Jingfei Du
Coarse-to-Fine Contrastive Learning in Image-Text-Graph Space for Improved Vision-Language Compositionality
May 23, 2023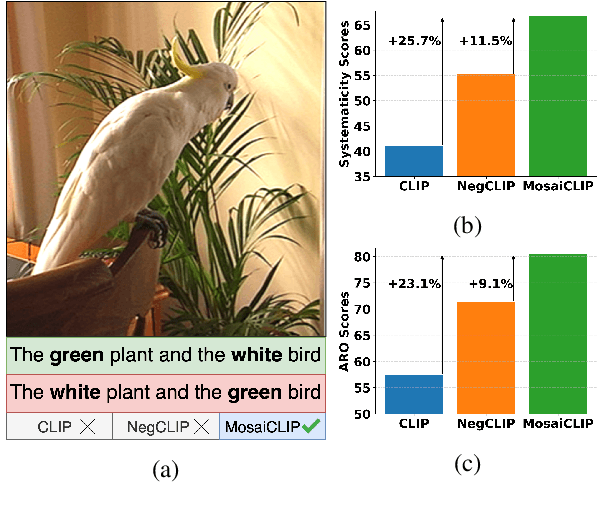



Abstract:Contrastively trained vision-language models have achieved remarkable progress in vision and language representation learning, leading to state-of-the-art models for various downstream multimodal tasks. However, recent research has highlighted severe limitations of these models in their ability to perform compositional reasoning over objects, attributes, and relations. Scene graphs have emerged as an effective way to understand images compositionally. These are graph-structured semantic representations of images that contain objects, their attributes, and relations with other objects in a scene. In this work, we consider the scene graph parsed from text as a proxy for the image scene graph and propose a graph decomposition and augmentation framework along with a coarse-to-fine contrastive learning objective between images and text that aligns sentences of various complexities to the same image. Along with this, we propose novel negative mining techniques in the scene graph space for improving attribute binding and relation understanding. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach that significantly improves attribute binding, relation understanding, systematic generalization, and productivity on multiple recently proposed benchmarks (For example, improvements upto $18\%$ for systematic generalization, $16.5\%$ for relation understanding over a strong baseline), while achieving similar or better performance than CLIP on various general multimodal tasks.
Speech-to-Speech Translation For A Real-world Unwritten Language
Nov 11, 2022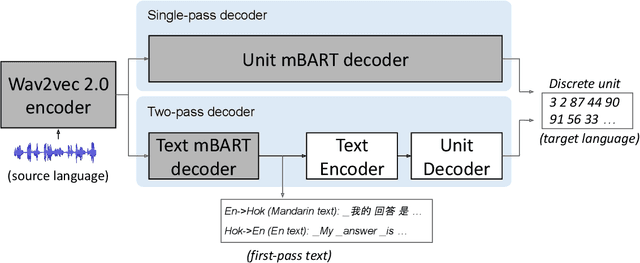
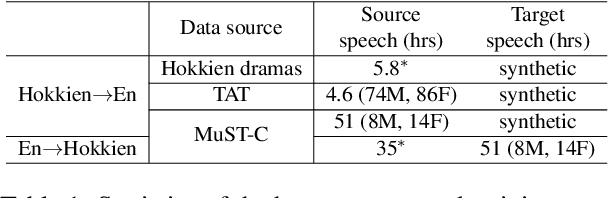
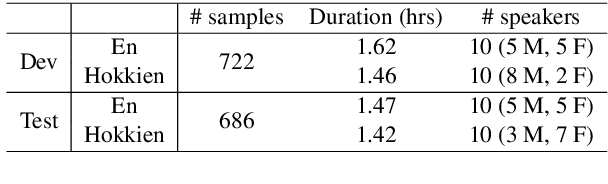
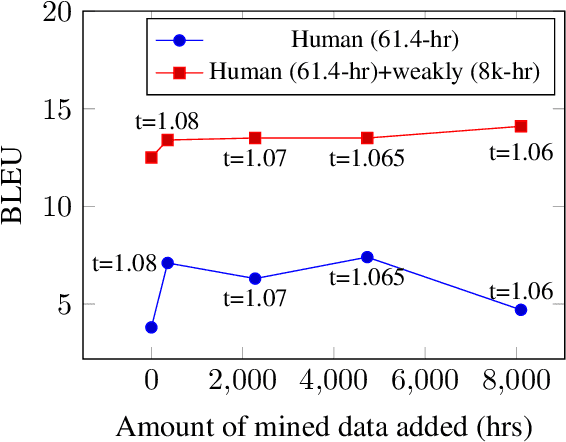
Abstract:We study speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) that translates speech from one language into another language and focuses on building systems to support languages without standard text writing systems. We use English-Taiwanese Hokkien as a case study, and present an end-to-end solution from training data collection, modeling choices to benchmark dataset release. First, we present efforts on creating human annotated data, automatically mining data from large unlabeled speech datasets, and adopting pseudo-labeling to produce weakly supervised data. On the modeling, we take advantage of recent advances in applying self-supervised discrete representations as target for prediction in S2ST and show the effectiveness of leveraging additional text supervision from Mandarin, a language similar to Hokkien, in model training. Finally, we release an S2ST benchmark set to facilitate future research in this field. The demo can be found at https://huggingface.co/spaces/facebook/Hokkien_Translation .
SpeechMatrix: A Large-Scale Mined Corpus of Multilingual Speech-to-Speech Translations
Nov 08, 2022


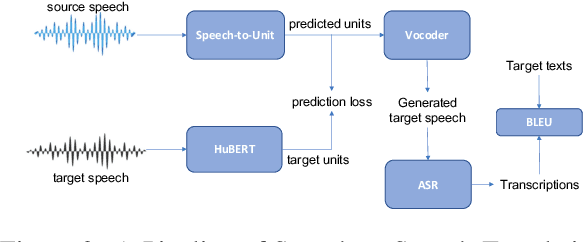
Abstract:We present SpeechMatrix, a large-scale multilingual corpus of speech-to-speech translations mined from real speech of European Parliament recordings. It contains speech alignments in 136 language pairs with a total of 418 thousand hours of speech. To evaluate the quality of this parallel speech, we train bilingual speech-to-speech translation models on mined data only and establish extensive baseline results on EuroParl-ST, VoxPopuli and FLEURS test sets. Enabled by the multilinguality of SpeechMatrix, we also explore multilingual speech-to-speech translation, a topic which was addressed by few other works. We also demonstrate that model pre-training and sparse scaling using Mixture-of-Experts bring large gains to translation performance. The mined data and models are freely available.
Prompting ELECTRA: Few-Shot Learning with Discriminative Pre-Trained Models
Jun 08, 2022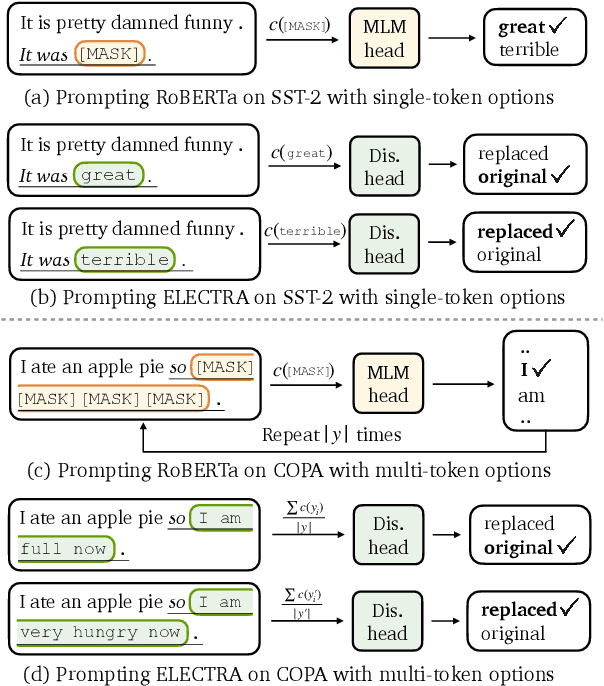
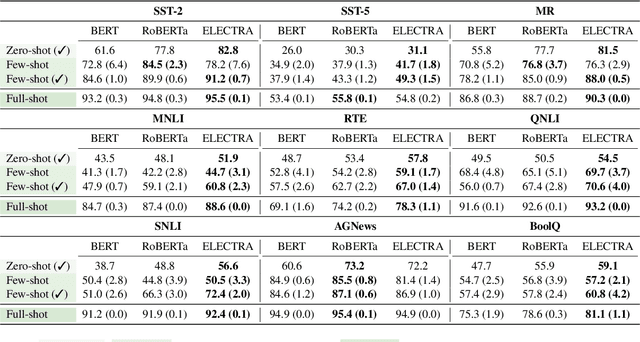
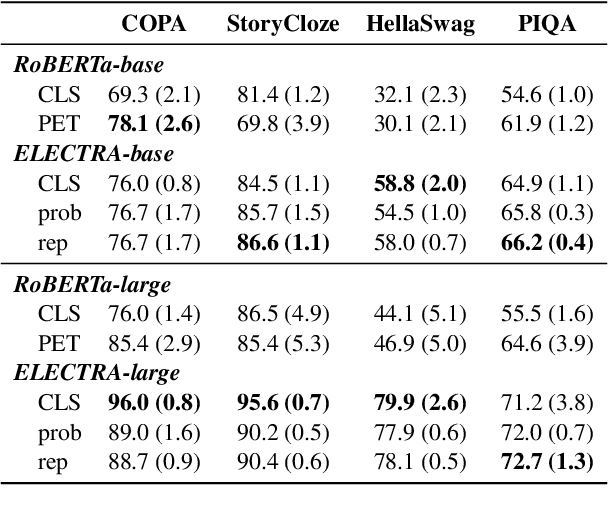
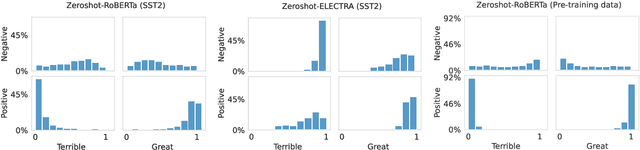
Abstract:Pre-trained masked language models successfully perform few-shot learning by formulating downstream tasks as text infilling. However, as a strong alternative in full-shot settings, discriminative pre-trained models like ELECTRA do not fit into the paradigm. In this work, we adapt prompt-based few-shot learning to ELECTRA and show that it outperforms masked language models in a wide range of tasks. ELECTRA is pre-trained to distinguish if a token is generated or original. We naturally extend that to prompt-based few-shot learning by training to score the originality of the target options without introducing new parameters. Our method can be easily adapted to tasks involving multi-token predictions without extra computation overhead. Analysis shows that ELECTRA learns distributions that align better with downstream tasks.
On the Role of Bidirectionality in Language Model Pre-Training
May 24, 2022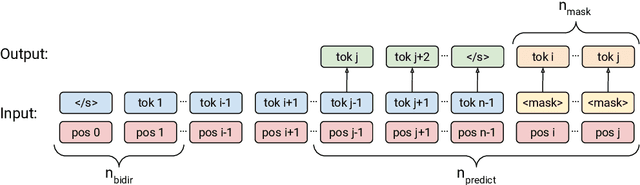
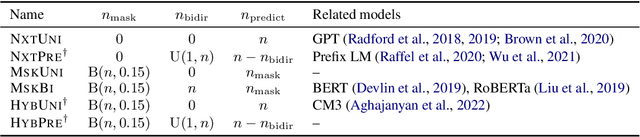
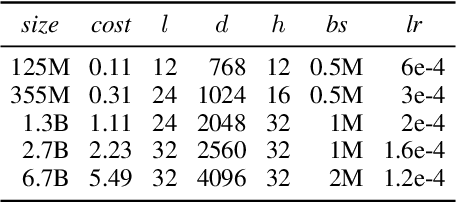
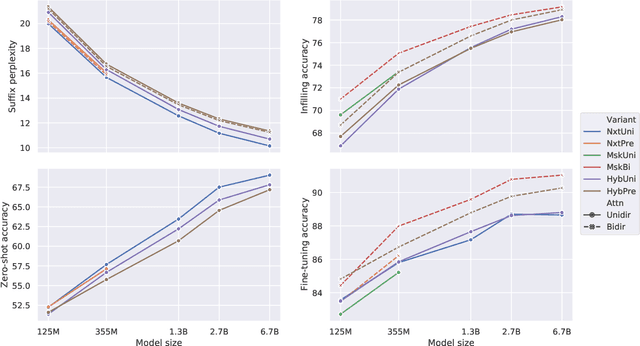
Abstract:Prior work on language model pre-training has explored different architectures and learning objectives, but differences in data, hyperparameters and evaluation make a principled comparison difficult. In this work, we focus on bidirectionality as a key factor that differentiates existing approaches, and present a comprehensive study of its role in next token prediction, text infilling, zero-shot priming and fine-tuning. We propose a new framework that generalizes prior approaches, including fully unidirectional models like GPT, fully bidirectional models like BERT, and hybrid models like CM3 and prefix LM. Our framework distinguishes between two notions of bidirectionality (bidirectional context and bidirectional attention) and allows us to control each of them separately. We find that the optimal configuration is largely application-dependent (e.g., bidirectional attention is beneficial for fine-tuning and infilling, but harmful for next token prediction and zero-shot priming). We train models with up to 6.7B parameters, and find differences to remain consistent at scale. While prior work on scaling has focused on left-to-right autoregressive models, our results suggest that this approach comes with some trade-offs, and it might be worthwhile to develop very large bidirectional models.
Improving In-Context Few-Shot Learning via Self-Supervised Training
May 03, 2022

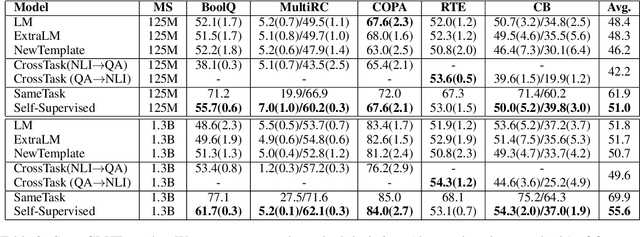

Abstract:Self-supervised pretraining has made few-shot learning possible for many NLP tasks. But the pretraining objectives are not typically adapted specifically for in-context few-shot learning. In this paper, we propose to use self-supervision in an intermediate training stage between pretraining and downstream few-shot usage with the goal to teach the model to perform in-context few shot learning. We propose and evaluate four self-supervised objectives on two benchmarks. We find that the intermediate self-supervision stage produces models that outperform strong baselines. Ablation study shows that several factors affect the downstream performance, such as the amount of training data and the diversity of the self-supervised objectives. Human-annotated cross-task supervision and self-supervision are complementary. Qualitative analysis suggests that the self-supervised-trained models are better at following task requirements.
Efficient Large Scale Language Modeling with Mixtures of Experts
Dec 20, 2021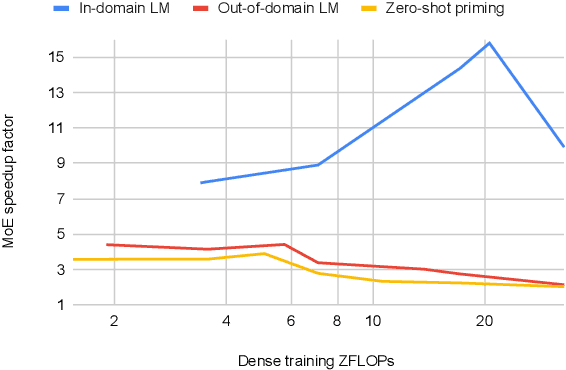
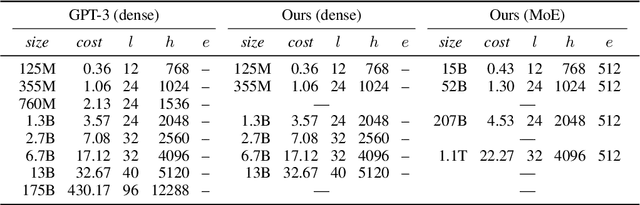
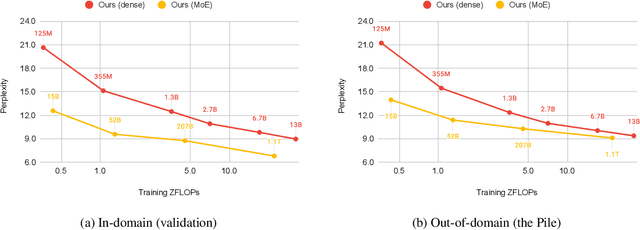
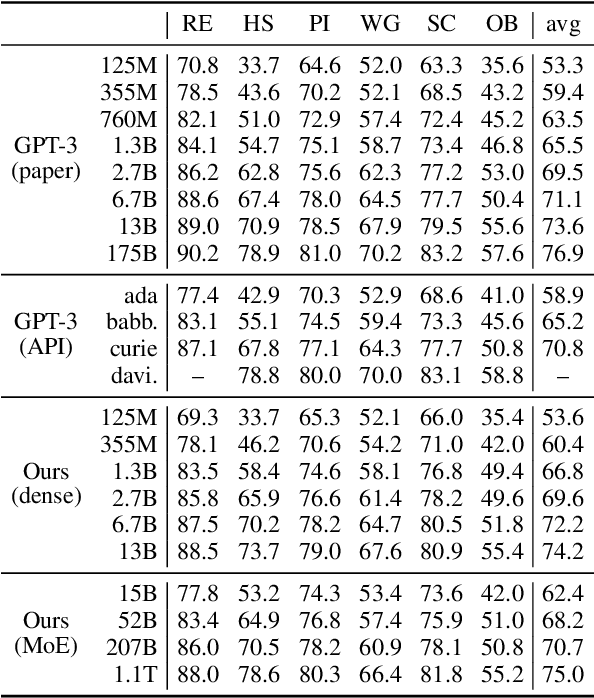
Abstract:Mixture of Experts layers (MoEs) enable efficient scaling of language models through conditional computation. This paper presents a detailed empirical study of how autoregressive MoE language models scale in comparison with dense models in a wide range of settings: in- and out-of-domain language modeling, zero- and few-shot priming, and full fine-tuning. With the exception of fine-tuning, we find MoEs to be substantially more compute efficient. At more modest training budgets, MoEs can match the performance of dense models using $\sim$4 times less compute. This gap narrows at scale, but our largest MoE model (1.1T parameters) consistently outperforms a compute-equivalent dense model (6.7B parameters). Overall, this performance gap varies greatly across tasks and domains, suggesting that MoE and dense models generalize differently in ways that are worthy of future study. We make our code and models publicly available for research use.
Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models
Dec 20, 2021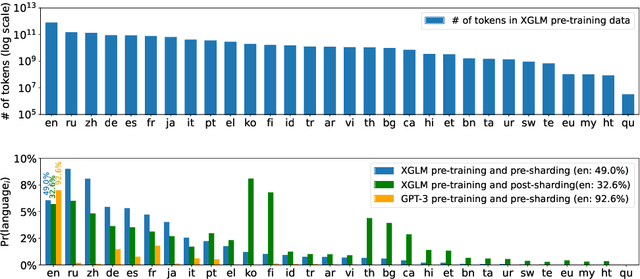
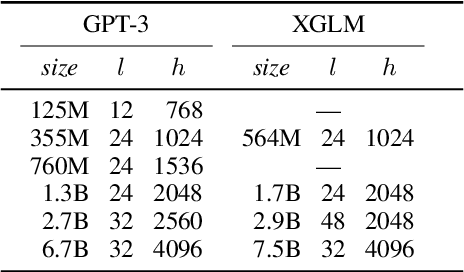
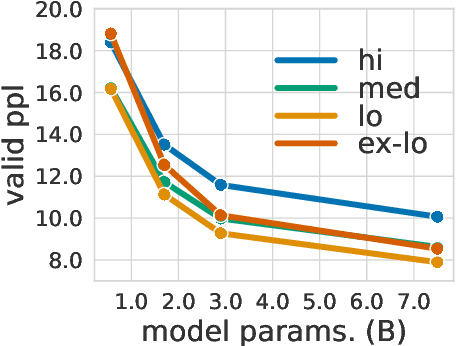

Abstract:Large-scale autoregressive language models such as GPT-3 are few-shot learners that can perform a wide range of language tasks without fine-tuning. While these models are known to be able to jointly represent many different languages, their training data is dominated by English, potentially limiting their cross-lingual generalization. In this work, we train multilingual autoregressive language models on a balanced corpus covering a diverse set of languages, and study their few- and zero-shot learning capabilities in a wide range of tasks. Our largest model with 7.5 billion parameters sets new state of the art in few-shot learning in more than 20 representative languages, outperforming GPT-3 of comparable size in multilingual commonsense reasoning (with +7.4% absolute accuracy improvement in 0-shot settings and +9.4% in 4-shot settings) and natural language inference (+5.4% in each of 0-shot and 4-shot settings). On the FLORES-101 machine translation benchmark, our model outperforms GPT-3 on 171 out of 182 translation directions with 32 training examples, while surpassing the official supervised baseline in 45 directions. We present a detailed analysis of where the model succeeds and fails, showing in particular that it enables cross-lingual in-context learning on some tasks, while there is still room for improvement on surface form robustness and adaptation to tasks that do not have a natural cloze form. Finally, we evaluate our models in social value tasks such as hate speech detection in five languages and find it has limitations similar to comparable sized GPT-3 models.
Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling
May 02, 2021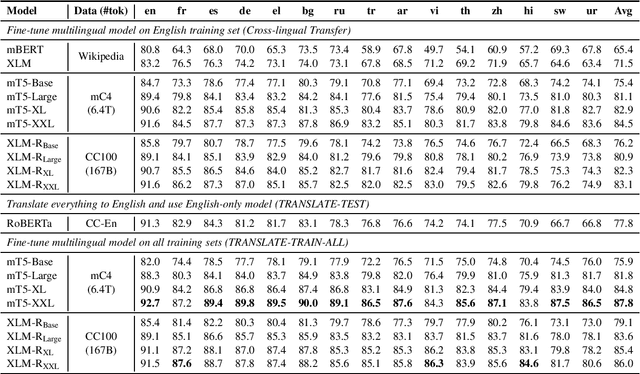
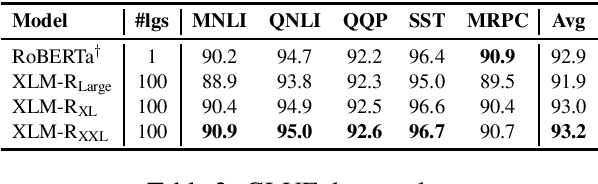
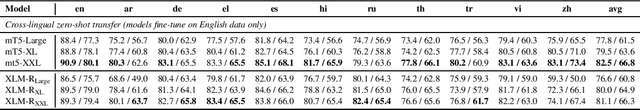
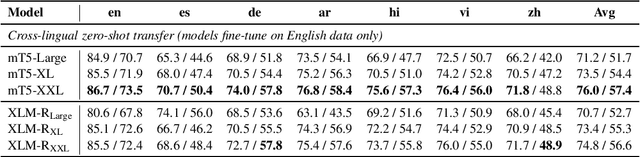
Abstract:Recent work has demonstrated the effectiveness of cross-lingual language model pretraining for cross-lingual understanding. In this study, we present the results of two larger multilingual masked language models, with 3.5B and 10.7B parameters. Our two new models dubbed XLM-R XL and XLM-R XXL outperform XLM-R by 1.8% and 2.4% average accuracy on XNLI. Our model also outperforms the RoBERTa-Large model on several English tasks of the GLUE benchmark by 0.3% on average while handling 99 more languages. This suggests pretrained models with larger capacity may obtain both strong performance on high-resource languages while greatly improving low-resource languages. We make our code and models publicly available.
Supervised Contrastive Learning for Pre-trained Language Model Fine-tuning
Nov 12, 2020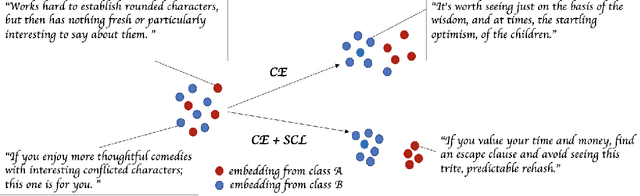

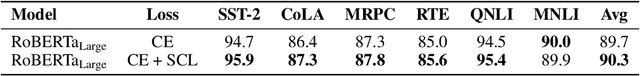
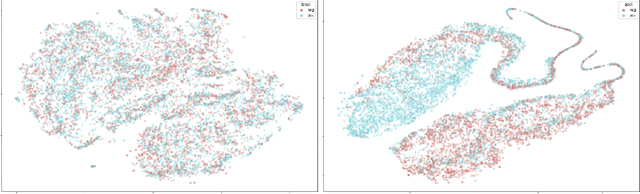
Abstract:State-of-the-art natural language understanding classification models follow two-stages: pre-training a large language model on an auxiliary task, and then fine-tuning the model on a task-specific labeled dataset using cross-entropy loss. Cross-entropy loss has several shortcomings that can lead to sub-optimal generalization and instability. Driven by the intuition that good generalization requires capturing the similarity between examples in one class and contrasting them with examples in other classes, we propose a supervised contrastive learning (SCL) objective for the fine-tuning stage. Combined with cross-entropy, the SCL loss we propose obtains improvements over a strong RoBERTa-Large baseline on multiple datasets of the GLUE benchmark in both the high-data and low-data regimes, and it does not require any specialized architecture, data augmentation of any kind, memory banks, or additional unsupervised data. We also demonstrate that the new objective leads to models that are more robust to different levels of noise in the training data, and can generalize better to related tasks with limited labeled task data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge