Yilin Yang
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Prototype-Driven Multi-Feature Generation for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:The primary challenges in visible-infrared person re-identification arise from the differences between visible (vis) and infrared (ir) images, including inter-modal and intra-modal variations. These challenges are further complicated by varying viewpoints and irregular movements. Existing methods often rely on horizontal partitioning to align part-level features, which can introduce inaccuracies and have limited effectiveness in reducing modality discrepancies. In this paper, we propose a novel Prototype-Driven Multi-feature generation framework (PDM) aimed at mitigating cross-modal discrepancies by constructing diversified features and mining latent semantically similar features for modal alignment. PDM comprises two key components: Multi-Feature Generation Module (MFGM) and Prototype Learning Module (PLM). The MFGM generates diversity features closely distributed from modality-shared features to represent pedestrians. Additionally, the PLM utilizes learnable prototypes to excavate latent semantic similarities among local features between visible and infrared modalities, thereby facilitating cross-modal instance-level alignment. We introduce the cosine heterogeneity loss to enhance prototype diversity for extracting rich local features. Extensive experiments conducted on the SYSU-MM01 and LLCM datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. Our codes are available at https://github.com/mmunhappy/ICASSP2025-PDM.
Language-Informed Beam Search Decoding for Multilingual Machine Translation
Aug 11, 2024Abstract:Beam search decoding is the de-facto method for decoding auto-regressive Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models, including multilingual NMT where the target language is specified as an input. However, decoding multilingual NMT models commonly produces ``off-target'' translations -- yielding translation outputs not in the intended language. In this paper, we first conduct an error analysis of off-target translations for a strong multilingual NMT model and identify how these decodings are produced during beam search. We then propose Language-informed Beam Search (LiBS), a general decoding algorithm incorporating an off-the-shelf Language Identification (LiD) model into beam search decoding to reduce off-target translations. LiBS is an inference-time procedure that is NMT-model agnostic and does not require any additional parallel data. Results show that our proposed LiBS algorithm on average improves +1.1 BLEU and +0.9 BLEU on WMT and OPUS datasets, and reduces off-target rates from 22.9\% to 7.7\% and 65.8\% to 25.3\% respectively.
An Empirical Study of Speech Language Models for Prompt-Conditioned Speech Synthesis
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:Speech language models (LMs) are promising for high-quality speech synthesis through in-context learning. A typical speech LM takes discrete semantic units as content and a short utterance as prompt, and synthesizes speech which preserves the content's semantics but mimics the prompt's style. However, there is no systematic understanding on how the synthesized audio is controlled by the prompt and content. In this work, we conduct an empirical study of the widely used autoregressive (AR) and non-autoregressive (NAR) speech LMs and provide insights into the prompt design and content semantic units. Our analysis reveals that heterogeneous and nonstationary prompts hurt the audio quality in contrast to the previous finding that longer prompts always lead to better synthesis. Moreover, we find that the speaker style of the synthesized audio is also affected by the content in addition to the prompt. We further show that semantic units carry rich acoustic information such as pitch, tempo, volume and speech emphasis, which might be leaked from the content to the synthesized audio.
MSLM-S2ST: A Multitask Speech Language Model for Textless Speech-to-Speech Translation with Speaker Style Preservation
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:There have been emerging research interest and advances in speech-to-speech translation (S2ST), translating utterances from one language to another. This work proposes Multitask Speech Language Model (MSLM), which is a decoder-only speech language model trained in a multitask setting. Without reliance on text training data, our model is able to support multilingual S2ST with speaker style preserved.
Seamless: Multilingual Expressive and Streaming Speech Translation
Dec 08, 2023
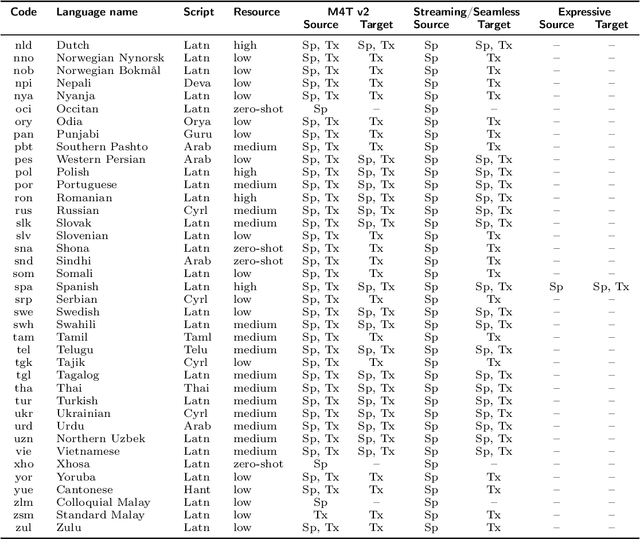
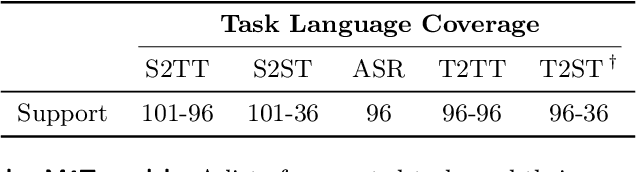
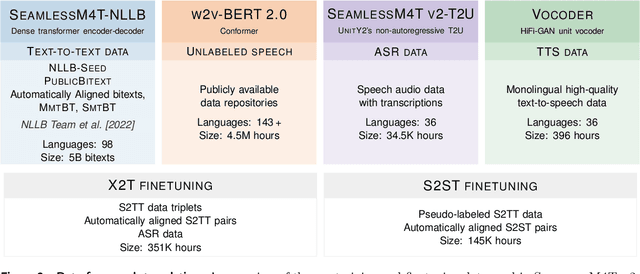
Abstract:Large-scale automatic speech translation systems today lack key features that help machine-mediated communication feel seamless when compared to human-to-human dialogue. In this work, we introduce a family of models that enable end-to-end expressive and multilingual translations in a streaming fashion. First, we contribute an improved version of the massively multilingual and multimodal SeamlessM4T model-SeamlessM4T v2. This newer model, incorporating an updated UnitY2 framework, was trained on more low-resource language data. SeamlessM4T v2 provides the foundation on which our next two models are initiated. SeamlessExpressive enables translation that preserves vocal styles and prosody. Compared to previous efforts in expressive speech research, our work addresses certain underexplored aspects of prosody, such as speech rate and pauses, while also preserving the style of one's voice. As for SeamlessStreaming, our model leverages the Efficient Monotonic Multihead Attention mechanism to generate low-latency target translations without waiting for complete source utterances. As the first of its kind, SeamlessStreaming enables simultaneous speech-to-speech/text translation for multiple source and target languages. To ensure that our models can be used safely and responsibly, we implemented the first known red-teaming effort for multimodal machine translation, a system for the detection and mitigation of added toxicity, a systematic evaluation of gender bias, and an inaudible localized watermarking mechanism designed to dampen the impact of deepfakes. Consequently, we bring major components from SeamlessExpressive and SeamlessStreaming together to form Seamless, the first publicly available system that unlocks expressive cross-lingual communication in real-time. The contributions to this work are publicly released and accessible at https://github.com/facebookresearch/seamless_communication
SeamlessM4T-Massively Multilingual & Multimodal Machine Translation
Aug 23, 2023
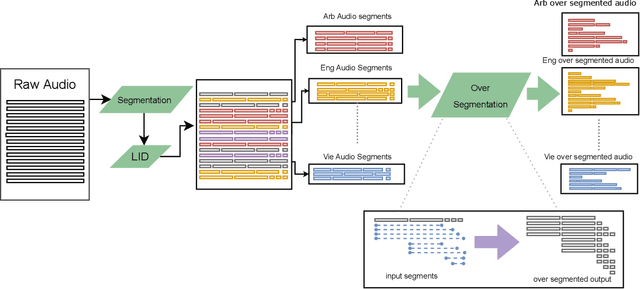
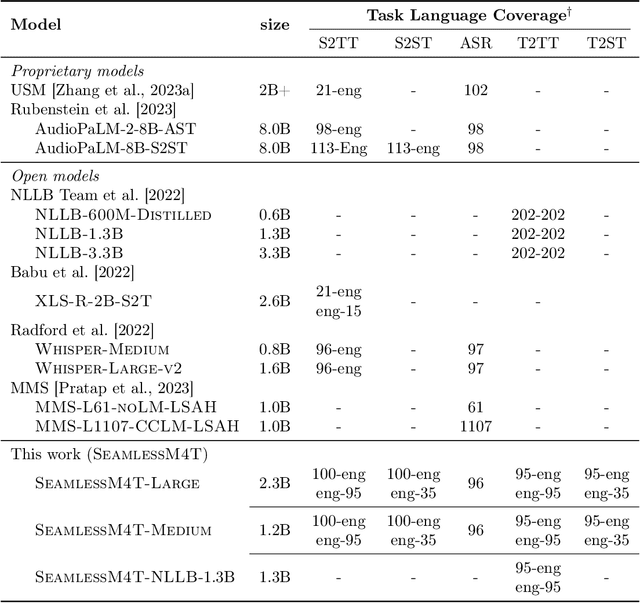
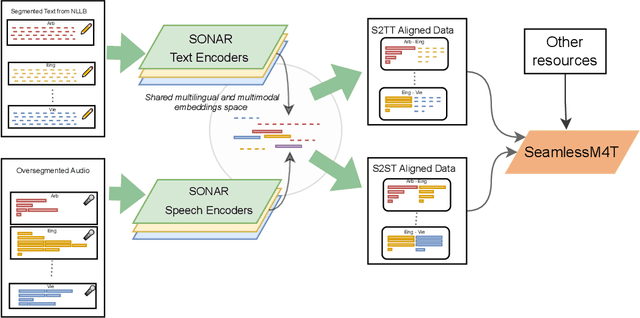
Abstract:What does it take to create the Babel Fish, a tool that can help individuals translate speech between any two languages? While recent breakthroughs in text-based models have pushed machine translation coverage beyond 200 languages, unified speech-to-speech translation models have yet to achieve similar strides. More specifically, conventional speech-to-speech translation systems rely on cascaded systems that perform translation progressively, putting high-performing unified systems out of reach. To address these gaps, we introduce SeamlessM4T, a single model that supports speech-to-speech translation, speech-to-text translation, text-to-speech translation, text-to-text translation, and automatic speech recognition for up to 100 languages. To build this, we used 1 million hours of open speech audio data to learn self-supervised speech representations with w2v-BERT 2.0. Subsequently, we created a multimodal corpus of automatically aligned speech translations. Filtered and combined with human-labeled and pseudo-labeled data, we developed the first multilingual system capable of translating from and into English for both speech and text. On FLEURS, SeamlessM4T sets a new standard for translations into multiple target languages, achieving an improvement of 20% BLEU over the previous SOTA in direct speech-to-text translation. Compared to strong cascaded models, SeamlessM4T improves the quality of into-English translation by 1.3 BLEU points in speech-to-text and by 2.6 ASR-BLEU points in speech-to-speech. Tested for robustness, our system performs better against background noises and speaker variations in speech-to-text tasks compared to the current SOTA model. Critically, we evaluated SeamlessM4T on gender bias and added toxicity to assess translation safety. Finally, all contributions in this work are open-sourced and accessible at https://github.com/facebookresearch/seamless_communication
Differentially Private Neural Tangent Kernels for Privacy-Preserving Data Generation
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Maximum mean discrepancy (MMD) is a particularly useful distance metric for differentially private data generation: when used with finite-dimensional features it allows us to summarize and privatize the data distribution once, which we can repeatedly use during generator training without further privacy loss. An important question in this framework is, then, what features are useful to distinguish between real and synthetic data distributions, and whether those enable us to generate quality synthetic data. This work considers the using the features of $\textit{neural tangent kernels (NTKs)}$, more precisely $\textit{empirical}$ NTKs (e-NTKs). We find that, perhaps surprisingly, the expressiveness of the untrained e-NTK features is comparable to that of the features taken from pre-trained perceptual features using public data. As a result, our method improves the privacy-accuracy trade-off compared to other state-of-the-art methods, without relying on any public data, as demonstrated on several tabular and image benchmark datasets.
Differentiated Federated Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic and Heterogeneous Network
Dec 05, 2022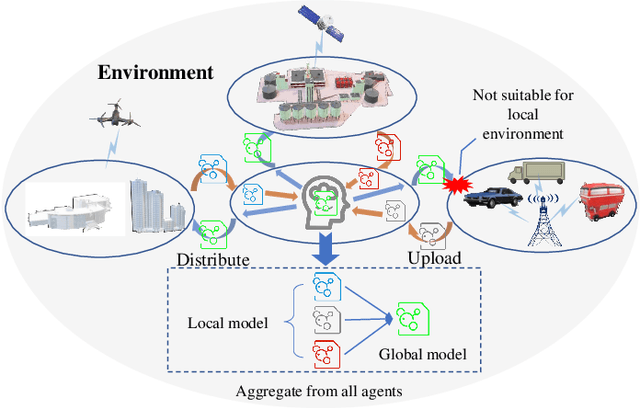
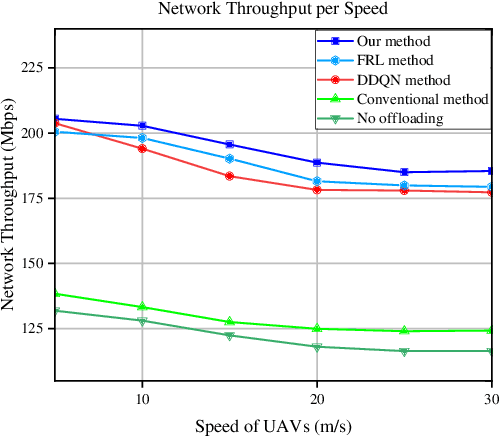
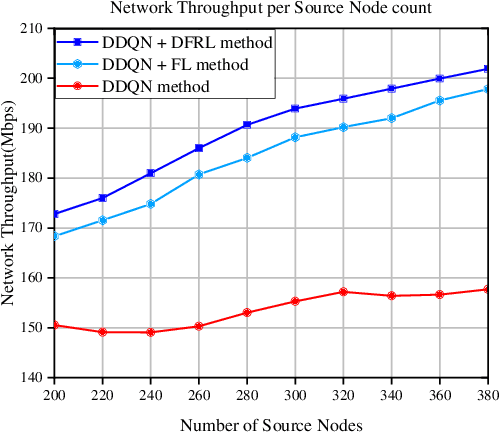
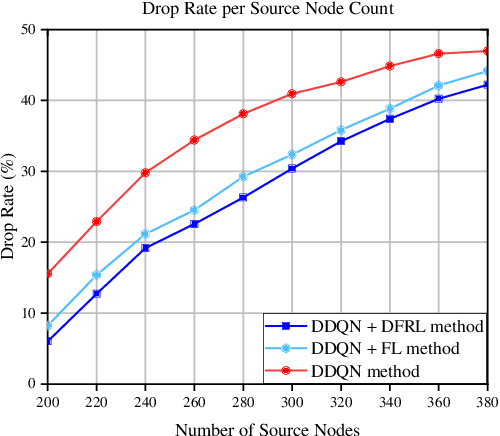
Abstract:The modern dynamic and heterogeneous network brings differential environments with respective state transition probability to agents, which leads to the local strategy trap problem of traditional federated reinforcement learning (FRL) based network optimization algorithm. To solve this problem, we propose a novel Differentiated Federated Reinforcement Learning (DFRL), which evolves the global policy model integration and local inference with the global policy model in traditional FRL to a collaborative learning process with parallel global trends learning and differential local policy model learning. In the DFRL, the local policy learning model is adaptively updated with the global trends model and local environment and achieves better differentiated adaptation. We evaluate the outperformance of the proposal compared with the state-of-the-art FRL in a classical CartPole game with heterogeneous environments. Furthermore, we implement the proposal in the heterogeneous Space-air-ground Integrated Network (SAGIN) for the classical traffic offloading problem in network. The simulation result shows that the proposal shows better global performance and fairness than baselines in terms of throughput, delay, and packet drop rate.
Speech-to-Speech Translation For A Real-world Unwritten Language
Nov 11, 2022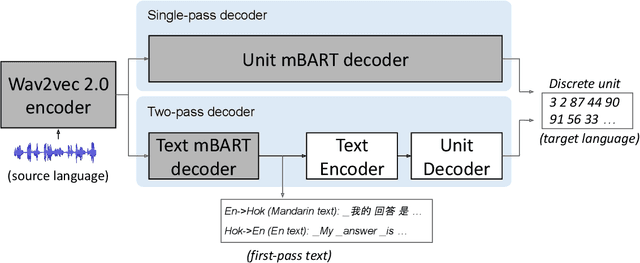
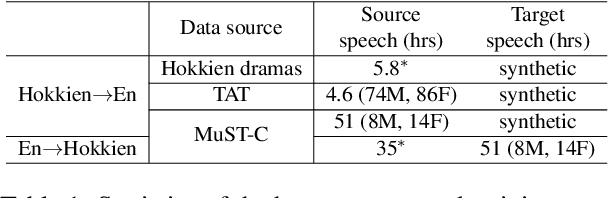
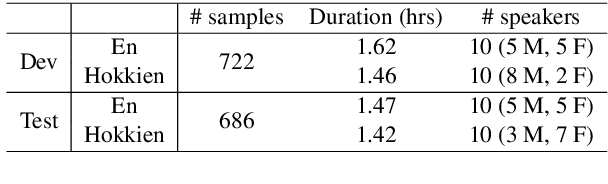
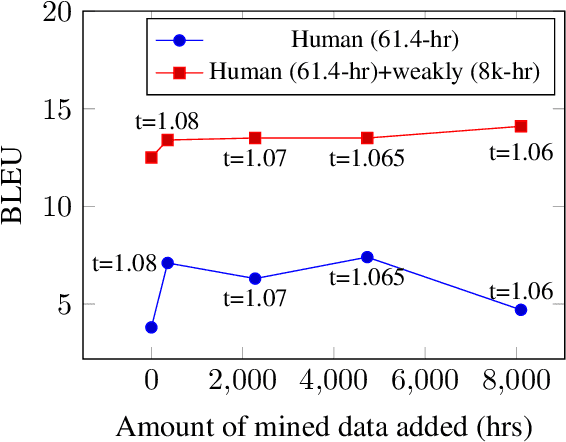
Abstract:We study speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) that translates speech from one language into another language and focuses on building systems to support languages without standard text writing systems. We use English-Taiwanese Hokkien as a case study, and present an end-to-end solution from training data collection, modeling choices to benchmark dataset release. First, we present efforts on creating human annotated data, automatically mining data from large unlabeled speech datasets, and adopting pseudo-labeling to produce weakly supervised data. On the modeling, we take advantage of recent advances in applying self-supervised discrete representations as target for prediction in S2ST and show the effectiveness of leveraging additional text supervision from Mandarin, a language similar to Hokkien, in model training. Finally, we release an S2ST benchmark set to facilitate future research in this field. The demo can be found at https://huggingface.co/spaces/facebook/Hokkien_Translation .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge