Shuo Miao
LegalOne: A Family of Foundation Models for Reliable Legal Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive general capabilities, their direct application in the legal domain is often hindered by a lack of precise domain knowledge and complexity of performing rigorous multi-step judicial reasoning. To address this gap, we present LegalOne, a family of foundational models specifically tailored for the Chinese legal domain. LegalOne is developed through a comprehensive three-phase pipeline designed to master legal reasoning. First, during mid-training phase, we propose Plasticity-Adjusted Sampling (PAS) to address the challenge of domain adaptation. This perplexity-based scheduler strikes a balance between the acquisition of new knowledge and the retention of original capabilities, effectively establishing a robust legal foundation. Second, during supervised fine-tuning, we employ Legal Agentic CoT Distillation (LEAD) to distill explicit reasoning from raw legal texts. Unlike naive distillation, LEAD utilizes an agentic workflow to convert complex judicial processes into structured reasoning trajectories, thereby enforcing factual grounding and logical rigor. Finally, we implement a Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (RL) strategy. Through a progressive reinforcement process spanning memorization, understanding, and reasoning, LegalOne evolves from simple pattern matching to autonomous and reliable legal reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that LegalOne achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of legal tasks, surpassing general-purpose LLMs with vastly larger parameter counts through enhanced knowledge density and efficiency. We publicly release the LegalOne weights and the LegalKit evaluation framework to advance the field of Legal AI, paving the way for deploying trustworthy and interpretable foundation models in high-stakes judicial applications.
MOBIUS: Towards the Next Generation of Query-Ad Matching in Baidu's Sponsored Search
Sep 05, 2024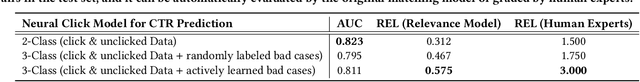


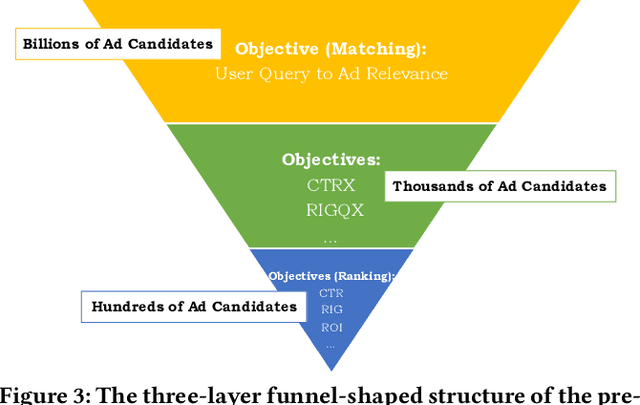
Abstract:Baidu runs the largest commercial web search engine in China, serving hundreds of millions of online users every day in response to a great variety of queries. In order to build a high-efficiency sponsored search engine, we used to adopt a three-layer funnel-shaped structure to screen and sort hundreds of ads from billions of ad candidates subject to the requirement of low response latency and the restraints of computing resources. Given a user query, the top matching layer is responsible for providing semantically relevant ad candidates to the next layer, while the ranking layer at the bottom concerns more about business indicators (e.g., CPM, ROI, etc.) of those ads. The clear separation between the matching and ranking objectives results in a lower commercial return. The Mobius project has been established to address this serious issue. It is our first attempt to train the matching layer to consider CPM as an additional optimization objective besides the query-ad relevance, via directly predicting CTR (click-through rate) from billions of query-ad pairs. Specifically, this paper will elaborate on how we adopt active learning to overcome the insufficiency of click history at the matching layer when training our neural click networks offline, and how we use the SOTA ANN search technique for retrieving ads more efficiently (Here ``ANN'' stands for approximate nearest neighbor search). We contribute the solutions to Mobius-V1 as the first version of our next generation query-ad matching system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge