Kwangho Lee
Chupa: Carving 3D Clothed Humans from Skinned Shape Priors using 2D Diffusion Probabilistic Models
May 19, 2023



Abstract:We propose a 3D generation pipeline that uses diffusion models to generate realistic human digital avatars. Due to the wide variety of human identities, poses, and stochastic details, the generation of 3D human meshes has been a challenging problem. To address this, we decompose the problem into 2D normal map generation and normal map-based 3D reconstruction. Specifically, we first simultaneously generate realistic normal maps for the front and backside of a clothed human, dubbed dual normal maps, using a pose-conditional diffusion model. For 3D reconstruction, we ``carve'' the prior SMPL-X mesh to a detailed 3D mesh according to the normal maps through mesh optimization. To further enhance the high-frequency details, we present a diffusion resampling scheme on both body and facial regions, thus encouraging the generation of realistic digital avatars. We also seamlessly incorporate a recent text-to-image diffusion model to support text-based human identity control. Our method, namely, Chupa, is capable of generating realistic 3D clothed humans with better perceptual quality and identity variety.
LPMM: Intuitive Pose Control for Neural Talking-Head Model via Landmark-Parameter Morphable Model
May 17, 2023



Abstract:While current talking head models are capable of generating photorealistic talking head videos, they provide limited pose controllability. Most methods require specific video sequences that should exactly contain the head pose desired, being far from user-friendly pose control. Three-dimensional morphable models (3DMM) offer semantic pose control, but they fail to capture certain expressions. We present a novel method that utilizes parametric control of head orientation and facial expression over a pre-trained neural-talking head model. To enable this, we introduce a landmark-parameter morphable model (LPMM), which offers control over the facial landmark domain through a set of semantic parameters. Using LPMM, it is possible to adjust specific head pose factors, without distorting other facial attributes. The results show our approach provides intuitive rig-like control over neural talking head models, allowing both parameter and image-based inputs.
Cross-Domain Style Mixing for Face Cartoonization
May 25, 2022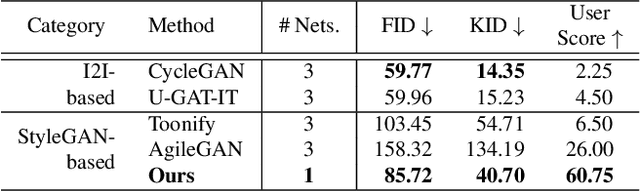
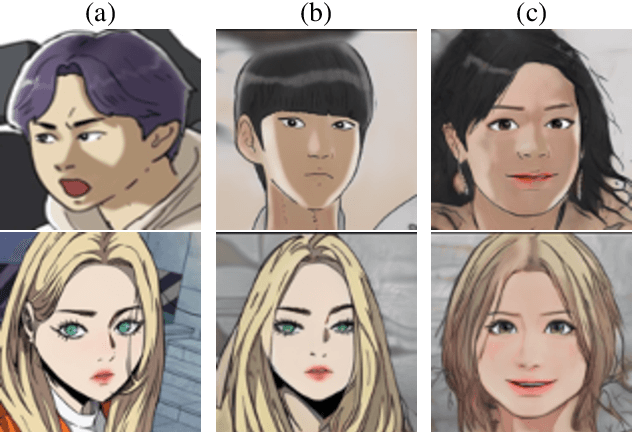
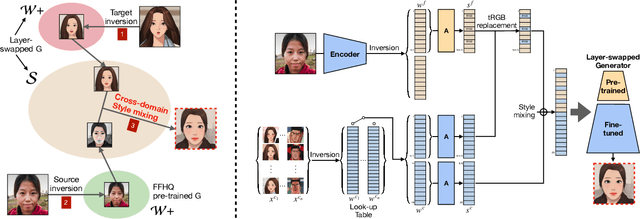
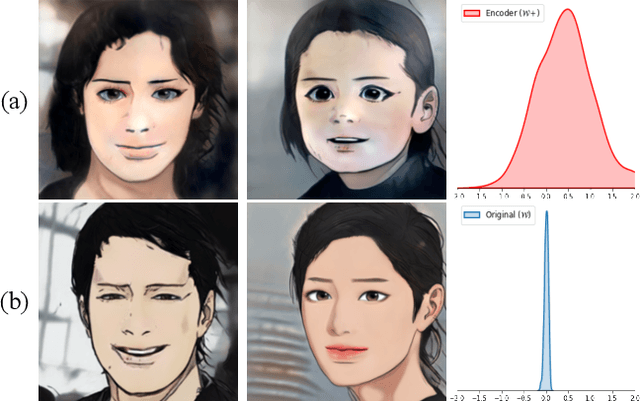
Abstract:Cartoon domain has recently gained increasing popularity. Previous studies have attempted quality portrait stylization into the cartoon domain; however, this poses a great challenge since they have not properly addressed the critical constraints, such as requiring a large number of training images or the lack of support for abstract cartoon faces. Recently, a layer swapping method has been used for stylization requiring only a limited number of training images; however, its use cases are still narrow as it inherits the remaining issues. In this paper, we propose a novel method called Cross-domain Style mixing, which combines two latent codes from two different domains. Our method effectively stylizes faces into multiple cartoon characters at various face abstraction levels using only a single generator without even using a large number of training images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge