Yingqing Guo
Training-Free Guidance Beyond Differentiability: Scalable Path Steering with Tree Search in Diffusion and Flow Models
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Training-free guidance enables controlled generation in diffusion and flow models, but most existing methods assume differentiable objectives and rely on gradients. This work focuses on training-free guidance addressing challenges from non-differentiable objectives and discrete data distributions. We propose an algorithmic framework TreeG: Tree Search-Based Path Steering Guidance, applicable to both continuous and discrete settings in diffusion and flow models. TreeG offers a unified perspective on training-free guidance: proposing candidates for the next step, evaluating candidates, and selecting the best to move forward, enhanced by a tree search mechanism over active paths or parallelizing exploration. We comprehensively investigate the design space of TreeG over the candidate proposal module and the evaluation function, instantiating TreeG into three novel algorithms. Our experiments show that TreeG consistently outperforms the top guidance baselines in symbolic music generation, small molecule generation, and enhancer DNA design, all of which involve non-differentiable challenges. Additionally, we identify an inference-time scaling law showing TreeG's scalability in inference-time computation.
MATH-Perturb: Benchmarking LLMs' Math Reasoning Abilities against Hard Perturbations
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models have demonstrated impressive performance on challenging mathematical reasoning tasks, which has triggered the discussion of whether the performance is achieved by true reasoning capability or memorization. To investigate this question, prior work has constructed mathematical benchmarks when questions undergo simple perturbations -- modifications that still preserve the underlying reasoning patterns of the solutions. However, no work has explored hard perturbations, which fundamentally change the nature of the problem so that the original solution steps do not apply. To bridge the gap, we construct MATH-P-Simple and MATH-P-Hard via simple perturbation and hard perturbation, respectively. Each consists of 279 perturbed math problems derived from level-5 (hardest) problems in the MATH dataset (Hendrycksmath et. al., 2021). We observe significant performance drops on MATH-P-Hard across various models, including o1-mini (-16.49%) and gemini-2.0-flash-thinking (-12.9%). We also raise concerns about a novel form of memorization where models blindly apply learned problem-solving skills without assessing their applicability to modified contexts. This issue is amplified when using original problems for in-context learning. We call for research efforts to address this challenge, which is critical for developing more robust and reliable reasoning models.
Gradient Guidance for Diffusion Models: An Optimization Perspective
Apr 23, 2024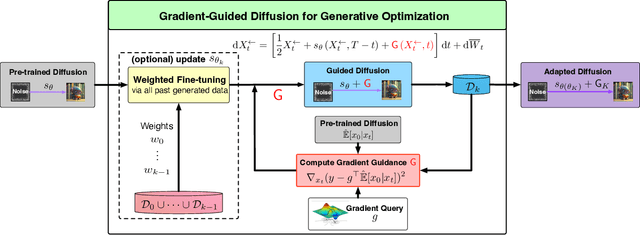
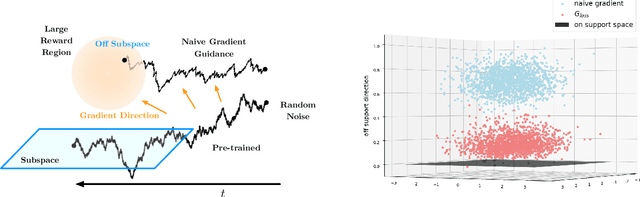
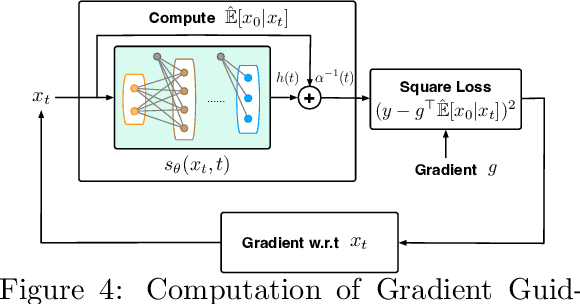
Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated empirical successes in various applications and can be adapted to task-specific needs via guidance. This paper introduces a form of gradient guidance for adapting or fine-tuning diffusion models towards user-specified optimization objectives. We study the theoretic aspects of a guided score-based sampling process, linking the gradient-guided diffusion model to first-order optimization. We show that adding gradient guidance to the sampling process of a pre-trained diffusion model is essentially equivalent to solving a regularized optimization problem, where the regularization term acts as a prior determined by the pre-training data. Diffusion models are able to learn data's latent subspace, however, explicitly adding the gradient of an external objective function to the sample process would jeopardize the structure in generated samples. To remedy this issue, we consider a modified form of gradient guidance based on a forward prediction loss, which leverages the pre-trained score function to preserve the latent structure in generated samples. We further consider an iteratively fine-tuned version of gradient-guided diffusion where one can query gradients at newly generated data points and update the score network using new samples. This process mimics a first-order optimization iteration in expectation, for which we proved O(1/K) convergence rate to the global optimum when the objective function is concave.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge