Anurag Roy
Convolutional Prompting meets Language Models for Continual Learning
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) enables machine learning models to learn from continuously shifting new training data in absence of data from old tasks. Recently, pretrained vision transformers combined with prompt tuning have shown promise for overcoming catastrophic forgetting in CL. These approaches rely on a pool of learnable prompts which can be inefficient in sharing knowledge across tasks leading to inferior performance. In addition, the lack of fine-grained layer specific prompts does not allow these to fully express the strength of the prompts for CL. We address these limitations by proposing ConvPrompt, a novel convolutional prompt creation mechanism that maintains layer-wise shared embeddings, enabling both layer-specific learning and better concept transfer across tasks. The intelligent use of convolution enables us to maintain a low parameter overhead without compromising performance. We further leverage Large Language Models to generate fine-grained text descriptions of each category which are used to get task similarity and dynamically decide the number of prompts to be learned. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of ConvPrompt and improves SOTA by ~3% with significantly less parameter overhead. We also perform strong ablation over various modules to disentangle the importance of different components.
Exemplar-Free Continual Transformer with Convolutions
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) involves training a machine learning model in a sequential manner to learn new information while retaining previously learned tasks without the presence of previous training data. Although there has been significant interest in CL, most recent CL approaches in computer vision have focused on convolutional architectures only. However, with the recent success of vision transformers, there is a need to explore their potential for CL. Although there have been some recent CL approaches for vision transformers, they either store training instances of previous tasks or require a task identifier during test time, which can be limiting. This paper proposes a new exemplar-free approach for class/task incremental learning called ConTraCon, which does not require task-id to be explicitly present during inference and avoids the need for storing previous training instances. The proposed approach leverages the transformer architecture and involves re-weighting the key, query, and value weights of the multi-head self-attention layers of a transformer trained on a similar task. The re-weighting is done using convolution, which enables the approach to maintain low parameter requirements per task. Additionally, an image augmentation-based entropic task identification approach is used to predict tasks without requiring task-ids during inference. Experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms several competitive approaches while requiring fewer parameters.
Few-Shot Visual Question Generation: A Novel Task and Benchmark Datasets
Oct 13, 2022
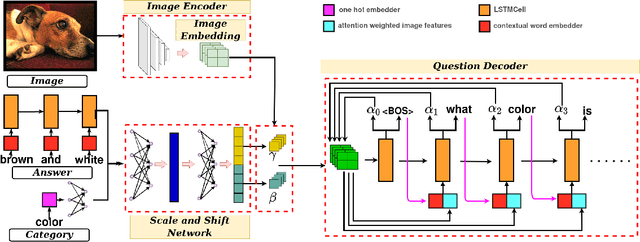
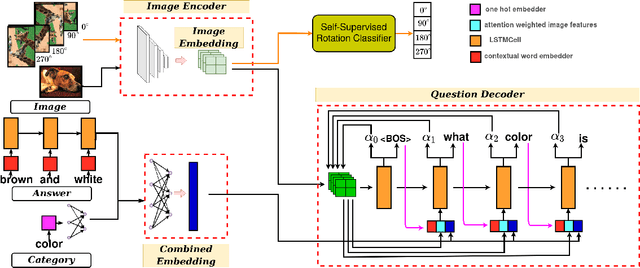
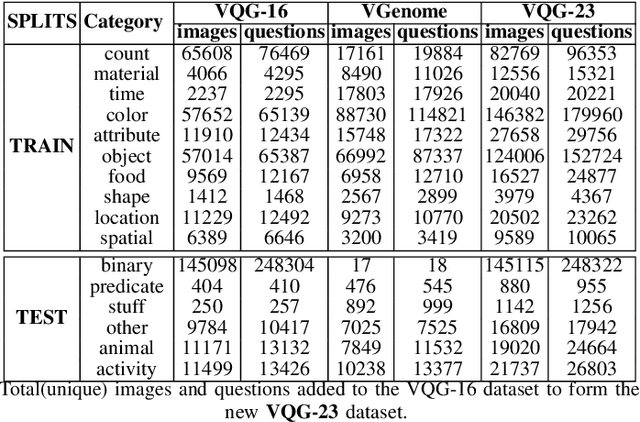
Abstract:Generating natural language questions from visual scenes, known as Visual Question Generation (VQG), has been explored in the recent past where large amounts of meticulously labeled data provide the training corpus. However, in practice, it is not uncommon to have only a few images with question annotations corresponding to a few types of answers. In this paper, we propose a new and challenging Few-Shot Visual Question Generation (FS-VQG) task and provide a comprehensive benchmark to it. Specifically, we evaluate various existing VQG approaches as well as popular few-shot solutions based on meta-learning and self-supervised strategies for the FS-VQG task. We conduct experiments on two popular existing datasets VQG and Visual7w. In addition, we have also cleaned and extended the VQG dataset for use in a few-shot scenario, with additional image-question pairs as well as additional answer categories. We call this new dataset VQG-23. Several important findings emerge from our experiments, that shed light on the limits of current models in few-shot vision and language generation tasks. We find that trivially extending existing VQG approaches with transfer learning or meta-learning may not be enough to tackle the inherent challenges in few-shot VQG. We believe that this work will contribute to accelerating the progress in few-shot learning research.
An Unsupervised Normalization Algorithm for Noisy Text: A Case Study for Information Retrieval and Stance Detection
Jan 09, 2021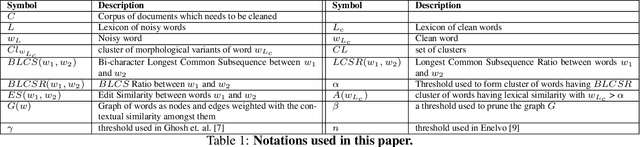
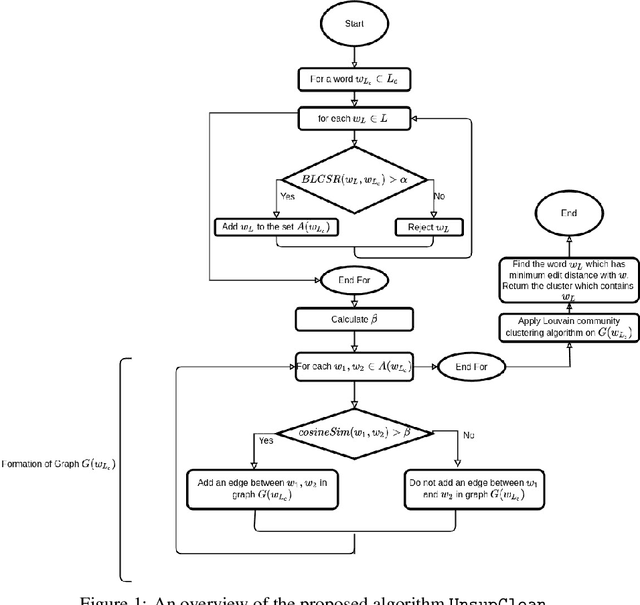
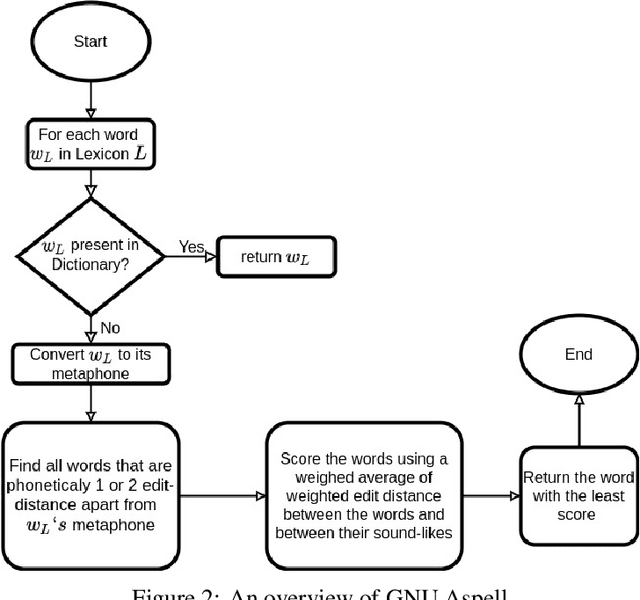

Abstract:A large fraction of textual data available today contains various types of 'noise', such as OCR noise in digitized documents, noise due to informal writing style of users on microblogging sites, and so on. To enable tasks such as search/retrieval and classification over all the available data, we need robust algorithms for text normalization, i.e., for cleaning different kinds of noise in the text. There have been several efforts towards cleaning or normalizing noisy text; however, many of the existing text normalization methods are supervised and require language-dependent resources or large amounts of training data that is difficult to obtain. We propose an unsupervised algorithm for text normalization that does not need any training data / human intervention. The proposed algorithm is applicable to text over different languages, and can handle both machine-generated and human-generated noise. Experiments over several standard datasets show that text normalization through the proposed algorithm enables better retrieval and stance detection, as compared to that using several baseline text normalization methods. Implementation of our algorithm can be found at https://github.com/ranarag/UnsupClean.
ZSCRGAN: A GAN-based Expectation Maximization Model for Zero-Shot Retrieval of Images from Textual Descriptions
Jul 27, 2020



Abstract:Most existing algorithms for cross-modal Information Retrieval are based on a supervised train-test setup, where a model learns to align the mode of the query (e.g., text) to the mode of the documents (e.g., images) from a given training set. Such a setup assumes that the training set contains an exhaustive representation of all possible classes of queries. In reality, a retrieval model may need to be deployed on previously unseen classes, which implies a zero-shot IR setup. In this paper, we propose a novel GAN-based model for zero-shot text to image retrieval. When given a textual description as the query, our model can retrieve relevant images in a zero-shot setup. The proposed model is trained using an Expectation-Maximization framework. Experiments on multiple benchmark datasets show that our proposed model comfortably outperforms several state-of-the-art zero-shot text to image retrieval models, as well as zero-shot classification and hashing models suitably used for retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge