Rutav Shah
Casper: Inferring Diverse Intents for Assistive Teleoperation with Vision Language Models
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Assistive teleoperation, where control is shared between a human and a robot, enables efficient and intuitive human-robot collaboration in diverse and unstructured environments. A central challenge in real-world assistive teleoperation is for the robot to infer a wide range of human intentions from user control inputs and to assist users with correct actions. Existing methods are either confined to simple, predefined scenarios or restricted to task-specific data distributions at training, limiting their support for real-world assistance. We introduce Casper, an assistive teleoperation system that leverages commonsense knowledge embedded in pre-trained visual language models (VLMs) for real-time intent inference and flexible skill execution. Casper incorporates an open-world perception module for a generalized understanding of novel objects and scenes, a VLM-powered intent inference mechanism that leverages commonsense reasoning to interpret snippets of teleoperated user input, and a skill library that expands the scope of prior assistive teleoperation systems to support diverse, long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks. Extensive empirical evaluation, including human studies and system ablations, demonstrates that Casper improves task performance, reduces human cognitive load, and achieves higher user satisfaction than direct teleoperation and assistive teleoperation baselines.
SCIZOR: A Self-Supervised Approach to Data Curation for Large-Scale Imitation Learning
May 28, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning advances robot capabilities by enabling the acquisition of diverse behaviors from human demonstrations. However, large-scale datasets used for policy training often introduce substantial variability in quality, which can negatively impact performance. As a result, automatically curating datasets by filtering low-quality samples to improve quality becomes essential. Existing robotic curation approaches rely on costly manual annotations and perform curation at a coarse granularity, such as the dataset or trajectory level, failing to account for the quality of individual state-action pairs. To address this, we introduce SCIZOR, a self-supervised data curation framework that filters out low-quality state-action pairs to improve the performance of imitation learning policies. SCIZOR targets two complementary sources of low-quality data: suboptimal data, which hinders learning with undesirable actions, and redundant data, which dilutes training with repetitive patterns. SCIZOR leverages a self-supervised task progress predictor for suboptimal data to remove samples lacking task progression, and a deduplication module operating on joint state-action representation for samples with redundant patterns. Empirically, we show that SCIZOR enables imitation learning policies to achieve higher performance with less data, yielding an average improvement of 15.4% across multiple benchmarks. More information is available at: https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/SCIZOR/
BUMBLE: Unifying Reasoning and Acting with Vision-Language Models for Building-wide Mobile Manipulation
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:To operate at a building scale, service robots must perform very long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks by navigating to different rooms, accessing different floors, and interacting with a wide and unseen range of everyday objects. We refer to these tasks as Building-wide Mobile Manipulation. To tackle these inherently long-horizon tasks, we introduce BUMBLE, a unified Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based framework integrating open-world RGBD perception, a wide spectrum of gross-to-fine motor skills, and dual-layered memory. Our extensive evaluation (90+ hours) indicates that BUMBLE outperforms multiple baselines in long-horizon building-wide tasks that require sequencing up to 12 ground truth skills spanning 15 minutes per trial. BUMBLE achieves 47.1% success rate averaged over 70 trials in different buildings, tasks, and scene layouts from different starting rooms and floors. Our user study demonstrates 22% higher satisfaction with our method than state-of-the-art mobile manipulation methods. Finally, we demonstrate the potential of using increasingly-capable foundation models to push performance further. For more information, see https://robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu/BUMBLE/
LOTUS: Continual Imitation Learning for Robot Manipulation Through Unsupervised Skill Discovery
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:We introduce LOTUS, a continual imitation learning algorithm that empowers a physical robot to continuously and efficiently learn to solve new manipulation tasks throughout its lifespan. The core idea behind LOTUS is constructing an ever-growing skill library from a sequence of new tasks with a small number of human demonstrations. LOTUS starts with a continual skill discovery process using an open-vocabulary vision model, which extracts skills as recurring patterns presented in unsegmented demonstrations. Continual skill discovery updates existing skills to avoid catastrophic forgetting of previous tasks and adds new skills to solve novel tasks. LOTUS trains a meta-controller that flexibly composes various skills to tackle vision-based manipulation tasks in the lifelong learning process. Our comprehensive experiments show that LOTUS outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by over 11% in success rate, showing its superior knowledge transfer ability compared to prior methods. More results and videos can be found on the project website: https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/Lotus/.
Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models
Oct 17, 2023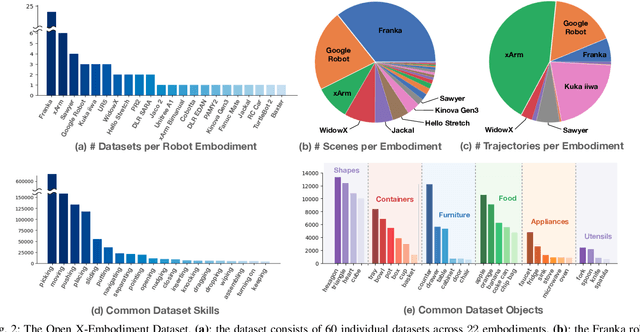
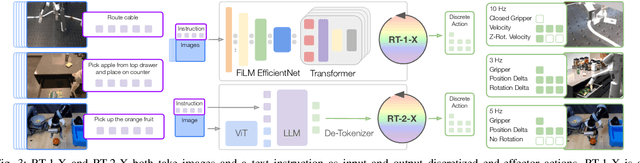
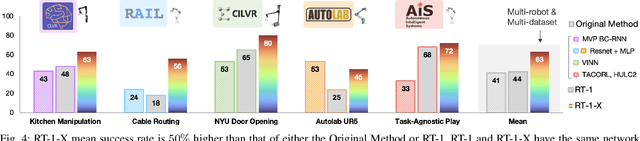
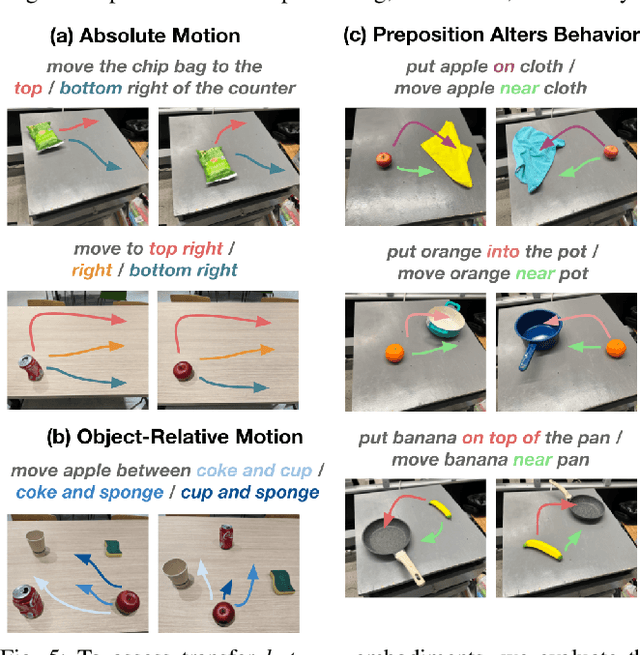
Abstract:Large, high-capacity models trained on diverse datasets have shown remarkable successes on efficiently tackling downstream applications. In domains from NLP to Computer Vision, this has led to a consolidation of pretrained models, with general pretrained backbones serving as a starting point for many applications. Can such a consolidation happen in robotics? Conventionally, robotic learning methods train a separate model for every application, every robot, and even every environment. Can we instead train generalist X-robot policy that can be adapted efficiently to new robots, tasks, and environments? In this paper, we provide datasets in standardized data formats and models to make it possible to explore this possibility in the context of robotic manipulation, alongside experimental results that provide an example of effective X-robot policies. We assemble a dataset from 22 different robots collected through a collaboration between 21 institutions, demonstrating 527 skills (160266 tasks). We show that a high-capacity model trained on this data, which we call RT-X, exhibits positive transfer and improves the capabilities of multiple robots by leveraging experience from other platforms. More details can be found on the project website $\href{https://robotics-transformer-x.github.io}{\text{robotics-transformer-x.github.io}}$.
RoboHive: A Unified Framework for Robot Learning
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:We present RoboHive, a comprehensive software platform and ecosystem for research in the field of Robot Learning and Embodied Artificial Intelligence. Our platform encompasses a diverse range of pre-existing and novel environments, including dexterous manipulation with the Shadow Hand, whole-arm manipulation tasks with Franka and Fetch robots, quadruped locomotion, among others. Included environments are organized within and cover multiple domains such as hand manipulation, locomotion, multi-task, multi-agent, muscles, etc. In comparison to prior works, RoboHive offers a streamlined and unified task interface taking dependency on only a minimal set of well-maintained packages, features tasks with high physics fidelity and rich visual diversity, and supports common hardware drivers for real-world deployment. The unified interface of RoboHive offers a convenient and accessible abstraction for algorithmic research in imitation, reinforcement, multi-task, and hierarchical learning. Furthermore, RoboHive includes expert demonstrations and baseline results for most environments, providing a standard for benchmarking and comparisons. Details: https://sites.google.com/view/robohive
MUTEX: Learning Unified Policies from Multimodal Task Specifications
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:Humans use different modalities, such as speech, text, images, videos, etc., to communicate their intent and goals with teammates. For robots to become better assistants, we aim to endow them with the ability to follow instructions and understand tasks specified by their human partners. Most robotic policy learning methods have focused on one single modality of task specification while ignoring the rich cross-modal information. We present MUTEX, a unified approach to policy learning from multimodal task specifications. It trains a transformer-based architecture to facilitate cross-modal reasoning, combining masked modeling and cross-modal matching objectives in a two-stage training procedure. After training, MUTEX can follow a task specification in any of the six learned modalities (video demonstrations, goal images, text goal descriptions, text instructions, speech goal descriptions, and speech instructions) or a combination of them. We systematically evaluate the benefits of MUTEX in a newly designed dataset with 100 tasks in simulation and 50 tasks in the real world, annotated with multiple instances of task specifications in different modalities, and observe improved performance over methods trained specifically for any single modality. More information at https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/MUTEX/
Contrast and Mix: Temporal Contrastive Video Domain Adaptation with Background Mixing
Oct 28, 2021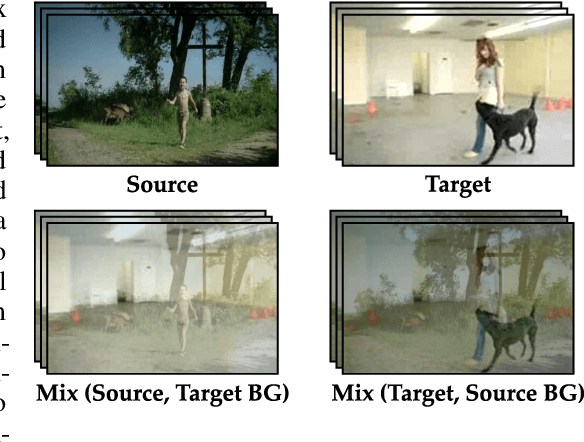
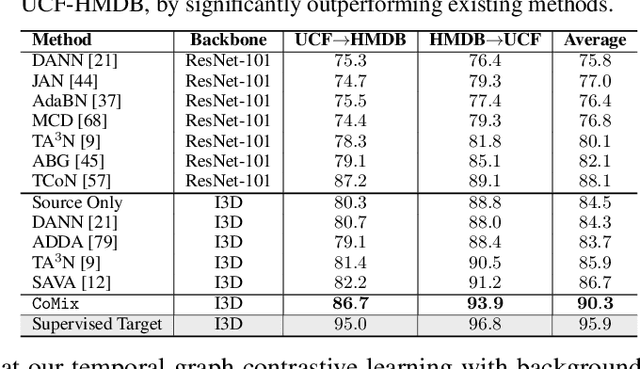
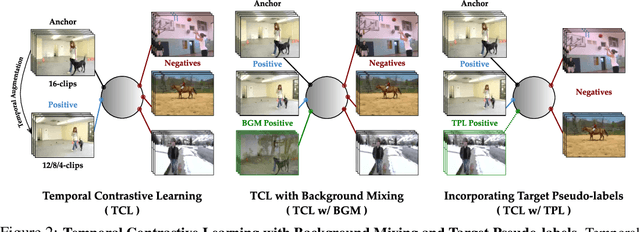
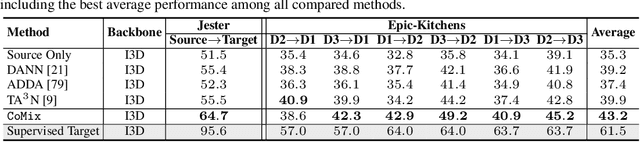
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation which aims to adapt models trained on a labeled source domain to a completely unlabeled target domain has attracted much attention in recent years. While many domain adaptation techniques have been proposed for images, the problem of unsupervised domain adaptation in videos remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we introduce Contrast and Mix (CoMix), a new contrastive learning framework that aims to learn discriminative invariant feature representations for unsupervised video domain adaptation. First, unlike existing methods that rely on adversarial learning for feature alignment, we utilize temporal contrastive learning to bridge the domain gap by maximizing the similarity between encoded representations of an unlabeled video at two different speeds as well as minimizing the similarity between different videos played at different speeds. Second, we propose a novel extension to the temporal contrastive loss by using background mixing that allows additional positives per anchor, thus adapting contrastive learning to leverage action semantics shared across both domains. Moreover, we also integrate a supervised contrastive learning objective using target pseudo-labels to enhance discriminability of the latent space for video domain adaptation. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed approach over state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://cvir.github.io/projects/comix
RRL: Resnet as representation for Reinforcement Learning
Jul 09, 2021



Abstract:The ability to autonomously learn behaviors via direct interactions in uninstrumented environments can lead to generalist robots capable of enhancing productivity or providing care in unstructured settings like homes. Such uninstrumented settings warrant operations only using the robot's proprioceptive sensor such as onboard cameras, joint encoders, etc which can be challenging for policy learning owing to the high dimensionality and partial observability issues. We propose RRL: Resnet as representation for Reinforcement Learning -- a straightforward yet effective approach that can learn complex behaviors directly from proprioceptive inputs. RRL fuses features extracted from pre-trained Resnet into the standard reinforcement learning pipeline and delivers results comparable to learning directly from the state. In a simulated dexterous manipulation benchmark, where the state of the art methods fail to make significant progress, RRL delivers contact rich behaviors. The appeal of RRL lies in its simplicity in bringing together progress from the fields of Representation Learning, Imitation Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. Its effectiveness in learning behaviors directly from visual inputs with performance and sample efficiency matching learning directly from the state, even in complex high dimensional domains, is far from obvious.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge