Gastao Cruz
Subspace Implicit Neural Representations for Real-Time Cardiac Cine MR Imaging
Dec 17, 2024
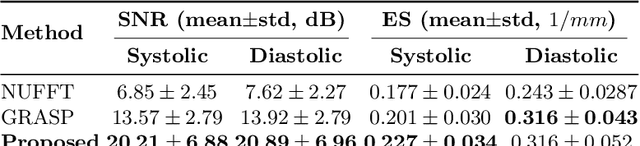
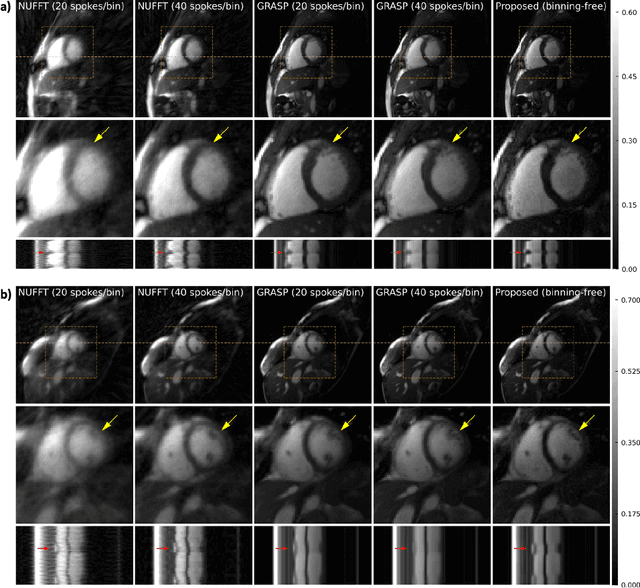
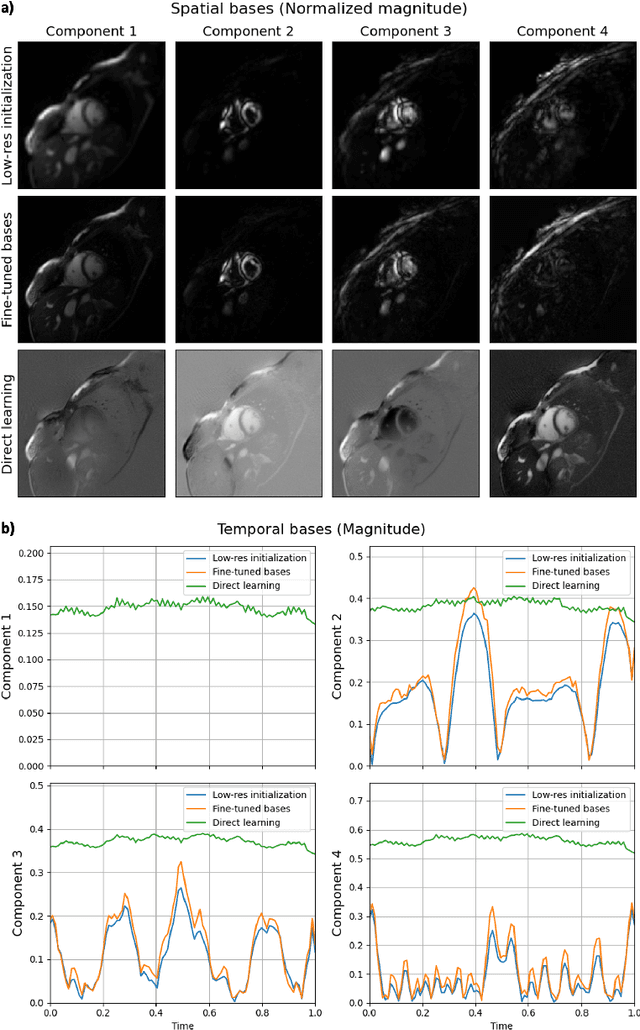
Abstract:Conventional cardiac cine MRI methods rely on retrospective gating, which limits temporal resolution and the ability to capture continuous cardiac dynamics, particularly in patients with arrhythmias and beat-to-beat variations. To address these challenges, we propose a reconstruction framework based on subspace implicit neural representations for real-time cardiac cine MRI of continuously sampled radial data. This approach employs two multilayer perceptrons to learn spatial and temporal subspace bases, leveraging the low-rank properties of cardiac cine MRI. Initialized with low-resolution reconstructions, the networks are fine-tuned using spoke-specific loss functions to recover spatial details and temporal fidelity. Our method directly utilizes the continuously sampled radial k-space spokes during training, thereby eliminating the need for binning and non-uniform FFT. This approach achieves superior spatial and temporal image quality compared to conventional binned methods at the acceleration rate of 10 and 20, demonstrating potential for high-resolution imaging of dynamic cardiac events and enhancing diagnostic capability.
Neural Implicit k-Space for Binning-free Non-Cartesian Cardiac MR Imaging
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:In this work, we propose a novel image reconstruction framework that directly learns a neural implicit representation in k-space for ECG-triggered non-Cartesian Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CMR). While existing methods bin acquired data from neighboring time points to reconstruct one phase of the cardiac motion, our framework allows for a continuous, binning-free, and subject-specific k-space representation.We assign a unique coordinate that consists of time, coil index, and frequency domain location to each sampled k-space point. We then learn the subject-specific mapping from these unique coordinates to k-space intensities using a multi-layer perceptron with frequency domain regularization. During inference, we obtain a complete k-space for Cartesian coordinates and an arbitrary temporal resolution. A simple inverse Fourier transform recovers the image, eliminating the need for density compensation and costly non-uniform Fourier transforms for non-Cartesian data. This novel imaging framework was tested on 42 radially sampled datasets from 6 subjects. The proposed method outperforms other techniques qualitatively and quantitatively using data from four and one heartbeat(s) and 30 cardiac phases. Our results for one heartbeat reconstruction of 50 cardiac phases show improved artifact removal and spatio-temporal resolution, leveraging the potential for real-time CMR.
Quality-aware Cine Cardiac MRI Reconstruction and Analysis from Undersampled k-space Data
Sep 16, 2021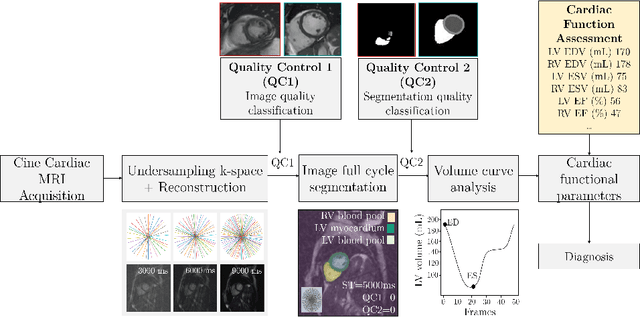
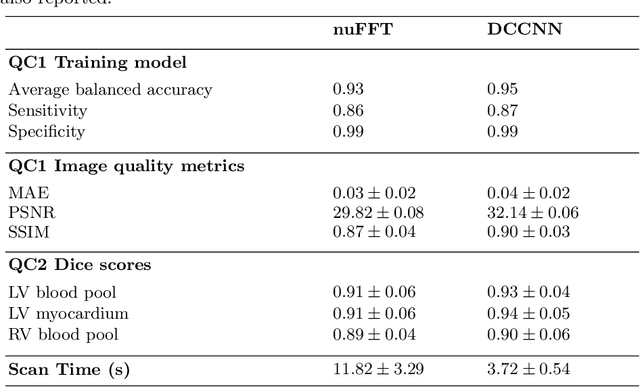
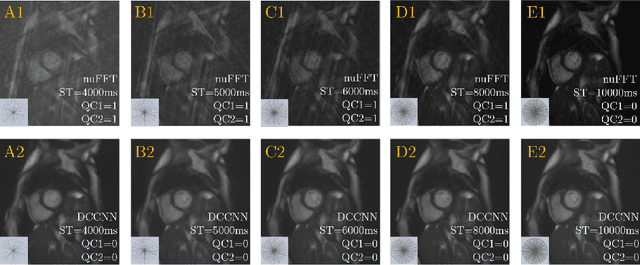
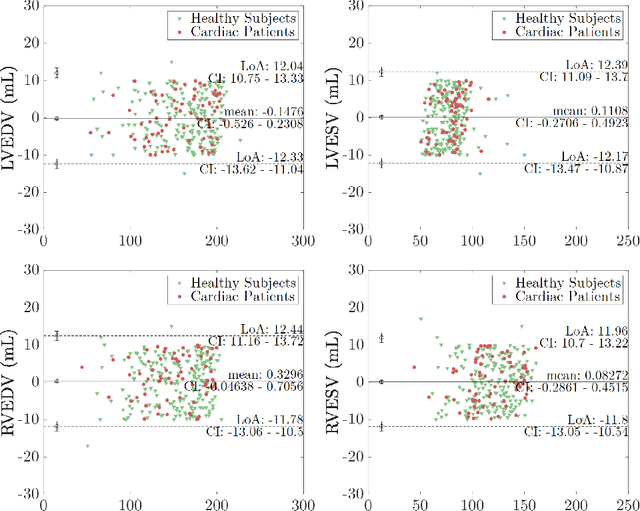
Abstract:Cine cardiac MRI is routinely acquired for the assessment of cardiac health, but the imaging process is slow and typically requires several breath-holds to acquire sufficient k-space profiles to ensure good image quality. Several undersampling-based reconstruction techniques have been proposed during the last decades to speed up cine cardiac MRI acquisition. However, the undersampling factor is commonly fixed to conservative values before acquisition to ensure diagnostic image quality, potentially leading to unnecessarily long scan times. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end quality-aware cine short-axis cardiac MRI framework that combines image acquisition and reconstruction with downstream tasks such as segmentation, volume curve analysis and estimation of cardiac functional parameters. The goal is to reduce scan time by acquiring only a fraction of k-space data to enable the reconstruction of images that can pass quality control checks and produce reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters. The framework consists of a deep learning model for the reconstruction of 2D+t cardiac cine MRI images from undersampled data, an image quality-control step to detect good quality reconstructions, followed by a deep learning model for bi-ventricular segmentation, a quality-control step to detect good quality segmentations and automated calculation of cardiac functional parameters. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we perform simulations using a cohort of selected participants from the UK Biobank (n=270), 200 healthy subjects and 70 patients with cardiomyopathies. Our results show that we can produce quality-controlled images in a scan time reduced from 12 to 4 seconds per slice, enabling reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters such as ejection fraction within 5% mean absolute error.
LAPNet: Non-rigid Registration derived in k-space for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Jul 19, 2021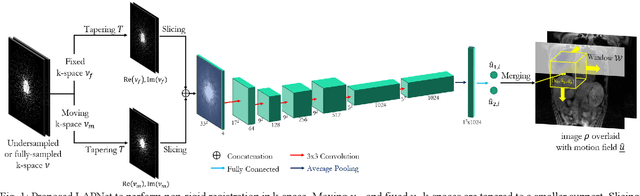

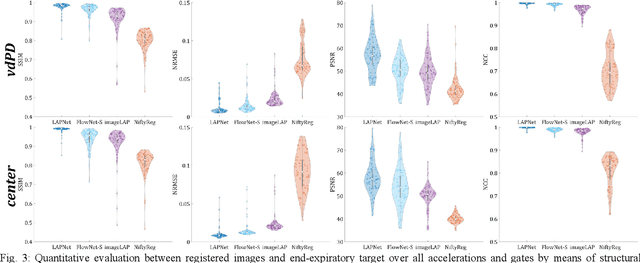
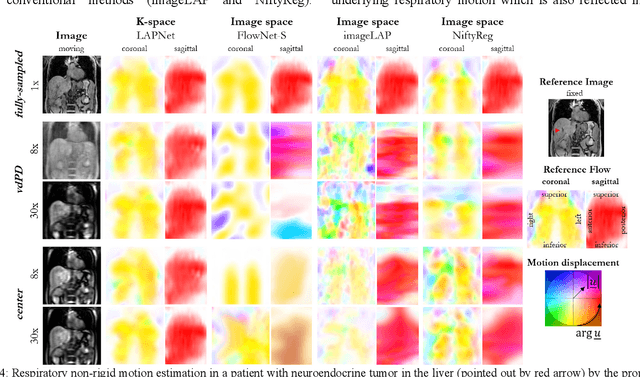
Abstract:Physiological motion, such as cardiac and respiratory motion, during Magnetic Resonance (MR) image acquisition can cause image artifacts. Motion correction techniques have been proposed to compensate for these types of motion during thoracic scans, relying on accurate motion estimation from undersampled motion-resolved reconstruction. A particular interest and challenge lie in the derivation of reliable non-rigid motion fields from the undersampled motion-resolved data. Motion estimation is usually formulated in image space via diffusion, parametric-spline, or optical flow methods. However, image-based registration can be impaired by remaining aliasing artifacts due to the undersampled motion-resolved reconstruction. In this work, we describe a formalism to perform non-rigid registration directly in the sampled Fourier space, i.e. k-space. We propose a deep-learning based approach to perform fast and accurate non-rigid registration from the undersampled k-space data. The basic working principle originates from the Local All-Pass (LAP) technique, a recently introduced optical flow-based registration. The proposed LAPNet is compared against traditional and deep learning image-based registrations and tested on fully-sampled and highly-accelerated (with two undersampling strategies) 3D respiratory motion-resolved MR images in a cohort of 40 patients with suspected liver or lung metastases and 25 healthy subjects. The proposed LAPNet provided consistent and superior performance to image-based approaches throughout different sampling trajectories and acceleration factors.
Magnetization Transfer-Mediated MR Fingerprinting
Apr 06, 2021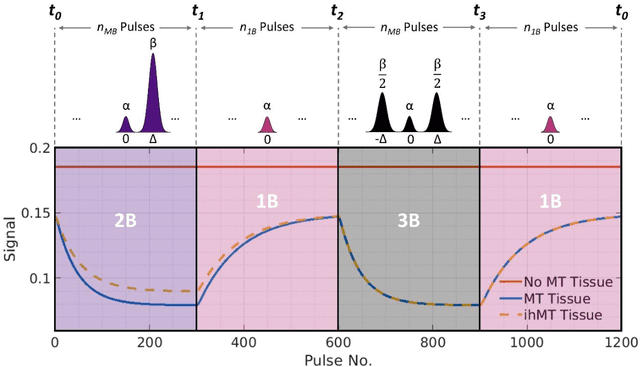
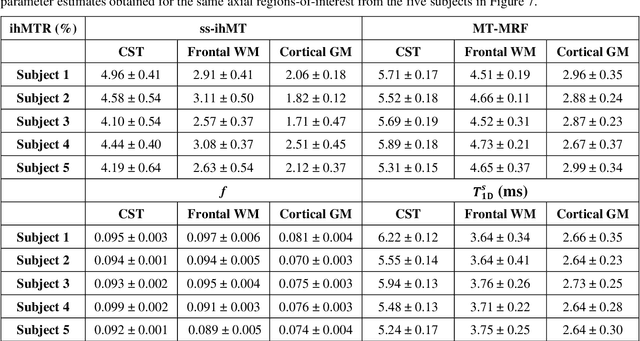
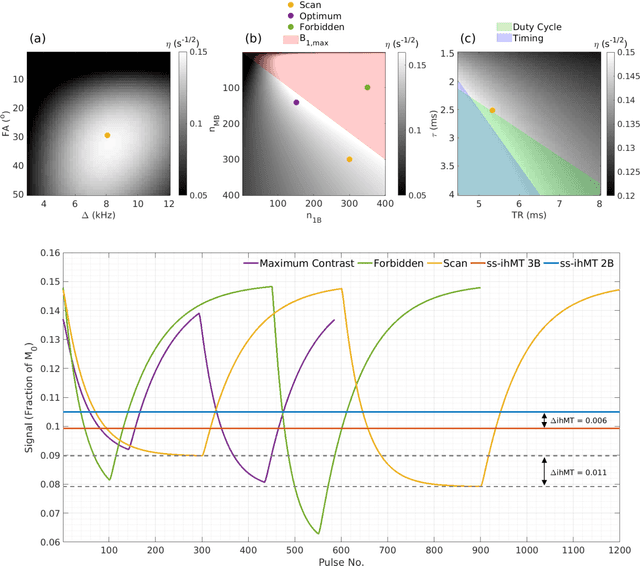
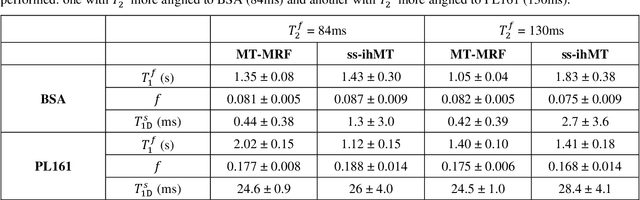
Abstract:Purpose: Magnetization transfer (MT) and inhomogeneous MT (ihMT) contrasts are used in MRI to provide information about macromolecular tissue content. In particular, MT is sensitive to macromolecules and ihMT appears to be specific to myelinated tissue. This study proposes a technique to characterize MT and ihMT properties from a single acquisition, producing both semiquantitative contrast ratios, and quantitative parameter maps. Theory and Methods: Building upon previous work that uses multiband radiofrequency (RF) pulses to efficiently generate ihMT contrast, we propose a cyclic-steady-state approach that cycles between multiband and single-band pulses to boost the achieved contrast. Resultant time-variable signals are reminiscent of a magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) acquisition, except that the signal fluctuations are entirely mediated by magnetization transfer effects. A dictionary-based low-rank inversion method is used to reconstruct the resulting images and to produce both semiquantitative MT ratio (MTR) and ihMT ratio (ihMTR) maps, as well as quantitative parameter estimates corresponding to an ihMT tissue model. Results: Phantom and in vivo brain data acquired at 1.5T demonstrate the expected contrast trends, with ihMTR maps showing contrast more specific to white matter (WM), as has been reported by others. Quantitative estimation of semisolid fraction and dipolar T1 was also possible and yielded measurements consistent with literature values in the brain. Conclusions: By cycling between multiband and single-band pulses, an entirely magnetization transfer mediated 'fingerprinting' method was demonstrated. This proof-of-concept approach can be used to generate semiquantitative maps and quantitatively estimate some macromolecular specific tissue parameters.
Channel Attention Networks for Robust MR Fingerprinting Matching
Dec 02, 2020



Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) enables simultaneous mapping of multiple tissue parameters such as T1 and T2 relaxation times. The working principle of MRF relies on varying acquisition parameters pseudo-randomly, so that each tissue generates its unique signal evolution during scanning. Even though MRF provides faster scanning, it has disadvantages such as erroneous and slow generation of the corresponding parametric maps, which needs to be improved. Moreover, there is a need for explainable architectures for understanding the guiding signals to generate accurate parametric maps. In this paper, we addressed both of these shortcomings by proposing a novel neural network architecture consisting of a channel-wise attention module and a fully convolutional network. The proposed approach, evaluated over 3 simulated MRF signals, reduces error in the reconstruction of tissue parameters by 8.88% for T1 and 75.44% for T2 with respect to state-of-the-art methods. Another contribution of this study is a new channel selection method: attention-based channel selection. Furthermore, the effect of patch size and temporal frames of MRF signal on channel reduction are analyzed by employing a channel-wise attention.
Deep Learning Based Detection and Correction of Cardiac MR Motion Artefacts During Reconstruction for High-Quality Segmentation
Oct 21, 2019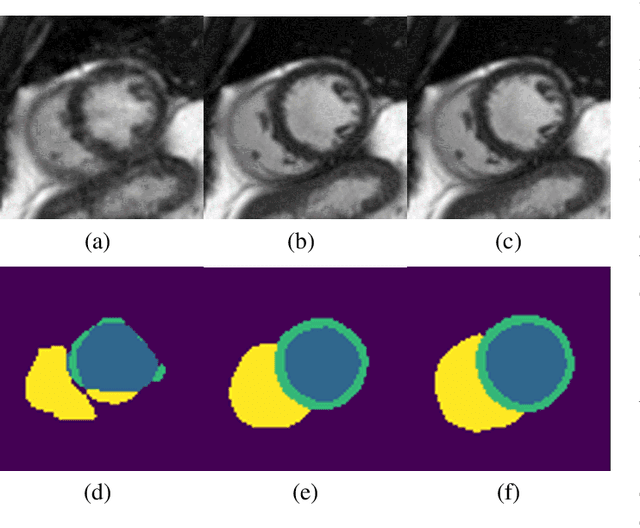
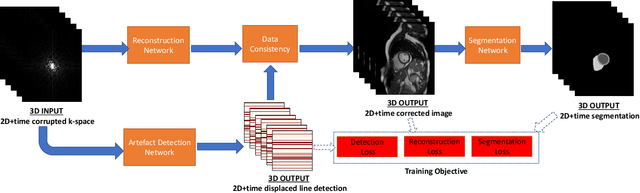
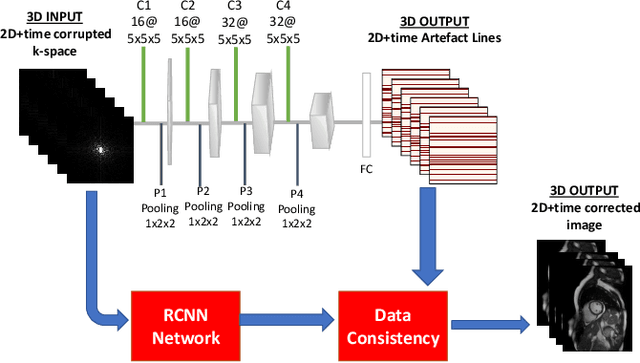
Abstract:Segmenting anatomical structures in medical images has been successfully addressed with deep learning methods for a range of applications. However, this success is heavily dependent on the quality of the image that is being segmented. A commonly neglected point in the medical image analysis community is the vast amount of clinical images that have severe image artefacts due to organ motion, movement of the patient and/or image acquisition related issues. In this paper, we discuss the implications of image motion artefacts on cardiac MR segmentation and compare a variety of approaches for jointly correcting for artefacts and segmenting the cardiac cavity. We propose to use a segmentation network coupled with this in an end-to-end framework. Our training optimises three different tasks: 1) image artefact detection, 2) artefact correction and 3) image segmentation. We train the reconstruction network to automatically correct for motion-related artefacts using synthetically corrupted cardiac MR k-space data and uncorrected reconstructed images. Using a test set of 500 2D+time cine MR acquisitions from the UK Biobank data set, we achieve demonstrably good image quality and high segmentation accuracy in the presence of synthetic motion artefacts. We quantitatively compare our method with a variety of techniques for jointly recovering image quality and performing image segmentation. We showcase better performance compared to state-of-the-art image correction techniques. Moreover, our method preserves the quality of uncorrupted images and therefore can be utilised as a global image reconstruction algorithm.
Detection and Correction of Cardiac MR Motion Artefacts during Reconstruction from K-space
Jun 12, 2019



Abstract:In fully sampled cardiac MR (CMR) acquisitions, motion can lead to corruption of k-space lines, which can result in artefacts in the reconstructed images. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically detect and correct motion-related artefacts in CMR acquisitions during reconstruction from k-space data. Our correction method is inspired by work on undersampled CMR reconstruction, and uses deep learning to optimize a data-consistency term for under-sampled k-space reconstruction. Our main methodological contribution is the addition of a detection network to classify motion-corrupted k-space lines to convert the problem of artefact correction to a problem of reconstruction using the data consistency term. We train our network to automatically correct for motion-related artefacts using synthetically corrupted cine CMR k-space data as well as uncorrupted CMR images. Using a test set of 50 2D+time cine CMR datasets from the UK Biobank, we achieve good image quality in the presence of synthetic motion artefacts. We quantitatively compare our method with a variety of techniques for recovering good image quality and showcase better performance compared to state of the art denoising techniques with a PSNR of 37.1. Moreover, we show that our method preserves the quality of uncorrupted images and therefore can be also utilized as a general image reconstruction algorithm.
Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting using Recurrent Neural Networks
Dec 19, 2018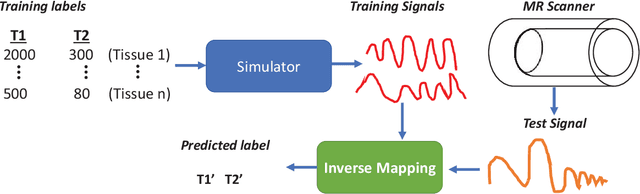
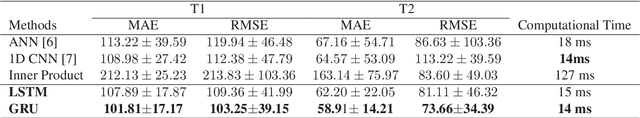
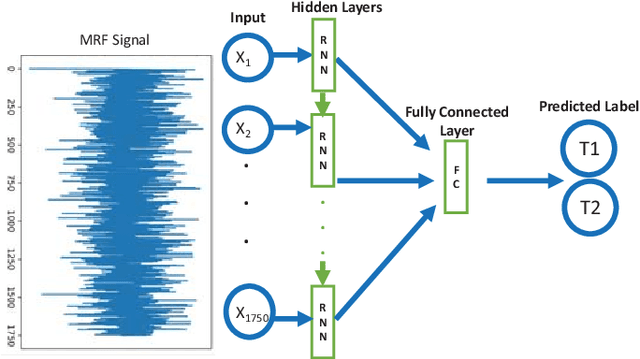
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) is a new approach to quantitative magnetic resonance imaging that allows simultaneous measurement of multiple tissue properties in a single, time-efficient acquisition. Standard MRF reconstructs parametric maps using dictionary matching and lacks scalability due to computational inefficiency. We propose to perform MRF map reconstruction using a recurrent neural network, which exploits the time-dependent information of the MRF signal evolution. We evaluate our method on multiparametric synthetic signals and compare it to existing MRF map reconstruction approaches, including those based on neural networks. Our method achieves state-of-the-art estimates of T1 and T2 values. In addition, the reconstruction time is significantly reduced compared to dictionary-matching based approaches.
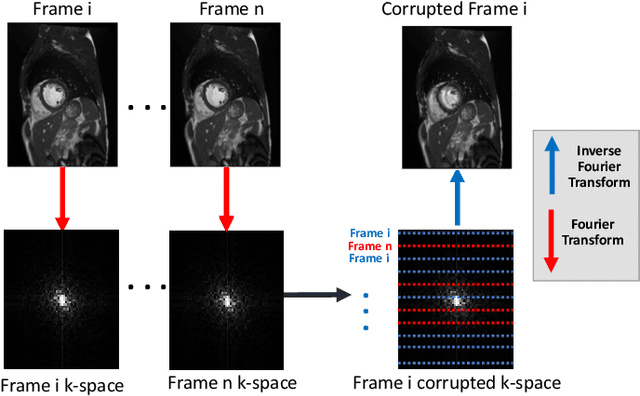
Automatic CNN-based detection of cardiac MR motion artefacts using k-space data augmentation and curriculum learning
Oct 29, 2018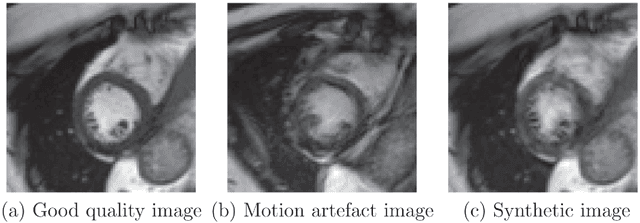
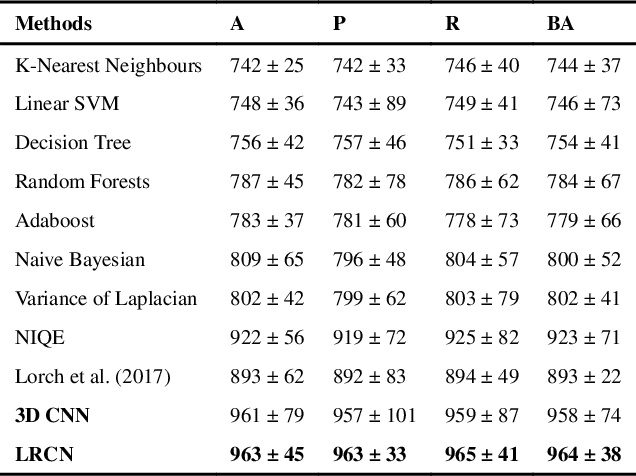

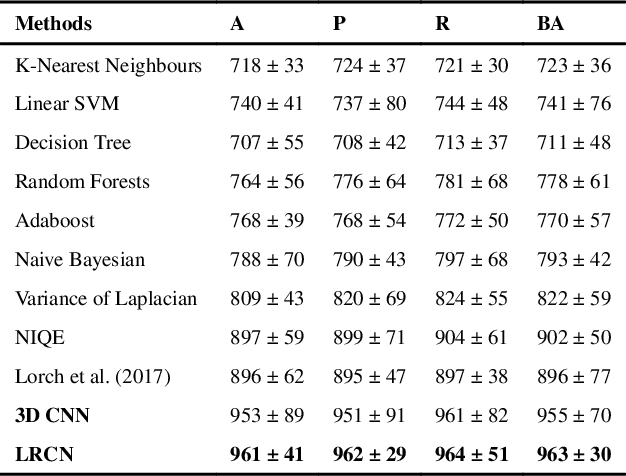
Abstract:Good quality of medical images is a prerequisite for the success of subsequent image analysis pipelines. Quality assessment of medical images is therefore an essential activity and for large population studies such as the UK Biobank (UKBB), manual identification of artefacts such as those caused by unanticipated motion is tedious and time-consuming. Therefore, there is an urgent need for automatic image quality assessment techniques. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically detect the presence of motion-related artefacts in cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) cine images. We compare two deep learning architectures to classify poor quality CMR images: 1) 3D spatio-temporal Convolutional Neural Networks (3D-CNN), 2) Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network (LRCN). Though in real clinical setup motion artefacts are common, high-quality imaging of UKBB, which comprises cross-sectional population data of volunteers who do not necessarily have health problems creates a highly imbalanced classification problem. Due to the high number of good quality images compared to the relatively low number of images with motion artefacts, we propose a novel data augmentation scheme based on synthetic artefact creation in k-space. We also investigate a learning approach using a predetermined curriculum based on synthetic artefact severity. We evaluate our pipeline on a subset of the UK Biobank data set consisting of 3510 CMR images. The LRCN architecture outperformed the 3D-CNN architecture and was able to detect 2D+time short axis images with motion artefacts in less than 1ms with high recall. We compare our approach to a range of state-of-the-art quality assessment methods. The novel data augmentation and curriculum learning approaches both improved classification performance achieving overall area under the ROC curve of 0.89.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge