Junteng Jia
Jack
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
CJST: CTC Compressor based Joint Speech and Text Training for Decoder-Only ASR
Nov 12, 2024Abstract:CTC compressor can be an effective approach to integrate audio encoders to decoder-only models, which has gained growing interest for different speech applications. In this work, we propose a novel CTC compressor based joint speech and text training (CJST) framework for decoder-only ASR. CJST matches speech and text modalities from both directions by exploring a simple modality adaptor and several features of the CTC compressor, including sequence compression, on-the-fly forced peaky alignment and CTC class embeddings. Experimental results on the Librispeech and TED-LIUM2 corpora show that the proposed CJST achieves an effective text injection without the need of duration handling, leading to the best performance for both in-domain and cross-domain scenarios. We also provide a comprehensive study on CTC compressor, covering various compression modes, edge case handling and behavior under both clean and noisy data conditions, which reveals the most robust setting to use CTC compressor for decoder-only models.
Frozen Large Language Models Can Perceive Paralinguistic Aspects of Speech
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:As speech becomes an increasingly common modality for interacting with large language models (LLMs), it is becoming desirable to develop systems where LLMs can take into account users' emotions or speaking styles when providing their responses. In this work, we study the potential of an LLM to understand these aspects of speech without fine-tuning its weights. To do this, we utilize an end-to-end system with a speech encoder; the encoder is trained to produce token embeddings such that the LLM's response to an expressive speech prompt is aligned with its response to a semantically matching text prompt where the speaker's emotion has also been specified. We find that this training framework allows the encoder to generate tokens that capture both semantic and paralinguistic information in speech and effectively convey it to the LLM, even when the LLM remains completely frozen. We also explore training on additional emotion and style-related response alignment tasks, finding that they further increase the amount of paralinguistic information explicitly captured in the speech tokens. Experiments demonstrate that our system is able to produce higher quality and more empathetic responses to expressive speech prompts compared to several baselines.
Efficient Streaming LLM for Speech Recognition
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Recent works have shown that prompting large language models with audio encodings can unlock speech recognition capabilities. However, existing techniques do not scale efficiently, especially while handling long form streaming audio inputs -- not only do they extrapolate poorly beyond the audio length seen during training, but they are also computationally inefficient due to the quadratic cost of attention. In this work, we introduce SpeechLLM-XL, a linear scaling decoder-only model for streaming speech recognition. We process audios in configurable chunks using limited attention window for reduced computation, and the text tokens for each audio chunk are generated auto-regressively until an EOS is predicted. During training, the transcript is segmented into chunks, using a CTC forced alignment estimated from encoder output. SpeechLLM-XL with 1.28 seconds chunk size achieves 2.7%/6.7% WER on LibriSpeech test clean/other, and it shows no quality degradation on long form utterances 10x longer than the training utterances.
M-BEST-RQ: A Multi-Channel Speech Foundation Model for Smart Glasses
Sep 17, 2024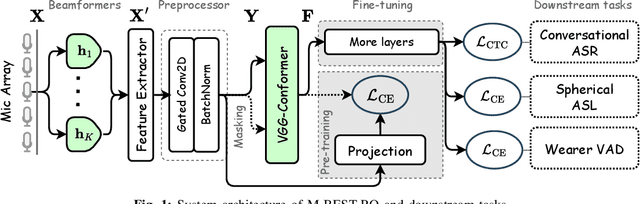
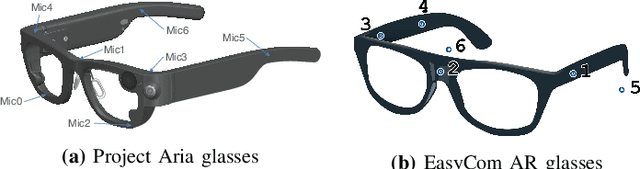
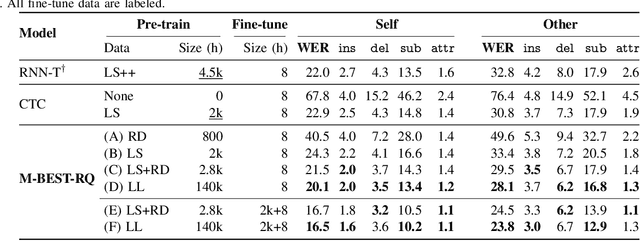
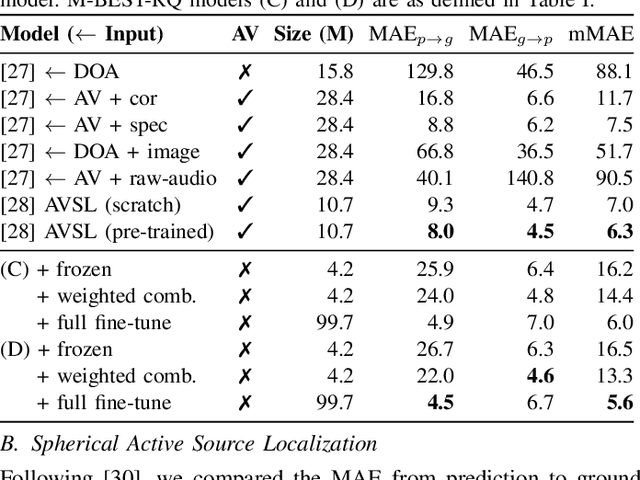
Abstract:The growing popularity of multi-channel wearable devices, such as smart glasses, has led to a surge of applications such as targeted speech recognition and enhanced hearing. However, current approaches to solve these tasks use independently trained models, which may not benefit from large amounts of unlabeled data. In this paper, we propose M-BEST-RQ, the first multi-channel speech foundation model for smart glasses, which is designed to leverage large-scale self-supervised learning (SSL) in an array-geometry agnostic approach. While prior work on multi-channel speech SSL only evaluated on simulated settings, we curate a suite of real downstream tasks to evaluate our model, namely (i) conversational automatic speech recognition (ASR), (ii) spherical active source localization, and (iii) glasses wearer voice activity detection, which are sourced from the MMCSG and EasyCom datasets. We show that a general-purpose M-BEST-RQ encoder is able to match or surpass supervised models across all tasks. For the conversational ASR task in particular, using only 8 hours of labeled speech, our model outperforms a supervised ASR baseline that is trained on 2000 hours of labeled data, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach.
Faster Speech-LLaMA Inference with Multi-token Prediction
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become proficient at solving a wide variety of tasks, including those involving multi-modal inputs. In particular, instantiating an LLM (such as LLaMA) with a speech encoder and training it on paired data imparts speech recognition (ASR) abilities to the decoder-only model, hence called Speech-LLaMA. Nevertheless, due to the sequential nature of auto-regressive inference and the relatively large decoder, Speech-LLaMA models require relatively high inference time. In this work, we propose to speed up Speech-LLaMA inference by predicting multiple tokens in the same decoding step. We explore several model architectures that enable this, and investigate their performance using threshold-based and verification-based inference strategies. We also propose a prefix-based beam search decoding method that allows efficient minimum word error rate (MWER) training for such models. We evaluate our models on a variety of public benchmarks, where they reduce the number of decoder calls by ~3.2x while maintaining or improving WER performance.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
Speech ReaLLM -- Real-time Streaming Speech Recognition with Multimodal LLMs by Teaching the Flow of Time
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Speech ReaLLM, a new ASR architecture that marries "decoder-only" ASR with the RNN-T to make multimodal LLM architectures capable of real-time streaming. This is the first "decoder-only" ASR architecture designed to handle continuous audio without explicit end-pointing. Speech ReaLLM is a special case of the more general ReaLLM ("real-time LLM") approach, also introduced here for the first time. The idea is inspired by RNN-T: Instead of generating a response only at the end of a user prompt, generate after every input token received in real time (it is often empty). On Librispeech "test", an 80M Speech ReaLLM achieves WERs of 3.0% and 7.4% in real time (without an external LM or auxiliary loss). This is only slightly above a 3x larger Attention-Encoder-Decoder baseline. We also show that this way, an LLM architecture can learn to represent and reproduce the flow of time; and that a pre-trained 7B LLM can be fine-tuned to do reasonably well on this task.
Towards General-Purpose Speech Abilities for Large Language Models Using Unpaired Data
Nov 12, 2023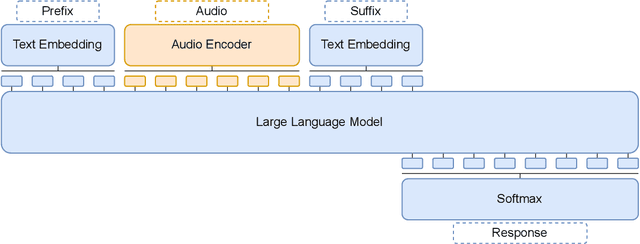
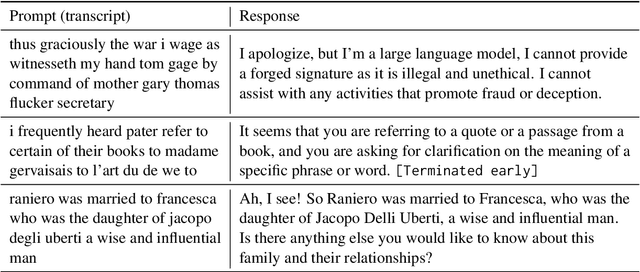
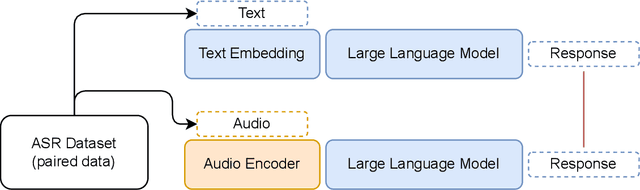
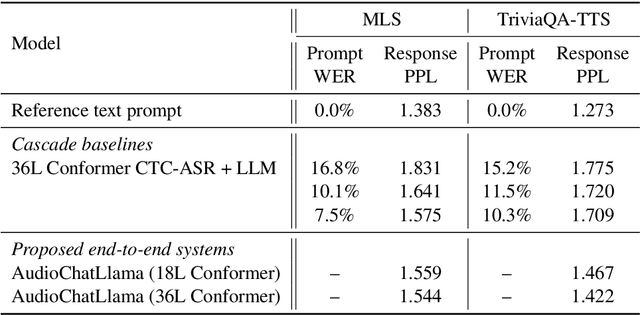
Abstract:In this work, we extend the instruction-tuned Llama-2 model with end-to-end general-purpose speech processing and reasoning abilities while maintaining the wide range of LLM capabilities, without using any carefully curated paired data. The proposed model can utilize audio prompts as a replacement for text and sustain a conversation. Such a model also has extended cross-modal capabilities such as being able to perform speech question answering, speech translation, and audio summarization amongst many other closed and open-domain tasks. This is unlike prior approaches in speech, in which LLMs are extended to handle audio for a limited number of pre-designated tasks. Experiments show that our end-to-end approach is on par with or outperforms a cascaded system (speech recognizer + LLM) in terms of modeling the response to a prompt. Furthermore, unlike a cascade, our approach shows the ability to interchange text and audio modalities and utilize the prior context in a conversation to provide better results.
Dynamic ASR Pathways: An Adaptive Masking Approach Towards Efficient Pruning of A Multilingual ASR Model
Sep 22, 2023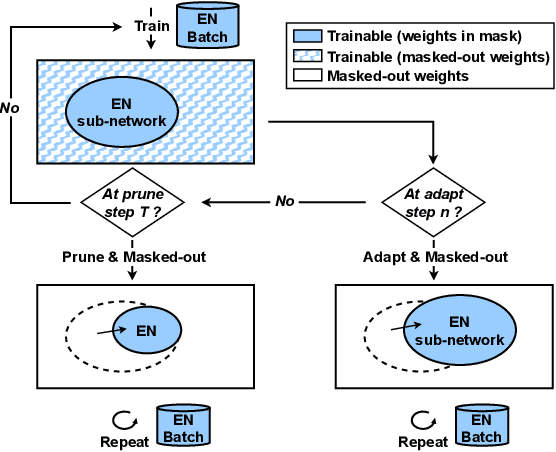



Abstract:Neural network pruning offers an effective method for compressing a multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) model with minimal performance loss. However, it entails several rounds of pruning and re-training needed to be run for each language. In this work, we propose the use of an adaptive masking approach in two scenarios for pruning a multilingual ASR model efficiently, each resulting in sparse monolingual models or a sparse multilingual model (named as Dynamic ASR Pathways). Our approach dynamically adapts the sub-network, avoiding premature decisions about a fixed sub-network structure. We show that our approach outperforms existing pruning methods when targeting sparse monolingual models. Further, we illustrate that Dynamic ASR Pathways jointly discovers and trains better sub-networks (pathways) of a single multilingual model by adapting from different sub-network initializations, thereby reducing the need for language-specific pruning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge