Abir Das
SITAR: Semi-supervised Image Transformer for Action Recognition
Sep 04, 2024

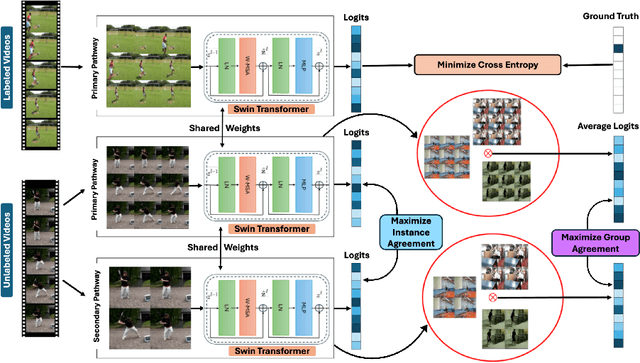

Abstract:Recognizing actions from a limited set of labeled videos remains a challenge as annotating visual data is not only tedious but also can be expensive due to classified nature. Moreover, handling spatio-temporal data using deep $3$D transformers for this can introduce significant computational complexity. In this paper, our objective is to address video action recognition in a semi-supervised setting by leveraging only a handful of labeled videos along with a collection of unlabeled videos in a compute efficient manner. Specifically, we rearrange multiple frames from the input videos in row-column form to construct super images. Subsequently, we capitalize on the vast pool of unlabeled samples and employ contrastive learning on the encoded super images. Our proposed approach employs two pathways to generate representations for temporally augmented super images originating from the same video. Specifically, we utilize a 2D image-transformer to generate representations and apply a contrastive loss function to minimize the similarity between representations from different videos while maximizing the representations of identical videos. Our method demonstrates superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches for semi-supervised action recognition across various benchmark datasets, all while significantly reducing computational costs.
Towards Adaptive IMFs -- Generalization of utility functions in Multi-Agent Frameworks
May 14, 2024Abstract:Intent Management Function (IMF) is an integral part of future-generation networks. In recent years, there has been some work on AI-based IMFs that can handle conflicting intents and prioritize the global objective based on apriori definition of the utility function and accorded priorities for competing intents. Some of the earlier works use Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) techniques with AdHoc Teaming (AHT) approaches for efficient conflict handling in IMF. However, the success of such frameworks in real-life scenarios requires them to be flexible to business situations. The intent priorities can change and the utility function, which measures the extent of intent fulfilment, may also vary in definition. This paper proposes a novel mechanism whereby the IMF can generalize to different forms of utility functions and change of intent priorities at run-time without additional training. Such generalization ability, without additional training requirements, would help to deploy IMF in live networks where customer intents and priorities change frequently. Results on the network emulator demonstrate the efficacy of the approach, scalability for new intents, outperforming existing techniques that require additional training to achieve the same degree of flexibility thereby saving cost, and increasing efficiency and adaptability.
Convolutional Prompting meets Language Models for Continual Learning
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) enables machine learning models to learn from continuously shifting new training data in absence of data from old tasks. Recently, pretrained vision transformers combined with prompt tuning have shown promise for overcoming catastrophic forgetting in CL. These approaches rely on a pool of learnable prompts which can be inefficient in sharing knowledge across tasks leading to inferior performance. In addition, the lack of fine-grained layer specific prompts does not allow these to fully express the strength of the prompts for CL. We address these limitations by proposing ConvPrompt, a novel convolutional prompt creation mechanism that maintains layer-wise shared embeddings, enabling both layer-specific learning and better concept transfer across tasks. The intelligent use of convolution enables us to maintain a low parameter overhead without compromising performance. We further leverage Large Language Models to generate fine-grained text descriptions of each category which are used to get task similarity and dynamically decide the number of prompts to be learned. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of ConvPrompt and improves SOTA by ~3% with significantly less parameter overhead. We also perform strong ablation over various modules to disentangle the importance of different components.
Goals are Enough: Inducing AdHoc cooperation among unseen Multi-Agent systems in IMFs
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:Intent-based management will play a critical role in achieving customers' expectations in the next-generation mobile networks. Traditional methods cannot perform efficient resource management since they tend to handle each expectation independently. Existing approaches, e.g., based on multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) allocate resources in an efficient fashion when there are conflicting expectations on the network slice. However, in reality, systems are often far more complex to be addressed by a standalone MARL formulation. Often there exists a hierarchical structure of intent fulfilment where multiple pre-trained, self-interested agents may need to be further orchestrated by a supervisor or controller agent. Such agents may arrive in the system adhoc, which then needs to be orchestrated along with other available agents. Retraining the whole system every time is often infeasible given the associated time and cost. Given the challenges, such adhoc coordination of pre-trained systems could be achieved through an intelligent supervisor agent which incentivizes pre-trained RL/MARL agents through sets of dynamic contracts (goals or bonuses) and encourages them to act as a cohesive unit towards fulfilling a global expectation. Some approaches use a rule-based supervisor agent and deploy the hierarchical constituent agents sequentially, based on human-coded rules. In the current work, we propose a framework whereby pre-trained agents can be orchestrated in parallel leveraging an AI-based supervisor agent. For this, we propose to use Adhoc-Teaming approaches which assign optimal goals to the MARL agents and incentivize them to exhibit certain desired behaviours. Results on the network emulator show that the proposed approach results in faster and improved fulfilment of expectations when compared to rule-based approaches and even generalizes to changes in environments.
Exemplar-Free Continual Transformer with Convolutions
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) involves training a machine learning model in a sequential manner to learn new information while retaining previously learned tasks without the presence of previous training data. Although there has been significant interest in CL, most recent CL approaches in computer vision have focused on convolutional architectures only. However, with the recent success of vision transformers, there is a need to explore their potential for CL. Although there have been some recent CL approaches for vision transformers, they either store training instances of previous tasks or require a task identifier during test time, which can be limiting. This paper proposes a new exemplar-free approach for class/task incremental learning called ConTraCon, which does not require task-id to be explicitly present during inference and avoids the need for storing previous training instances. The proposed approach leverages the transformer architecture and involves re-weighting the key, query, and value weights of the multi-head self-attention layers of a transformer trained on a similar task. The re-weighting is done using convolution, which enables the approach to maintain low parameter requirements per task. Additionally, an image augmentation-based entropic task identification approach is used to predict tasks without requiring task-ids during inference. Experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms several competitive approaches while requiring fewer parameters.
Domain Adaptation of Reinforcement Learning Agents based on Network Service Proximity
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:The dynamic and evolutionary nature of service requirements in wireless networks has motivated the telecom industry to consider intelligent self-adapting Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents for controlling the growing portfolio of network services. Infusion of many new types of services is anticipated with future adoption of 6G networks, and sometimes these services will be defined by applications that are external to the network. An RL agent trained for managing the needs of a specific service type may not be ideal for managing a different service type without domain adaptation. We provide a simple heuristic for evaluating a measure of proximity between a new service and existing services, and show that the RL agent of the most proximal service rapidly adapts to the new service type through a well defined process of domain adaptation. Our approach enables a trained source policy to adapt to new situations with changed dynamics without retraining a new policy, thereby achieving significant computing and cost-effectiveness. Such domain adaptation techniques may soon provide a foundation for more generalized RL-based service management under the face of rapidly evolving service types.
Few-Shot Visual Question Generation: A Novel Task and Benchmark Datasets
Oct 13, 2022
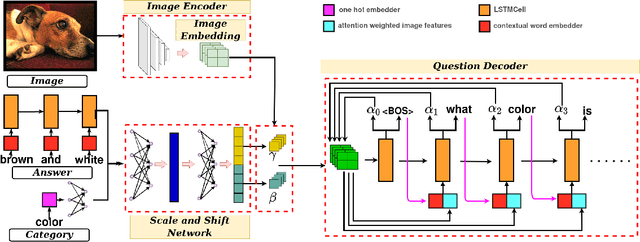
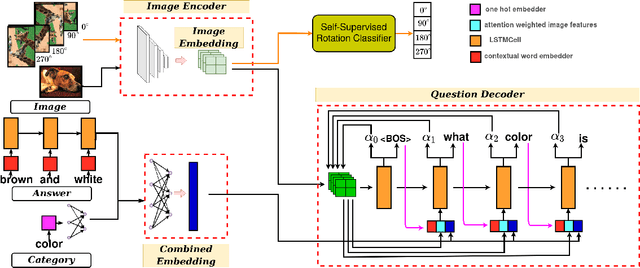
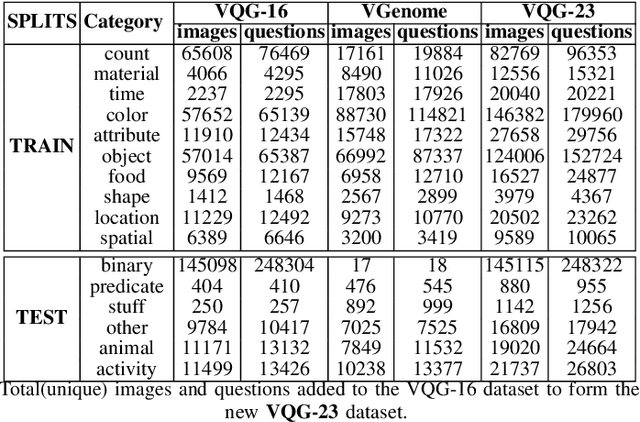
Abstract:Generating natural language questions from visual scenes, known as Visual Question Generation (VQG), has been explored in the recent past where large amounts of meticulously labeled data provide the training corpus. However, in practice, it is not uncommon to have only a few images with question annotations corresponding to a few types of answers. In this paper, we propose a new and challenging Few-Shot Visual Question Generation (FS-VQG) task and provide a comprehensive benchmark to it. Specifically, we evaluate various existing VQG approaches as well as popular few-shot solutions based on meta-learning and self-supervised strategies for the FS-VQG task. We conduct experiments on two popular existing datasets VQG and Visual7w. In addition, we have also cleaned and extended the VQG dataset for use in a few-shot scenario, with additional image-question pairs as well as additional answer categories. We call this new dataset VQG-23. Several important findings emerge from our experiments, that shed light on the limits of current models in few-shot vision and language generation tasks. We find that trivially extending existing VQG approaches with transfer learning or meta-learning may not be enough to tackle the inherent challenges in few-shot VQG. We believe that this work will contribute to accelerating the progress in few-shot learning research.
Reinforcement Explanation Learning
Nov 26, 2021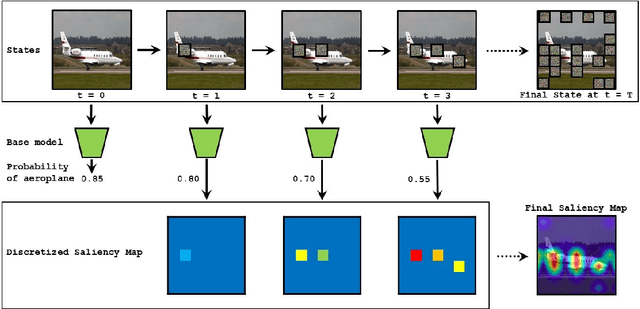
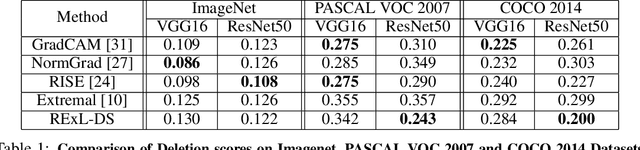
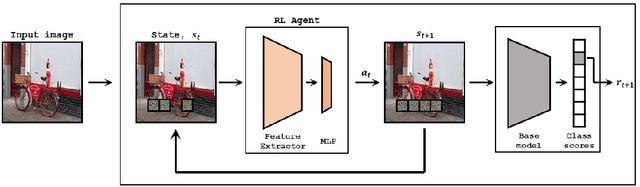
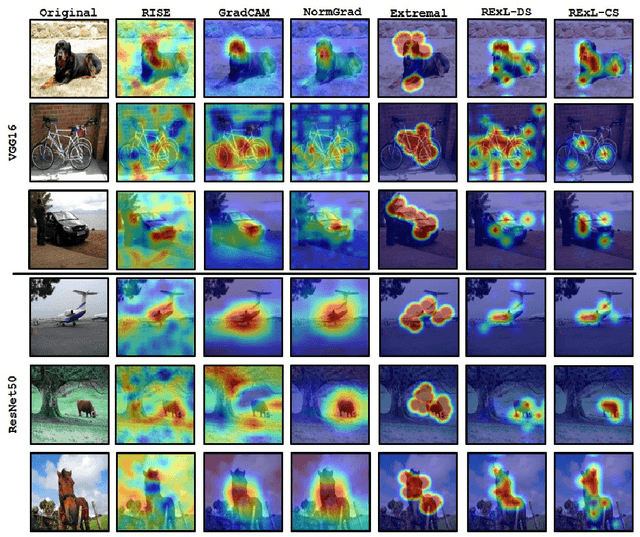
Abstract:Deep Learning has become overly complicated and has enjoyed stellar success in solving several classical problems like image classification, object detection, etc. Several methods for explaining these decisions have been proposed. Black-box methods to generate saliency maps are particularly interesting due to the fact that they do not utilize the internals of the model to explain the decision. Most black-box methods perturb the input and observe the changes in the output. We formulate saliency map generation as a sequential search problem and leverage upon Reinforcement Learning (RL) to accumulate evidence from input images that most strongly support decisions made by a classifier. Such a strategy encourages to search intelligently for the perturbations that will lead to high-quality explanations. While successful black box explanation approaches need to rely on heavy computations and suffer from small sample approximation, the deterministic policy learned by our method makes it a lot more efficient during the inference. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach in inference time over state-of-the-arts without hurting the performance. Project Page: https://cvir.github.io/projects/rexl.html
Contrast and Mix: Temporal Contrastive Video Domain Adaptation with Background Mixing
Oct 28, 2021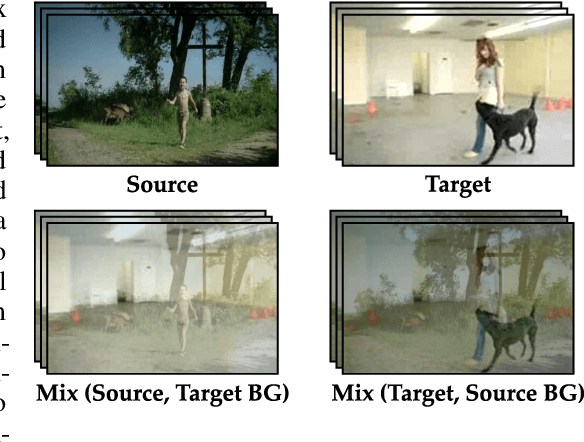
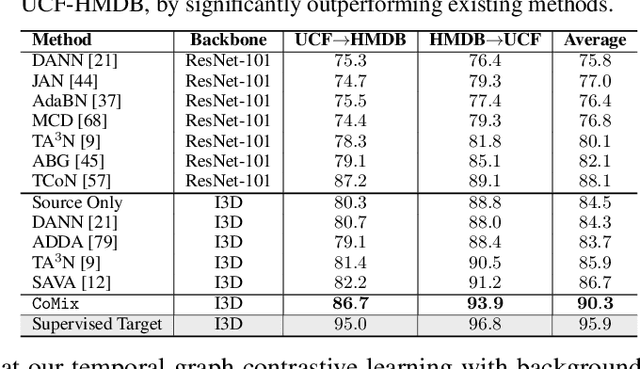
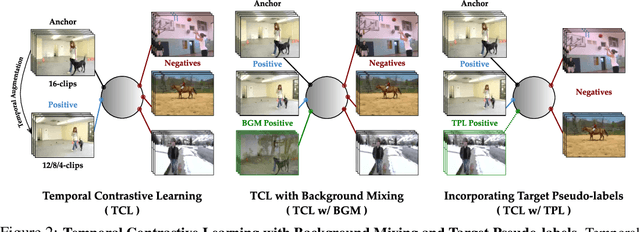
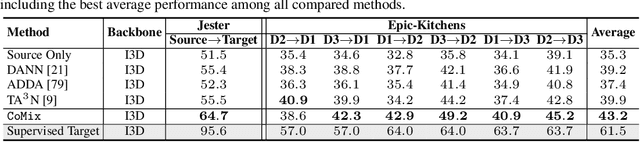
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation which aims to adapt models trained on a labeled source domain to a completely unlabeled target domain has attracted much attention in recent years. While many domain adaptation techniques have been proposed for images, the problem of unsupervised domain adaptation in videos remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we introduce Contrast and Mix (CoMix), a new contrastive learning framework that aims to learn discriminative invariant feature representations for unsupervised video domain adaptation. First, unlike existing methods that rely on adversarial learning for feature alignment, we utilize temporal contrastive learning to bridge the domain gap by maximizing the similarity between encoded representations of an unlabeled video at two different speeds as well as minimizing the similarity between different videos played at different speeds. Second, we propose a novel extension to the temporal contrastive loss by using background mixing that allows additional positives per anchor, thus adapting contrastive learning to leverage action semantics shared across both domains. Moreover, we also integrate a supervised contrastive learning objective using target pseudo-labels to enhance discriminability of the latent space for video domain adaptation. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed approach over state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://cvir.github.io/projects/comix
Semi-Supervised Action Recognition with Temporal Contrastive Learning
Feb 04, 2021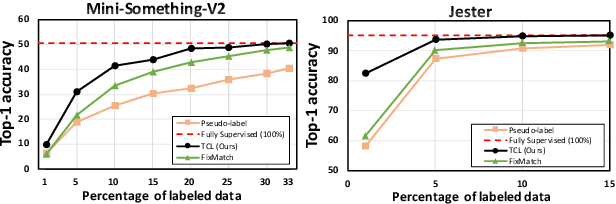
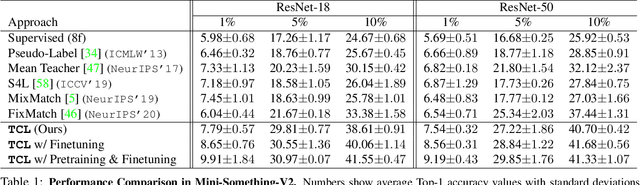
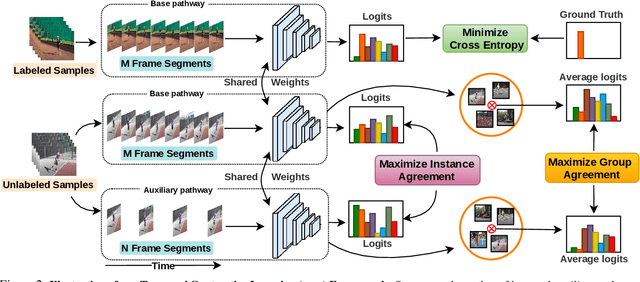
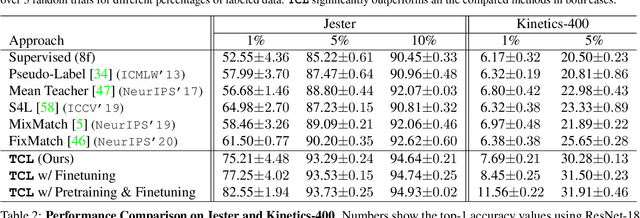
Abstract:Learning to recognize actions from only a handful of labeled videos is a challenging problem due to the scarcity of tediously collected activity labels. We approach this problem by learning a two-pathway temporal contrastive model using unlabeled videos at two different speeds leveraging the fact that changing video speed does not change an action. Specifically, we propose to maximize the similarity between encoded representations of the same video at two different speeds as well as minimize the similarity between different videos played at different speeds. This way we use the rich supervisory information in terms of 'time' that is present in otherwise unsupervised pool of videos. With this simple yet effective strategy of manipulating video playback rates, we considerably outperform video extensions of sophisticated state-of-the-art semi-supervised image recognition methods across multiple diverse benchmark datasets and network architectures. Interestingly, our proposed approach benefits from out-of-domain unlabeled videos showing generalization and robustness. We also perform rigorous ablations and analysis to validate our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge