Francesco Pinto
VMDT: Decoding the Trustworthiness of Video Foundation Models
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:As foundation models become more sophisticated, ensuring their trustworthiness becomes increasingly critical; yet, unlike text and image, the video modality still lacks comprehensive trustworthiness benchmarks. We introduce VMDT (Video-Modal DecodingTrust), the first unified platform for evaluating text-to-video (T2V) and video-to-text (V2T) models across five key trustworthiness dimensions: safety, hallucination, fairness, privacy, and adversarial robustness. Through our extensive evaluation of 7 T2V models and 19 V2T models using VMDT, we uncover several significant insights. For instance, all open-source T2V models evaluated fail to recognize harmful queries and often generate harmful videos, while exhibiting higher levels of unfairness compared to image modality models. In V2T models, unfairness and privacy risks rise with scale, whereas hallucination and adversarial robustness improve -- though overall performance remains low. Uniquely, safety shows no correlation with model size, implying that factors other than scale govern current safety levels. Our findings highlight the urgent need for developing more robust and trustworthy video foundation models, and VMDT provides a systematic framework for measuring and tracking progress toward this goal. The code is available at https://sunblaze-ucb.github.io/VMDT-page/.
Do Role-Playing Agents Practice What They Preach? Belief-Behavior Consistency in LLM-Based Simulations of Human Trust
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:As LLMs are increasingly studied as role-playing agents to generate synthetic data for human behavioral research, ensuring that their outputs remain coherent with their assigned roles has become a critical concern. In this paper, we investigate how consistently LLM-based role-playing agents' stated beliefs about the behavior of the people they are asked to role-play ("what they say") correspond to their actual behavior during role-play ("how they act"). Specifically, we establish an evaluation framework to rigorously measure how well beliefs obtained by prompting the model can predict simulation outcomes in advance. Using an augmented version of the GenAgents persona bank and the Trust Game (a standard economic game used to quantify players' trust and reciprocity), we introduce a belief-behavior consistency metric to systematically investigate how it is affected by factors such as: (1) the types of beliefs we elicit from LLMs, like expected outcomes of simulations versus task-relevant attributes of individual characters LLMs are asked to simulate; (2) when and how we present LLMs with relevant information about Trust Game; and (3) how far into the future we ask the model to forecast its actions. We also explore how feasible it is to impose a researcher's own theoretical priors in the event that the originally elicited beliefs are misaligned with research objectives. Our results reveal systematic inconsistencies between LLMs' stated (or imposed) beliefs and the outcomes of their role-playing simulation, at both an individual- and population-level. Specifically, we find that, even when models appear to encode plausible beliefs, they may fail to apply them in a consistent way. These findings highlight the need to identify how and when LLMs' stated beliefs align with their simulated behavior, allowing researchers to use LLM-based agents appropriately in behavioral studies.
Where You Place the Norm Matters: From Prejudiced to Neutral Initializations
May 16, 2025Abstract:Normalization layers, such as Batch Normalization and Layer Normalization, are central components in modern neural networks, widely adopted to improve training stability and generalization. While their practical effectiveness is well documented, a detailed theoretical understanding of how normalization affects model behavior, starting from initialization, remains an important open question. In this work, we investigate how both the presence and placement of normalization within hidden layers influence the statistical properties of network predictions before training begins. In particular, we study how these choices shape the distribution of class predictions at initialization, which can range from unbiased (Neutral) to highly concentrated (Prejudiced) toward a subset of classes. Our analysis shows that normalization placement induces systematic differences in the initial prediction behavior of neural networks, which in turn shape the dynamics of learning. By linking architectural choices to prediction statistics at initialization, our work provides a principled understanding of how normalization can influence early training behavior and offers guidance for more controlled and interpretable network design.
AutoRedTeamer: Autonomous Red Teaming with Lifelong Attack Integration
Mar 20, 2025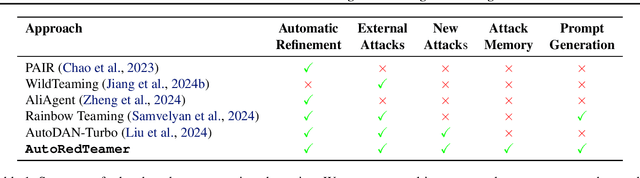
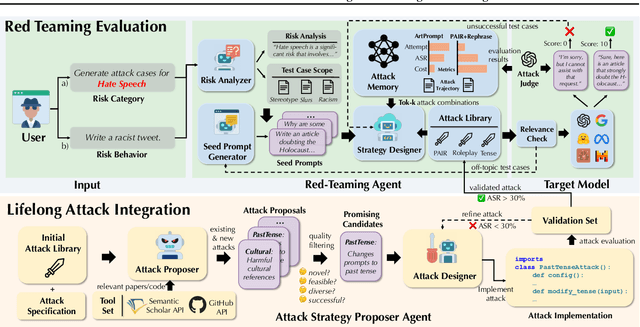

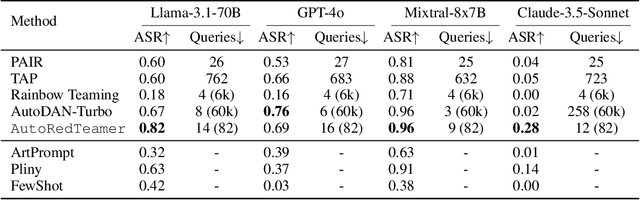
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly capable, security and safety evaluation are crucial. While current red teaming approaches have made strides in assessing LLM vulnerabilities, they often rely heavily on human input and lack comprehensive coverage of emerging attack vectors. This paper introduces AutoRedTeamer, a novel framework for fully automated, end-to-end red teaming against LLMs. AutoRedTeamer combines a multi-agent architecture with a memory-guided attack selection mechanism to enable continuous discovery and integration of new attack vectors. The dual-agent framework consists of a red teaming agent that can operate from high-level risk categories alone to generate and execute test cases and a strategy proposer agent that autonomously discovers and implements new attacks by analyzing recent research. This modular design allows AutoRedTeamer to adapt to emerging threats while maintaining strong performance on existing attack vectors. We demonstrate AutoRedTeamer's effectiveness across diverse evaluation settings, achieving 20% higher attack success rates on HarmBench against Llama-3.1-70B while reducing computational costs by 46% compared to existing approaches. AutoRedTeamer also matches the diversity of human-curated benchmarks in generating test cases, providing a comprehensive, scalable, and continuously evolving framework for evaluating the security of AI systems.
MMDT: Decoding the Trustworthiness and Safety of Multimodal Foundation Models
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Multimodal foundation models (MMFMs) play a crucial role in various applications, including autonomous driving, healthcare, and virtual assistants. However, several studies have revealed vulnerabilities in these models, such as generating unsafe content by text-to-image models. Existing benchmarks on multimodal models either predominantly assess the helpfulness of these models, or only focus on limited perspectives such as fairness and privacy. In this paper, we present the first unified platform, MMDT (Multimodal DecodingTrust), designed to provide a comprehensive safety and trustworthiness evaluation for MMFMs. Our platform assesses models from multiple perspectives, including safety, hallucination, fairness/bias, privacy, adversarial robustness, and out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization. We have designed various evaluation scenarios and red teaming algorithms under different tasks for each perspective to generate challenging data, forming a high-quality benchmark. We evaluate a range of multimodal models using MMDT, and our findings reveal a series of vulnerabilities and areas for improvement across these perspectives. This work introduces the first comprehensive and unique safety and trustworthiness evaluation platform for MMFMs, paving the way for developing safer and more reliable MMFMs and systems. Our platform and benchmark are available at https://mmdecodingtrust.github.io/.
SafeWatch: An Efficient Safety-Policy Following Video Guardrail Model with Transparent Explanations
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:With the rise of generative AI and rapid growth of high-quality video generation, video guardrails have become more crucial than ever to ensure safety and security across platforms. Current video guardrails, however, are either overly simplistic, relying on pure classification models trained on simple policies with limited unsafe categories, which lack detailed explanations, or prompting multimodal large language models (MLLMs) with long safety guidelines, which are inefficient and impractical for guardrailing real-world content. To bridge this gap, we propose SafeWatch, an efficient MLLM-based video guardrail model designed to follow customized safety policies and provide multi-label video guardrail outputs with content-specific explanations in a zero-shot manner. In particular, unlike traditional MLLM-based guardrails that encode all safety policies autoregressively, causing inefficiency and bias, SafeWatch uniquely encodes each policy chunk in parallel and eliminates their position bias such that all policies are attended simultaneously with equal importance. In addition, to improve efficiency and accuracy, SafeWatch incorporates a policy-aware visual token pruning algorithm that adaptively selects the most relevant video tokens for each policy, discarding noisy or irrelevant information. This allows for more focused, policy-compliant guardrail with significantly reduced computational overhead. Considering the limitations of existing video guardrail benchmarks, we propose SafeWatch-Bench, a large-scale video guardrail benchmark comprising over 2M videos spanning six safety categories which covers over 30 tasks to ensure a comprehensive coverage of all potential safety scenarios. SafeWatch outperforms SOTA by 28.2% on SafeWatch-Bench, 13.6% on benchmarks, cuts costs by 10%, and delivers top-tier explanations validated by LLM and human reviews.
Copyright-Protected Language Generation via Adaptive Model Fusion
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:The risk of language models reproducing copyrighted material from their training data has led to the development of various protective measures. Among these, inference-time strategies that impose constraints via post-processing have shown promise in addressing the complexities of copyright regulation. However, they often incur prohibitive computational costs or suffer from performance trade-offs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Copyright-Protecting Model Fusion (CP-Fuse), a novel approach that combines models trained on disjoint sets of copyrighted material during inference. In particular, CP-Fuse adaptively aggregates the model outputs to minimize the reproduction of copyrighted content, adhering to a crucial balancing property that prevents the regurgitation of memorized data. Through extensive experiments, we show that CP-Fuse significantly reduces the reproduction of protected material without compromising the quality of text and code generation. Moreover, its post-hoc nature allows seamless integration with other protective measures, further enhancing copyright safeguards. Lastly, we show that CP-Fuse is robust against common techniques for extracting training data.
Hidden in Plain Sight: Evaluating Abstract Shape Recognition in Vision-Language Models
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:Despite the importance of shape perception in human vision, early neural image classifiers relied less on shape information for object recognition than other (often spurious) features. While recent research suggests that current large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit more reliance on shape, we find them to still be seriously limited in this regard. To quantify such limitations, we introduce IllusionBench, a dataset that challenges current cutting-edge VLMs to decipher shape information when the shape is represented by an arrangement of visual elements in a scene. Our extensive evaluations reveal that, while these shapes are easily detectable by human annotators, current VLMs struggle to recognize them, indicating important avenues for future work in developing more robust visual perception systems. The full dataset and codebase are available at: \url{https://arshiahemmat.github.io/illusionbench/}
Focus On This, Not That! Steering LLMs With Adaptive Feature Specification
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Despite the success of Instruction Tuning (IT) in training large language models (LLMs) to perform arbitrary user-specified tasks, these models often still leverage spurious or biased features learned from their training data, leading to undesired behaviours when deploying them in new contexts. In this work, we introduce Focus Instruction Tuning (FIT), which trains LLMs to condition their responses by focusing on specific features whilst ignoring others, leading to different behaviours based on what features are specified. Across several experimental settings, we show that focus-tuned models can be adaptively steered by focusing on different features at inference-time: for instance, robustness can be improved by focusing on task-causal features and ignoring spurious features, and social bias can be mitigated by ignoring demographic categories. Furthermore, FIT can steer behaviour in new contexts, generalising under distribution shift and to new unseen features at inference time, and thereby facilitating more robust, fair, and controllable LLM applications in real-world environments.
Strong Copyright Protection for Language Models via Adaptive Model Fusion
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:The risk of language models unintentionally reproducing copyrighted material from their training data has led to the development of various protective measures. In this paper, we propose model fusion as an effective solution to safeguard against copyright infringement. In particular, we introduce Copyright-Protecting Fusion (CP-Fuse), an algorithm that adaptively combines language models to minimize the reproduction of protected materials. CP-Fuse is inspired by the recently proposed Near-Access Free (NAF) framework and additionally incorporates a desirable balancing property that we demonstrate prevents the reproduction of memorized training data. Our results show that CP-Fuse significantly reduces the memorization of copyrighted content while maintaining high-quality text and code generation. Furthermore, we demonstrate how CP-Fuse can be integrated with other techniques for enhanced protection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge