James Clough
Detection and Correction of Cardiac MR Motion Artefacts during Reconstruction from K-space
Jun 12, 2019



Abstract:In fully sampled cardiac MR (CMR) acquisitions, motion can lead to corruption of k-space lines, which can result in artefacts in the reconstructed images. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically detect and correct motion-related artefacts in CMR acquisitions during reconstruction from k-space data. Our correction method is inspired by work on undersampled CMR reconstruction, and uses deep learning to optimize a data-consistency term for under-sampled k-space reconstruction. Our main methodological contribution is the addition of a detection network to classify motion-corrupted k-space lines to convert the problem of artefact correction to a problem of reconstruction using the data consistency term. We train our network to automatically correct for motion-related artefacts using synthetically corrupted cine CMR k-space data as well as uncorrupted CMR images. Using a test set of 50 2D+time cine CMR datasets from the UK Biobank, we achieve good image quality in the presence of synthetic motion artefacts. We quantitatively compare our method with a variety of techniques for recovering good image quality and showcase better performance compared to state of the art denoising techniques with a PSNR of 37.1. Moreover, we show that our method preserves the quality of uncorrupted images and therefore can be also utilized as a general image reconstruction algorithm.
Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting using Recurrent Neural Networks
Dec 19, 2018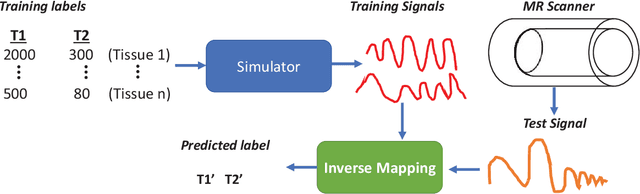
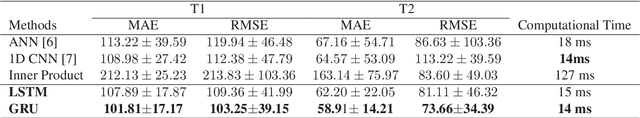
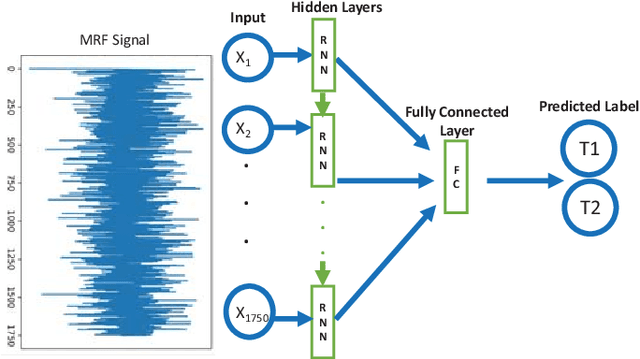
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) is a new approach to quantitative magnetic resonance imaging that allows simultaneous measurement of multiple tissue properties in a single, time-efficient acquisition. Standard MRF reconstructs parametric maps using dictionary matching and lacks scalability due to computational inefficiency. We propose to perform MRF map reconstruction using a recurrent neural network, which exploits the time-dependent information of the MRF signal evolution. We evaluate our method on multiparametric synthetic signals and compare it to existing MRF map reconstruction approaches, including those based on neural networks. Our method achieves state-of-the-art estimates of T1 and T2 values. In addition, the reconstruction time is significantly reduced compared to dictionary-matching based approaches.
Automatic CNN-based detection of cardiac MR motion artefacts using k-space data augmentation and curriculum learning
Oct 29, 2018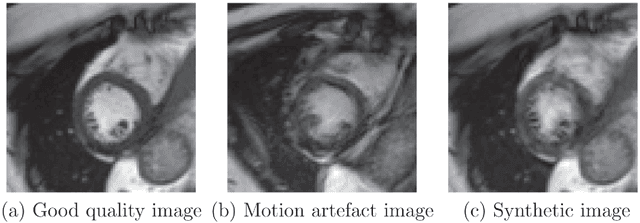
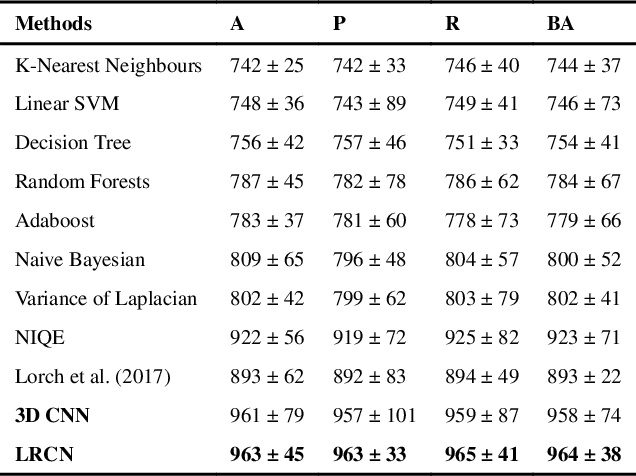

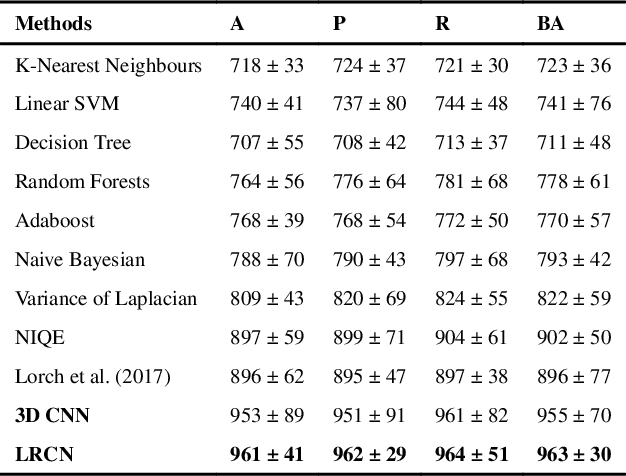
Abstract:Good quality of medical images is a prerequisite for the success of subsequent image analysis pipelines. Quality assessment of medical images is therefore an essential activity and for large population studies such as the UK Biobank (UKBB), manual identification of artefacts such as those caused by unanticipated motion is tedious and time-consuming. Therefore, there is an urgent need for automatic image quality assessment techniques. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically detect the presence of motion-related artefacts in cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) cine images. We compare two deep learning architectures to classify poor quality CMR images: 1) 3D spatio-temporal Convolutional Neural Networks (3D-CNN), 2) Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network (LRCN). Though in real clinical setup motion artefacts are common, high-quality imaging of UKBB, which comprises cross-sectional population data of volunteers who do not necessarily have health problems creates a highly imbalanced classification problem. Due to the high number of good quality images compared to the relatively low number of images with motion artefacts, we propose a novel data augmentation scheme based on synthetic artefact creation in k-space. We also investigate a learning approach using a predetermined curriculum based on synthetic artefact severity. We evaluate our pipeline on a subset of the UK Biobank data set consisting of 3510 CMR images. The LRCN architecture outperformed the 3D-CNN architecture and was able to detect 2D+time short axis images with motion artefacts in less than 1ms with high recall. We compare our approach to a range of state-of-the-art quality assessment methods. The novel data augmentation and curriculum learning approaches both improved classification performance achieving overall area under the ROC curve of 0.89.
Neural Embeddings of Graphs in Hyperbolic Space
May 29, 2017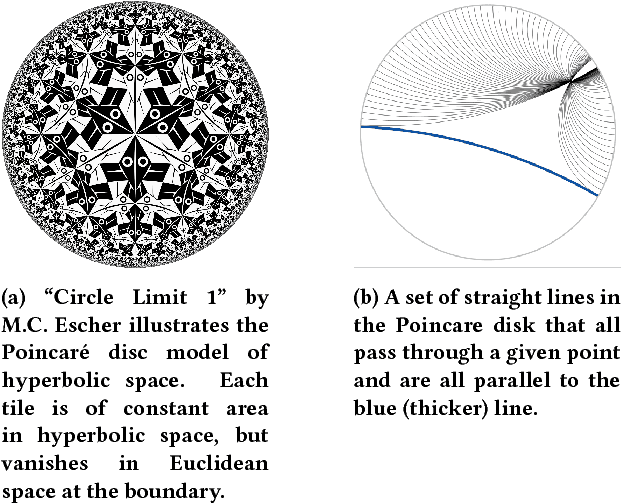
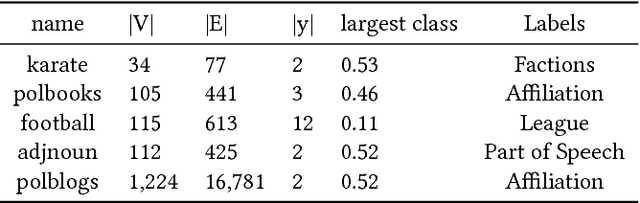
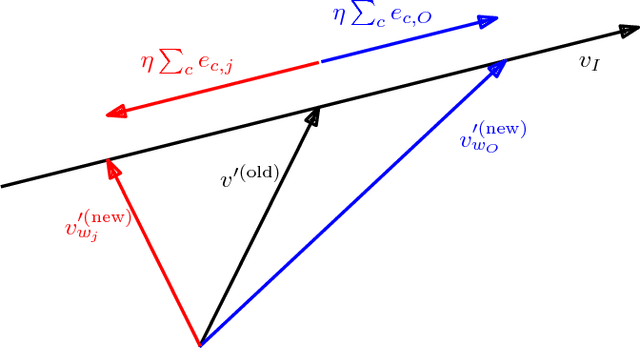
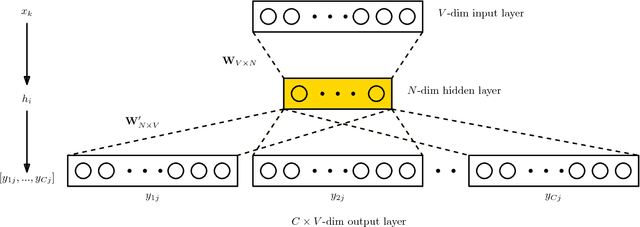
Abstract:Neural embeddings have been used with great success in Natural Language Processing (NLP). They provide compact representations that encapsulate word similarity and attain state-of-the-art performance in a range of linguistic tasks. The success of neural embeddings has prompted significant amounts of research into applications in domains other than language. One such domain is graph-structured data, where embeddings of vertices can be learned that encapsulate vertex similarity and improve performance on tasks including edge prediction and vertex labelling. For both NLP and graph based tasks, embeddings have been learned in high-dimensional Euclidean spaces. However, recent work has shown that the appropriate isometric space for embedding complex networks is not the flat Euclidean space, but negatively curved, hyperbolic space. We present a new concept that exploits these recent insights and propose learning neural embeddings of graphs in hyperbolic space. We provide experimental evidence that embedding graphs in their natural geometry significantly improves performance on downstream tasks for several real-world public datasets.
* 7 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge