Miguel Castelo-Branco
Self-mediated exploration in artificial intelligence inspired by cognitive psychology
Feb 13, 2023



Abstract:Exploration of the physical environment is an indispensable precursor to data acquisition and enables knowledge generation via analytical or direct trialing. Artificial Intelligence lacks the exploratory capabilities of even the most underdeveloped organisms, hindering its autonomy and adaptability. Supported by cognitive psychology, this works links human behavior and artificial agents to endorse self-development. In accordance with reported data, paradigms of epistemic and achievement emotion are embedded to machine-learning methodology contingent on their impact when decision making. A study is subsequently designed to mirror previous human trials, which artificial agents are made to undergo repeatedly towards convergence. Results demonstrate causality, learned by the vast majority of agents, between their internal states and exploration to match those reported for human counterparts. The ramifications of these findings are pondered for both research into human cognition and betterment of artificial intelligence.
A Deep Learning-based Integrated Framework for Quality-aware Undersampled Cine Cardiac MRI Reconstruction and Analysis
May 02, 2022



Abstract:Cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is considered the gold standard for cardiac function evaluation. However, cine CMR acquisition is inherently slow and in recent decades considerable effort has been put into accelerating scan times without compromising image quality or the accuracy of derived results. In this paper, we present a fully-automated, quality-controlled integrated framework for reconstruction, segmentation and downstream analysis of undersampled cine CMR data. The framework enables active acquisition of radial k-space data, in which acquisition can be stopped as soon as acquired data are sufficient to produce high quality reconstructions and segmentations. This results in reduced scan times and automated analysis, enabling robust and accurate estimation of functional biomarkers. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we perform realistic simulations of radial k-space acquisitions on a dataset of subjects from the UK Biobank and present results on in-vivo cine CMR k-space data collected from healthy subjects. The results demonstrate that our method can produce quality-controlled images in a mean scan time reduced from 12 to 4 seconds per slice, and that image quality is sufficient to allow clinically relevant parameters to be automatically estimated to within 5% mean absolute difference.
Quality-aware Cine Cardiac MRI Reconstruction and Analysis from Undersampled k-space Data
Sep 16, 2021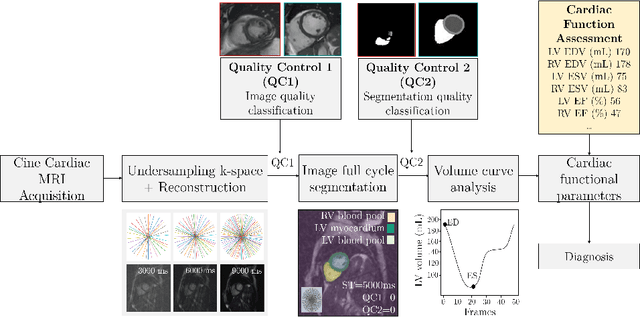
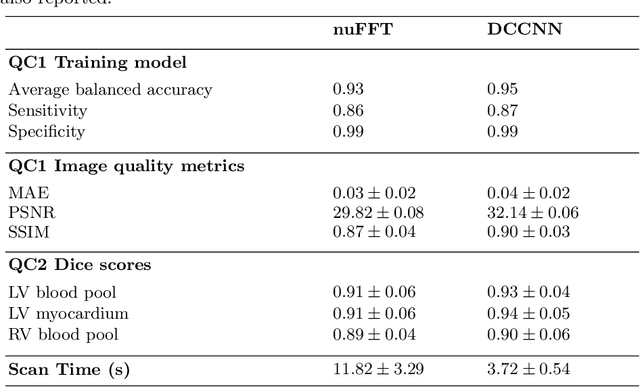
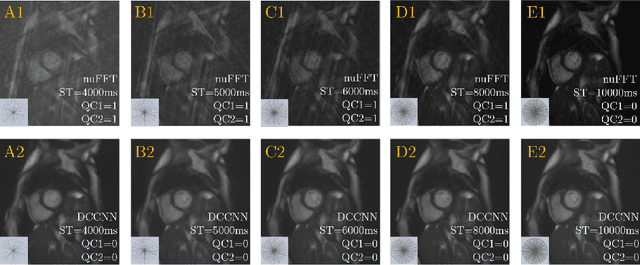
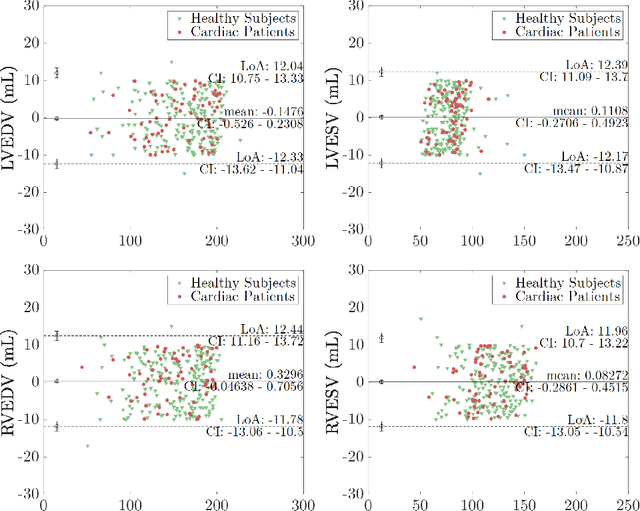
Abstract:Cine cardiac MRI is routinely acquired for the assessment of cardiac health, but the imaging process is slow and typically requires several breath-holds to acquire sufficient k-space profiles to ensure good image quality. Several undersampling-based reconstruction techniques have been proposed during the last decades to speed up cine cardiac MRI acquisition. However, the undersampling factor is commonly fixed to conservative values before acquisition to ensure diagnostic image quality, potentially leading to unnecessarily long scan times. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end quality-aware cine short-axis cardiac MRI framework that combines image acquisition and reconstruction with downstream tasks such as segmentation, volume curve analysis and estimation of cardiac functional parameters. The goal is to reduce scan time by acquiring only a fraction of k-space data to enable the reconstruction of images that can pass quality control checks and produce reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters. The framework consists of a deep learning model for the reconstruction of 2D+t cardiac cine MRI images from undersampled data, an image quality-control step to detect good quality reconstructions, followed by a deep learning model for bi-ventricular segmentation, a quality-control step to detect good quality segmentations and automated calculation of cardiac functional parameters. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we perform simulations using a cohort of selected participants from the UK Biobank (n=270), 200 healthy subjects and 70 patients with cardiomyopathies. Our results show that we can produce quality-controlled images in a scan time reduced from 12 to 4 seconds per slice, enabling reliable estimates of cardiac functional parameters such as ejection fraction within 5% mean absolute error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge