Claudia Prieto
Enabling Ultra-Fast Cardiovascular Imaging Across Heterogeneous Clinical Environments with a Generalist Foundation Model and Multimodal Database
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Multimodal cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging provides comprehensive and non-invasive insights into cardiovascular disease (CVD) diagnosis and underlying mechanisms. Despite decades of advancements, its widespread clinical adoption remains constrained by prolonged scan times and heterogeneity across medical environments. This underscores the urgent need for a generalist reconstruction foundation model for ultra-fast CMR imaging, one capable of adapting across diverse imaging scenarios and serving as the essential substrate for all downstream analyses. To enable this goal, we curate MMCMR-427K, the largest and most comprehensive multimodal CMR k-space database to date, comprising 427,465 multi-coil k-space data paired with structured metadata across 13 international centers, 12 CMR modalities, 15 scanners, and 17 CVD categories in populations across three continents. Building on this unprecedented resource, we introduce CardioMM, a generalist reconstruction foundation model capable of dynamically adapting to heterogeneous fast CMR imaging scenarios. CardioMM unifies semantic contextual understanding with physics-informed data consistency to deliver robust reconstructions across varied scanners, protocols, and patient presentations. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that CardioMM achieves state-of-the-art performance in the internal centers and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to unseen external settings. Even at imaging acceleration up to 24x, CardioMM reliably preserves key cardiac phenotypes, quantitative myocardial biomarkers, and diagnostic image quality, enabling a substantial increase in CMR examination throughput without compromising clinical integrity. Together, our open-access MMCMR-427K database and CardioMM framework establish a scalable pathway toward high-throughput, high-quality, and clinically accessible cardiovascular imaging.
Towards Universal Learning-based Model for Cardiac Image Reconstruction: Summary of the CMRxRecon2024 Challenge
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) offers diverse imaging contrasts for assessment of cardiac function and tissue characterization. However, acquiring each single CMR modality is often time-consuming, and comprehensive clinical protocols require multiple modalities with various sampling patterns, further extending the overall acquisition time and increasing susceptibility to motion artifacts. Existing deep learning-based reconstruction methods are often designed for specific acquisition parameters, which limits their ability to generalize across a variety of scan scenarios. As part of the CMRxRecon Series, the CMRxRecon2024 challenge provides diverse datasets encompassing multi-modality multi-view imaging with various sampling patterns, and a platform for the international community to develop and benchmark reconstruction solutions in two well-crafted tasks. Task 1 is a modality-universal setting, evaluating the out-of-distribution generalization of the reconstructed model, while Task 2 follows sampling-universal setting assessing the one-for-all adaptability of the universal model. Main contributions include providing the first and largest publicly available multi-modality, multi-view cardiac k-space dataset; developing a benchmarking platform that simulates clinical acceleration protocols, with a shared code library and tutorial for various k-t undersampling patterns and data processing; giving technical insights of enhanced data consistency based on physic-informed networks and adaptive prompt-learning embedding to be versatile to different clinical settings; additional finding on evaluation metrics to address the limitations of conventional ground-truth references in universal reconstruction tasks.
MR imaging in the low-field: Leveraging the power of machine learning
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Recent innovations in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) hardware and software have reignited interest in low-field ($<1\,\mathrm{T}$) and ultra-low-field MRI ($<0.1\,\mathrm{T}$). These technologies offer advantages such as lower power consumption, reduced specific absorption rate, reduced field-inhomogeneities, and cost-effectiveness, presenting a promising alternative for resource-limited and point-of-care settings. However, low-field MRI faces inherent challenges like reduced signal-to-noise ratio and therefore, potentially lower spatial resolution or longer scan times. This chapter examines the challenges and opportunities of low-field and ultra-low-field MRI, with a focus on the role of machine learning (ML) in overcoming these limitations. We provide an overview of deep neural networks and their application in enhancing low-field and ultra-low-field MRI performance. Specific ML-based solutions, including advanced image reconstruction, denoising, and super-resolution algorithms, are discussed. The chapter concludes by exploring how integrating ML with low-field MRI could expand its clinical applications and improve accessibility, potentially revolutionizing its use in diverse healthcare settings.
PISCO: Self-Supervised k-Space Regularization for Improved Neural Implicit k-Space Representations of Dynamic MRI
Jan 16, 2025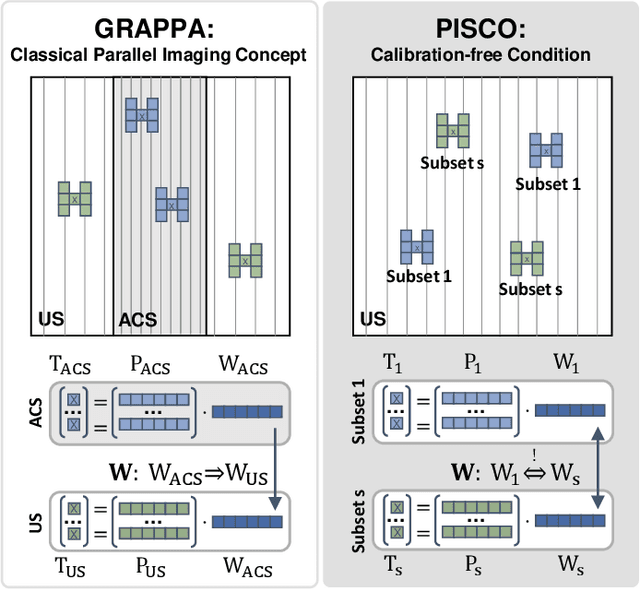
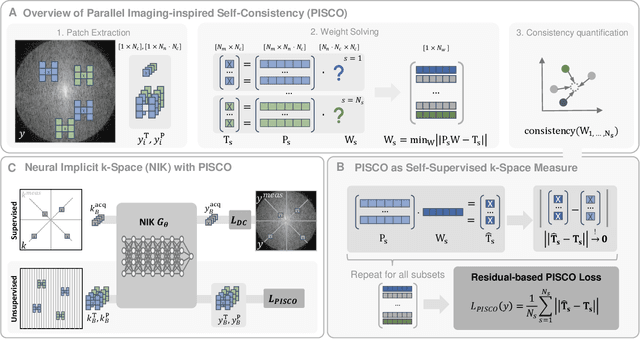
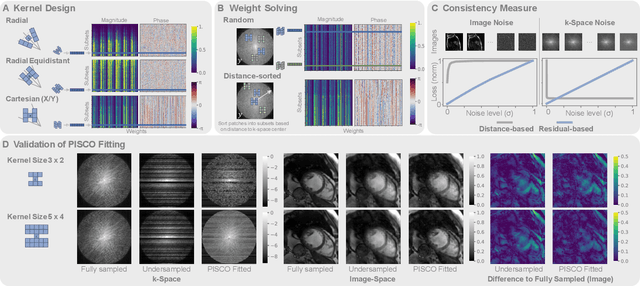
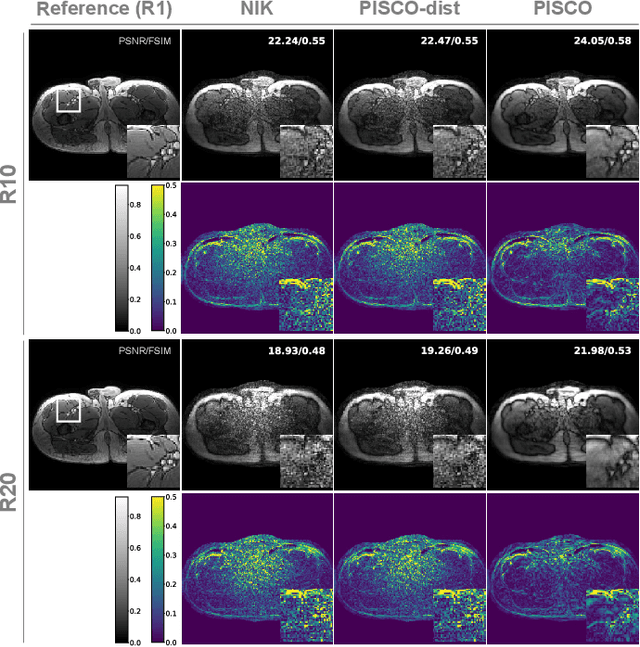
Abstract:Neural implicit k-space representations (NIK) have shown promising results for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at high temporal resolutions. Yet, reducing acquisition time, and thereby available training data, results in severe performance drops due to overfitting. To address this, we introduce a novel self-supervised k-space loss function $\mathcal{L}_\mathrm{PISCO}$, applicable for regularization of NIK-based reconstructions. The proposed loss function is based on the concept of parallel imaging-inspired self-consistency (PISCO), enforcing a consistent global k-space neighborhood relationship without requiring additional data. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations on static and dynamic MR reconstructions show that integrating PISCO significantly improves NIK representations. Particularly for high acceleration factors (R$\geq$54), NIK with PISCO achieves superior spatio-temporal reconstruction quality compared to state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, an extensive analysis of the loss assumptions and stability shows PISCO's potential as versatile self-supervised k-space loss function for further applications and architectures. Code is available at: https://github.com/compai-lab/2025-pisco-spieker
Subspace Implicit Neural Representations for Real-Time Cardiac Cine MR Imaging
Dec 17, 2024
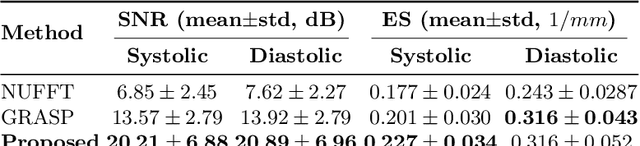
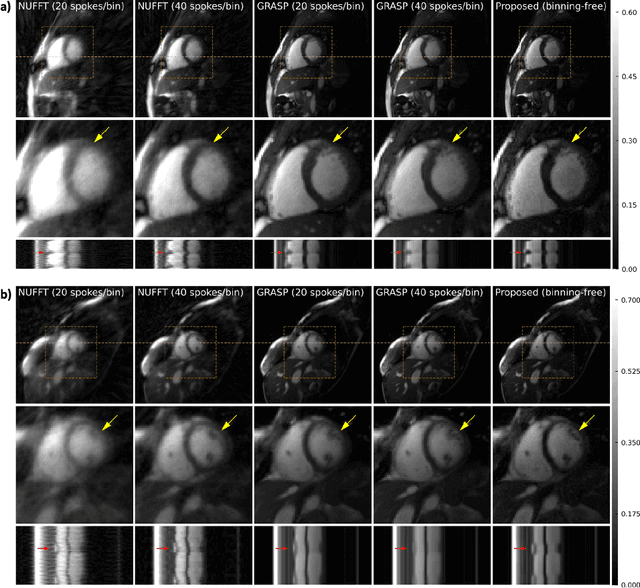
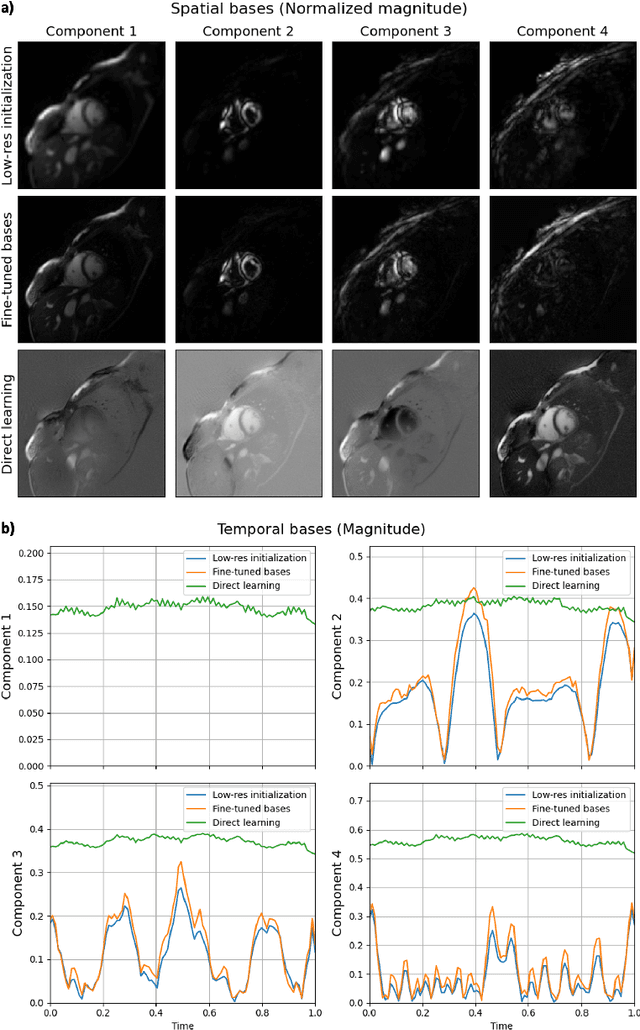
Abstract:Conventional cardiac cine MRI methods rely on retrospective gating, which limits temporal resolution and the ability to capture continuous cardiac dynamics, particularly in patients with arrhythmias and beat-to-beat variations. To address these challenges, we propose a reconstruction framework based on subspace implicit neural representations for real-time cardiac cine MRI of continuously sampled radial data. This approach employs two multilayer perceptrons to learn spatial and temporal subspace bases, leveraging the low-rank properties of cardiac cine MRI. Initialized with low-resolution reconstructions, the networks are fine-tuned using spoke-specific loss functions to recover spatial details and temporal fidelity. Our method directly utilizes the continuously sampled radial k-space spokes during training, thereby eliminating the need for binning and non-uniform FFT. This approach achieves superior spatial and temporal image quality compared to conventional binned methods at the acceleration rate of 10 and 20, demonstrating potential for high-resolution imaging of dynamic cardiac events and enhancing diagnostic capability.
CMRxRecon2024: A Multi-Modality, Multi-View K-Space Dataset Boosting Universal Machine Learning for Accelerated Cardiac MRI
Jun 27, 2024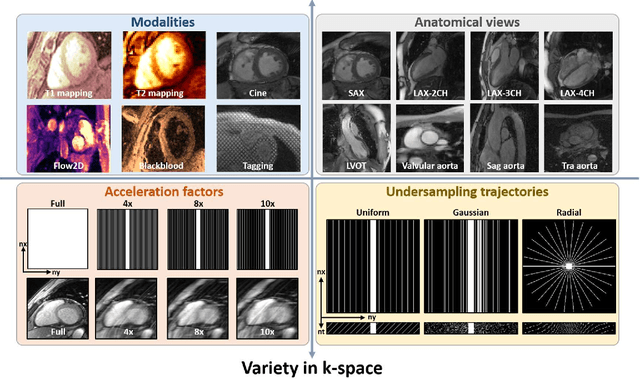
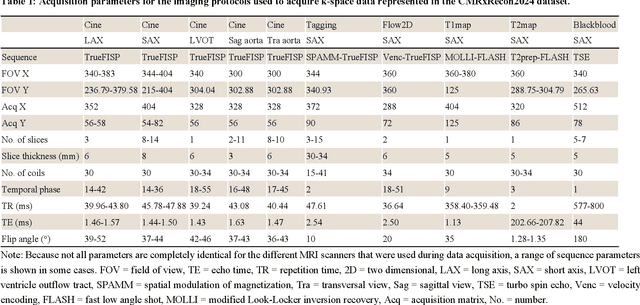
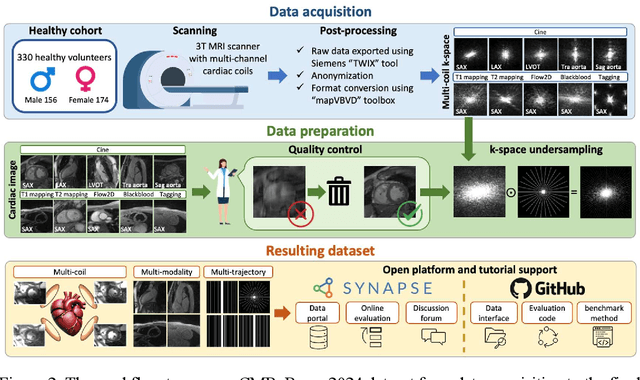
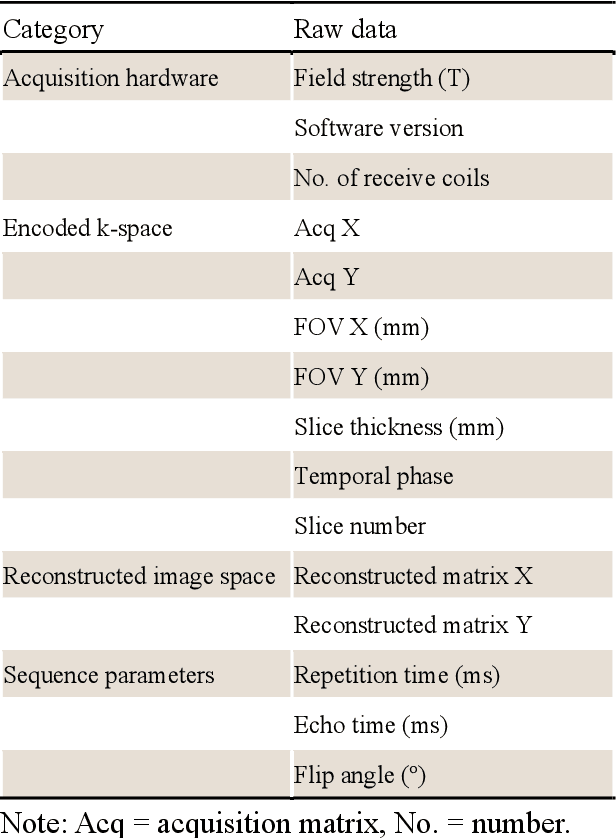
Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as a clinically gold-standard technique for diagnosing cardiac diseases, thanks to its ability to provide diverse information with multiple modalities and anatomical views. Accelerated cardiac MRI is highly expected to achieve time-efficient and patient-friendly imaging, and then advanced image reconstruction approaches are required to recover high-quality, clinically interpretable images from undersampled measurements. However, the lack of publicly available cardiac MRI k-space dataset in terms of both quantity and diversity has severely hindered substantial technological progress, particularly for data-driven artificial intelligence. Here, we provide a standardized, diverse, and high-quality CMRxRecon2024 dataset to facilitate the technical development, fair evaluation, and clinical transfer of cardiac MRI reconstruction approaches, towards promoting the universal frameworks that enable fast and robust reconstructions across different cardiac MRI protocols in clinical practice. To the best of our knowledge, the CMRxRecon2024 dataset is the largest and most diverse publicly available cardiac k-space dataset. It is acquired from 330 healthy volunteers, covering commonly used modalities, anatomical views, and acquisition trajectories in clinical cardiac MRI workflows. Besides, an open platform with tutorials, benchmarks, and data processing tools is provided to facilitate data usage, advanced method development, and fair performance evaluation.
Self-Supervised k-Space Regularization for Motion-Resolved Abdominal MRI Using Neural Implicit k-Space Representation
Apr 12, 2024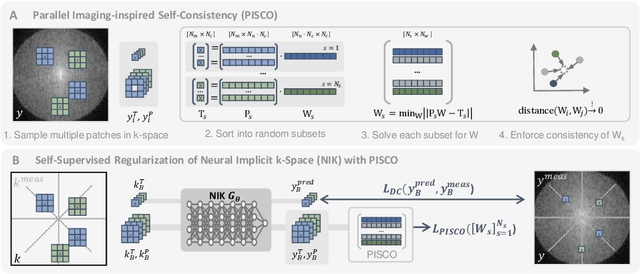
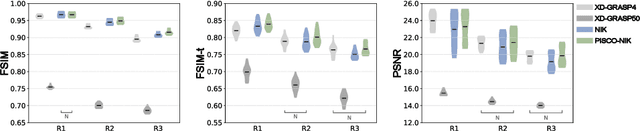
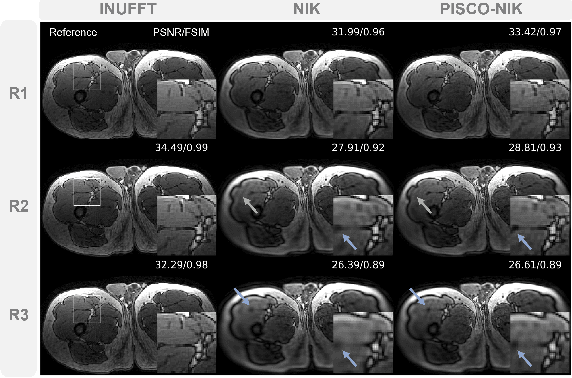
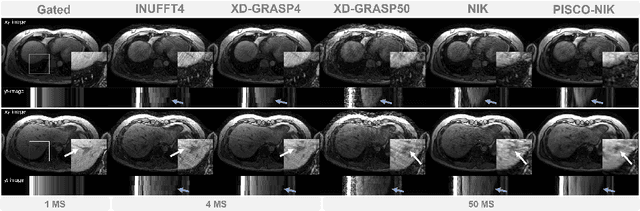
Abstract:Neural implicit k-space representations have shown promising results for dynamic MRI at high temporal resolutions. Yet, their exclusive training in k-space limits the application of common image regularization methods to improve the final reconstruction. In this work, we introduce the concept of parallel imaging-inspired self-consistency (PISCO), which we incorporate as novel self-supervised k-space regularization enforcing a consistent neighborhood relationship. At no additional data cost, the proposed regularization significantly improves neural implicit k-space reconstructions on simulated data. Abdominal in-vivo reconstructions using PISCO result in enhanced spatio-temporal image quality compared to state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/vjspi/PISCO-NIK.
Unsupervised reconstruction of accelerated cardiac cine MRI using Neural Fields
Jul 24, 2023



Abstract:Cardiac cine MRI is the gold standard for cardiac functional assessment, but the inherently slow acquisition process creates the necessity of reconstruction approaches for accelerated undersampled acquisitions. Several regularization approaches that exploit spatial-temporal redundancy have been proposed to reconstruct undersampled cardiac cine MRI. More recently, methods based on supervised deep learning have been also proposed to further accelerate acquisition and reconstruction. However, these techniques rely on usually large dataset for training, which are not always available. In this work, we propose an unsupervised approach based on implicit neural field representations for cardiac cine MRI (so called NF-cMRI). The proposed method was evaluated in in-vivo undersampled golden-angle radial multi-coil acquisitions for undersampling factors of 26x and 52x, achieving good image quality, and comparable spatial and improved temporal depiction than a state-of-the-art reconstruction technique.
A Deep Learning-based Integrated Framework for Quality-aware Undersampled Cine Cardiac MRI Reconstruction and Analysis
May 02, 2022



Abstract:Cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is considered the gold standard for cardiac function evaluation. However, cine CMR acquisition is inherently slow and in recent decades considerable effort has been put into accelerating scan times without compromising image quality or the accuracy of derived results. In this paper, we present a fully-automated, quality-controlled integrated framework for reconstruction, segmentation and downstream analysis of undersampled cine CMR data. The framework enables active acquisition of radial k-space data, in which acquisition can be stopped as soon as acquired data are sufficient to produce high quality reconstructions and segmentations. This results in reduced scan times and automated analysis, enabling robust and accurate estimation of functional biomarkers. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we perform realistic simulations of radial k-space acquisitions on a dataset of subjects from the UK Biobank and present results on in-vivo cine CMR k-space data collected from healthy subjects. The results demonstrate that our method can produce quality-controlled images in a mean scan time reduced from 12 to 4 seconds per slice, and that image quality is sufficient to allow clinically relevant parameters to be automatically estimated to within 5% mean absolute difference.
Quality-aware Cine Cardiac MRI Reconstruction and Analysis from Undersampled k-space Data
Sep 16, 2021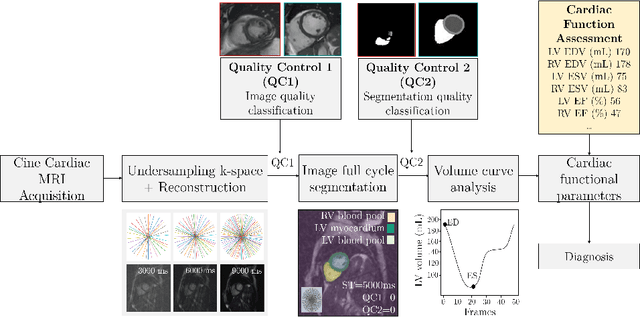
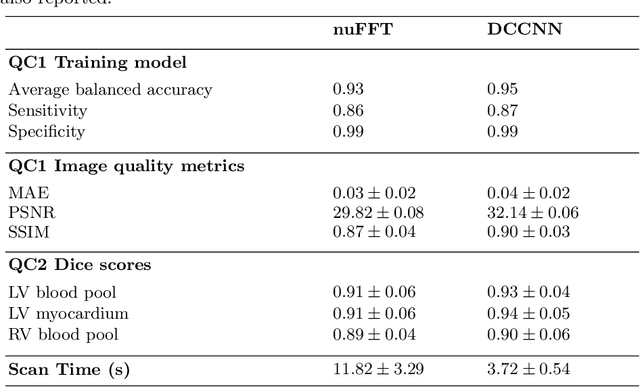
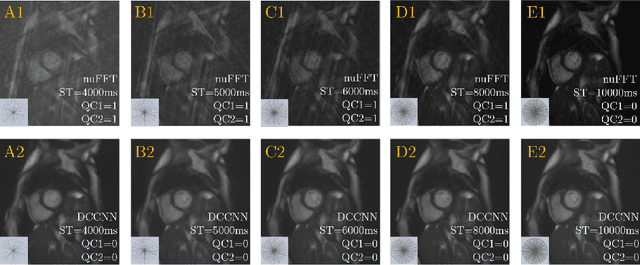
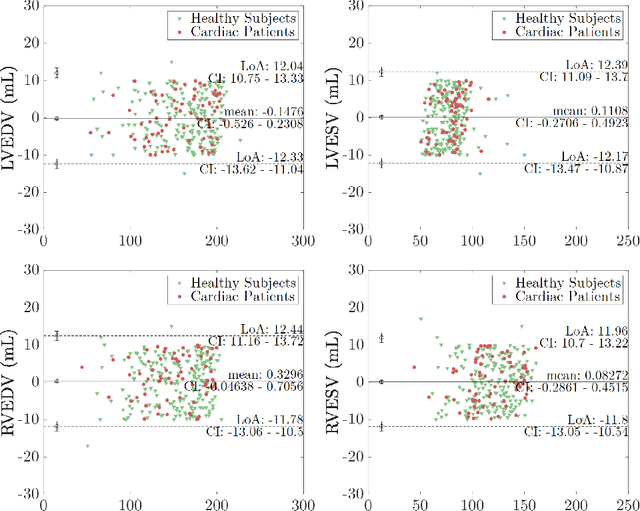
Abstract:Cine cardiac MRI is routinely acquired for the assessment of cardiac health, but the imaging process is slow and typically requires several breath-holds to acquire sufficient k-space profiles to ensure good image quality. Several undersampling-based reconstruction techniques have been proposed during the last decades to speed up cine cardiac MRI acquisition. However, the undersampling factor is commonly fixed to conservative values before acquisition to ensure diagnostic image quality, potentially leading to unnecessarily long scan times. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end quality-aware cine short-axis cardiac MRI framework that combines image acquisition and reconstruction with downstream tasks such as segmentation, volume curve analysis and estimation of cardiac functional parameters. The goal is to reduce scan time by acquiring only a fraction of k-space data to enable the reconstruction of images that can pass quality control checks and produce reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters. The framework consists of a deep learning model for the reconstruction of 2D+t cardiac cine MRI images from undersampled data, an image quality-control step to detect good quality reconstructions, followed by a deep learning model for bi-ventricular segmentation, a quality-control step to detect good quality segmentations and automated calculation of cardiac functional parameters. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we perform simulations using a cohort of selected participants from the UK Biobank (n=270), 200 healthy subjects and 70 patients with cardiomyopathies. Our results show that we can produce quality-controlled images in a scan time reduced from 12 to 4 seconds per slice, enabling reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters such as ejection fraction within 5% mean absolute error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge