Jinxi Guo
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Transducer-Llama: Integrating LLMs into Streamable Transducer-based Speech Recognition
Dec 21, 2024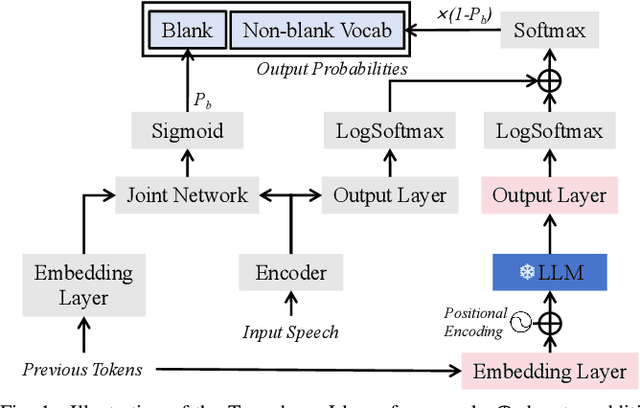
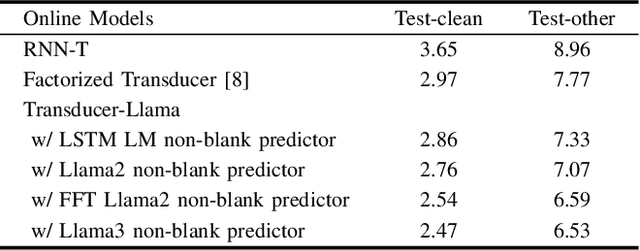
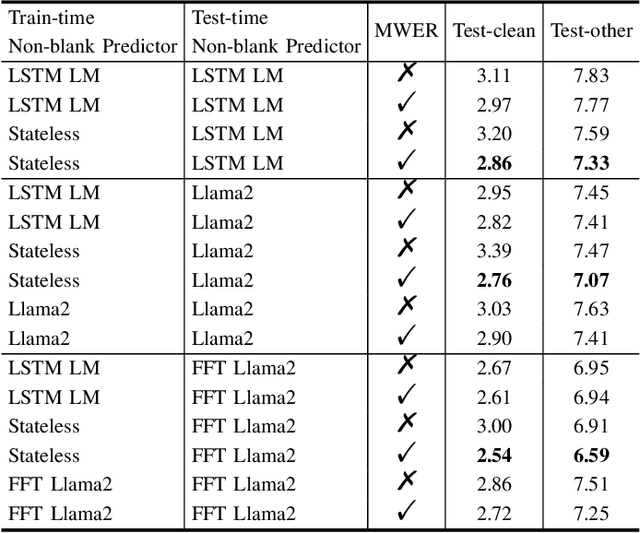
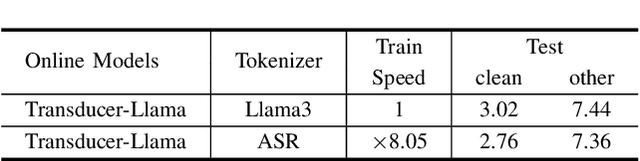
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have been applied to automatic speech recognition (ASR), the task of making the model streamable remains a challenge. This paper proposes a novel model architecture, Transducer-Llama, that integrates LLMs into a Factorized Transducer (FT) model, naturally enabling streaming capabilities. Furthermore, given that the large vocabulary of LLMs can cause data sparsity issue and increased training costs for spoken language systems, this paper introduces an efficient vocabulary adaptation technique to align LLMs with speech system vocabularies. The results show that directly optimizing the FT model with a strong pre-trained LLM-based predictor using the RNN-T loss yields some but limited improvements over a smaller pre-trained LM predictor. Therefore, this paper proposes a weak-to-strong LM swap strategy, using a weak LM predictor during RNN-T loss training and then replacing it with a strong LLM. After LM replacement, the minimum word error rate (MWER) loss is employed to finetune the integration of the LLM predictor with the Transducer-Llama model. Experiments on the LibriSpeech and large-scale multi-lingual LibriSpeech corpora show that the proposed streaming Transducer-Llama approach gave a 17% relative WER reduction (WERR) over a strong FT baseline and a 32% WERR over an RNN-T baseline.
Towards scalable efficient on-device ASR with transfer learning
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Multilingual pretraining for transfer learning significantly boosts the robustness of low-resource monolingual ASR models. This study systematically investigates three main aspects: (a) the impact of transfer learning on model performance during initial training or fine-tuning, (b) the influence of transfer learning across dataset domains and languages, and (c) the effect on rare-word recognition compared to non-rare words. Our finding suggests that RNNT-loss pretraining, followed by monolingual fine-tuning with Minimum Word Error Rate (MinWER) loss, consistently reduces Word Error Rates (WER) across languages like Italian and French. WER Reductions (WERR) reach 36.2% and 42.8% compared to monolingual baselines for MLS and in-house datasets. Out-of-domain pretraining leads to 28% higher WERR than in-domain pretraining. Both rare and non-rare words benefit, with rare words showing greater improvements with out-of-domain pretraining, and non-rare words with in-domain pretraining.
Effective internal language model training and fusion for factorized transducer model
Apr 02, 2024


Abstract:The internal language model (ILM) of the neural transducer has been widely studied. In most prior work, it is mainly used for estimating the ILM score and is subsequently subtracted during inference to facilitate improved integration with external language models. Recently, various of factorized transducer models have been proposed, which explicitly embrace a standalone internal language model for non-blank token prediction. However, even with the adoption of factorized transducer models, limited improvement has been observed compared to shallow fusion. In this paper, we propose a novel ILM training and decoding strategy for factorized transducer models, which effectively combines the blank, acoustic and ILM scores. Our experiments show a 17% relative improvement over the standard decoding method when utilizing a well-trained ILM and the proposed decoding strategy on LibriSpeech datasets. Furthermore, when compared to a strong RNN-T baseline enhanced with external LM fusion, the proposed model yields a 5.5% relative improvement on general-sets and an 8.9% WER reduction for rare words. The proposed model can achieve superior performance without relying on external language models, rendering it highly efficient for production use-cases. To further improve the performance, we propose a novel and memory-efficient ILM-fusion-aware minimum word error rate (MWER) training method which improves ILM integration significantly.
Dynamic ASR Pathways: An Adaptive Masking Approach Towards Efficient Pruning of A Multilingual ASR Model
Sep 22, 2023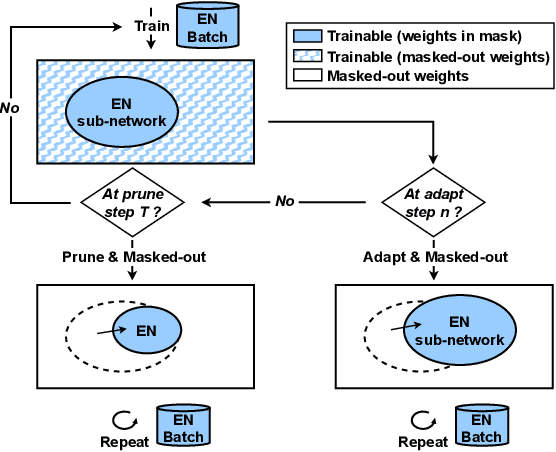



Abstract:Neural network pruning offers an effective method for compressing a multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) model with minimal performance loss. However, it entails several rounds of pruning and re-training needed to be run for each language. In this work, we propose the use of an adaptive masking approach in two scenarios for pruning a multilingual ASR model efficiently, each resulting in sparse monolingual models or a sparse multilingual model (named as Dynamic ASR Pathways). Our approach dynamically adapts the sub-network, avoiding premature decisions about a fixed sub-network structure. We show that our approach outperforms existing pruning methods when targeting sparse monolingual models. Further, we illustrate that Dynamic ASR Pathways jointly discovers and trains better sub-networks (pathways) of a single multilingual model by adapting from different sub-network initializations, thereby reducing the need for language-specific pruning.
Prompting Large Language Models with Speech Recognition Abilities
Jul 21, 2023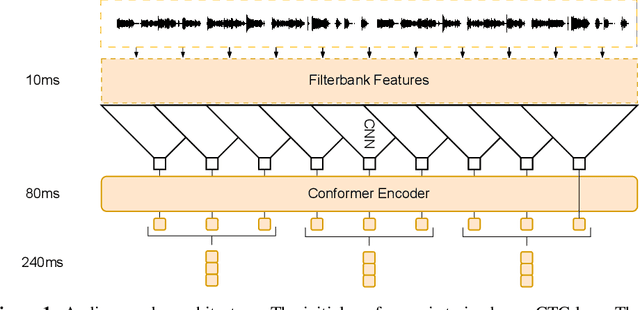
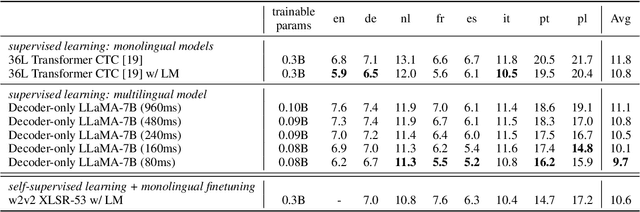
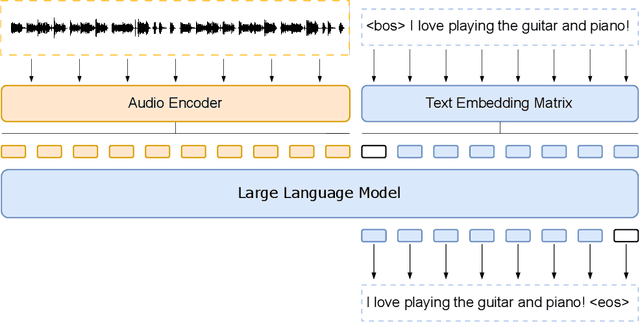
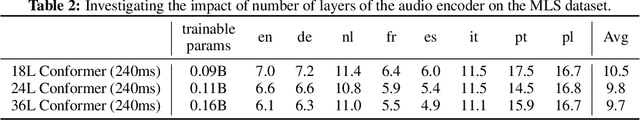
Abstract:Large language models have proven themselves highly flexible, able to solve a wide range of generative tasks, such as abstractive summarization and open-ended question answering. In this paper we extend the capabilities of LLMs by directly attaching a small audio encoder allowing it to perform speech recognition. By directly prepending a sequence of audial embeddings to the text token embeddings, the LLM can be converted to an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system, and be used in the exact same manner as its textual counterpart. Experiments on Multilingual LibriSpeech (MLS) show that incorporating a conformer encoder into the open sourced LLaMA-7B allows it to outperform monolingual baselines by 18% and perform multilingual speech recognition despite LLaMA being trained overwhelmingly on English text. Furthermore, we perform ablation studies to investigate whether the LLM can be completely frozen during training to maintain its original capabilities, scaling up the audio encoder, and increasing the audio encoder striding to generate fewer embeddings. The results from these studies show that multilingual ASR is possible even when the LLM is frozen or when strides of almost 1 second are used in the audio encoder opening up the possibility for LLMs to operate on long-form audio.
Improving Fast-slow Encoder based Transducer with Streaming Deliberation
Dec 15, 2022Abstract:This paper introduces a fast-slow encoder based transducer with streaming deliberation for end-to-end automatic speech recognition. We aim to improve the recognition accuracy of the fast-slow encoder based transducer while keeping its latency low by integrating a streaming deliberation model. Specifically, the deliberation model leverages partial hypotheses from the streaming fast encoder and implicitly learns to correct recognition errors. We modify the parallel beam search algorithm for fast-slow encoder based transducer to be efficient and compatible with the deliberation model. In addition, the deliberation model is designed to process streaming data. To further improve the deliberation performance, a simple text augmentation approach is explored. We also compare LSTM and Conformer models for encoding partial hypotheses. Experiments on Librispeech and in-house data show relative WER reductions (WERRs) from 3% to 5% with a slight increase in model size and negligible extra token emission latency compared with fast-slow encoder based transducer. Compared with vanilla neural transducers, the proposed deliberation model together with fast-slow encoder based transducer obtains relative 10-11% WERRs on Librispeech and around relative 6% WERR on in-house data with smaller emission delays.
Biased Self-supervised learning for ASR
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:Self-supervised learning via masked prediction pre-training (MPPT) has shown impressive performance on a range of speech-processing tasks. This paper proposes a method to bias self-supervised learning towards a specific task. The core idea is to slightly finetune the model that is used to obtain the target sequence. This leads to better performance and a substantial increase in training speed. Furthermore, this paper proposes a variant of MPPT that allows low-footprint streaming models to be trained effectively by computing the MPPT loss on masked and unmasked frames. These approaches are evaluated for automatic speech recognition on the Librispeech corpus, where 100 hours of data served as the labelled data and 860 hours as the unlabelled data. The biased training outperforms the unbiased training by 15.5% after 250k updates and 23.8% after 100k updates on test-other. For the streaming models, the pre-training approach yields a reduction in word error rate of 44.1%.
VADOI:Voice-Activity-Detection Overlapping Inference For End-to-end Long-form Speech Recognition
Feb 22, 2022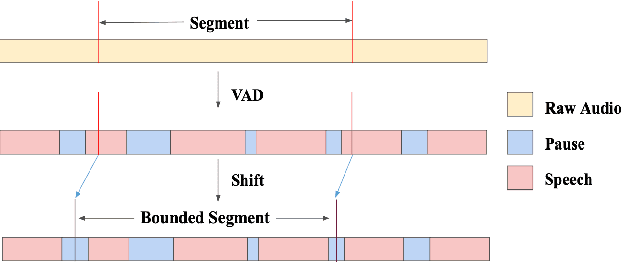
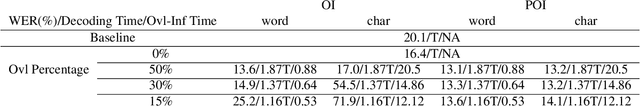
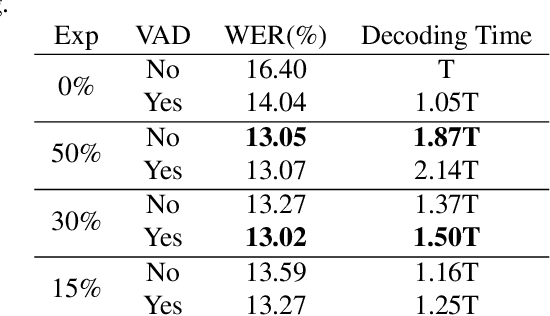
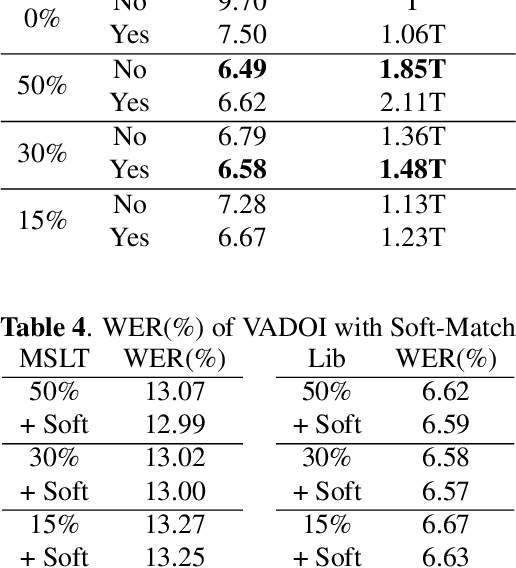
Abstract:While end-to-end models have shown great success on the Automatic Speech Recognition task, performance degrades severely when target sentences are long-form. The previous proposed methods, (partial) overlapping inference are shown to be effective on long-form decoding. For both methods, word error rate (WER) decreases monotonically when overlapping percentage decreases. Setting aside computational cost, the setup with 50% overlapping during inference can achieve the best performance. However, a lower overlapping percentage has an advantage of fast inference speed. In this paper, we first conduct comprehensive experiments comparing overlapping inference and partial overlapping inference with various configurations. We then propose Voice-Activity-Detection Overlapping Inference to provide a trade-off between WER and computation cost. Results show that the proposed method can achieve a 20% relative computation cost reduction on Librispeech and Microsoft Speech Language Translation long-form corpus while maintaining the WER performance when comparing to the best performing overlapping inference algorithm. We also propose Soft-Match to compensate for similar words mis-aligned problem.
REDAT: Accent-Invariant Representation for End-to-End ASR by Domain Adversarial Training with Relabeling
Dec 14, 2020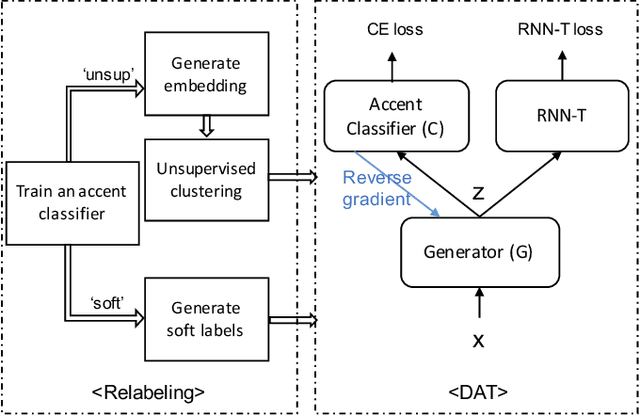
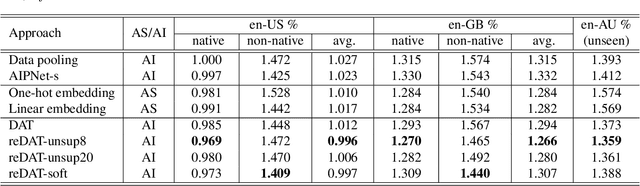
Abstract:Accents mismatching is a critical problem for end-to-end ASR. This paper aims to address this problem by building an accent-robust RNN-T system with domain adversarial training (DAT). We unveil the magic behind DAT and provide, for the first time, a theoretical guarantee that DAT learns accent-invariant representations. We also prove that performing the gradient reversal in DAT is equivalent to minimizing the Jensen-Shannon divergence between domain output distributions. Motivated by the proof of equivalence, we introduce reDAT, a novel technique based on DAT, which relabels data using either unsupervised clustering or soft labels. Experiments on 23K hours of multi-accent data show that DAT achieves competitive results over accent-specific baselines on both native and non-native English accents but up to 13% relative WER reduction on unseen accents; our reDAT yields further improvements over DAT by 3% and 8% relatively on non-native accents of American and British English.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge