Ran Wei
AXIOM: Learning to Play Games in Minutes with Expanding Object-Centric Models
May 30, 2025Abstract:Current deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance in various domains, but struggle with data efficiency compared to human learning, which leverages core priors about objects and their interactions. Active inference offers a principled framework for integrating sensory information with prior knowledge to learn a world model and quantify the uncertainty of its own beliefs and predictions. However, active inference models are usually crafted for a single task with bespoke knowledge, so they lack the domain flexibility typical of DRL approaches. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel architecture that integrates a minimal yet expressive set of core priors about object-centric dynamics and interactions to accelerate learning in low-data regimes. The resulting approach, which we call AXIOM, combines the usual data efficiency and interpretability of Bayesian approaches with the across-task generalization usually associated with DRL. AXIOM represents scenes as compositions of objects, whose dynamics are modeled as piecewise linear trajectories that capture sparse object-object interactions. The structure of the generative model is expanded online by growing and learning mixture models from single events and periodically refined through Bayesian model reduction to induce generalization. AXIOM masters various games within only 10,000 interaction steps, with both a small number of parameters compared to DRL, and without the computational expense of gradient-based optimization.
NVR: Vector Runahead on NPUs for Sparse Memory Access
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Deep Neural Networks are increasingly leveraging sparsity to reduce the scaling up of model parameter size. However, reducing wall-clock time through sparsity and pruning remains challenging due to irregular memory access patterns, leading to frequent cache misses. In this paper, we present NPU Vector Runahead (NVR), a prefetching mechanism tailored for NPUs to address cache miss problems in sparse DNN workloads. Rather than optimising memory patterns with high overhead and poor portability, NVR adapts runahead execution to the unique architecture of NPUs. NVR provides a general micro-architectural solution for sparse DNN workloads without requiring compiler or algorithmic support, operating as a decoupled, speculative, lightweight hardware sub-thread alongside the NPU, with minimal hardware overhead (under 5%). NVR achieves an average 90% reduction in cache misses compared to SOTA prefetching in general-purpose processors, delivering 4x average speedup on sparse workloads versus NPUs without prefetching. Moreover, we investigate the advantages of incorporating a small cache (16KB) into the NPU combined with NVR. Our evaluation shows that expanding this modest cache delivers 5x higher performance benefits than increasing the L2 cache size by the same amount.
Navigation under uncertainty: Trajectory prediction and occlusion reasoning with switching dynamical systems
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Predicting future trajectories of nearby objects, especially under occlusion, is a crucial task in autonomous driving and safe robot navigation. Prior works typically neglect to maintain uncertainty about occluded objects and only predict trajectories of observed objects using high-capacity models such as Transformers trained on large datasets. While these approaches are effective in standard scenarios, they can struggle to generalize to the long-tail, safety-critical scenarios. In this work, we explore a conceptual framework unifying trajectory prediction and occlusion reasoning under the same class of structured probabilistic generative model, namely, switching dynamical systems. We then present some initial experiments illustrating its capabilities using the Waymo open dataset.
Value of Information and Reward Specification in Active Inference and POMDPs
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Expected free energy (EFE) is a central quantity in active inference which has recently gained popularity due to its intuitive decomposition of the expected value of control into a pragmatic and an epistemic component. While numerous conjectures have been made to justify EFE as a decision making objective function, the most widely accepted is still its intuitiveness and resemblance to variational free energy in approximate Bayesian inference. In this work, we take a bottom up approach and ask: taking EFE as given, what's the resulting agent's optimality gap compared with a reward-driven reinforcement learning (RL) agent, which is well understood? By casting EFE under a particular class of belief MDP and using analysis tools from RL theory, we show that EFE approximates the Bayes optimal RL policy via information value. We discuss the implications for objective specification of active inference agents.
Chromosomal Structural Abnormality Diagnosis by Homologous Similarity
Jul 11, 2024Abstract:Pathogenic chromosome abnormalities are very common among the general population. While numerical chromosome abnormalities can be quickly and precisely detected, structural chromosome abnormalities are far more complex and typically require considerable efforts by human experts for identification. This paper focuses on investigating the modeling of chromosome features and the identification of chromosomes with structural abnormalities. Most existing data-driven methods concentrate on a single chromosome and consider each chromosome independently, overlooking the crucial aspect of homologous chromosomes. In normal cases, homologous chromosomes share identical structures, with the exception that one of them is abnormal. Therefore, we propose an adaptive method to align homologous chromosomes and diagnose structural abnormalities through homologous similarity. Inspired by the process of human expert diagnosis, we incorporate information from multiple pairs of homologous chromosomes simultaneously, aiming to reduce noise disturbance and improve prediction performance. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets validate the effectiveness of our model compared to baselines.
Scan-to-BIM for As-built Roads: Automatic Road Digital Twinning from Semantically Labeled Point Cloud Data
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Creating geometric digital twins (gDT) for as-built roads still faces many challenges, such as low automation level and accuracy, limited asset types and shapes, and reliance on engineering experience. A novel scan-to-building information modeling (scan-to-BIM) framework is proposed for automatic road gDT creation based on semantically labeled point cloud data (PCD), which considers six asset types: Road Surface, Road Side (Slope), Road Lane (Marking), Road Sign, Road Light, and Guardrail. The framework first segments the semantic PCD into spatially independent instances or parts, then extracts the sectional polygon contours as their representative geometric information, stored in JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) files using a new data structure. Primitive gDTs are finally created from JSON files using corresponding conversion algorithms. The proposed method achieves an average distance error of 1.46 centimeters and a processing speed of 6.29 meters per second on six real-world road segments with a total length of 1,200 meters.
Cypher4BIM: Releasing the Power of Graph for Building Knowledge Discovery
May 25, 2024Abstract:Graph is considered a promising way for managing building information. A new graphic form of IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) data has just been developed, referred to as IFC-Graph. However, understanding of IFC-Graph is insufficient, especially for information query. This study aims to explore graphic building information query and develop a graph query language tailored for IFC-Graph. A series of tasks were carried out, including a) investigating the structure of IFC data and the main types of information in IFC, b) investigating the graph query language Cypher, and c) developing a set of tailored functional query patterns. The developed language is referred to as Cypher4BIM. Five IFC models were used for validation, and the result shows that Cypher4BIM can query individual instances and complex relations from IFC, such as spatial structure, space boundary, and space accessibility. This study contributes to applications that require effective building information query, such as digital twin.
Resolving uncertainty on the fly: Modeling adaptive driving behavior as active inference
Nov 10, 2023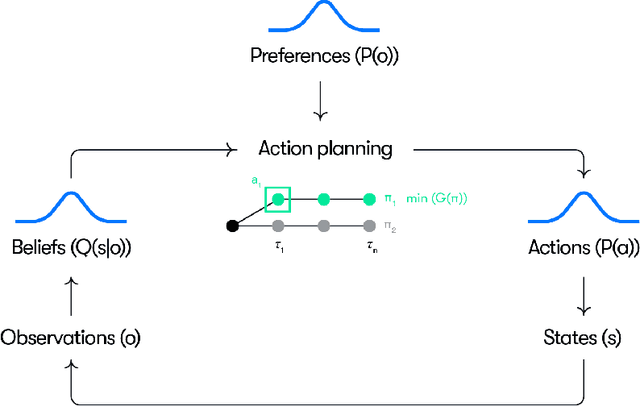
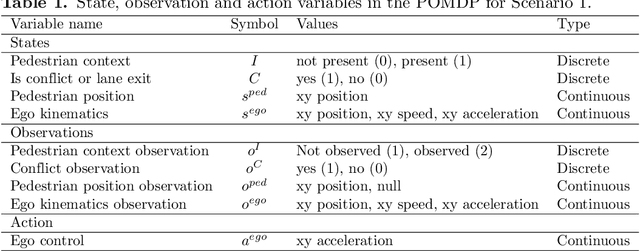
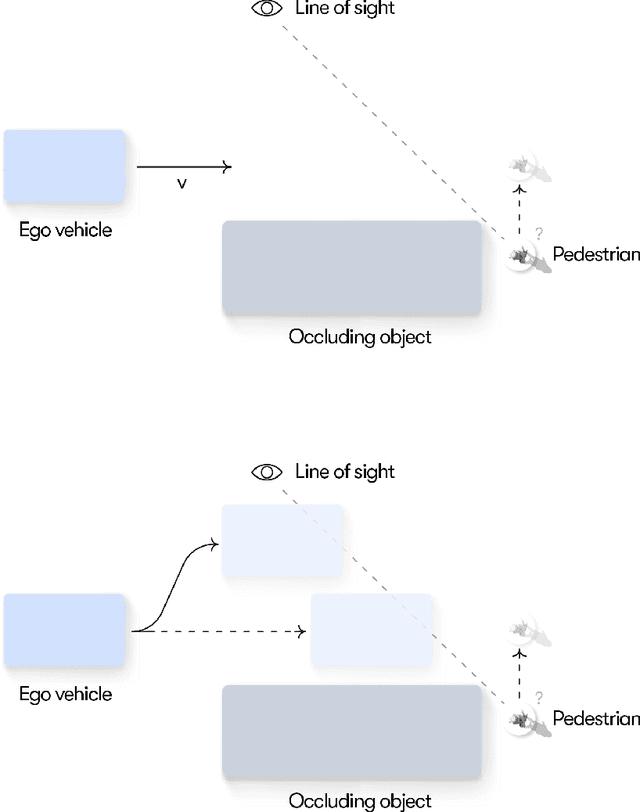

Abstract:Understanding adaptive human driving behavior, in particular how drivers manage uncertainty, is of key importance for developing simulated human driver models that can be used in the evaluation and development of autonomous vehicles. However, existing traffic psychology models of adaptive driving behavior either lack computational rigor or only address specific scenarios and/or behavioral phenomena. While models developed in the fields of machine learning and robotics can effectively learn adaptive driving behavior from data, due to their black box nature, they offer little or no explanation of the mechanisms underlying the adaptive behavior. Thus, a generalizable, interpretable, computational model of adaptive human driving behavior is still lacking. This paper proposes such a model based on active inference, a behavioral modeling framework originating in computational neuroscience. The model offers a principled solution to how humans trade progress against caution through policy selection based on the single mandate to minimize expected free energy. This casts goal-seeking and information-seeking (uncertainty-resolving) behavior under a single objective function, allowing the model to seamlessly resolve uncertainty as a means to obtain its goals. We apply the model in two apparently disparate driving scenarios that require managing uncertainty, (1) driving past an occluding object and (2) visual time sharing between driving and a secondary task, and show how human-like adaptive driving behavior emerges from the single principle of expected free energy minimization.
A Unified View on Solving Objective Mismatch in Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Model-based Reinforcement Learning (MBRL) aims to make agents more sample-efficient, adaptive, and explainable by learning an explicit model of the environment. While the capabilities of MBRL agents have significantly improved in recent years, how to best learn the model is still an unresolved question. The majority of MBRL algorithms aim at training the model to make accurate predictions about the environment and subsequently using the model to determine the most rewarding actions. However, recent research has shown that model predictive accuracy is often not correlated with action quality, tracing the root cause to the \emph{objective mismatch} between accurate dynamics model learning and policy optimization of rewards. A number of interrelated solution categories to the objective mismatch problem have emerged as MBRL continues to mature as a research area. In this work, we provide an in-depth survey of these solution categories and propose a taxonomy to foster future research.
A Bayesian Approach to Robust Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:We consider a Bayesian approach to offline model-based inverse reinforcement learning (IRL). The proposed framework differs from existing offline model-based IRL approaches by performing simultaneous estimation of the expert's reward function and subjective model of environment dynamics. We make use of a class of prior distributions which parameterizes how accurate the expert's model of the environment is to develop efficient algorithms to estimate the expert's reward and subjective dynamics in high-dimensional settings. Our analysis reveals a novel insight that the estimated policy exhibits robust performance when the expert is believed (a priori) to have a highly accurate model of the environment. We verify this observation in the MuJoCo environments and show that our algorithms outperform state-of-the-art offline IRL algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge