human demos through reinforcement learning. These sim-augmented datasets enable robust skill training, with a Skill Routing Transformer (SRT) policy effectively chaining the learned skills together to execute complex long-horizon manipulation tasks. Experimental evaluations on three challenging real-world long-horizon dexterous manipulation tasks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves task performance and robustness compared to previous baselines. Videos are available at lodestar-robot.github.io.
ManiTaskGen: A Comprehensive Task Generator for Benchmarking and Improving Vision-Language Agents on Embodied Decision-Making
May 27, 2025Abstract:Building embodied agents capable of accomplishing arbitrary tasks is a core objective towards achieving embodied artificial general intelligence (E-AGI). While recent work has advanced such general robot policies, their training and evaluation are often limited to tasks within specific scenes, involving restricted instructions and scenarios. Existing benchmarks also typically rely on manual annotation of limited tasks in a few scenes. We argue that exploring the full spectrum of feasible tasks within any given scene is crucial, as they provide both extensive benchmarks for evaluation and valuable resources for agent improvement. Towards this end, we introduce ManiTaskGen, a novel system that automatically generates comprehensive, diverse, feasible mobile manipulation tasks for any given scene. The generated tasks encompass both process-based, specific instructions (e.g., "move object from X to Y") and outcome-based, abstract instructions (e.g., "clear the table"). We apply ManiTaskGen to both simulated and real-world scenes, demonstrating the validity and diversity of the generated tasks. We then leverage these tasks to automatically construct benchmarks, thoroughly evaluating the embodied decision-making capabilities of agents built upon existing vision-language models (VLMs). Furthermore, we propose a simple yet effective method that utilizes ManiTaskGen tasks to enhance embodied decision-making. Overall, this work presents a universal task generation framework for arbitrary scenes, facilitating both benchmarking and improvement of embodied decision-making agents.
RoboVerse: Towards a Unified Platform, Dataset and Benchmark for Scalable and Generalizable Robot Learning
Apr 26, 2025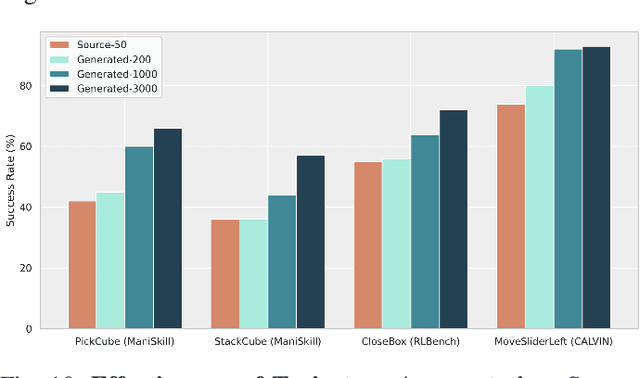
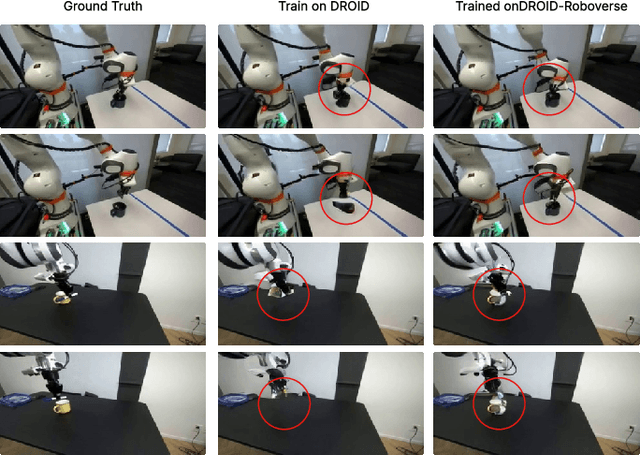

Abstract:Data scaling and standardized evaluation benchmarks have driven significant advances in natural language processing and computer vision. However, robotics faces unique challenges in scaling data and establishing evaluation protocols. Collecting real-world data is resource-intensive and inefficient, while benchmarking in real-world scenarios remains highly complex. Synthetic data and simulation offer promising alternatives, yet existing efforts often fall short in data quality, diversity, and benchmark standardization. To address these challenges, we introduce RoboVerse, a comprehensive framework comprising a simulation platform, a synthetic dataset, and unified benchmarks. Our simulation platform supports multiple simulators and robotic embodiments, enabling seamless transitions between different environments. The synthetic dataset, featuring high-fidelity physics and photorealistic rendering, is constructed through multiple approaches. Additionally, we propose unified benchmarks for imitation learning and reinforcement learning, enabling evaluation across different levels of generalization. At the core of the simulation platform is MetaSim, an infrastructure that abstracts diverse simulation environments into a universal interface. It restructures existing simulation environments into a simulator-agnostic configuration system, as well as an API aligning different simulator functionalities, such as launching simulation environments, loading assets with initial states, stepping the physics engine, etc. This abstraction ensures interoperability and extensibility. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that RoboVerse enhances the performance of imitation learning, reinforcement learning, world model learning, and sim-to-real transfer. These results validate the reliability of our dataset and benchmarks, establishing RoboVerse as a robust solution for advancing robot learning.
DexMimicGen: Automated Data Generation for Bimanual Dexterous Manipulation via Imitation Learning
Oct 31, 2024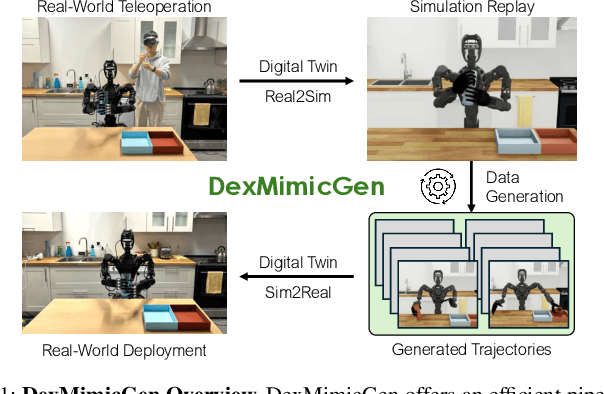
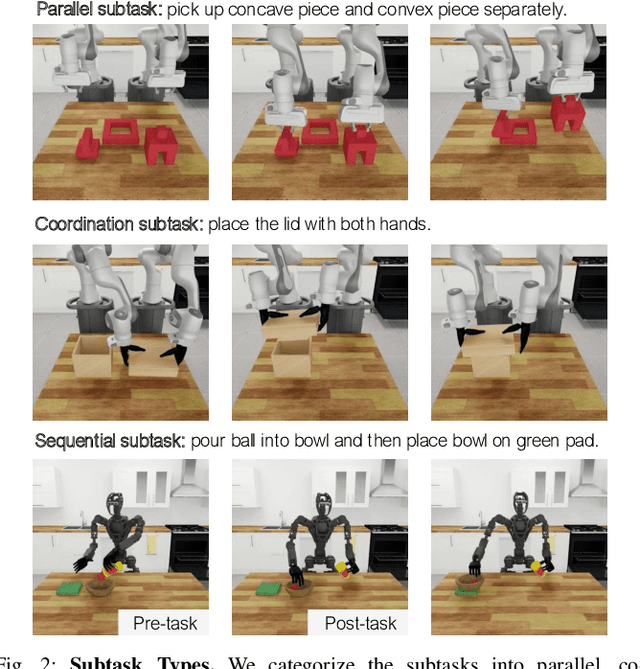
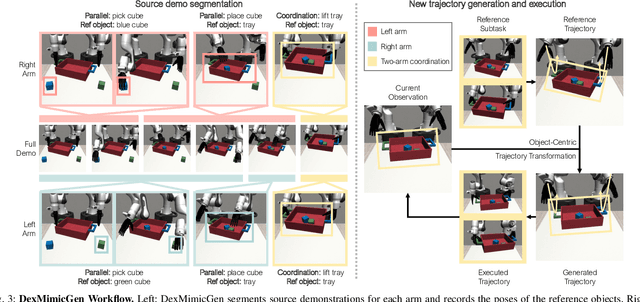
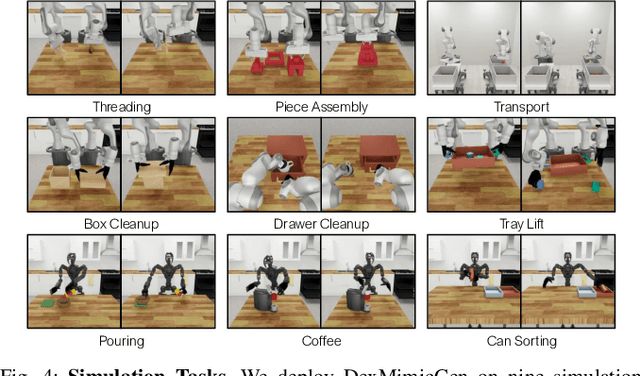
Abstract:Imitation learning from human demonstrations is an effective means to teach robots manipulation skills. But data acquisition is a major bottleneck in applying this paradigm more broadly, due to the amount of cost and human effort involved. There has been significant interest in imitation learning for bimanual dexterous robots, like humanoids. Unfortunately, data collection is even more challenging here due to the challenges of simultaneously controlling multiple arms and multi-fingered hands. Automated data generation in simulation is a compelling, scalable alternative to fuel this need for data. To this end, we introduce DexMimicGen, a large-scale automated data generation system that synthesizes trajectories from a handful of human demonstrations for humanoid robots with dexterous hands. We present a collection of simulation environments in the setting of bimanual dexterous manipulation, spanning a range of manipulation behaviors and different requirements for coordination among the two arms. We generate 21K demos across these tasks from just 60 source human demos and study the effect of several data generation and policy learning decisions on agent performance. Finally, we present a real-to-sim-to-real pipeline and deploy it on a real-world humanoid can sorting task. Videos and more are at https://dexmimicgen.github.io/
DiffTOP: Differentiable Trajectory Optimization for Deep Reinforcement and Imitation Learning
Feb 08, 2024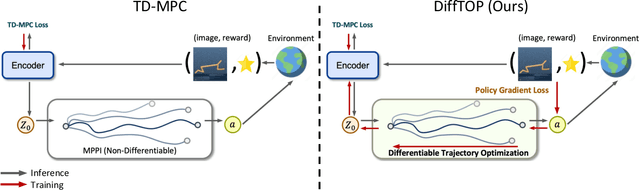
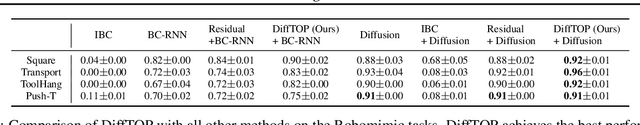
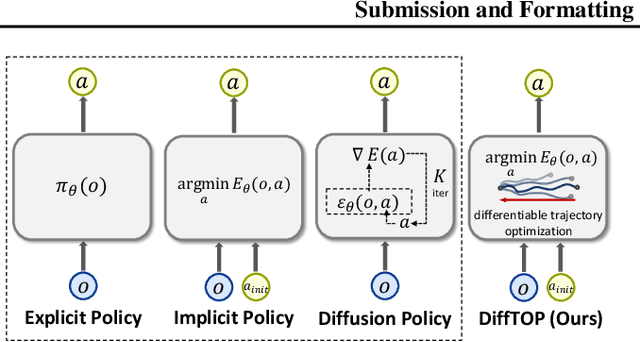
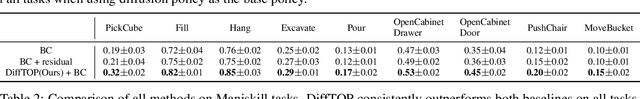
Abstract:This paper introduces DiffTOP, which utilizes Differentiable Trajectory OPtimization as the policy representation to generate actions for deep reinforcement and imitation learning. Trajectory optimization is a powerful and widely used algorithm in control, parameterized by a cost and a dynamics function. The key to our approach is to leverage the recent progress in differentiable trajectory optimization, which enables computing the gradients of the loss with respect to the parameters of trajectory optimization. As a result, the cost and dynamics functions of trajectory optimization can be learned end-to-end. DiffTOP addresses the ``objective mismatch'' issue of prior model-based RL algorithms, as the dynamics model in DiffTOP is learned to directly maximize task performance by differentiating the policy gradient loss through the trajectory optimization process. We further benchmark DiffTOP for imitation learning on standard robotic manipulation task suites with high-dimensional sensory observations and compare our method to feed-forward policy classes as well as Energy-Based Models (EBM) and Diffusion. Across 15 model-based RL tasks and 13 imitation learning tasks with high-dimensional image and point cloud inputs, DiffTOP outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods in both domains.
LOTUS: Continual Imitation Learning for Robot Manipulation Through Unsupervised Skill Discovery
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:We introduce LOTUS, a continual imitation learning algorithm that empowers a physical robot to continuously and efficiently learn to solve new manipulation tasks throughout its lifespan. The core idea behind LOTUS is constructing an ever-growing skill library from a sequence of new tasks with a small number of human demonstrations. LOTUS starts with a continual skill discovery process using an open-vocabulary vision model, which extracts skills as recurring patterns presented in unsegmented demonstrations. Continual skill discovery updates existing skills to avoid catastrophic forgetting of previous tasks and adds new skills to solve novel tasks. LOTUS trains a meta-controller that flexibly composes various skills to tackle vision-based manipulation tasks in the lifelong learning process. Our comprehensive experiments show that LOTUS outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by over 11% in success rate, showing its superior knowledge transfer ability compared to prior methods. More results and videos can be found on the project website: https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/Lotus/.
UniDexGrasp++: Improving Dexterous Grasping Policy Learning via Geometry-aware Curriculum and Iterative Generalist-Specialist Learning
Apr 04, 2023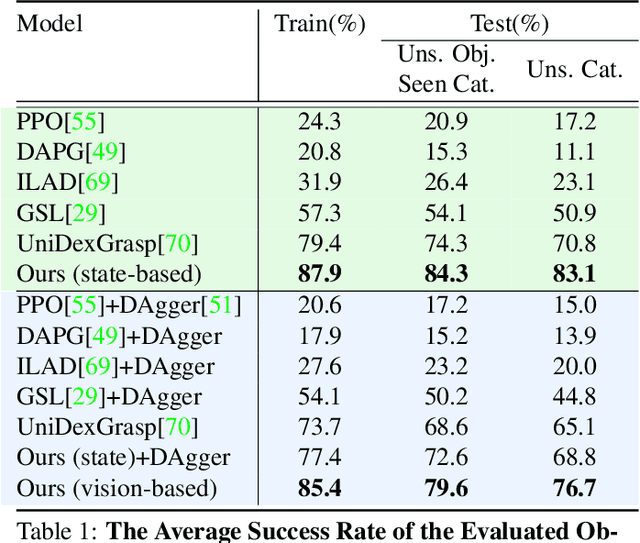
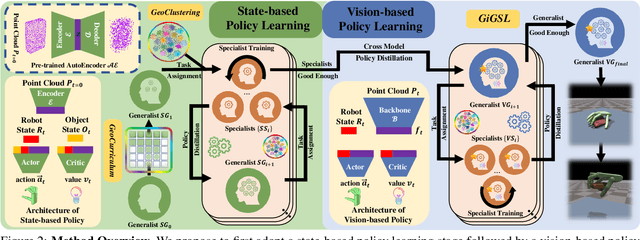
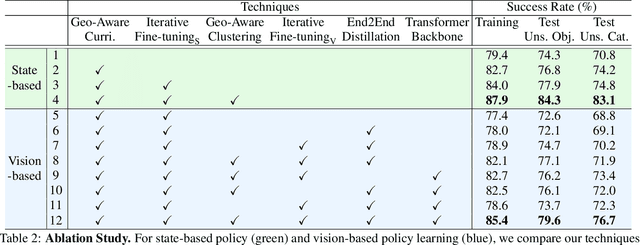
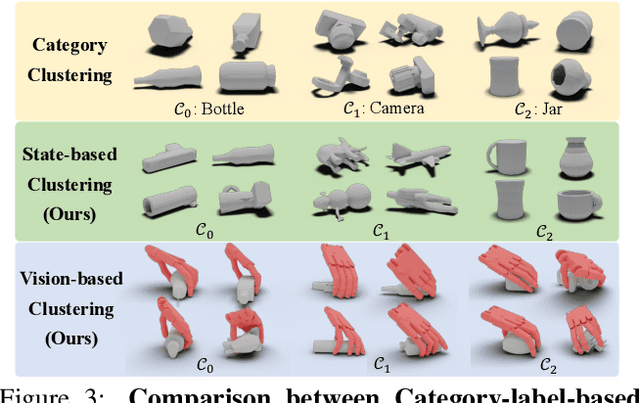
Abstract:We propose a novel, object-agnostic method for learning a universal policy for dexterous object grasping from realistic point cloud observations and proprioceptive information under a table-top setting, namely UniDexGrasp++. To address the challenge of learning the vision-based policy across thousands of object instances, we propose Geometry-aware Curriculum Learning (GeoCurriculum) and Geometry-aware iterative Generalist-Specialist Learning (GiGSL) which leverage the geometry feature of the task and significantly improve the generalizability. With our proposed techniques, our final policy shows universal dexterous grasping on thousands of object instances with 85.4% and 78.2% success rate on the train set and test set which outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline UniDexGrasp by 11.7% and 11.3%, respectively.
UniDexGrasp: Universal Robotic Dexterous Grasping via Learning Diverse Proposal Generation and Goal-Conditioned Policy
Mar 02, 2023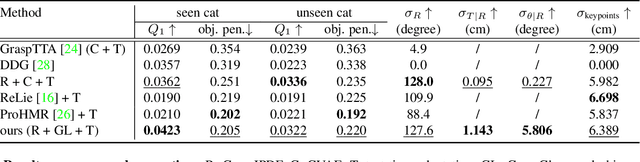
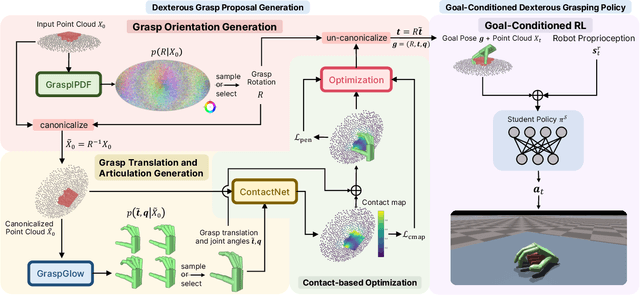
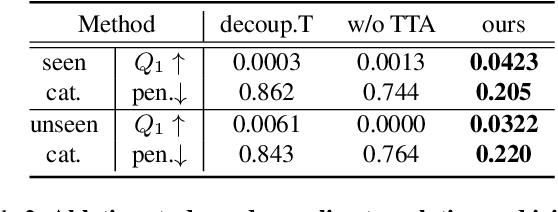
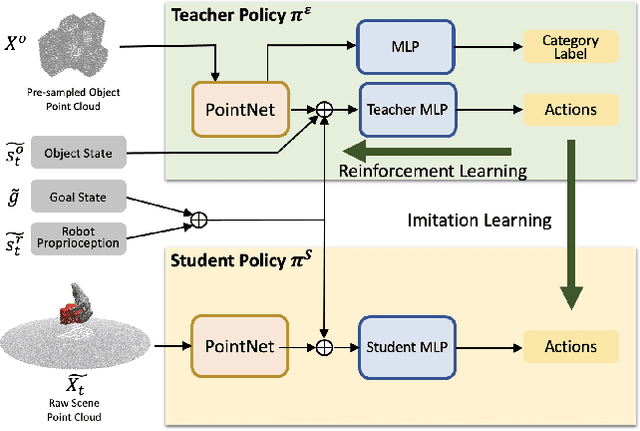
Abstract:In this work, we tackle the problem of learning universal robotic dexterous grasping from a point cloud observation under a table-top setting. The goal is to grasp and lift up objects in high-quality and diverse ways and generalize across hundreds of categories and even the unseen. Inspired by successful pipelines used in parallel gripper grasping, we split the task into two stages: 1) grasp proposal (pose) generation and 2) goal-conditioned grasp execution. For the first stage, we propose a novel probabilistic model of grasp pose conditioned on the point cloud observation that factorizes rotation from translation and articulation. Trained on our synthesized large-scale dexterous grasp dataset, this model enables us to sample diverse and high-quality dexterous grasp poses for the object in the point cloud. For the second stage, we propose to replace the motion planning used in parallel gripper grasping with a goal-conditioned grasp policy, due to the complexity involved in dexterous grasping execution. Note that it is very challenging to learn this highly generalizable grasp policy that only takes realistic inputs without oracle states. We thus propose several important innovations, including state canonicalization, object curriculum, and teacher-student distillation. Integrating the two stages, our final pipeline becomes the first to achieve universal generalization for dexterous grasping, demonstrating an average success rate of more than 60% on thousands of object instances, which significantly out performs all baselines, meanwhile showing only a minimal generalization gap.
HOI4D: A 4D Egocentric Dataset for Category-Level Human-Object Interaction
Apr 08, 2022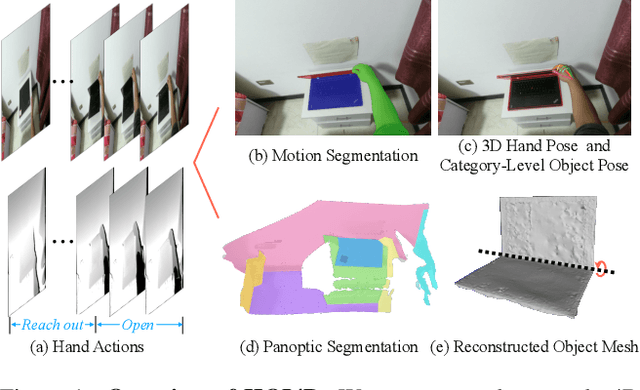

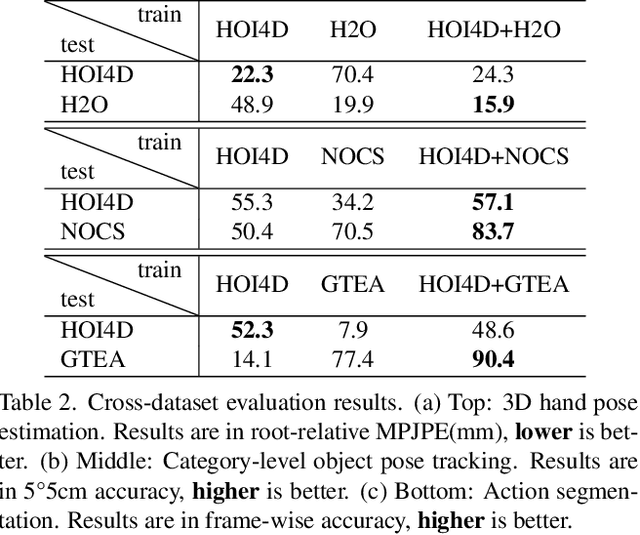
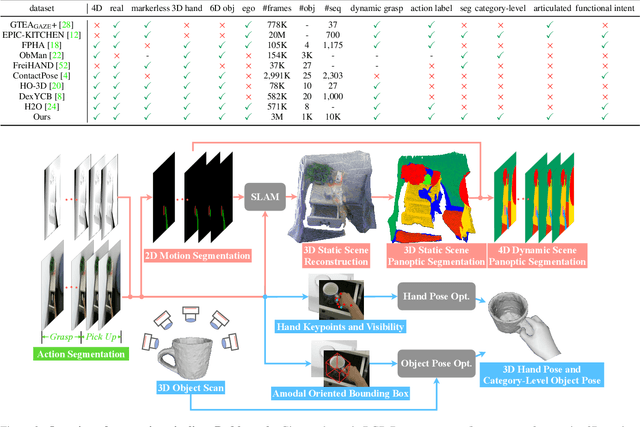
Abstract:We present HOI4D, a large-scale 4D egocentric dataset with rich annotations, to catalyze the research of category-level human-object interaction. HOI4D consists of 2.4M RGB-D egocentric video frames over 4000 sequences collected by 4 participants interacting with 800 different object instances from 16 categories over 610 different indoor rooms. Frame-wise annotations for panoptic segmentation, motion segmentation, 3D hand pose, category-level object pose and hand action have also been provided, together with reconstructed object meshes and scene point clouds. With HOI4D, we establish three benchmarking tasks to promote category-level HOI from 4D visual signals including semantic segmentation of 4D dynamic point cloud sequences, category-level object pose tracking, and egocentric action segmentation with diverse interaction targets. In-depth analysis shows HOI4D poses great challenges to existing methods and produces great research opportunities.
Learning Category-Level Generalizable Object Manipulation Policy via Generative Adversarial Self-Imitation Learning from Demonstrations
Mar 04, 2022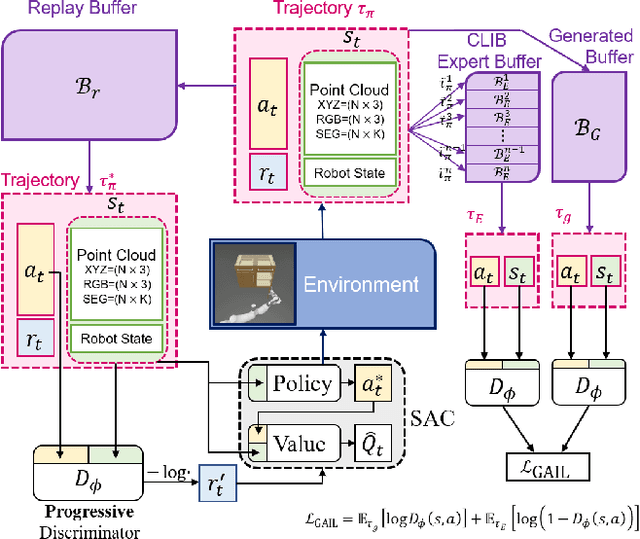
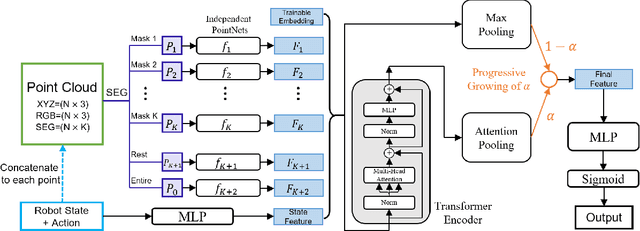
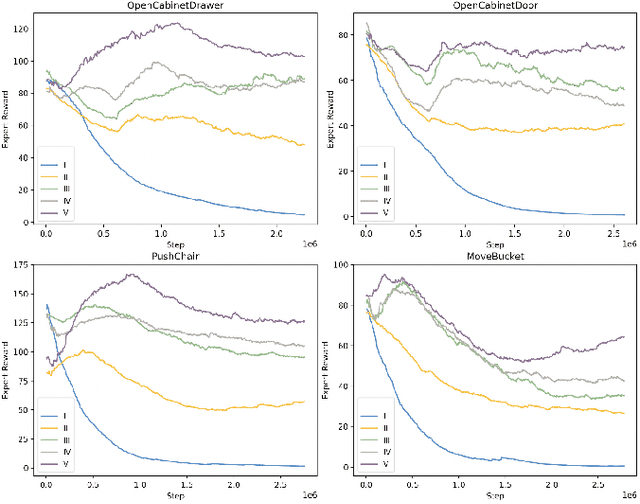
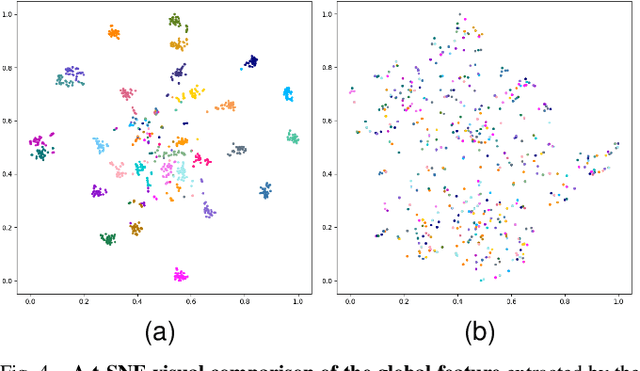
Abstract:Generalizable object manipulation skills are critical for intelligent and multi-functional robots to work in real-world complex scenes. Despite the recent progress in reinforcement learning, it is still very challenging to learn a generalizable manipulation policy that can handle a category of geometrically diverse articulated objects. In this work, we tackle this category-level object manipulation policy learning problem via imitation learning in a task-agnostic manner, where we assume no handcrafted dense rewards but only a terminal reward. Given this novel and challenging generalizable policy learning problem, we identify several key issues that can fail the previous imitation learning algorithms and hinder the generalization to unseen instances. We then propose several general but critical techniques, including generative adversarial self-imitation learning from demonstrations, progressive growing of discriminator, and instance-balancing for expert buffer, that accurately pinpoints and tackles these issues and can benefit category-level manipulation policy learning regardless of the tasks. Our experiments on ManiSkill benchmarks demonstrate a remarkable improvement on all tasks and our ablation studies further validate the contribution of each proposed technique.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge