Junsoo Lee
TCAN: Animating Human Images with Temporally Consistent Pose Guidance using Diffusion Models
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Pose-driven human-image animation diffusion models have shown remarkable capabilities in realistic human video synthesis. Despite the promising results achieved by previous approaches, challenges persist in achieving temporally consistent animation and ensuring robustness with off-the-shelf pose detectors. In this paper, we present TCAN, a pose-driven human image animation method that is robust to erroneous poses and consistent over time. In contrast to previous methods, we utilize the pre-trained ControlNet without fine-tuning to leverage its extensive pre-acquired knowledge from numerous pose-image-caption pairs. To keep the ControlNet frozen, we adapt LoRA to the UNet layers, enabling the network to align the latent space between the pose and appearance features. Additionally, by introducing an additional temporal layer to the ControlNet, we enhance robustness against outliers of the pose detector. Through the analysis of attention maps over the temporal axis, we also designed a novel temperature map leveraging pose information, allowing for a more static background. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve promising results in video synthesis tasks encompassing various poses, like chibi. Project Page: https://eccv2024tcan.github.io/
SAVE: Protagonist Diversification with Structure Agnostic Video Editing
Dec 05, 2023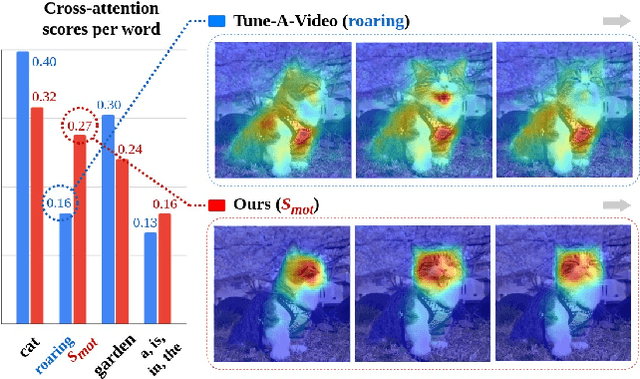
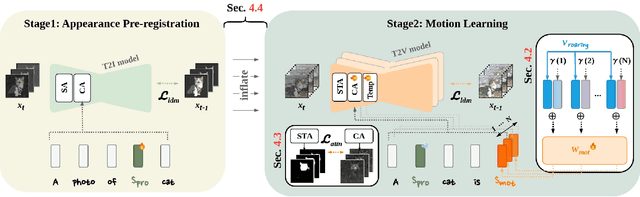
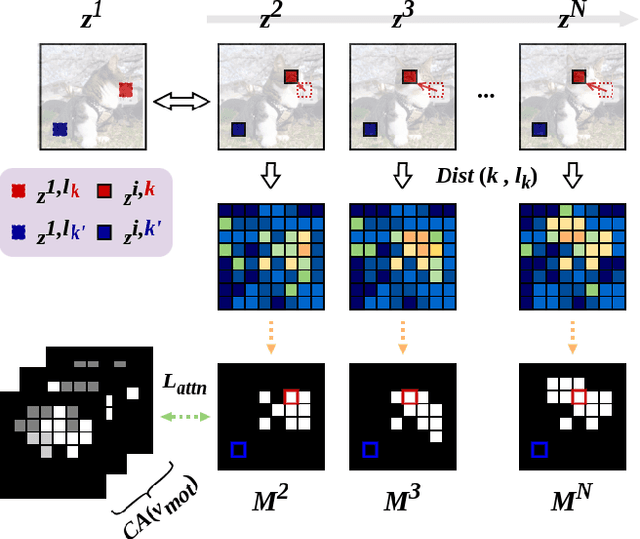
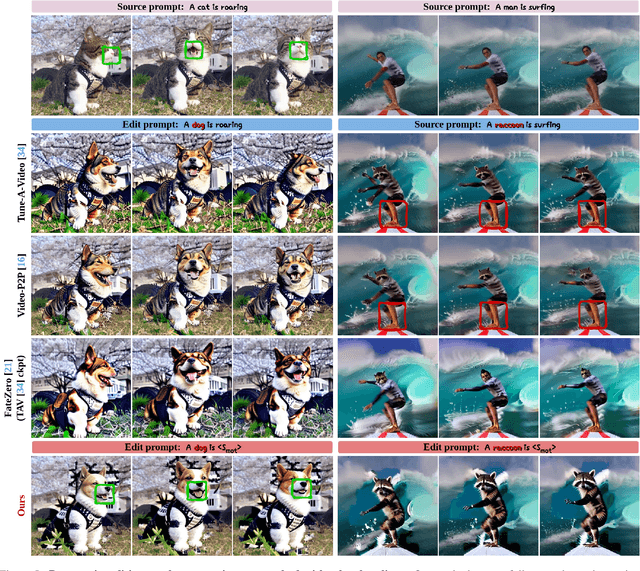
Abstract:Driven by the upsurge progress in text-to-image (T2I) generation models, text-to-video (T2V) generation has experienced a significant advance as well. Accordingly, tasks such as modifying the object or changing the style in a video have been possible. However, previous works usually work well on trivial and consistent shapes, and easily collapse on a difficult target that has a largely different body shape from the original one. In this paper, we spot the bias problem in the existing video editing method that restricts the range of choices for the new protagonist and attempt to address this issue using the conventional image-level personalization method. We adopt motion personalization that isolates the motion from a single source video and then modifies the protagonist accordingly. To deal with the natural discrepancy between image and video, we propose a motion word with an inflated textual embedding to properly represent the motion in a source video. We also regulate the motion word to attend to proper motion-related areas by introducing a novel pseudo optical flow, efficiently computed from the pre-calculated attention maps. Finally, we decouple the motion from the appearance of the source video with an additional pseudo word. Extensive experiments demonstrate the editing capability of our method, taking a step toward more diverse and extensive video editing.
DreamStyler: Paint by Style Inversion with Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Recent progresses in large-scale text-to-image models have yielded remarkable accomplishments, finding various applications in art domain. However, expressing unique characteristics of an artwork (e.g. brushwork, colortone, or composition) with text prompts alone may encounter limitations due to the inherent constraints of verbal description. To this end, we introduce DreamStyler, a novel framework designed for artistic image synthesis, proficient in both text-to-image synthesis and style transfer. DreamStyler optimizes a multi-stage textual embedding with a context-aware text prompt, resulting in prominent image quality. In addition, with content and style guidance, DreamStyler exhibits flexibility to accommodate a range of style references. Experimental results demonstrate its superior performance across multiple scenarios, suggesting its promising potential in artistic product creation.
AesPA-Net: Aesthetic Pattern-Aware Style Transfer Networks
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:To deliver the artistic expression of the target style, recent studies exploit the attention mechanism owing to its ability to map the local patches of the style image to the corresponding patches of the content image. However, because of the low semantic correspondence between arbitrary content and artworks, the attention module repeatedly abuses specific local patches from the style image, resulting in disharmonious and evident repetitive artifacts. To overcome this limitation and accomplish impeccable artistic style transfer, we focus on enhancing the attention mechanism and capturing the rhythm of patterns that organize the style. In this paper, we introduce a novel metric, namely pattern repeatability, that quantifies the repetition of patterns in the style image. Based on the pattern repeatability, we propose Aesthetic Pattern-Aware style transfer Networks (AesPA-Net) that discover the sweet spot of local and global style expressions. In addition, we propose a novel self-supervisory task to encourage the attention mechanism to learn precise and meaningful semantic correspondence. Lastly, we introduce the patch-wise style loss to transfer the elaborate rhythm of local patterns. Through qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we verify the reliability of the proposed pattern repeatability that aligns with human perception, and demonstrate the superiority of the proposed framework.
DiffBlender: Scalable and Composable Multimodal Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
May 24, 2023Abstract:The recent progress in diffusion-based text-to-image generation models has significantly expanded generative capabilities via conditioning the text descriptions. However, since relying solely on text prompts is still restrictive for fine-grained customization, we aim to extend the boundaries of conditional generation to incorporate diverse types of modalities, e.g., sketch, box, and style embedding, simultaneously. We thus design a multimodal text-to-image diffusion model, coined as DiffBlender, that achieves the aforementioned goal in a single model by training only a few small hypernetworks. DiffBlender facilitates a convenient scaling of input modalities, without altering the parameters of an existing large-scale generative model to retain its well-established knowledge. Furthermore, our study sets new standards for multimodal generation by conducting quantitative and qualitative comparisons with existing approaches. By diversifying the channels of conditioning modalities, DiffBlender faithfully reflects the provided information or, in its absence, creates imaginative generation.
LPMM: Intuitive Pose Control for Neural Talking-Head Model via Landmark-Parameter Morphable Model
May 17, 2023



Abstract:While current talking head models are capable of generating photorealistic talking head videos, they provide limited pose controllability. Most methods require specific video sequences that should exactly contain the head pose desired, being far from user-friendly pose control. Three-dimensional morphable models (3DMM) offer semantic pose control, but they fail to capture certain expressions. We present a novel method that utilizes parametric control of head orientation and facial expression over a pre-trained neural-talking head model. To enable this, we introduce a landmark-parameter morphable model (LPMM), which offers control over the facial landmark domain through a set of semantic parameters. Using LPMM, it is possible to adjust specific head pose factors, without distorting other facial attributes. The results show our approach provides intuitive rig-like control over neural talking head models, allowing both parameter and image-based inputs.
Reference-based Image Composition with Sketch via Structure-aware Diffusion Model
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:Recent remarkable improvements in large-scale text-to-image generative models have shown promising results in generating high-fidelity images. To further enhance editability and enable fine-grained generation, we introduce a multi-input-conditioned image composition model that incorporates a sketch as a novel modal, alongside a reference image. Thanks to the edge-level controllability using sketches, our method enables a user to edit or complete an image sub-part with a desired structure (i.e., sketch) and content (i.e., reference image). Our framework fine-tunes a pre-trained diffusion model to complete missing regions using the reference image while maintaining sketch guidance. Albeit simple, this leads to wide opportunities to fulfill user needs for obtaining the in-demand images. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed method offers unique use cases for image manipulation, enabling user-driven modifications of arbitrary scenes.
Guiding Users to Where to Give Color Hints for Efficient Interactive Sketch Colorization via Unsupervised Region Prioritization
Oct 25, 2022



Abstract:Existing deep interactive colorization models have focused on ways to utilize various types of interactions, such as point-wise color hints, scribbles, or natural-language texts, as methods to reflect a user's intent at runtime. However, another approach, which actively informs the user of the most effective regions to give hints for sketch image colorization, has been under-explored. This paper proposes a novel model-guided deep interactive colorization framework that reduces the required amount of user interactions, by prioritizing the regions in a colorization model. Our method, called GuidingPainter, prioritizes these regions where the model most needs a color hint, rather than just relying on the user's manual decision on where to give a color hint. In our extensive experiments, we show that our approach outperforms existing interactive colorization methods in terms of the conventional metrics, such as PSNR and FID, and reduces required amount of interactions.
Continuous-Time Video Generation via Learning Motion Dynamics with Neural ODE
Dec 21, 2021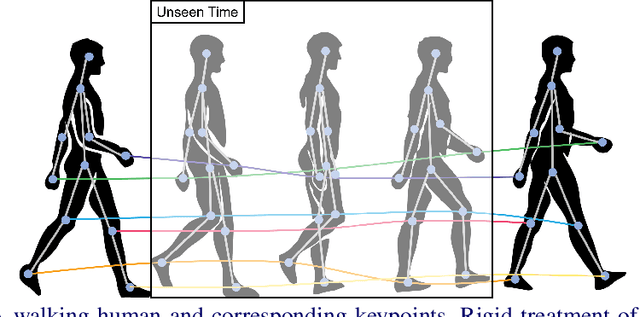
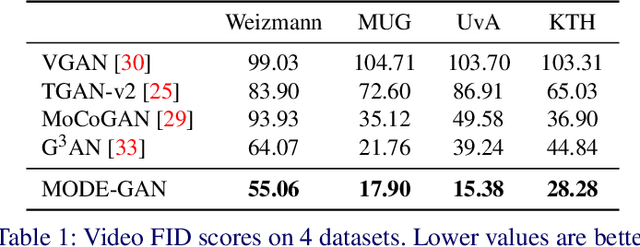
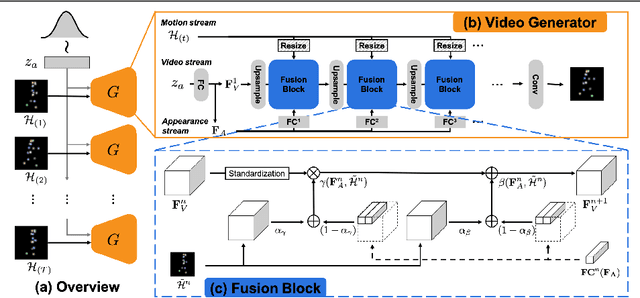

Abstract:In order to perform unconditional video generation, we must learn the distribution of the real-world videos. In an effort to synthesize high-quality videos, various studies attempted to learn a mapping function between noise and videos, including recent efforts to separate motion distribution and appearance distribution. Previous methods, however, learn motion dynamics in discretized, fixed-interval timesteps, which is contrary to the continuous nature of motion of a physical body. In this paper, we propose a novel video generation approach that learns separate distributions for motion and appearance, the former modeled by neural ODE to learn natural motion dynamics. Specifically, we employ a two-stage approach where the first stage converts a noise vector to a sequence of keypoints in arbitrary frame rates, and the second stage synthesizes videos based on the given keypoints sequence and the appearance noise vector. Our model not only quantitatively outperforms recent baselines for video generation, but also demonstrates versatile functionality such as dynamic frame rate manipulation and motion transfer between two datasets, thus opening new doors to diverse video generation applications.
AnimeCeleb: Large-Scale Animation CelebFaces Dataset via Controllable 3D Synthetic Models
Nov 15, 2021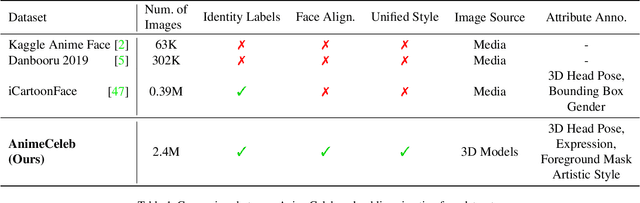
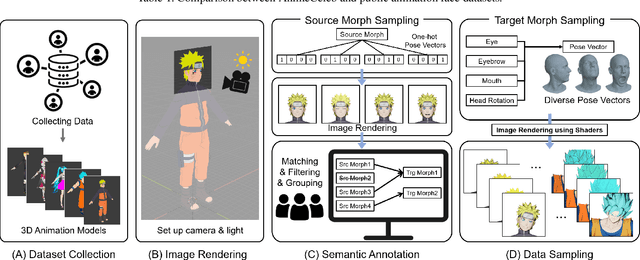
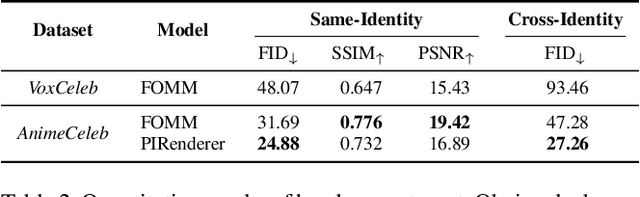
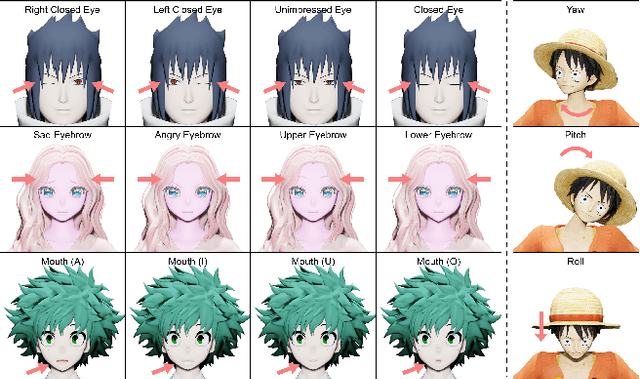
Abstract:Despite remarkable success in deep learning-based face-related models, these models are still limited to the domain of real human faces. On the other hand, the domain of animation faces has been studied less intensively due to the absence of a well-organized dataset. In this paper, we present a large-scale animation celebfaces dataset (AnimeCeleb) via controllable synthetic animation models to boost research on the animation face domain. To facilitate the data generation process, we build a semi-automatic pipeline based on an open 3D software and a developed annotation system. This leads to constructing a large-scale animation face dataset that includes multi-pose and multi-style animation faces with rich annotations. Experiments suggest that our dataset is applicable to various animation-related tasks such as head reenactment and colorization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge