John Yang
Terminal-Bench: Benchmarking Agents on Hard, Realistic Tasks in Command Line Interfaces
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:AI agents may soon become capable of autonomously completing valuable, long-horizon tasks in diverse domains. Current benchmarks either do not measure real-world tasks, or are not sufficiently difficult to meaningfully measure frontier models. To this end, we present Terminal-Bench 2.0: a carefully curated hard benchmark composed of 89 tasks in computer terminal environments inspired by problems from real workflows. Each task features a unique environment, human-written solution, and comprehensive tests for verification. We show that frontier models and agents score less than 65\% on the benchmark and conduct an error analysis to identify areas for model and agent improvement. We publish the dataset and evaluation harness to assist developers and researchers in future work at https://www.tbench.ai/ .
OpenThoughts: Data Recipes for Reasoning Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Reasoning models have made rapid progress on many benchmarks involving math, code, and science. Yet, there are still many open questions about the best training recipes for reasoning since state-of-the-art models often rely on proprietary datasets with little to no public information available. To address this, the goal of the OpenThoughts project is to create open-source datasets for training reasoning models. After initial explorations, our OpenThoughts2-1M dataset led to OpenThinker2-32B, the first model trained on public reasoning data to match DeepSeek-R1-Distill-32B on standard reasoning benchmarks such as AIME and LiveCodeBench. We then improve our dataset further by systematically investigating each step of our data generation pipeline with 1,000+ controlled experiments, which led to OpenThoughts3. Scaling the pipeline to 1.2M examples and using QwQ-32B as teacher yields our OpenThoughts3-7B model, which achieves state-of-the-art results: 53% on AIME 2025, 51% on LiveCodeBench 06/24-01/25, and 54% on GPQA Diamond - improvements of 15.3, 17.2, and 20.5 percentage points compared to the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B. All of our datasets and models are available on https://openthoughts.ai.
LongCodeBench: Evaluating Coding LLMs at 1M Context Windows
May 12, 2025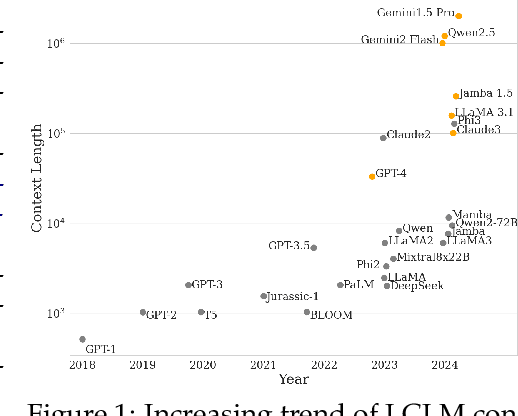
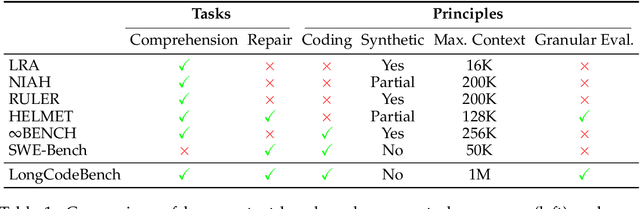
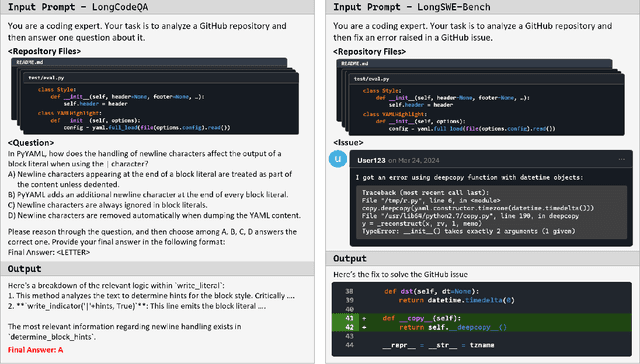
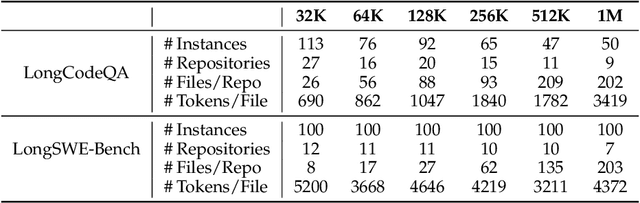
Abstract:Context lengths for models have grown rapidly, from thousands to millions of tokens in just a few years. The extreme context sizes of modern long-context models have made it difficult to construct realistic long-context benchmarks -- not only due to the cost of collecting million-context tasks but also in identifying realistic scenarios that require significant contexts. We identify code comprehension and repair as a natural testbed and challenge task for long-context models and introduce LongCodeBench (LCB), a benchmark to test LLM coding abilities in long-context scenarios. Our benchmark tests both the comprehension and repair capabilities of LCLMs in realistic and important settings by drawing from real-world GitHub issues and constructing QA (LongCodeQA) and bug fixing (LongSWE-Bench) tasks. We carefully stratify the complexity of our benchmark, enabling us to evaluate models across different scales -- ranging from Qwen2.5 14B Instruct to Google's flagship Gemini model. We find that long-context remains a weakness for all models, with performance drops such as from 29% to 3% for Claude 3.5 Sonnet, or from 70.2% to 40% for Qwen2.5.
SWE-smith: Scaling Data for Software Engineering Agents
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in Language Models (LMs) for software engineering, collecting training data remains a significant pain point. Existing datasets are small, with at most 1,000s of training instances from 11 or fewer GitHub repositories. The procedures to curate such datasets are often complex, necessitating hundreds of hours of human labor; companion execution environments also take up several terabytes of storage, severely limiting their scalability and usability. To address this pain point, we introduce SWE-smith, a novel pipeline for generating software engineering training data at scale. Given any Python codebase, SWE-smith constructs a corresponding execution environment, then automatically synthesizes 100s to 1,000s of task instances that break existing test(s) in the codebase. Using SWE-smith, we create a dataset of 50k instances sourced from 128 GitHub repositories, an order of magnitude larger than all previous works. We train SWE-agent-LM-32B, achieving 40.2% Pass@1 resolve rate on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, state of the art among open source models. We open source SWE-smith (collection procedure, task instances, trajectories, models) to lower the barrier of entry for research in LM systems for automated software engineering. All assets available at https://swesmith.com.
MMTEB: Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings are typically evaluated on a limited set of tasks, which are constrained by language, domain, and task diversity. To address these limitations and provide a more comprehensive evaluation, we introduce the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB) - a large-scale, community-driven expansion of MTEB, covering over 500 quality-controlled evaluation tasks across 250+ languages. MMTEB includes a diverse set of challenging, novel tasks such as instruction following, long-document retrieval, and code retrieval, representing the largest multilingual collection of evaluation tasks for embedding models to date. Using this collection, we develop several highly multilingual benchmarks, which we use to evaluate a representative set of models. We find that while large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters can achieve state-of-the-art performance on certain language subsets and task categories, the best-performing publicly available model is multilingual-e5-large-instruct with only 560 million parameters. To facilitate accessibility and reduce computational cost, we introduce a novel downsampling method based on inter-task correlation, ensuring a diverse selection while preserving relative model rankings. Furthermore, we optimize tasks such as retrieval by sampling hard negatives, creating smaller but effective splits. These optimizations allow us to introduce benchmarks that drastically reduce computational demands. For instance, our newly introduced zero-shot English benchmark maintains a ranking order similar to the full-scale version but at a fraction of the computational cost.
Collaborative Gym: A Framework for Enabling and Evaluating Human-Agent Collaboration
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in language models (LMs) have sparked growing interest in developing LM agents. While fully autonomous agents could excel in many scenarios, numerous use cases inherently require them to collaborate with humans due to humans' latent preferences, domain expertise, or need for control. To facilitate the study of human-agent collaboration, we present Collaborative Gym (Co-Gym), a general framework enabling asynchronous, tripartite interaction among agents, humans, and task environments. We instantiate Co-Gym with three representative tasks in both simulated and real-world conditions, and propose an evaluation framework that assesses both the collaboration outcomes and processes. Our findings reveal that collaborative agents consistently outperform their fully autonomous counterparts in task performance within those delivered cases, achieving win rates of 86% in Travel Planning, 74% in Tabular Analysis, and 66% in Related Work when evaluated by real users. However, our study also highlights significant challenges in developing collaborative agents, requiring advancements in core aspects of intelligence -- communication capabilities, situational awareness, and balancing autonomy and human control.
SWE-bench Multimodal: Do AI Systems Generalize to Visual Software Domains?
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous systems for software engineering are now capable of fixing bugs and developing features. These systems are commonly evaluated on SWE-bench (Jimenez et al., 2024a), which assesses their ability to solve software issues from GitHub repositories. However, SWE-bench uses only Python repositories, with problem statements presented predominantly as text and lacking visual elements such as images. This limited coverage motivates our inquiry into how existing systems might perform on unrepresented software engineering domains (e.g., front-end, game development, DevOps), which use different programming languages and paradigms. Therefore, we propose SWE-bench Multimodal (SWE-bench M), to evaluate systems on their ability to fix bugs in visual, user-facing JavaScript software. SWE-bench M features 617 task instances collected from 17 JavaScript libraries used for web interface design, diagramming, data visualization, syntax highlighting, and interactive mapping. Each SWE-bench M task instance contains at least one image in its problem statement or unit tests. Our analysis finds that top-performing SWE-bench systems struggle with SWE-bench M, revealing limitations in visual problem-solving and cross-language generalization. Lastly, we show that SWE-agent's flexible language-agnostic features enable it to substantially outperform alternatives on SWE-bench M, resolving 12% of task instances compared to 6% for the next best system.
EnIGMA: Enhanced Interactive Generative Model Agent for CTF Challenges
Sep 24, 2024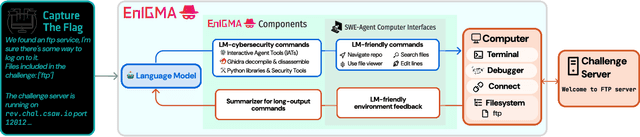
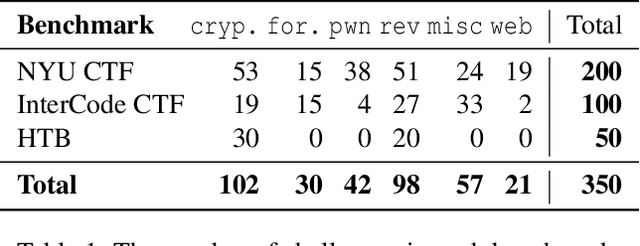

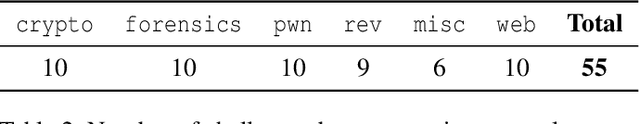
Abstract:Although language model (LM) agents are demonstrating growing potential in many domains, their success in cybersecurity has been limited due to simplistic design and the lack of fundamental features for this domain. We present EnIGMA, an LM agent for autonomously solving Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges. EnIGMA introduces new Agent-Computer Interfaces (ACIs) to improve the success rate on CTF challenges. We establish the novel Interactive Agent Tool concept, which enables LM agents to run interactive command-line utilities essential for these challenges. Empirical analysis of EnIGMA on over 350 CTF challenges from three different benchmarks indicates that providing a robust set of new tools with demonstration of their usage helps the LM solve complex problems and achieves state-of-the-art results on the NYU CTF and Intercode-CTF benchmarks. Finally, we discuss insights on ACI design and agent behavior on cybersecurity tasks that highlight the need to adapt real-world tools for LM agents.
ReduceFormer: Attention with Tensor Reduction by Summation
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:Transformers have excelled in many tasks including vision. However, efficient deployment of transformer models in low-latency or high-throughput applications is hindered by the computation in the attention mechanism which involves expensive operations such as matrix multiplication and Softmax. To address this, we introduce ReduceFormer, a family of models optimized for efficiency with the spirit of attention. ReduceFormer leverages only simple operations such as reduction and element-wise multiplication, leading to greatly simplified architecture and improved inference performance, with up to 37% reduction in latency and 44% improvement in throughput, while maintaining competitive accuracy comparable to other recent methods. The proposed model family is suitable for edge devices where compute resource and memory bandwidth are limited, as well as for cloud computing where high throughput is sought after.
DevBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Software Development
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced their coding capabilities. However, existing benchmarks predominantly focused on simplified or isolated aspects of programming, such as single-file code generation or repository issue debugging, falling short of measuring the full spectrum of challenges raised by real-world programming activities. To this end, we propose DevBench, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates LLMs across various stages of the software development lifecycle, including software design, environment setup, implementation, acceptance testing, and unit testing. DevBench features a wide range of programming languages and domains, high-quality data collection, and carefully designed and verified metrics for each task. Empirical studies show that current LLMs, including GPT-4-Turbo, fail to solve the challenges presented within DevBench. Analyses reveal that models struggle with understanding the complex structures in the repository, managing the compilation process, and grasping advanced programming concepts. Our findings offer actionable insights for the future development of LLMs toward real-world programming applications. Our benchmark is available at https://github.com/open-compass/DevBench
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge