Jiacheng Guo
FutureX-Pro: Extending Future Prediction to High-Value Vertical Domains
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Building upon FutureX, which established a live benchmark for general-purpose future prediction, this report introduces FutureX-Pro, including FutureX-Finance, FutureX-Retail, FutureX-PublicHealth, FutureX-NaturalDisaster, and FutureX-Search. These together form a specialized framework extending agentic future prediction to high-value vertical domains. While generalist agents demonstrate proficiency in open-domain search, their reliability in capital-intensive and safety-critical sectors remains under-explored. FutureX-Pro targets four economically and socially pivotal verticals: Finance, Retail, Public Health, and Natural Disaster. We benchmark agentic Large Language Models (LLMs) on entry-level yet foundational prediction tasks -- ranging from forecasting market indicators and supply chain demands to tracking epidemic trends and natural disasters. By adapting the contamination-free, live-evaluation pipeline of FutureX, we assess whether current State-of-the-Art (SOTA) agentic LLMs possess the domain grounding necessary for industrial deployment. Our findings reveal the performance gap between generalist reasoning and the precision required for high-value vertical applications.
GenEnv: Difficulty-Aligned Co-Evolution Between LLM Agents and Environment Simulators
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Training capable Large Language Model (LLM) agents is critically bottlenecked by the high cost and static nature of real-world interaction data. We address this by introducing GenEnv, a framework that establishes a difficulty-aligned co-evolutionary game between an agent and a scalable, generative environment simulator. Unlike traditional methods that evolve models on static datasets, GenEnv instantiates a dataevolving: the simulator acts as a dynamic curriculum policy, continuously generating tasks specifically tailored to the agent's ``zone of proximal development''. This process is guided by a simple but effective $α$-Curriculum Reward, which aligns task difficulty with the agent's current capabilities. We evaluate GenEnv on five benchmarks, including API-Bank, ALFWorld, BFCL, Bamboogle, and TravelPlanner. Across these tasks, GenEnv improves agent performance by up to \textbf{+40.3\%} over 7B baselines and matches or exceeds the average performance of larger models. Compared to Gemini 2.5 Pro-based offline data augmentation, GenEnv achieves better performance while using 3.3$\times$ less data. By shifting from static supervision to adaptive simulation, GenEnv provides a data-efficient pathway for scaling agent capabilities.
A Low-Rank Method for Vision Language Model Hallucination Mitigation in Autonomous Driving
Nov 09, 2025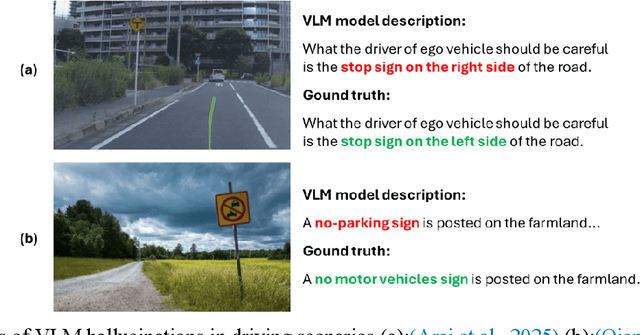
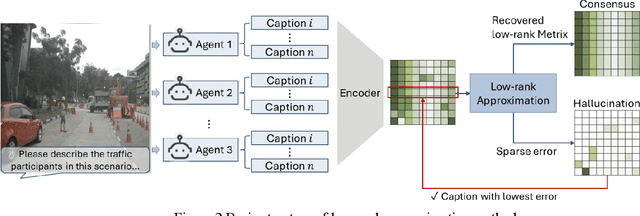

Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) are increasingly used in autonomous driving to help understand traffic scenes, but they sometimes produce hallucinations, which are false details not grounded in the visual input. Detecting and mitigating hallucinations is challenging when ground-truth references are unavailable and model internals are inaccessible. This paper proposes a novel self-contained low-rank approach to automatically rank multiple candidate captions generated by multiple VLMs based on their hallucination levels, using only the captions themselves without requiring external references or model access. By constructing a sentence-embedding matrix and decomposing it into a low-rank consensus component and a sparse residual, we use the residual magnitude to rank captions: selecting the one with the smallest residual as the most hallucination-free. Experiments on the NuScenes dataset demonstrate that our approach achieves 87% selection accuracy in identifying hallucination-free captions, representing a 19% improvement over the unfiltered baseline and a 6-10% improvement over multi-agent debate method. The sorting produced by sparse error magnitudes shows strong correlation with human judgments of hallucinations, validating our scoring mechanism. Additionally, our method, which can be easily parallelized, reduces inference time by 51-67% compared to debate approaches, making it practical for real-time autonomous driving applications.
AgentDistill: Training-Free Agent Distillation with Generalizable MCP Boxes
Jun 17, 2025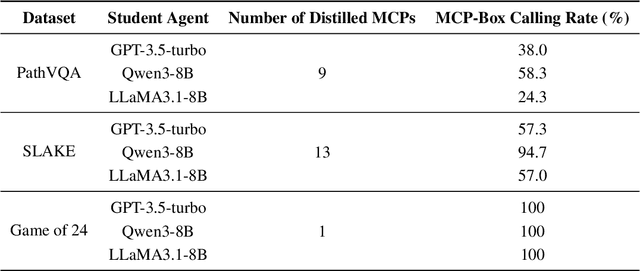
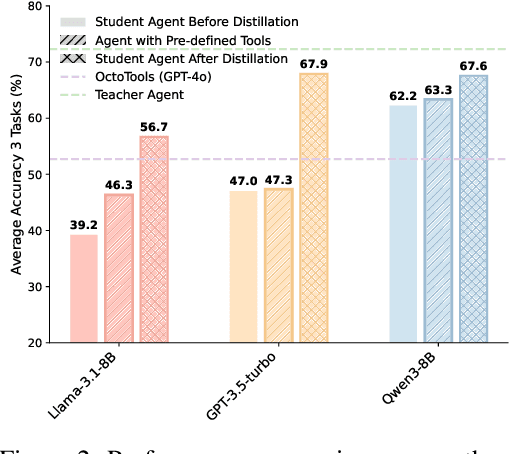
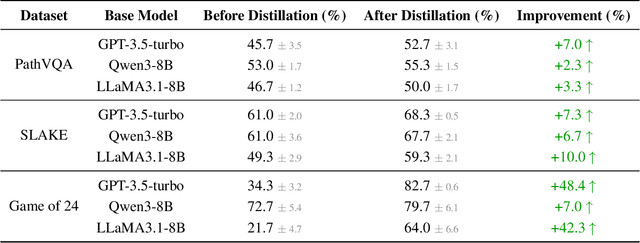
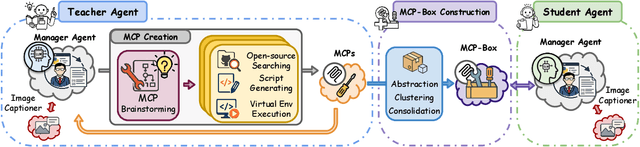
Abstract:While knowledge distillation has become a mature field for compressing large language models (LLMs) into smaller ones by aligning their outputs or internal representations, the distillation of LLM-based agents, which involve planning, memory, and tool use, remains relatively underexplored. Existing agent distillation methods typically replay full teacher trajectories or imitate step-by-step teacher tool usage, but they often struggle to train student agents to dynamically plan and act in novel environments. We propose AgentDistill, a novel, training-free agent distillation framework that enables efficient and scalable knowledge transfer via direct reuse of Model-Context-Protocols (MCPs), which are structured and reusable task-solving modules autonomously generated by teacher agents. The reuse of these distilled MCPs enables student agents to generalize their capabilities across domains and solve new problems with minimal supervision or human intervention. Experiments on biomedical and mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that our distilled student agents, built on small language models, can achieve performance comparable to advanced systems using large LLMs such as OctoTools (GPT-4o), highlighting the effectiveness of our framework in building scalable and cost-efficient intelligent agents.
Alita: Generalist Agent Enabling Scalable Agentic Reasoning with Minimal Predefinition and Maximal Self-Evolution
May 26, 2025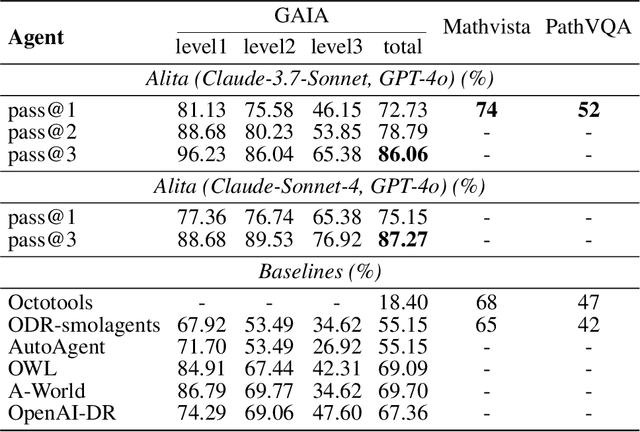
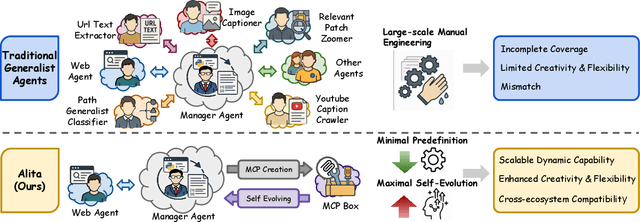
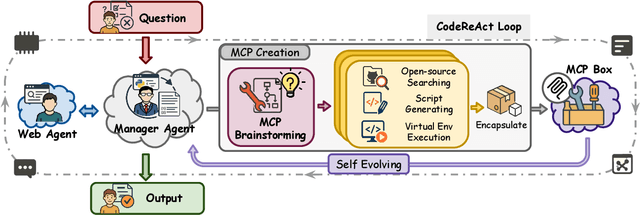
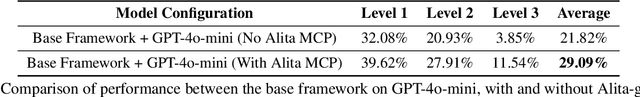
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled agents to autonomously perform complex, open-ended tasks. However, many existing frameworks depend heavily on manually predefined tools and workflows, which hinder their adaptability, scalability, and generalization across domains. In this work, we introduce Alita--a generalist agent designed with the principle of "Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication," enabling scalable agentic reasoning through minimal predefinition and maximal self-evolution. For minimal predefinition, Alita is equipped with only one component for direct problem-solving, making it much simpler and neater than previous approaches that relied heavily on hand-crafted, elaborate tools and workflows. This clean design enhances its potential to generalize to challenging questions, without being limited by tools. For Maximal self-evolution, we enable the creativity of Alita by providing a suite of general-purpose components to autonomously construct, refine, and reuse external capabilities by generating task-related model context protocols (MCPs) from open source, which contributes to scalable agentic reasoning. Notably, Alita achieves 75.15% pass@1 and 87.27% pass@3 accuracy, which is top-ranking among general-purpose agents, on the GAIA benchmark validation dataset, 74.00% and 52.00% pass@1, respectively, on Mathvista and PathVQA, outperforming many agent systems with far greater complexity. More details will be updated at $\href{https://github.com/CharlesQ9/Alita}{https://github.com/CharlesQ9/Alita}$.
On Path to Multimodal Historical Reasoning: HistBench and HistAgent
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to remarkable progress across domains, yet their capabilities in the humanities, particularly history, remain underexplored. Historical reasoning poses unique challenges for AI, involving multimodal source interpretation, temporal inference, and cross-linguistic analysis. While general-purpose agents perform well on many existing benchmarks, they lack the domain-specific expertise required to engage with historical materials and questions. To address this gap, we introduce HistBench, a new benchmark of 414 high-quality questions designed to evaluate AI's capacity for historical reasoning and authored by more than 40 expert contributors. The tasks span a wide range of historical problems-from factual retrieval based on primary sources to interpretive analysis of manuscripts and images, to interdisciplinary challenges involving archaeology, linguistics, or cultural history. Furthermore, the benchmark dataset spans 29 ancient and modern languages and covers a wide range of historical periods and world regions. Finding the poor performance of LLMs and other agents on HistBench, we further present HistAgent, a history-specific agent equipped with carefully designed tools for OCR, translation, archival search, and image understanding in History. On HistBench, HistAgent based on GPT-4o achieves an accuracy of 27.54% pass@1 and 36.47% pass@2, significantly outperforming LLMs with online search and generalist agents, including GPT-4o (18.60%), DeepSeek-R1(14.49%) and Open Deep Research-smolagents(20.29% pass@1 and 25.12% pass@2). These results highlight the limitations of existing LLMs and generalist agents and demonstrate the advantages of HistAgent for historical reasoning.
Temporal Consistency for LLM Reasoning Process Error Identification
Mar 18, 2025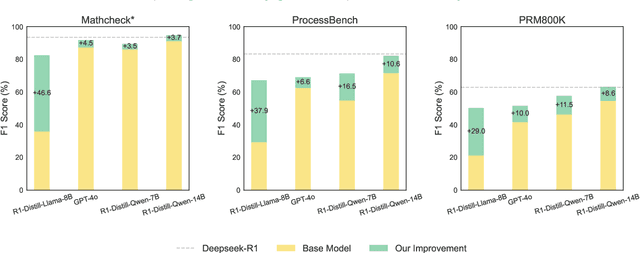



Abstract:Verification is crucial for effective mathematical reasoning. We present a new temporal consistency method where verifiers iteratively refine their judgments based on the previous assessment. Unlike one-round verification or multi-model debate approaches, our method leverages consistency in a sequence of self-reflection actions to improve verification accuracy. Empirical evaluations across diverse mathematical process error identification benchmarks (Mathcheck, ProcessBench, and PRM800K) show consistent performance improvements over baseline methods. When applied to the recent DeepSeek R1 distilled models, our method demonstrates strong performance, enabling 7B/8B distilled models to outperform all 70B/72B models and GPT-4o on ProcessBench. Notably, the distilled 14B model with our method achieves performance comparable to Deepseek-R1. Our codes are available at https://github.com/jcguo123/Temporal-Consistency
MATH-Perturb: Benchmarking LLMs' Math Reasoning Abilities against Hard Perturbations
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models have demonstrated impressive performance on challenging mathematical reasoning tasks, which has triggered the discussion of whether the performance is achieved by true reasoning capability or memorization. To investigate this question, prior work has constructed mathematical benchmarks when questions undergo simple perturbations -- modifications that still preserve the underlying reasoning patterns of the solutions. However, no work has explored hard perturbations, which fundamentally change the nature of the problem so that the original solution steps do not apply. To bridge the gap, we construct MATH-P-Simple and MATH-P-Hard via simple perturbation and hard perturbation, respectively. Each consists of 279 perturbed math problems derived from level-5 (hardest) problems in the MATH dataset (Hendrycksmath et. al., 2021). We observe significant performance drops on MATH-P-Hard across various models, including o1-mini (-16.49%) and gemini-2.0-flash-thinking (-12.9%). We also raise concerns about a novel form of memorization where models blindly apply learned problem-solving skills without assessing their applicability to modified contexts. This issue is amplified when using original problems for in-context learning. We call for research efforts to address this challenge, which is critical for developing more robust and reliable reasoning models.
Stealthy Multi-Task Adversarial Attacks
Nov 26, 2024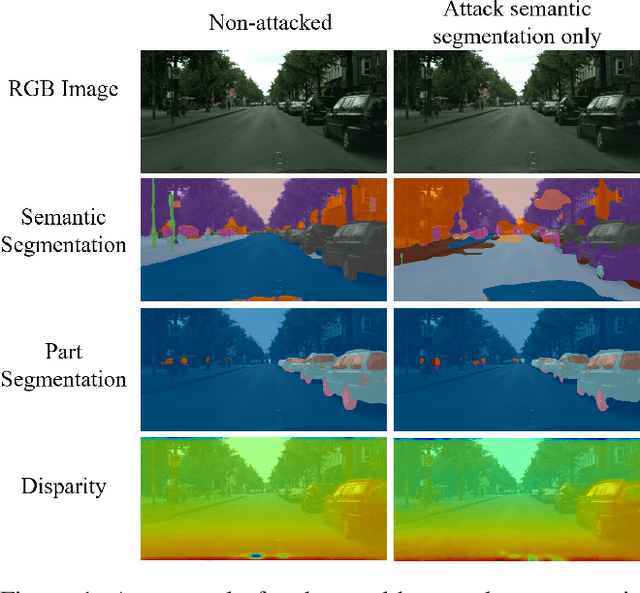
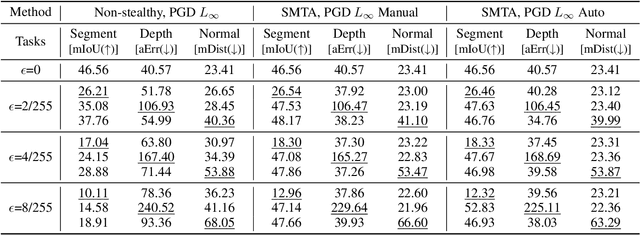
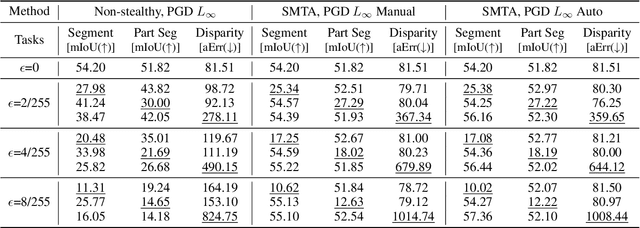
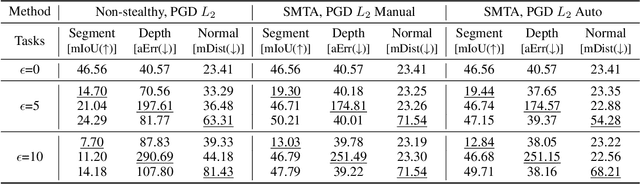
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks exhibit inherent vulnerabilities to adversarial attacks, which can significantly compromise their outputs and reliability. While existing research primarily focuses on attacking single-task scenarios or indiscriminately targeting all tasks in multi-task environments, we investigate selectively targeting one task while preserving performance in others within a multi-task framework. This approach is motivated by varying security priorities among tasks in real-world applications, such as autonomous driving, where misinterpreting critical objects (e.g., signs, traffic lights) poses a greater security risk than minor depth miscalculations. Consequently, attackers may hope to target security-sensitive tasks while avoiding non-critical tasks from being compromised, thus evading being detected before compromising crucial functions. In this paper, we propose a method for the stealthy multi-task attack framework that utilizes multiple algorithms to inject imperceptible noise into the input. This novel method demonstrates remarkable efficacy in compromising the target task while simultaneously maintaining or even enhancing performance across non-targeted tasks - a criterion hitherto unexplored in the field. Additionally, we introduce an automated approach for searching the weighting factors in the loss function, further enhancing attack efficiency. Experimental results validate our framework's ability to successfully attack the target task while preserving the performance of non-targeted tasks. The automated loss function weight searching method demonstrates comparable efficacy to manual tuning, establishing a state-of-the-art multi-task attack framework.
TreeBoN: Enhancing Inference-Time Alignment with Speculative Tree-Search and Best-of-N Sampling
Oct 18, 2024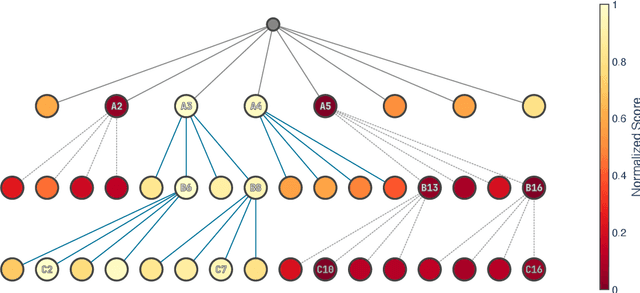
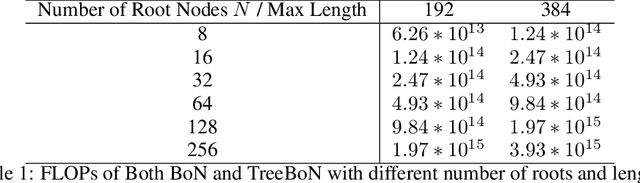
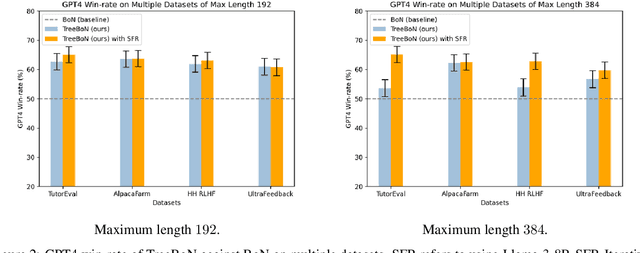

Abstract:Inference-time alignment enhances the performance of large language models without requiring additional training or fine-tuning but presents challenges due to balancing computational efficiency with high-quality output. Best-of-N (BoN) sampling, as a simple yet powerful approach, generates multiple responses and selects the best one, achieving improved performance but with a high computational cost. We propose TreeBoN, a novel framework that integrates a speculative tree-search strategy into Best-of-N (BoN) Sampling. TreeBoN maintains a set of parent nodes, iteratively branching and pruning low-quality responses, thereby reducing computational overhead while maintaining high output quality. Our approach also leverages token-level rewards from Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to guide tree expansion and prune low-quality paths. We evaluate TreeBoN using AlpacaFarm, UltraFeedback, GSM8K, HH-RLHF, and TutorEval datasets, demonstrating consistent improvements. Specifically, TreeBoN achieves a 65% win rate at maximum lengths of 192 and 384 tokens, outperforming standard BoN with the same computational cost. Furthermore, TreeBoN achieves around a 60% win rate across longer responses, showcasing its scalability and alignment efficacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge