Thomas Küstner
Towards a Unified Theoretical Framework for Self-Supervised MRI Reconstruction
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The demand for high-resolution, non-invasive imaging continues to drive innovation in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), yet prolonged acquisition times hinder accessibility and real-time applications. While deep learning-based reconstruction methods have accelerated MRI, their predominant supervised paradigm depends on fully-sampled reference data that are challenging to acquire. Recently, self-supervised learning (SSL) approaches have emerged as promising alternatives, but most are empirically designed and fragmented. Therefore, we introduce UNITS (Unified Theory for Self-supervision), a general framework for self-supervised MRI reconstruction. UNITS unifies prior SSL strategies within a common formalism, enabling consistent interpretation and systematic benchmarking. We prove that SSL can achieve the same expected performance as supervised learning. Under this theoretical guarantee, we introduce sampling stochasticity and flexible data utilization, which improve network generalization under out-of-domain distributions and stabilize training. Together, these contributions establish UNITS as a theoretical foundation and a practical paradigm for interpretable, generalizable, and clinically applicable self-supervised MRI reconstruction.
Retrospective motion correction in MRI using disentangled embeddings
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Physiological motion can affect the diagnostic quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). While various retrospective motion correction methods exist, many struggle to generalize across different motion types and body regions. In particular, machine learning (ML)-based corrections are often tailored to specific applications and datasets. We hypothesize that motion artifacts, though diverse, share underlying patterns that can be disentangled and exploited. To address this, we propose a hierarchical vector-quantized (VQ) variational auto-encoder that learns a disentangled embedding of motion-to-clean image features. A codebook is deployed to capture finite collection of motion patterns at multiple resolutions, enabling coarse-to-fine correction. An auto-regressive model is trained to learn the prior distribution of motion-free images and is used at inference to guide the correction process. Unlike conventional approaches, our method does not require artifact-specific training and can generalize to unseen motion patterns. We demonstrate the approach on simulated whole-body motion artifacts and observe robust correction across varying motion severity. Our results suggest that the model effectively disentangled physical motion of the simulated motion-effective scans, therefore, improving the generalizability of the ML-based MRI motion correction. Our work of disentangling the motion features shed a light on its potential application across anatomical regions and motion types.
CUTE-MRI: Conformalized Uncertainty-based framework for Time-adaptivE MRI
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers unparalleled soft-tissue contrast but is fundamentally limited by long acquisition times. While deep learning-based accelerated MRI can dramatically shorten scan times, the reconstruction from undersampled data introduces ambiguity resulting from an ill-posed problem with infinitely many possible solutions that propagates to downstream clinical tasks. This uncertainty is usually ignored during the acquisition process as acceleration factors are often fixed a priori, resulting in scans that are either unnecessarily long or of insufficient quality for a given clinical endpoint. This work introduces a dynamic, uncertainty-aware acquisition framework that adjusts scan time on a per-subject basis. Our method leverages a probabilistic reconstruction model to estimate image uncertainty, which is then propagated through a full analysis pipeline to a quantitative metric of interest (e.g., patellar cartilage volume or cardiac ejection fraction). We use conformal prediction to transform this uncertainty into a rigorous, calibrated confidence interval for the metric. During acquisition, the system iteratively samples k-space, updates the reconstruction, and evaluates the confidence interval. The scan terminates automatically once the uncertainty meets a user-predefined precision target. We validate our framework on both knee and cardiac MRI datasets. Our results demonstrate that this adaptive approach reduces scan times compared to fixed protocols while providing formal statistical guarantees on the precision of the final image. This framework moves beyond fixed acceleration factors, enabling patient-specific acquisitions that balance scan efficiency with diagnostic confidence, a critical step towards personalized and resource-efficient MRI.
Self-supervised feature learning for cardiac Cine MR image reconstruction
May 29, 2025Abstract:We propose a self-supervised feature learning assisted reconstruction (SSFL-Recon) framework for MRI reconstruction to address the limitation of existing supervised learning methods. Although recent deep learning-based methods have shown promising performance in MRI reconstruction, most require fully-sampled images for supervised learning, which is challenging in practice considering long acquisition times under respiratory or organ motion. Moreover, nearly all fully-sampled datasets are obtained from conventional reconstruction of mildly accelerated datasets, thus potentially biasing the achievable performance. The numerous undersampled datasets with different accelerations in clinical practice, hence, remain underutilized. To address these issues, we first train a self-supervised feature extractor on undersampled images to learn sampling-insensitive features. The pre-learned features are subsequently embedded in the self-supervised reconstruction network to assist in removing artifacts. Experiments were conducted retrospectively on an in-house 2D cardiac Cine dataset, including 91 cardiovascular patients and 38 healthy subjects. The results demonstrate that the proposed SSFL-Recon framework outperforms existing self-supervised MRI reconstruction methods and even exhibits comparable or better performance to supervised learning up to $16\times$ retrospective undersampling. The feature learning strategy can effectively extract global representations, which have proven beneficial in removing artifacts and increasing generalization ability during reconstruction.
Highly efficient non-rigid registration in k-space with application to cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:In Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), high temporal-resolved motion can be useful for image acquisition and reconstruction, MR-guided radiotherapy, dynamic contrast-enhancement, flow and perfusion imaging, and functional assessment of motion patterns in cardiovascular, abdominal, peristaltic, fetal, or musculoskeletal imaging. Conventionally, these motion estimates are derived through image-based registration, a particularly challenging task for complex motion patterns and high dynamic resolution. The accelerated scans in such applications result in imaging artifacts that compromise the motion estimation. In this work, we propose a novel self-supervised deep learning-based framework, dubbed the Local-All Pass Attention Network (LAPANet), for non-rigid motion estimation directly from the acquired accelerated Fourier space, i.e. k-space. The proposed approach models non-rigid motion as the cumulative sum of local translational displacements, following the Local All-Pass (LAP) registration technique. LAPANet was evaluated on cardiac motion estimation across various sampling trajectories and acceleration rates. Our results demonstrate superior accuracy compared to prior conventional and deep learning-based registration methods, accommodating as few as 2 lines/frame in a Cartesian trajectory and 3 spokes/frame in a non-Cartesian trajectory. The achieved high temporal resolution (less than 5 ms) for non-rigid motion opens new avenues for motion detection, tracking and correction in dynamic and real-time MRI applications.
Benchmarking Dependence Measures to Prevent Shortcut Learning in Medical Imaging
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Medical imaging cohorts are often confounded by factors such as acquisition devices, hospital sites, patient backgrounds, and many more. As a result, deep learning models tend to learn spurious correlations instead of causally related features, limiting their generalizability to new and unseen data. This problem can be addressed by minimizing dependence measures between intermediate representations of task-related and non-task-related variables. These measures include mutual information, distance correlation, and the performance of adversarial classifiers. Here, we benchmark such dependence measures for the task of preventing shortcut learning. We study a simplified setting using Morpho-MNIST and a medical imaging task with CheXpert chest radiographs. Our results provide insights into how to mitigate confounding factors in medical imaging.
TotalSegmentator MRI: Sequence-Independent Segmentation of 59 Anatomical Structures in MR images
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: To develop an open-source and easy-to-use segmentation model that can automatically and robustly segment most major anatomical structures in MR images independently of the MR sequence. Materials and Methods: In this study we extended the capabilities of TotalSegmentator to MR images. 298 MR scans and 227 CT scans were used to segment 59 anatomical structures (20 organs, 18 bones, 11 muscles, 7 vessels, 3 tissue types) relevant for use cases such as organ volumetry, disease characterization, and surgical planning. The MR and CT images were randomly sampled from routine clinical studies and thus represent a real-world dataset (different ages, pathologies, scanners, body parts, sequences, contrasts, echo times, repetition times, field strengths, slice thicknesses and sites). We trained an nnU-Net segmentation algorithm on this dataset and calculated Dice similarity coefficients (Dice) to evaluate the model's performance. Results: The model showed a Dice score of 0.824 (CI: 0.801, 0.842) on the test set, which included a wide range of clinical data with major pathologies. The model significantly outperformed two other publicly available segmentation models (Dice score, 0.824 versus 0.762; p<0.001 and 0.762 versus 0.542; p<0.001). On the CT image test set of the original TotalSegmentator paper it almost matches the performance of the original TotalSegmentator (Dice score, 0.960 versus 0.970; p<0.001). Conclusion: Our proposed model extends the capabilities of TotalSegmentator to MR images. The annotated dataset (https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.11367004) and open-source toolkit (https://www.github.com/wasserth/TotalSegmentator) are publicly available.
Attention-aware non-rigid image registration for accelerated MR imaging
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:Accurate motion estimation at high acceleration factors enables rapid motion-compensated reconstruction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) without compromising the diagnostic image quality. In this work, we introduce an attention-aware deep learning-based framework that can perform non-rigid pairwise registration for fully sampled and accelerated MRI. We extract local visual representations to build similarity maps between the registered image pairs at multiple resolution levels and additionally leverage long-range contextual information using a transformer-based module to alleviate ambiguities in the presence of artifacts caused by undersampling. We combine local and global dependencies to perform simultaneous coarse and fine motion estimation. The proposed method was evaluated on in-house acquired fully sampled and accelerated data of 101 patients and 62 healthy subjects undergoing cardiac and thoracic MRI. The impact of motion estimation accuracy on the downstream task of motion-compensated reconstruction was analyzed. We demonstrate that our model derives reliable and consistent motion fields across different sampling trajectories (Cartesian and radial) and acceleration factors of up to 16x for cardiac motion and 30x for respiratory motion and achieves superior image quality in motion-compensated reconstruction qualitatively and quantitatively compared to conventional and recent deep learning-based approaches. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/lab-midas/GMARAFT.
MedShapeNet -- A Large-Scale Dataset of 3D Medical Shapes for Computer Vision
Sep 12, 2023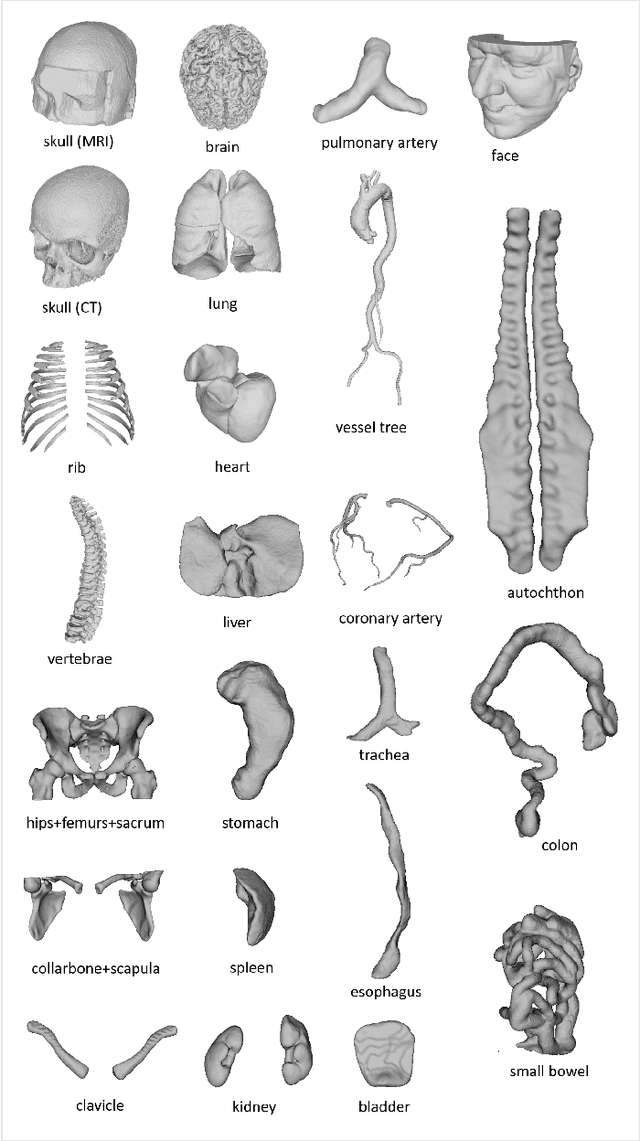

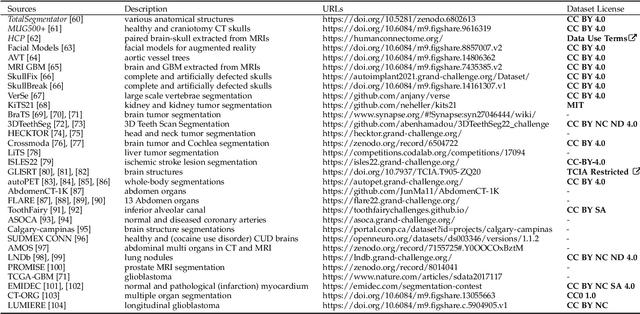
Abstract:We present MedShapeNet, a large collection of anatomical shapes (e.g., bones, organs, vessels) and 3D surgical instrument models. Prior to the deep learning era, the broad application of statistical shape models (SSMs) in medical image analysis is evidence that shapes have been commonly used to describe medical data. Nowadays, however, state-of-the-art (SOTA) deep learning algorithms in medical imaging are predominantly voxel-based. In computer vision, on the contrary, shapes (including, voxel occupancy grids, meshes, point clouds and implicit surface models) are preferred data representations in 3D, as seen from the numerous shape-related publications in premier vision conferences, such as the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), as well as the increasing popularity of ShapeNet (about 51,300 models) and Princeton ModelNet (127,915 models) in computer vision research. MedShapeNet is created as an alternative to these commonly used shape benchmarks to facilitate the translation of data-driven vision algorithms to medical applications, and it extends the opportunities to adapt SOTA vision algorithms to solve critical medical problems. Besides, the majority of the medical shapes in MedShapeNet are modeled directly on the imaging data of real patients, and therefore it complements well existing shape benchmarks comprising of computer-aided design (CAD) models. MedShapeNet currently includes more than 100,000 medical shapes, and provides annotations in the form of paired data. It is therefore also a freely available repository of 3D models for extended reality (virtual reality - VR, augmented reality - AR, mixed reality - MR) and medical 3D printing. This white paper describes in detail the motivations behind MedShapeNet, the shape acquisition procedures, the use cases, as well as the usage of the online shape search portal: https://medshapenet.ikim.nrw/
Uncertainty Estimation and Propagation in Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Aug 04, 2023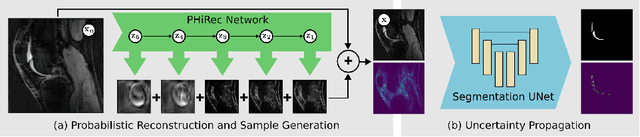



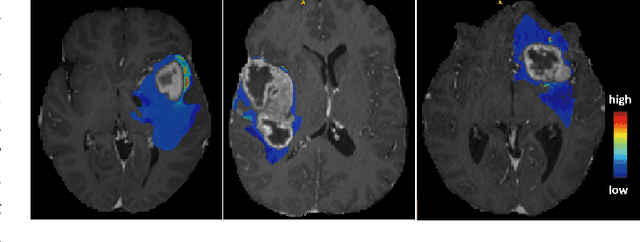
Abstract:MRI reconstruction techniques based on deep learning have led to unprecedented reconstruction quality especially in highly accelerated settings. However, deep learning techniques are also known to fail unexpectedly and hallucinate structures. This is particularly problematic if reconstructions are directly used for downstream tasks such as real-time treatment guidance or automated extraction of clinical paramters (e.g. via segmentation). Well-calibrated uncertainty quantification will be a key ingredient for safe use of this technology in clinical practice. In this paper we propose a novel probabilistic reconstruction technique (PHiRec) building on the idea of conditional hierarchical variational autoencoders. We demonstrate that our proposed method produces high-quality reconstructions as well as uncertainty quantification that is substantially better calibrated than several strong baselines. We furthermore demonstrate how uncertainties arising in the MR econstruction can be propagated to a downstream segmentation task, and show that PHiRec also allows well-calibrated estimation of segmentation uncertainties that originated in the MR reconstruction process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge