Jeesoo Kim
SAVE: Protagonist Diversification with Structure Agnostic Video Editing
Dec 05, 2023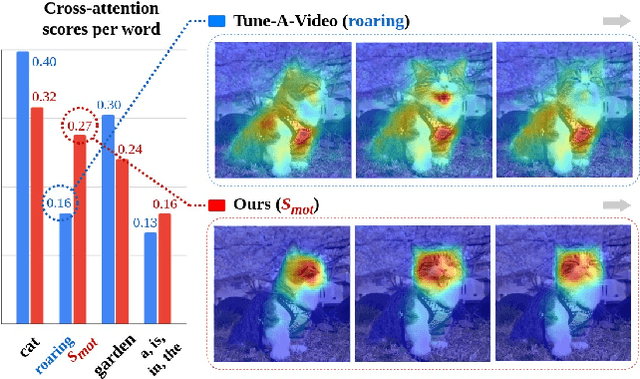
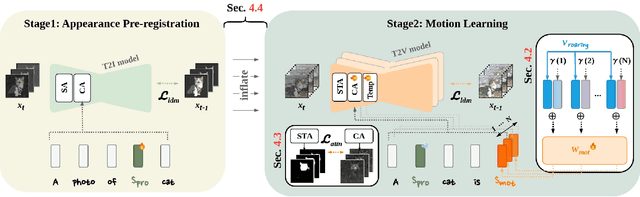
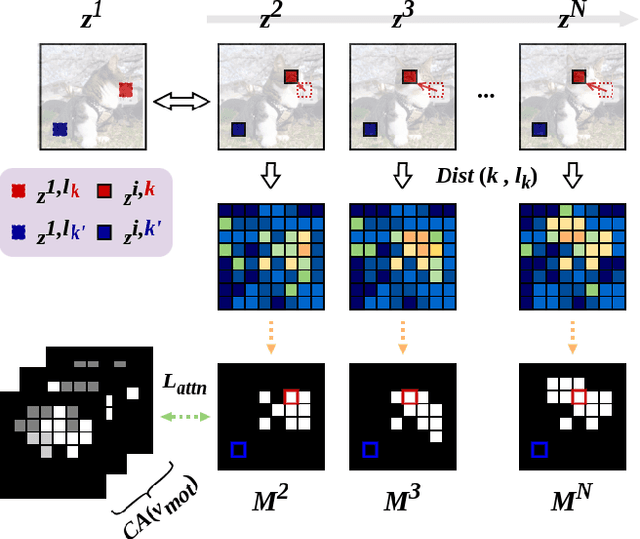
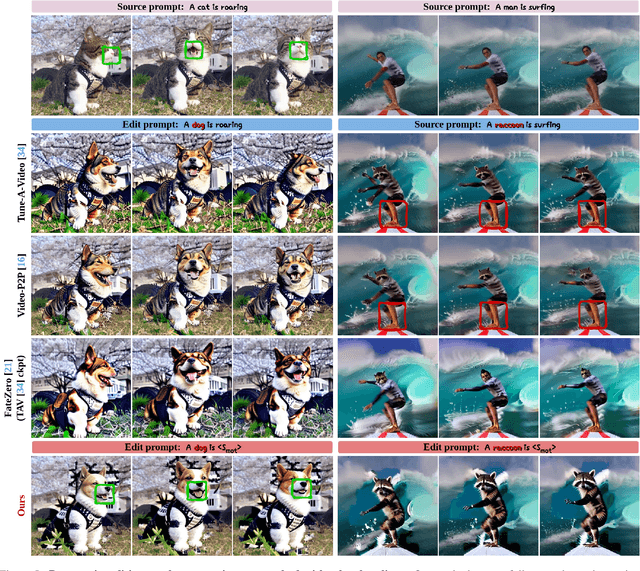
Abstract:Driven by the upsurge progress in text-to-image (T2I) generation models, text-to-video (T2V) generation has experienced a significant advance as well. Accordingly, tasks such as modifying the object or changing the style in a video have been possible. However, previous works usually work well on trivial and consistent shapes, and easily collapse on a difficult target that has a largely different body shape from the original one. In this paper, we spot the bias problem in the existing video editing method that restricts the range of choices for the new protagonist and attempt to address this issue using the conventional image-level personalization method. We adopt motion personalization that isolates the motion from a single source video and then modifies the protagonist accordingly. To deal with the natural discrepancy between image and video, we propose a motion word with an inflated textual embedding to properly represent the motion in a source video. We also regulate the motion word to attend to proper motion-related areas by introducing a novel pseudo optical flow, efficiently computed from the pre-calculated attention maps. Finally, we decouple the motion from the appearance of the source video with an additional pseudo word. Extensive experiments demonstrate the editing capability of our method, taking a step toward more diverse and extensive video editing.
Smoothing the Generative Latent Space with Mixup-based Distance Learning
Nov 23, 2021

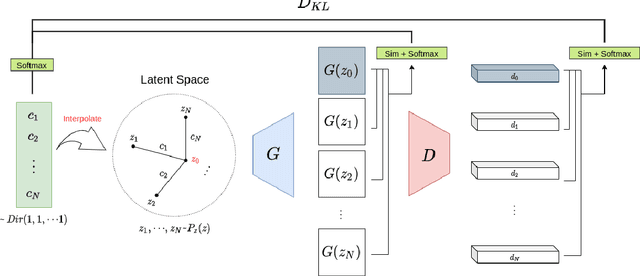
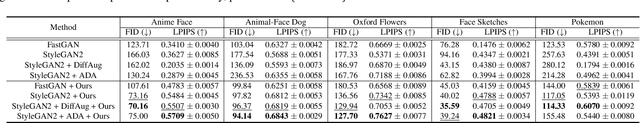
Abstract:Producing diverse and realistic images with generative models such as GANs typically requires large scale training with vast amount of images. GANs trained with extremely limited data can easily overfit to few training samples and display undesirable properties like "stairlike" latent space where transitions in latent space suffer from discontinuity, occasionally yielding abrupt changes in outputs. In this work, we consider the situation where neither large scale dataset of our interest nor transferable source dataset is available, and seek to train existing generative models with minimal overfitting and mode collapse. We propose latent mixup-based distance regularization on the feature space of both a generator and the counterpart discriminator that encourages the two players to reason not only about the scarce observed data points but the relative distances in the feature space they reside. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation on diverse datasets demonstrates that our method is generally applicable to existing models to enhance both fidelity and diversity under the constraint of limited data. Code will be made public.
Normalization Matters in Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Jul 28, 2021



Abstract:Weakly-supervised object localization (WSOL) enables finding an object using a dataset without any localization information. By simply training a classification model using only image-level annotations, the feature map of the model can be utilized as a score map for localization. In spite of many WSOL methods proposing novel strategies, there has not been any de facto standard about how to normalize the class activation map (CAM). Consequently, many WSOL methods have failed to fully exploit their own capacity because of the misuse of a normalization method. In this paper, we review many existing normalization methods and point out that they should be used according to the property of the given dataset. Additionally, we propose a new normalization method which substantially enhances the performance of any CAM-based WSOL methods. Using the proposed normalization method, we provide a comprehensive evaluation over three datasets (CUB, ImageNet and OpenImages) on three different architectures and observe significant performance gains over the conventional min-max normalization method in all the evaluated cases.
A Comprehensive Overhaul of Feature Distillation
Apr 03, 2019



Abstract:We investigate the design aspects of feature distillation methods achieving network compression and propose a novel feature distillation method in which the distillation loss is designed to make a synergy among various aspects: teacher transform, student transform, distillation feature position and distance function. Our proposed distillation loss includes a feature transform with a newly designed margin ReLU, a new distillation feature position, and a partial L2 distance function to skip redundant information giving adverse effects to the compression of student. In ImageNet, our proposed method achieves 21.65% of top-1 error with ResNet50, which outperforms the performance of the teacher network, ResNet152. Our proposed method is evaluated on various tasks such as image classification, object detection and semantic segmentation and achieves a significant performance improvement in all tasks.
HC-Net: Memory-based Incremental Dual-Network System for Continual learning
Sep 07, 2018



Abstract:Training a neural network for a classification task typically assumes that the data to train are given from the beginning. However, in the real world, additional data accumulate gradually and the model requires additional training without accessing the old training data. This usually leads to the catastrophic forgetting problem which is inevitable for the traditional training methodology of neural networks. In this paper, we propose a memory-based continual learning method that is able to learn additional tasks while retaining the performance of previously learned tasks. Composed of two complementary networks, the Hippocampus-net (H-net) and the Cortex-net (C-net), our model estimates the index of the corresponding task for an input sample and utilizes a particular portion of itself with the estimated index. The C-net guarantees no degradation in the performance of the previously learned tasks and the H-net shows high confidence in finding the origin of the input sample
Generating objects going well with the surroundings
Jul 09, 2018



Abstract:Since the generative adversarial network has made a breakthrough in the image generation problem, lots of researches on its applications have been studied such as image restoration, style transfer and image completion. However, there have been few researches generating objects in uncontrolled real-world environments. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for image generation in real-world scenes. The overall architecture consists of two different networks each of which completes the shape of the generating object and paints the context on it respectively. Using a subnetwork proposed in a precedent work of image completion, our model make the shape of an object. Unlike the approaches used in the image completion problem, details of trained objects are encoded into a latent variable by an additional subnetwork, resulting in a better quality of the generated objects. We evaluated our method using KITTI and City-scape datasets, which are widely used for object detection and image segmentation problems. The adequacy of the generated images by the proposed method has also been evaluated using a widely utilized object detection algorithm.
Dynamic Graph Generation Network: Generating Relational Knowledge from Diagrams
Nov 27, 2017



Abstract:In this work, we introduce a new algorithm for analyzing a diagram, which contains visual and textual information in an abstract and integrated way. Whereas diagrams contain richer information compared with individual image-based or language-based data, proper solutions for automatically understanding them have not been proposed due to their innate characteristics of multi-modality and arbitrariness of layouts. To tackle this problem, we propose a unified diagram-parsing network for generating knowledge from diagrams based on an object detector and a recurrent neural network designed for a graphical structure. Specifically, we propose a dynamic graph-generation network that is based on dynamic memory and graph theory. We explore the dynamics of information in a diagram with activation of gates in gated recurrent unit (GRU) cells. On publicly available diagram datasets, our model demonstrates a state-of-the-art result that outperforms other baselines. Moreover, further experiments on question answering shows potentials of the proposed method for various applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge