Rene M. Botnar
Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting using Recurrent Neural Networks
Dec 19, 2018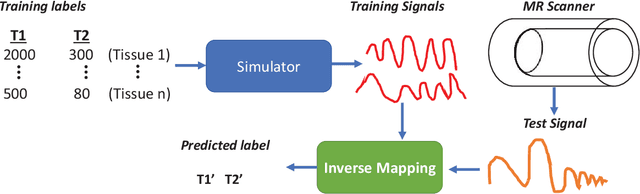
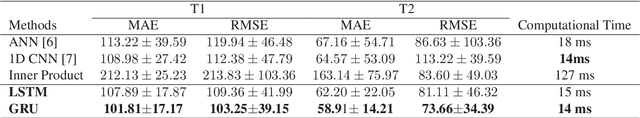
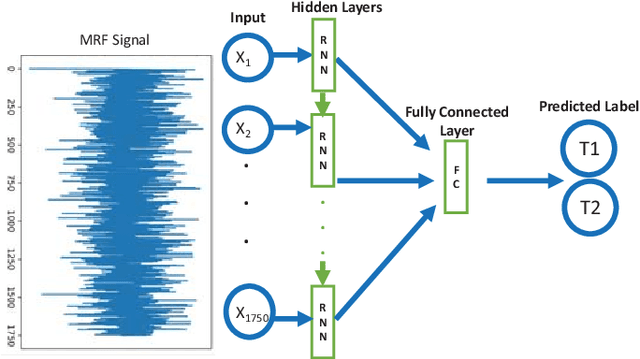
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) is a new approach to quantitative magnetic resonance imaging that allows simultaneous measurement of multiple tissue properties in a single, time-efficient acquisition. Standard MRF reconstructs parametric maps using dictionary matching and lacks scalability due to computational inefficiency. We propose to perform MRF map reconstruction using a recurrent neural network, which exploits the time-dependent information of the MRF signal evolution. We evaluate our method on multiparametric synthetic signals and compare it to existing MRF map reconstruction approaches, including those based on neural networks. Our method achieves state-of-the-art estimates of T1 and T2 values. In addition, the reconstruction time is significantly reduced compared to dictionary-matching based approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge