Alexander Tschantz
Active inference and artificial reasoning
Dec 24, 2025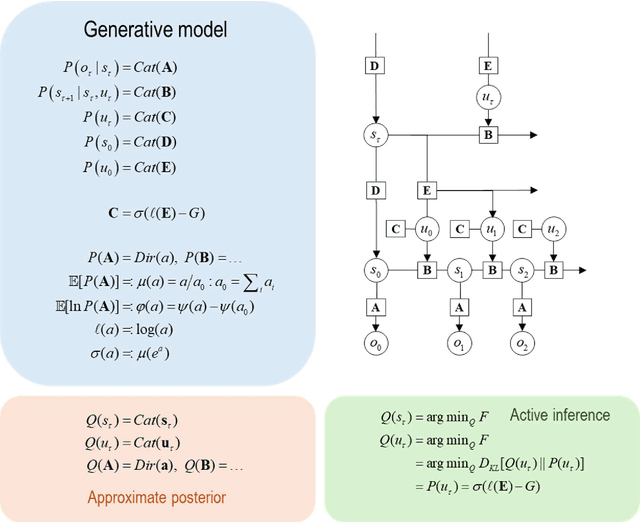
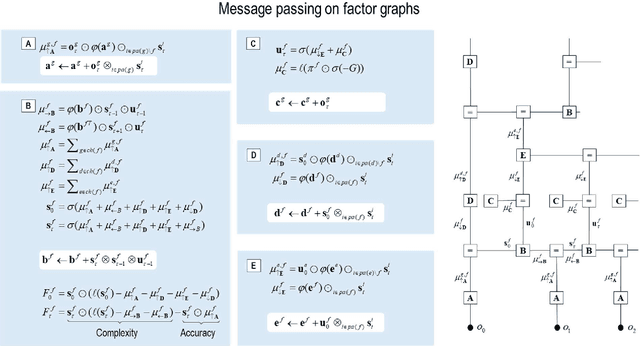
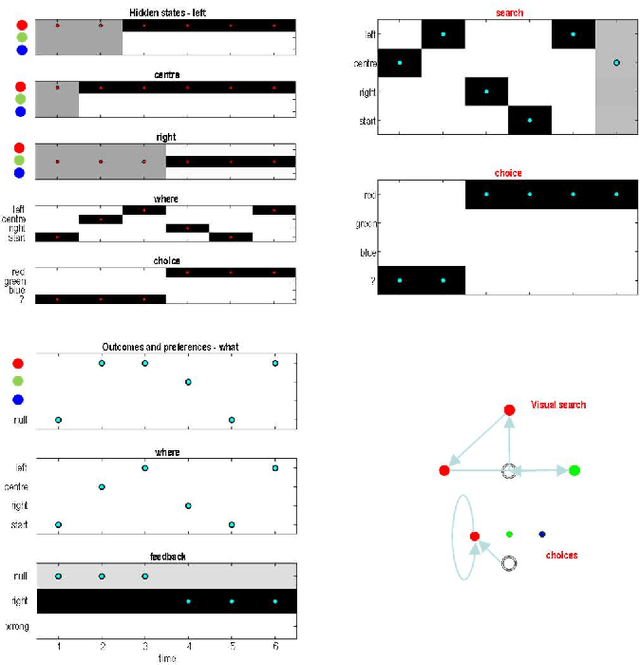
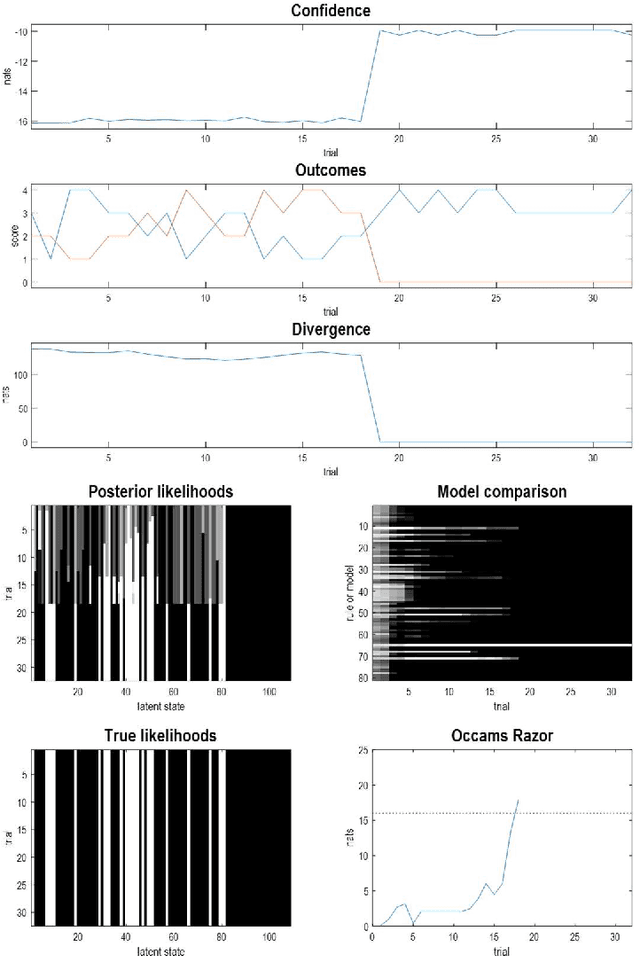
Abstract:This technical note considers the sampling of outcomes that provide the greatest amount of information about the structure of underlying world models. This generalisation furnishes a principled approach to structure learning under a plausible set of generative models or hypotheses. In active inference, policies - i.e., combinations of actions - are selected based on their expected free energy, which comprises expected information gain and value. Information gain corresponds to the KL divergence between predictive posteriors with, and without, the consequences of action. Posteriors over models can be evaluated quickly and efficiently using Bayesian Model Reduction, based upon accumulated posterior beliefs about model parameters. The ensuing information gain can then be used to select actions that disambiguate among alternative models, in the spirit of optimal experimental design. We illustrate this kind of active selection or reasoning using partially observed discrete models; namely, a 'three-ball' paradigm used previously to describe artificial insight and 'aha moments' via (synthetic) introspection or sleep. We focus on the sample efficiency afforded by seeking outcomes that resolve the greatest uncertainty about the world model, under which outcomes are generated.
Soft Geometric Inductive Bias for Object Centric Dynamics
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Equivariance is a powerful prior for learning physical dynamics, yet exact group equivariance can degrade performance if the symmetries are broken. We propose object-centric world models built with geometric algebra neural networks, providing a soft geometric inductive bias. Our models are evaluated using simulated environments of 2d rigid body dynamics with static obstacles, where we train for next-step predictions autoregressively. For long-horizon rollouts we show that the soft inductive bias of our models results in better performance in terms of physical fidelity compared to non-equivariant baseline models. The approach complements recent soft-equivariance ideas and aligns with the view that simple, well-chosen priors can yield robust generalization. These results suggest that geometric algebra offers an effective middle ground between hand-crafted physics and unstructured deep nets, delivering sample-efficient dynamics models for multi-object scenes.
AXIOM: Learning to Play Games in Minutes with Expanding Object-Centric Models
May 30, 2025Abstract:Current deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance in various domains, but struggle with data efficiency compared to human learning, which leverages core priors about objects and their interactions. Active inference offers a principled framework for integrating sensory information with prior knowledge to learn a world model and quantify the uncertainty of its own beliefs and predictions. However, active inference models are usually crafted for a single task with bespoke knowledge, so they lack the domain flexibility typical of DRL approaches. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel architecture that integrates a minimal yet expressive set of core priors about object-centric dynamics and interactions to accelerate learning in low-data regimes. The resulting approach, which we call AXIOM, combines the usual data efficiency and interpretability of Bayesian approaches with the across-task generalization usually associated with DRL. AXIOM represents scenes as compositions of objects, whose dynamics are modeled as piecewise linear trajectories that capture sparse object-object interactions. The structure of the generative model is expanded online by growing and learning mixture models from single events and periodically refined through Bayesian model reduction to induce generalization. AXIOM masters various games within only 10,000 interaction steps, with both a small number of parameters compared to DRL, and without the computational expense of gradient-based optimization.
Bayesian Predictive Coding
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Predictive coding (PC) is an influential theory of information processing in the brain, providing a biologically plausible alternative to backpropagation. It is motivated in terms of Bayesian inference, as hidden states and parameters are optimised via gradient descent on variational free energy. However, implementations of PC rely on maximum \textit{a posteriori} (MAP) estimates of hidden states and maximum likelihood (ML) estimates of parameters, limiting their ability to quantify epistemic uncertainty. In this work, we investigate a Bayesian extension to PC that estimates a posterior distribution over network parameters. This approach, termed Bayesian Predictive coding (BPC), preserves the locality of PC and results in closed-form Hebbian weight updates. Compared to PC, our BPC algorithm converges in fewer epochs in the full-batch setting and remains competitive in the mini-batch setting. Additionally, we demonstrate that BPC offers uncertainty quantification comparable to existing methods in Bayesian deep learning, while also improving convergence properties. Together, these results suggest that BPC provides a biologically plausible method for Bayesian learning in the brain, as well as an attractive approach to uncertainty quantification in deep learning.
Navigation under uncertainty: Trajectory prediction and occlusion reasoning with switching dynamical systems
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Predicting future trajectories of nearby objects, especially under occlusion, is a crucial task in autonomous driving and safe robot navigation. Prior works typically neglect to maintain uncertainty about occluded objects and only predict trajectories of observed objects using high-capacity models such as Transformers trained on large datasets. While these approaches are effective in standard scenarios, they can struggle to generalize to the long-tail, safety-critical scenarios. In this work, we explore a conceptual framework unifying trajectory prediction and occlusion reasoning under the same class of structured probabilistic generative model, namely, switching dynamical systems. We then present some initial experiments illustrating its capabilities using the Waymo open dataset.
Variational Bayes Gaussian Splatting
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a promising approach for modeling 3D scenes using mixtures of Gaussians. The predominant optimization method for these models relies on backpropagating gradients through a differentiable rendering pipeline, which struggles with catastrophic forgetting when dealing with continuous streams of data. To address this limitation, we propose Variational Bayes Gaussian Splatting (VBGS), a novel approach that frames training a Gaussian splat as variational inference over model parameters. By leveraging the conjugacy properties of multivariate Gaussians, we derive a closed-form variational update rule, allowing efficient updates from partial, sequential observations without the need for replay buffers. Our experiments show that VBGS not only matches state-of-the-art performance on static datasets, but also enables continual learning from sequentially streamed 2D and 3D data, drastically improving performance in this setting.
Gradient-free variational learning with conditional mixture networks
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Balancing computational efficiency with robust predictive performance is crucial in supervised learning, especially for critical applications. Standard deep learning models, while accurate and scalable, often lack probabilistic features like calibrated predictions and uncertainty quantification. Bayesian methods address these issues but can be computationally expensive as model and data complexity increase. Previous work shows that fast variational methods can reduce the compute requirements of Bayesian methods by eliminating the need for gradient computation or sampling, but are often limited to simple models. We demonstrate that conditional mixture networks (CMNs), a probabilistic variant of the mixture-of-experts (MoE) model, are suitable for fast, gradient-free inference and can solve complex classification tasks. CMNs employ linear experts and a softmax gating network. By exploiting conditional conjugacy and P\'olya-Gamma augmentation, we furnish Gaussian likelihoods for the weights of both the linear experts and the gating network. This enables efficient variational updates using coordinate ascent variational inference (CAVI), avoiding traditional gradient-based optimization. We validate this approach by training two-layer CMNs on standard benchmarks from the UCI repository. Our method, CAVI-CMN, achieves competitive and often superior predictive accuracy compared to maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) with backpropagation, while maintaining competitive runtime and full posterior distributions over all model parameters. Moreover, as input size or the number of experts increases, computation time scales competitively with MLE and other gradient-based solutions like black-box variational inference (BBVI), making CAVI-CMN a promising tool for deep, fast, and gradient-free Bayesian networks.
From pixels to planning: scale-free active inference
Jul 27, 2024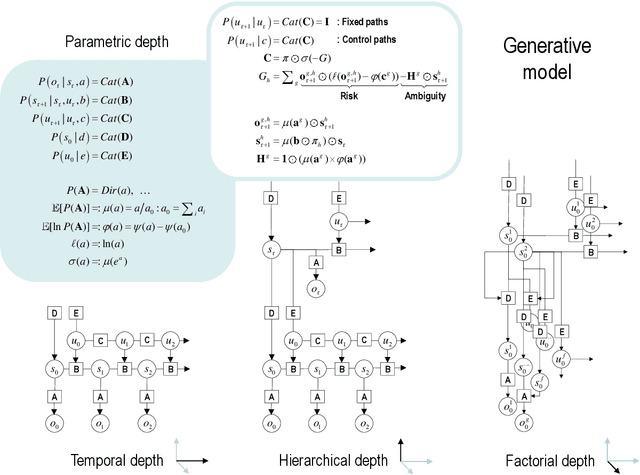
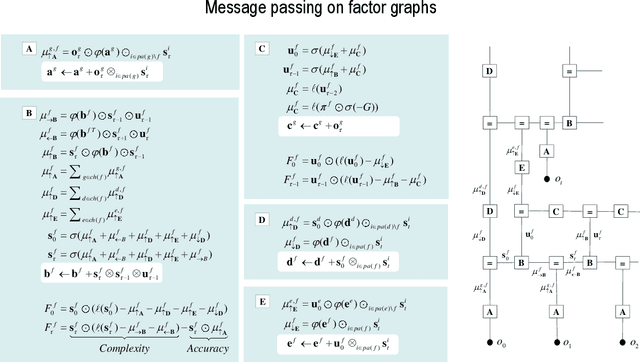
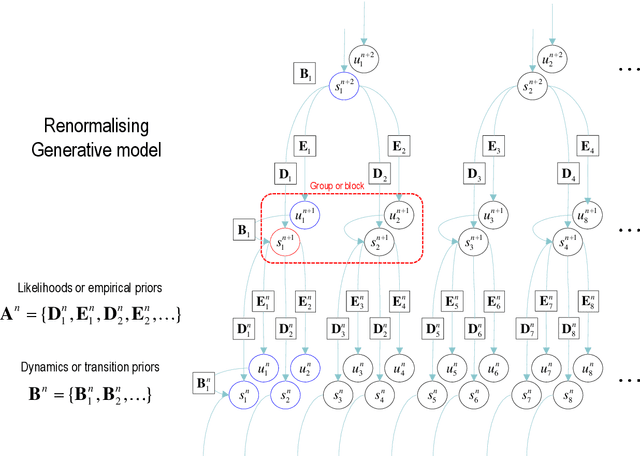
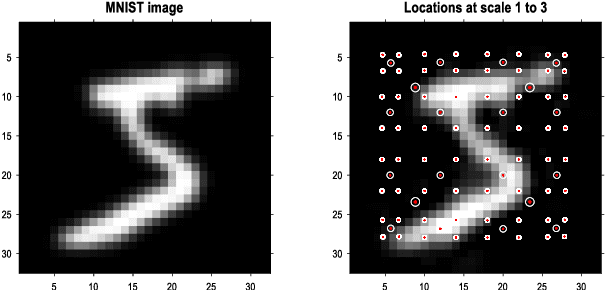
Abstract:This paper describes a discrete state-space model -- and accompanying methods -- for generative modelling. This model generalises partially observed Markov decision processes to include paths as latent variables, rendering it suitable for active inference and learning in a dynamic setting. Specifically, we consider deep or hierarchical forms using the renormalisation group. The ensuing renormalising generative models (RGM) can be regarded as discrete homologues of deep convolutional neural networks or continuous state-space models in generalised coordinates of motion. By construction, these scale-invariant models can be used to learn compositionality over space and time, furnishing models of paths or orbits; i.e., events of increasing temporal depth and itinerancy. This technical note illustrates the automatic discovery, learning and deployment of RGMs using a series of applications. We start with image classification and then consider the compression and generation of movies and music. Finally, we apply the same variational principles to the learning of Atari-like games.
Active Inference and Intentional Behaviour
Dec 16, 2023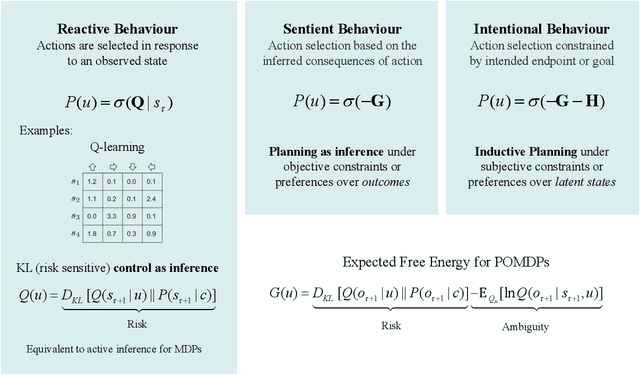
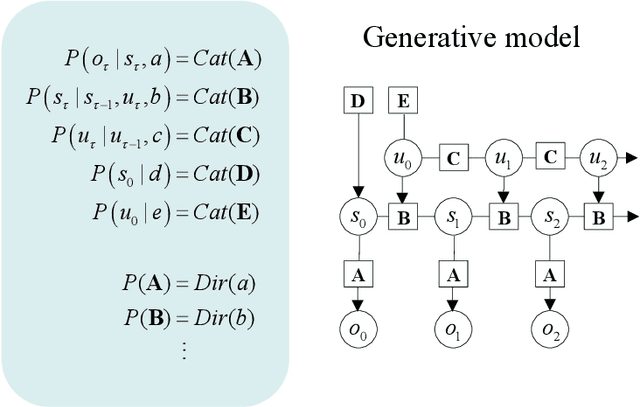

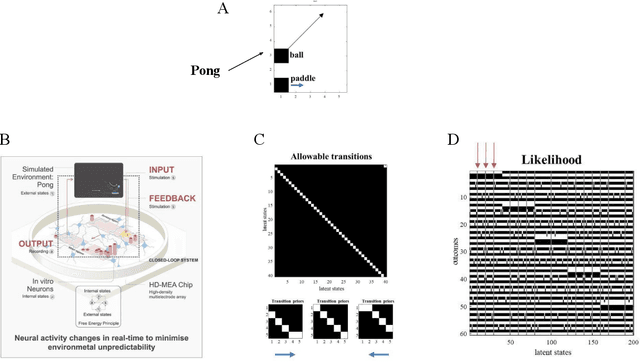
Abstract:Recent advances in theoretical biology suggest that basal cognition and sentient behaviour are emergent properties of in vitro cell cultures and neuronal networks, respectively. Such neuronal networks spontaneously learn structured behaviours in the absence of reward or reinforcement. In this paper, we characterise this kind of self-organisation through the lens of the free energy principle, i.e., as self-evidencing. We do this by first discussing the definitions of reactive and sentient behaviour in the setting of active inference, which describes the behaviour of agents that model the consequences of their actions. We then introduce a formal account of intentional behaviour, that describes agents as driven by a preferred endpoint or goal in latent state-spaces. We then investigate these forms of (reactive, sentient, and intentional) behaviour using simulations. First, we simulate the aforementioned in vitro experiments, in which neuronal cultures spontaneously learn to play Pong, by implementing nested, free energy minimising processes. The simulations are then used to deconstruct the ensuing predictive behaviour, leading to the distinction between merely reactive, sentient, and intentional behaviour, with the latter formalised in terms of inductive planning. This distinction is further studied using simple machine learning benchmarks (navigation in a grid world and the Tower of Hanoi problem), that show how quickly and efficiently adaptive behaviour emerges under an inductive form of active inference.
Supervised structure learning
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:This paper concerns structure learning or discovery of discrete generative models. It focuses on Bayesian model selection and the assimilation of training data or content, with a special emphasis on the order in which data are ingested. A key move - in the ensuing schemes - is to place priors on the selection of models, based upon expected free energy. In this setting, expected free energy reduces to a constrained mutual information, where the constraints inherit from priors over outcomes (i.e., preferred outcomes). The resulting scheme is first used to perform image classification on the MNIST dataset to illustrate the basic idea, and then tested on a more challenging problem of discovering models with dynamics, using a simple sprite-based visual disentanglement paradigm and the Tower of Hanoi (cf., blocks world) problem. In these examples, generative models are constructed autodidactically to recover (i.e., disentangle) the factorial structure of latent states - and their characteristic paths or dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge