Paul Bogdan
Towards Reducible Uncertainty Modeling for Reliable Large Language Model Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) for large language models (LLMs) is a key building block for safety guardrails of daily LLM applications. Yet, even as LLM agents are increasingly deployed in highly complex tasks, most UQ research still centers on single-turn question-answering. We argue that UQ research must shift to realistic settings with interactive agents, and that a new principled framework for agent UQ is needed. This paper presents the first general formulation of agent UQ that subsumes broad classes of existing UQ setups. Under this formulation, we show that prior works implicitly treat LLM UQ as an uncertainty accumulation process, a viewpoint that breaks down for interactive agents in an open world. In contrast, we propose a novel perspective, a conditional uncertainty reduction process, that explicitly models reducible uncertainty over an agent's trajectory by highlighting "interactivity" of actions. From this perspective, we outline a conceptual framework to provide actionable guidance for designing UQ in LLM agent setups. Finally, we conclude with practical implications of the agent UQ in frontier LLM development and domain-specific applications, as well as open remaining problems.
Structural Complexity of Brain MRI reveals age-associated patterns
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We adapt structural complexity analysis to three-dimensional signals, with an emphasis on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This framework captures the multiscale organization of volumetric data by coarse-graining the signal at progressively larger spatial scales and quantifying the information lost between successive resolutions. While the traditional block-based approach can become unstable at coarse resolutions due to limited sampling, we introduce a sliding-window coarse-graining scheme that provides smoother estimates and improved robustness at large scales. Using this refined method, we analyze large structural MRI datasets spanning mid- to late adulthood and find that structural complexity decreases systematically with age, with the strongest effects emerging at coarser scales. These findings highlight structural complexity as a reliable signal processing tool for multiscale analysis of 3D imaging data, while also demonstrating its utility in predicting biological age from brain MRI.
Analyzing Neural Network Information Flow Using Differential Geometry
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:This paper provides a fresh view of the neural network (NN) data flow problem, i.e., identifying the NN connections that are most important for the performance of the full model, through the lens of graph theory. Understanding the NN data flow provides a tool for symbolic NN analysis, e.g.,~robustness analysis or model repair. Unlike the standard approach to NN data flow analysis, which is based on information theory, we employ the notion of graph curvature, specifically Ollivier-Ricci curvature (ORC). The ORC has been successfully used to identify important graph edges in various domains such as road traffic analysis, biological and social networks. In particular, edges with negative ORC are considered bottlenecks and as such are critical to the graph's overall connectivity, whereas positive-ORC edges are not essential. We use this intuition for the case of NNs as well: we 1)~construct a graph induced by the NN structure and introduce the notion of neural curvature (NC) based on the ORC; 2)~calculate curvatures based on activation patterns for a set of input examples; 3)~aim to demonstrate that NC can indeed be used to rank edges according to their importance for the overall NN functionality. We evaluate our method through pruning experiments and show that removing negative-ORC edges quickly degrades the overall NN performance, whereas positive-ORC edges have little impact. The proposed method is evaluated on a variety of models trained on three image datasets, namely MNIST, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100. The results indicate that our method can identify a larger number of unimportant edges as compared to state-of-the-art pruning methods.
EMoE: Eigenbasis-Guided Routing for Mixture-of-Experts
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:The relentless scaling of deep learning models has led to unsustainable computational demands, positioning Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures as a promising path towards greater efficiency. However, MoE models are plagued by two fundamental challenges: 1) a load imbalance problem known as the``rich get richer" phenomenon, where a few experts are over-utilized, and 2) an expert homogeneity problem, where experts learn redundant representations, negating their purpose. Current solutions typically employ an auxiliary load-balancing loss that, while mitigating imbalance, often exacerbates homogeneity by enforcing uniform routing at the expense of specialization. To resolve this, we introduce the Eigen-Mixture-of-Experts (EMoE), a novel architecture that leverages a routing mechanism based on a learned orthonormal eigenbasis. EMoE projects input tokens onto this shared eigenbasis and routes them based on their alignment with the principal components of the feature space. This principled, geometric partitioning of data intrinsically promotes both balanced expert utilization and the development of diverse, specialized experts, all without the need for a conflicting auxiliary loss function. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Belis0811/EMoE.
ERMoE: Eigen-Reparameterized Mixture-of-Experts for Stable Routing and Interpretable Specialization
Nov 14, 2025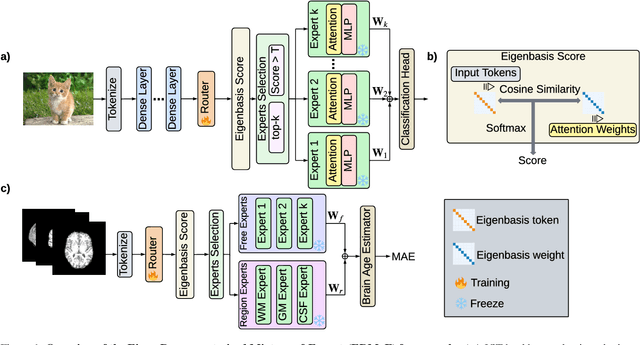
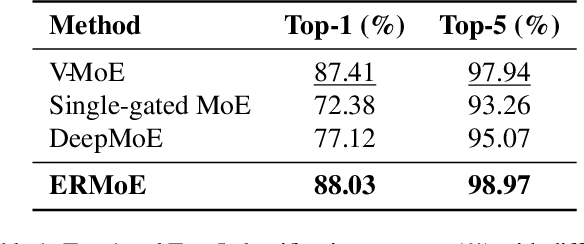
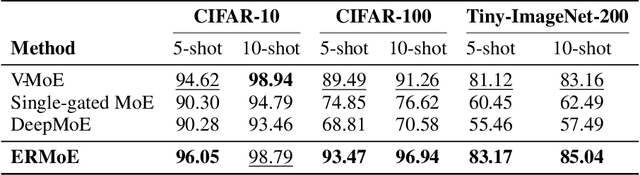
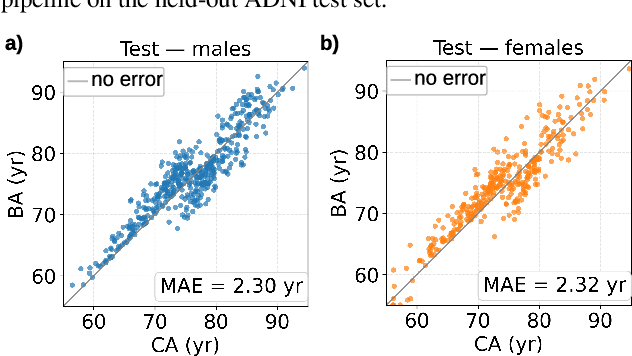
Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures expand model capacity by sparsely activating experts but face two core challenges: misalignment between router logits and each expert's internal structure leads to unstable routing and expert underutilization, and load imbalances create straggler bottlenecks. Standard solutions, such as auxiliary load-balancing losses, can reduce load disparities but often weaken expert specialization and hurt downstream performance. To address these issues, we propose ERMoE, a sparse MoE transformer that reparameterizes each expert in a learned orthonormal eigenbasis and replaces learned gating logits with an "Eigenbasis Score", defined as the cosine similarity between input features and an expert's basis. This content-aware routing ties token assignments directly to experts' representation spaces, stabilizing utilization and promoting interpretable specialization without sacrificing sparsity. Crucially, ERMoE removes the need for explicit balancing losses and avoids the interfering gradients they introduce. We show that ERMoE achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on ImageNet classification and cross-modal image-text retrieval benchmarks (e.g., COCO, Flickr30K), while naturally producing flatter expert load distributions. Moreover, a 3D MRI variant (ERMoE-ba) improves brain age prediction accuracy by more than 7\% and yields anatomically interpretable expert specializations. ERMoE thus introduces a new architectural principle for sparse expert models that directly addresses routing instabilities and enables improved performance with scalable, interpretable specialization.
Maestro: Learning to Collaborate via Conditional Listwise Policy Optimization for Multi-Agent LLMs
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) built on Large Language Models (LLMs) are being used to approach complex problems and can surpass single model inference. However, their success hinges on navigating a fundamental cognitive tension: the need to balance broad, divergent exploration of the solution space with a principled, convergent synthesis to the optimal solution. Existing paradigms often struggle to manage this duality, leading to premature consensus, error propagation, and a critical credit assignment problem that fails to distinguish between genuine reasoning and superficially plausible arguments. To resolve this core challenge, we propose the Multi-Agent Exploration-Synthesis framework Through Role Orchestration (Maestro), a principled paradigm for collaboration that structurally decouples these cognitive modes. Maestro uses a collective of parallel Execution Agents for diverse exploration and a specialized Central Agent for convergent, evaluative synthesis. To operationalize this critical synthesis phase, we introduce Conditional Listwise Policy Optimization (CLPO), a reinforcement learning objective that disentangles signals for strategic decisions and tactical rationales. By combining decision-focused policy gradients with a list-wise ranking loss over justifications, CLPO achieves clean credit assignment and stronger comparative supervision. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and general problem-solving benchmarks demonstrate that Maestro, coupled with CLPO, consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art multi-agent approaches, delivering absolute accuracy gains of 6% on average and up to 10% at best.
VeriMoA: A Mixture-of-Agents Framework for Spec-to-HDL Generation
Oct 31, 2025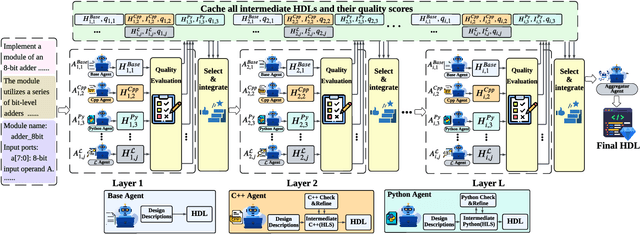
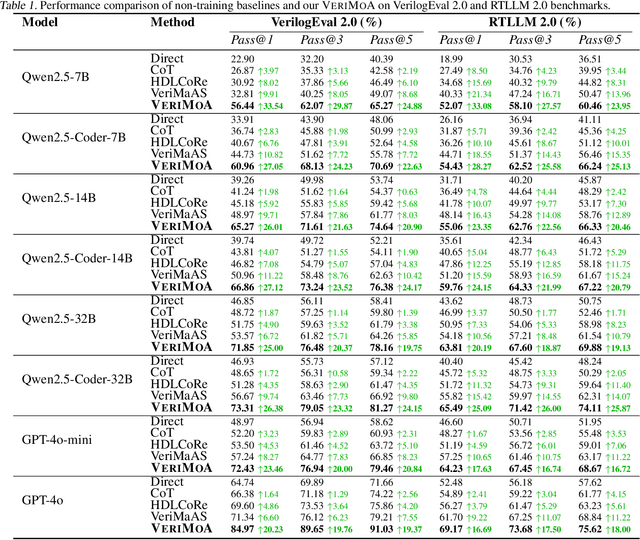
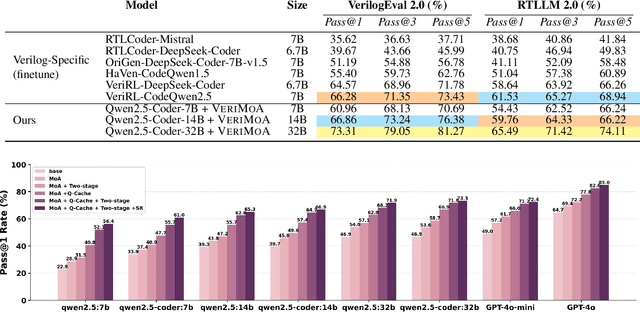
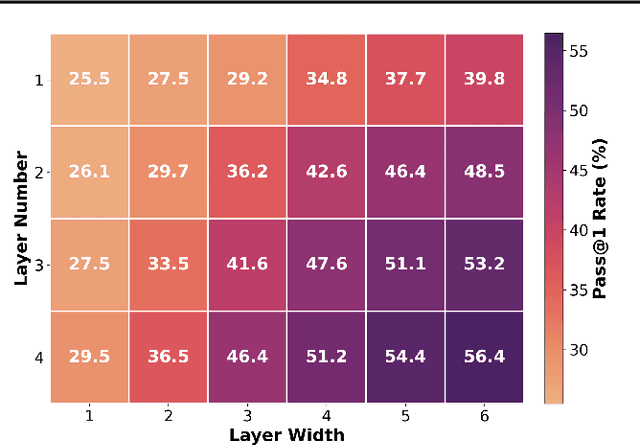
Abstract:Automation of Register Transfer Level (RTL) design can help developers meet increasing computational demands. Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise for Hardware Description Language (HDL) generation, but face challenges due to limited parametric knowledge and domain-specific constraints. While prompt engineering and fine-tuning have limitations in knowledge coverage and training costs, multi-agent architectures offer a training-free paradigm to enhance reasoning through collaborative generation. However, current multi-agent approaches suffer from two critical deficiencies: susceptibility to noise propagation and constrained reasoning space exploration. We propose VeriMoA, a training-free mixture-of-agents (MoA) framework with two synergistic innovations. First, a quality-guided caching mechanism to maintain all intermediate HDL outputs and enables quality-based ranking and selection across the entire generation process, encouraging knowledge accumulation over layers of reasoning. Second, a multi-path generation strategy that leverages C++ and Python as intermediate representations, decomposing specification-to-HDL translation into two-stage processes that exploit LLM fluency in high-resource languages while promoting solution diversity. Comprehensive experiments on VerilogEval 2.0 and RTLLM 2.0 benchmarks demonstrate that VeriMoA achieves 15--30% improvements in Pass@1 across diverse LLM backbones, especially enabling smaller models to match larger models and fine-tuned alternatives without requiring costly training.
MaskAttn-SDXL: Controllable Region-Level Text-To-Image Generation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models achieve impressive realism but often suffer from compositional failures on prompts with multiple objects, attributes, and spatial relations, resulting in cross-token interference where entities entangle, attributes mix across objects, and spatial cues are violated. To address these failures, we propose MaskAttn-SDXL,a region-level gating mechanism applied to the cross-attention logits of Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)'s UNet. MaskAttn-SDXL learns a binary mask per layer, injecting it into each cross-attention logit map before softmax to sparsify token-to-latent interactions so that only semantically relevant connections remain active. The method requires no positional encodings, auxiliary tokens, or external region masks, and preserves the original inference path with negligible overhead. In practice, our model improves spatial compliance and attribute binding in multi-object prompts while preserving overall image quality and diversity. These findings demonstrate that logit-level maksed cross-attention is an data-efficient primitve for enforcing compositional control, and our method thus serves as a practical extension for spatial control in text-to-image generation.
H$^2$GFM: Towards unifying Homogeneity and Heterogeneity on Text-Attributed Graphs
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:The growing interests and applications of graph learning in diverse domains have propelled the development of a unified model generalizing well across different graphs and tasks, known as the Graph Foundation Model (GFM). Existing research has leveraged text-attributed graphs (TAGs) to tackle the heterogeneity in node features among graphs. However, they primarily focus on homogeneous TAGs (HoTAGs), leaving heterogeneous TAGs (HeTAGs), where multiple types of nodes/edges reside, underexplored. To enhance the capabilities and applications of GFM, we introduce H$^2$GFM, a novel framework designed to generalize across both HoTAGs and HeTAGs. Our model projects diverse meta-relations among graphs under a unified textual space, and employs a context encoding to capture spatial and higher-order semantic relationships. To achieve robust node representations, we propose a novel context-adaptive graph transformer (CGT), effectively capturing information from both context neighbors and their relationships. Furthermore, we employ a mixture of CGT experts to capture the heterogeneity in structural patterns among graph types. Comprehensive experiments on a wide range of HoTAGs and HeTAGs as well as learning scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of our model.
HDLCoRe: A Training-Free Framework for Mitigating Hallucinations in LLM-Generated HDL
Mar 18, 2025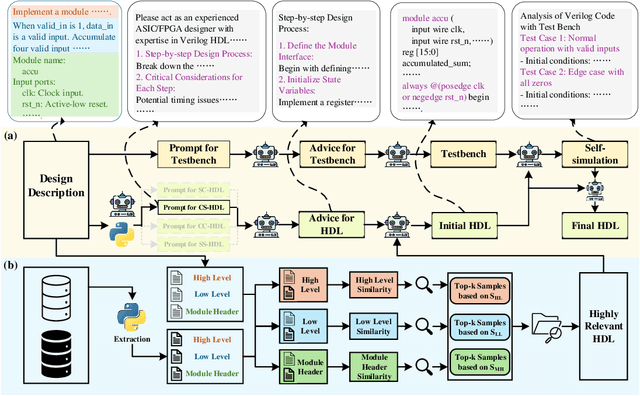



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in code generation tasks. However, when applied to hardware description languages (HDL), these models exhibit significant limitations due to data scarcity, resulting in hallucinations and incorrect code generation. To address these challenges, we propose HDLCoRe, a training-free framework that enhances LLMs' HDL generation capabilities through prompt engineering techniques and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Our approach consists of two main components: (1) an HDL-aware Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting technique with self-verification that classifies tasks by complexity and type, incorporates domain-specific knowledge, and guides LLMs through step-by-step self-simulation for error correction; and (2) a two-stage heterogeneous RAG system that addresses formatting inconsistencies through key component extraction and efficiently retrieves relevant HDL examples through sequential filtering and re-ranking. HDLCoRe eliminates the need for model fine-tuning while substantially improving LLMs' HDL generation capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves superior performance on the RTLLM2.0 benchmark, significantly reducing hallucinations and improving both syntactic and functional correctness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge