Corrado Pezzato
Mobile Manipulation with Active Inference for Long-Horizon Rearrangement Tasks
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Despite growing interest in active inference for robotic control, its application to complex, long-horizon tasks remains untested. We address this gap by introducing a fully hierarchical active inference architecture for goal-directed behavior in realistic robotic settings. Our model combines a high-level active inference model that selects among discrete skills realized via a whole-body active inference controller. This unified approach enables flexible skill composition, online adaptability, and recovery from task failures without requiring offline training. Evaluated on the Habitat Benchmark for mobile manipulation, our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across the three long-horizon tasks, demonstrating for the first time that active inference can scale to the complexity of modern robotics benchmarks.
AXIOM: Learning to Play Games in Minutes with Expanding Object-Centric Models
May 30, 2025Abstract:Current deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance in various domains, but struggle with data efficiency compared to human learning, which leverages core priors about objects and their interactions. Active inference offers a principled framework for integrating sensory information with prior knowledge to learn a world model and quantify the uncertainty of its own beliefs and predictions. However, active inference models are usually crafted for a single task with bespoke knowledge, so they lack the domain flexibility typical of DRL approaches. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel architecture that integrates a minimal yet expressive set of core priors about object-centric dynamics and interactions to accelerate learning in low-data regimes. The resulting approach, which we call AXIOM, combines the usual data efficiency and interpretability of Bayesian approaches with the across-task generalization usually associated with DRL. AXIOM represents scenes as compositions of objects, whose dynamics are modeled as piecewise linear trajectories that capture sparse object-object interactions. The structure of the generative model is expanded online by growing and learning mixture models from single events and periodically refined through Bayesian model reduction to induce generalization. AXIOM masters various games within only 10,000 interaction steps, with both a small number of parameters compared to DRL, and without the computational expense of gradient-based optimization.
Multi-Modal MPPI and Active Inference for Reactive Task and Motion Planning
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) has made strides in complex manipulation tasks, yet the execution robustness of the planned solutions remains overlooked. In this work, we propose a method for reactive TAMP to cope with runtime uncertainties and disturbances. We combine an Active Inference planner (AIP) for adaptive high-level action selection and a novel Multi-Modal Model Predictive Path Integral controller (M3P2I) for low-level control. This results in a scheme that simultaneously adapts both high-level actions and low-level motions. The AIP generates alternative symbolic plans, each linked to a cost function for M3P2I. The latter employs a physics simulator for diverse trajectory rollouts, deriving optimal control by weighing the different samples according to their cost. This idea enables blending different robot skills for fluid and reactive plan execution, accommodating plan adjustments at both the high and low levels to cope, for instance, with dynamic obstacles or disturbances that invalidate the current plan. We have tested our approach in simulations and real-world scenarios.
Sampling-based Model Predictive Control Leveraging Parallelizable Physics Simulations
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:We present a method for sampling-based model predictive control that makes use of a generic physics simulator as the dynamical model. In particular, we propose a Model Predictive Path Integral controller (MPPI), that uses the GPU-parallelizable IsaacGym simulator to compute the forward dynamics of a problem. By doing so, we eliminate the need for manual encoding of robot dynamics and interactions among objects and allow one to effortlessly solve complex navigation and contact-rich tasks. Since no explicit dynamic modeling is required, the method is easily extendable to different objects and robots. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method in several simulated and real-world settings, among which mobile navigation with collision avoidance, non-prehensile manipulation, and whole-body control for high-dimensional configuration spaces. This method is a powerful and accessible tool to solve a large variety of contact-rich motion planning tasks.
Unbiased Active Inference for Classical Control
Jul 27, 2022
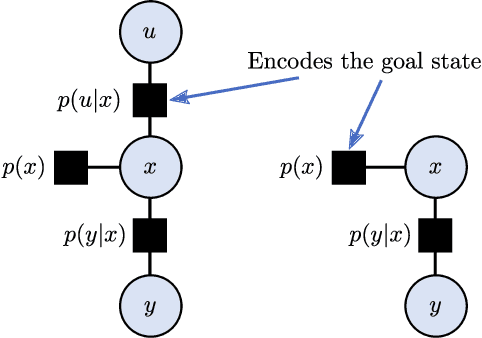
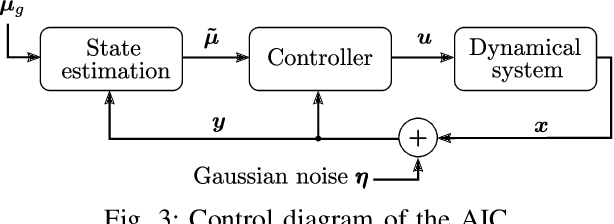
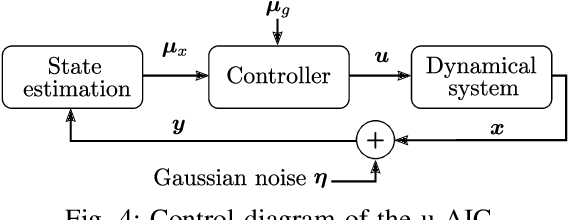
Abstract:Active inference is a mathematical framework that originated in computational neuroscience. Recently, it has been demonstrated as a promising approach for constructing goal-driven behavior in robotics. Specifically, the active inference controller (AIC) has been successful on several continuous control and state-estimation tasks. Despite its relative success, some established design choices lead to a number of practical limitations for robot control. These include having a biased estimate of the state, and only an implicit model of control actions. In this paper, we highlight these limitations and propose an extended version of the unbiased active inference controller (u-AIC). The u-AIC maintains all the compelling benefits of the AIC and removes its limitations. Simulation results on a 2-DOF arm and experiments on a real 7-DOF manipulator show the improved performance of the u-AIC with respect to the standard AIC. The code can be found at https://github.com/cpezzato/unbiased_aic.
Adaptation through prediction: multisensory active inference torque control
Dec 13, 2021
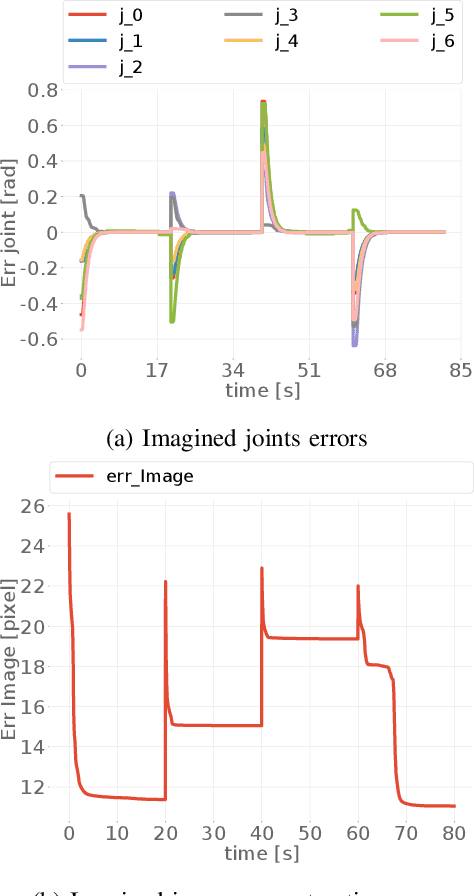
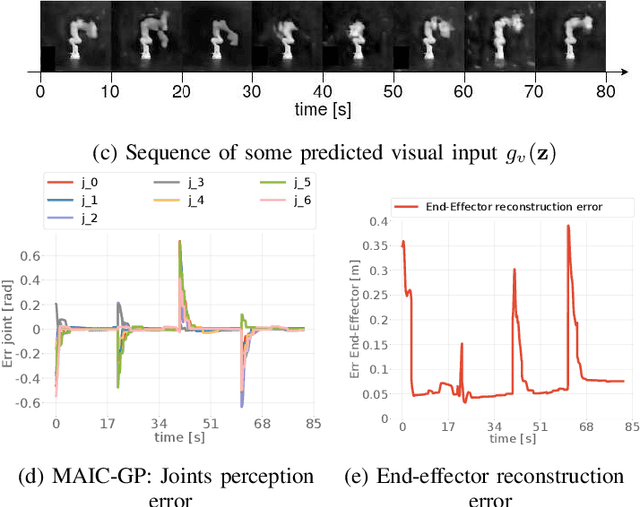
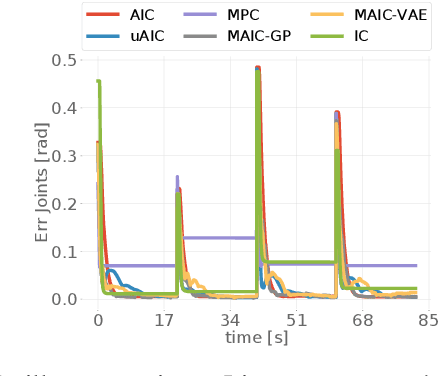
Abstract:Adaptation to external and internal changes is major for robotic systems in uncertain environments. Here we present a novel multisensory active inference torque controller for industrial arms that shows how prediction can be used to resolve adaptation. Our controller, inspired by the predictive brain hypothesis, improves the capabilities of current active inference approaches by incorporating learning and multimodal integration of low and high-dimensional sensor inputs (e.g., raw images) while simplifying the architecture. We performed a systematic evaluation of our model on a 7DoF Franka Emika Panda robot arm by comparing its behavior with previous active inference baselines and classic controllers, analyzing both qualitatively and quantitatively adaptation capabilities and control accuracy. Results showed improved control accuracy in goal-directed reaching with high noise rejection due to multimodal filtering, and adaptability to dynamical inertial changes, elasticity constraints and human disturbances without the need to relearn the model nor parameter retuning.
Active Inference in Robotics and Artificial Agents: Survey and Challenges
Dec 03, 2021
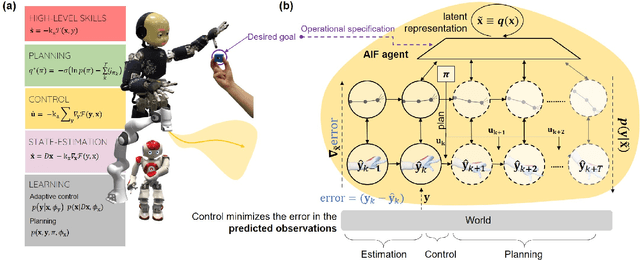
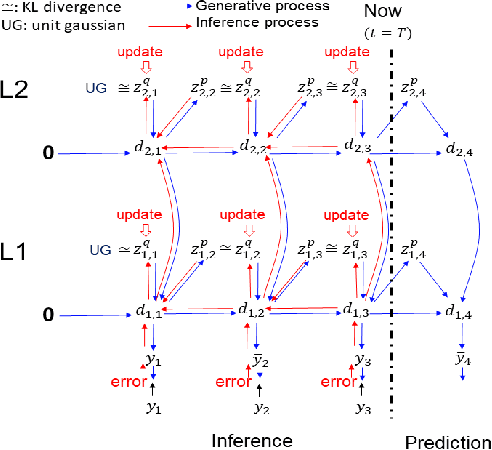
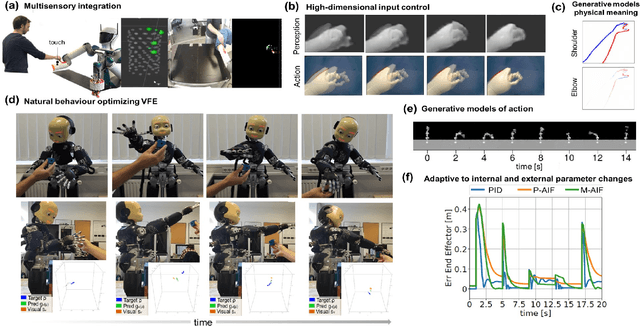
Abstract:Active inference is a mathematical framework which originated in computational neuroscience as a theory of how the brain implements action, perception and learning. Recently, it has been shown to be a promising approach to the problems of state-estimation and control under uncertainty, as well as a foundation for the construction of goal-driven behaviours in robotics and artificial agents in general. Here, we review the state-of-the-art theory and implementations of active inference for state-estimation, control, planning and learning; describing current achievements with a particular focus on robotics. We showcase relevant experiments that illustrate its potential in terms of adaptation, generalization and robustness. Furthermore, we connect this approach with other frameworks and discuss its expected benefits and challenges: a unified framework with functional biological plausibility using variational Bayesian inference.
Towards Stochastic Fault-tolerant Control using Precision Learning and Active Inference
Sep 13, 2021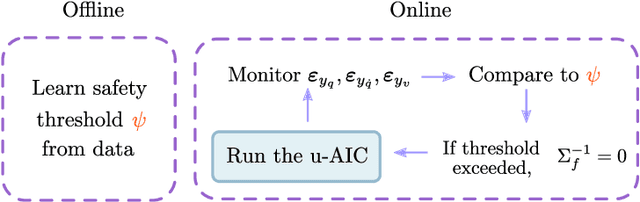
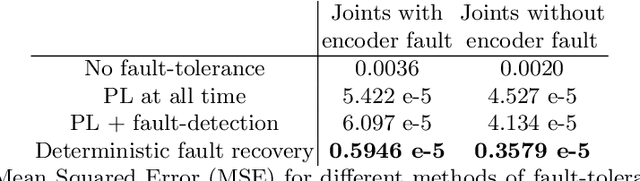
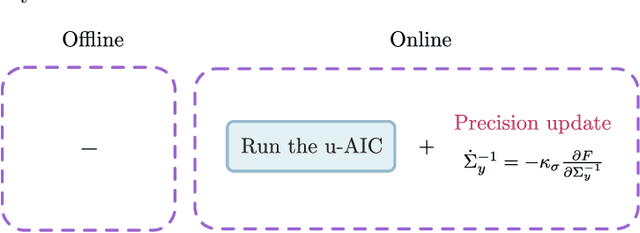
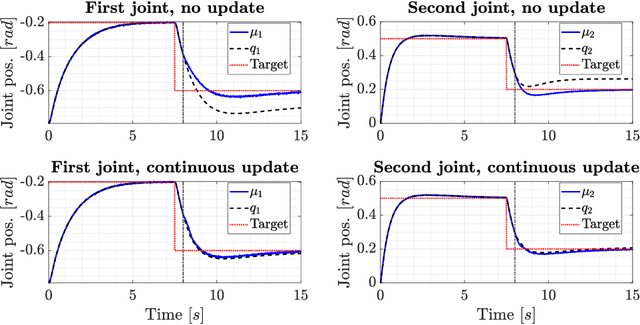
Abstract:This work presents a fault-tolerant control scheme for sensory faults in robotic manipulators based on active inference. In the majority of existing schemes, a binary decision of whether a sensor is healthy (functional) or faulty is made based on measured data. The decision boundary is called a threshold and it is usually deterministic. Following a faulty decision, fault recovery is obtained by excluding the malfunctioning sensor. We propose a stochastic fault-tolerant scheme based on active inference and precision learning which does not require a priori threshold definitions to trigger fault recovery. Instead, the sensor precision, which represents its health status, is learned online in a model-free way allowing the system to gradually, and not abruptly exclude a failing unit. Experiments on a robotic manipulator show promising results and directions for future work are discussed.
Fault-tolerant Control of Robot Manipulators with Sensory Faults using Unbiased Active Inference
Apr 05, 2021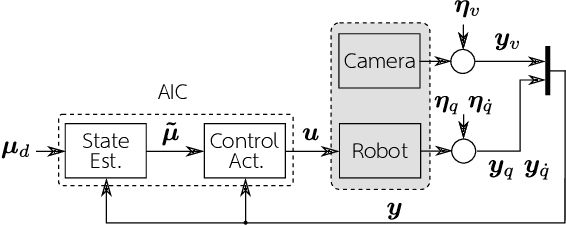
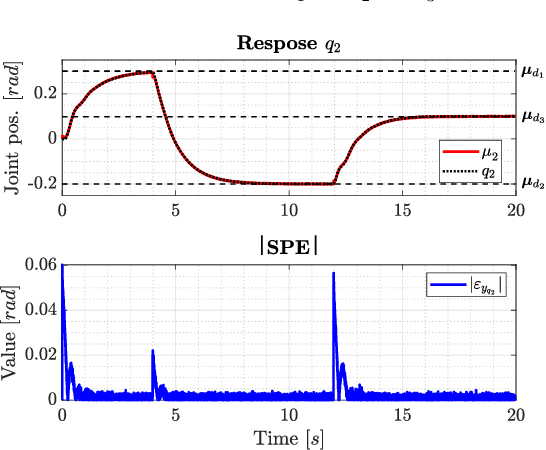
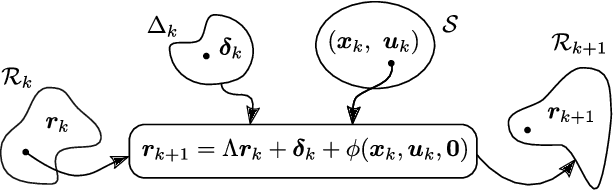
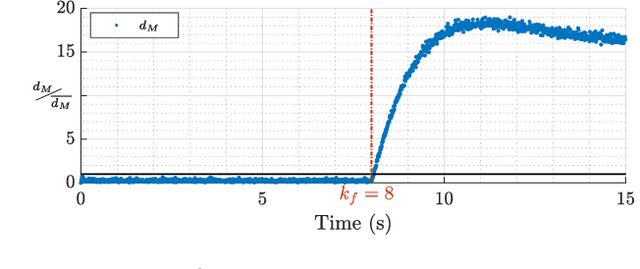
Abstract:This work presents a novel fault-tolerant control scheme based on active inference. Specifically, a new formulation of active inference which, unlike previous solutions, provides unbiased state estimation and simplifies the definition of probabilistically robust thresholds for fault-tolerant control of robotic systems using the free-energy. The proposed solution makes use of the sensory prediction errors in the free-energy for the generation of residuals and thresholds for fault detection and isolation of sensory faults, and it does not require additional controllers for fault recovery. Results validating the benefits in a simulated 2-DOF manipulator are presented, and future directions to improve the current fault recovery approach are discussed.
Active Inference and Behavior Trees for Reactive Action Planning and Execution in Robotics
Nov 19, 2020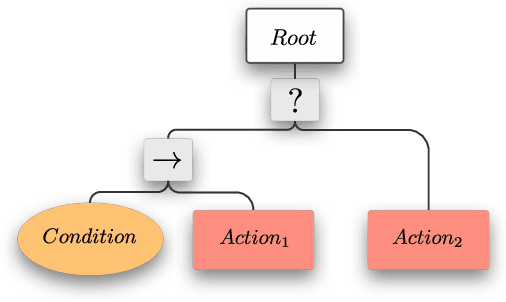
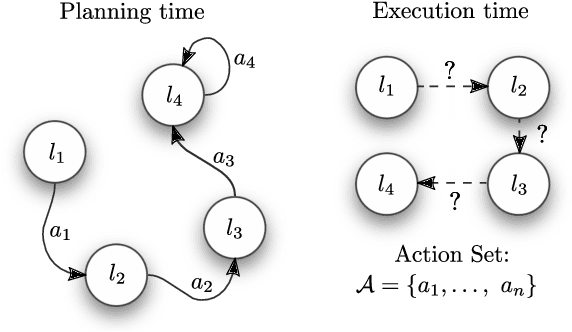
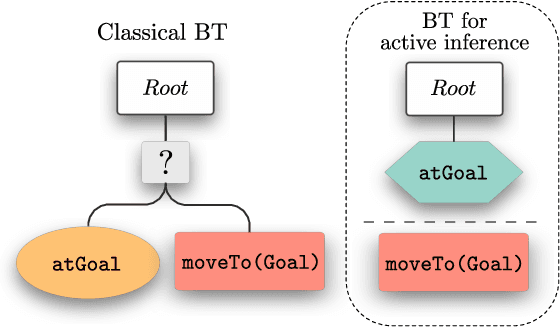
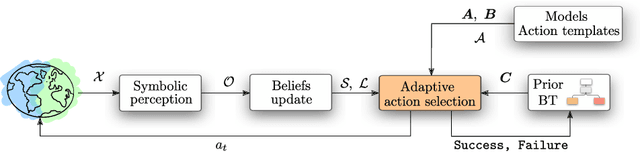
Abstract:This paper presents how the hybrid combination of behavior trees and the neuroscientific principle of active inference can be used for action planning and execution for reactive robot behaviors in dynamic environments. We show how complex robotic tasks can be formulated as a free-energy minimisation problem, and how state estimation and symbolic decision making are handled within the same framework. The general behavior is specified offline through behavior trees, where the leaf nodes represent desired states, not actions as in classical behavior trees. The decision of which action to execute to reach a state is left to the online active inference routine, in order to resolve unexpected contingencies. This hybrid combination improves the robustness of plans specified through behavior trees, while allowing to cope with the curse of dimensionality in active inference. The properties of the proposed algorithm are analysed in terms of robustness and convergence, and the theoretical results are validated using a mobile manipulator in a retail environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge