Chenxu Zhao
UPA: Unsupervised Prompt Agent via Tree-Based Search and Selection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Prompt agents have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for automated prompt optimization, framing refinement as a sequential decision-making problem over a structured prompt space. While this formulation enables the use of advanced planning algorithms, these methods typically assume access to supervised reward signals, which are often unavailable in practical scenarios. In this work, we propose UPA, an Unsupervised Prompt Agent that realizes structured search and selection without relying on supervised feedback. Specifically, during search, UPA iteratively constructs an evolving tree structure to navigate the prompt space, guided by fine-grained and order-invariant pairwise comparisons from Large Language Models (LLMs). Crucially, as these local comparisons do not inherently yield a consistent global scale, we decouple systematic prompt exploration from final selection, introducing a two-stage framework grounded in the Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model. This framework first performs path-wise Bayesian aggregation of local comparisons to filter candidates under uncertainty, followed by global tournament-style comparisons to infer latent prompt quality and identify the optimal prompt. Experiments across multiple tasks demonstrate that UPA consistently outperforms existing prompt optimization methods, showing that agent-style optimization remains highly effective even in fully unsupervised settings.
Incentivizing Cardiologist-Like Reasoning in MLLMs for Interpretable Echocardiographic Diagnosis
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Echocardiographic diagnosis is vital for cardiac screening yet remains challenging. Existing echocardiography foundation models do not effectively capture the relationships between quantitative measurements and clinical manifestations, whereas medical reasoning multimodal large language models (MLLMs) require costly construction of detailed reasoning paths and remain ineffective at directly incorporating such echocardiographic priors into their reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach comprising Cardiac Reasoning Template (CRT) and CardiacMind to enhance MLLM's echocardiographic reasoning by introducing cardiologist-like mindset. Specifically, CRT provides stepwise canonical diagnostic procedures for complex cardiac diseases to streamline reasoning path construction without the need for costly case-by-case verification. To incentivize reasoning MLLM under CRT, we develop CardiacMind, a new reinforcement learning scheme with three novel rewards: Procedural Quantity Reward (PQtR), Procedural Quality Reward (PQlR), and Echocardiographic Semantic Reward (ESR). PQtR promotes detailed reasoning; PQlR promotes integration of evidence across views and modalities, while ESR grounds stepwise descriptions in visual content. Our methods show a 48% improvement in multiview echocardiographic diagnosis for 15 complex cardiac diseases and a 5% improvement on CardiacNet-PAH over prior methods. The user study on our method's reasoning outputs shows 93.33% clinician agreement with cardiologist-like reasoning logic. Our code will be available.
Smooth Operator: Smooth Verifiable Reward Activates Spatial Reasoning Ability of Vision-Language Model
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) face a critical bottleneck in achieving precise numerical prediction for 3D scene understanding. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) approaches, primarily based on relative ranking, often suffer from severe reward sparsity and gradient instability, failing to effectively exploit the verifiable signals provided by 3D physical constraints. Notably, in standard GRPO frameworks, relative normalization causes "near-miss" samples (characterized by small but non-zero errors) to suffer from advantage collapse. This leads to a severe data utilization bottleneck where valuable boundary samples are discarded during optimization. To address this, we introduce the Smooth Numerical Reward Activation (SNRA) operator and the Absolute-Preserving GRPO (AP-GRPO) framework. SNRA employs a dynamically parameterized Sigmoid function to transform raw feedback into a dense, continuous reward continuum. Concurrently, AP-GRPO integrates absolute scalar gradients to mitigate the numerical information loss inherent in conventional relative-ranking mechanisms. By leveraging this approach, we constructed Numerical3D-50k, a dataset comprising 50,000 verifiable 3D subtasks. Empirical results indicate that AP-GRPO achieves performance parity with large-scale supervised methods while maintaining higher data efficiency, effectively activating latent 3D reasoning in VLMs without requiring architectural modifications.
HATS: High-Accuracy Triple-Set Watermarking for Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Misuse of LLM-generated text can be curbed by watermarking techniques that embed implicit signals into the output. We propose a watermark that partitions the vocabulary at each decoding step into three sets (Green/Yellow/Red) with fixed ratios and restricts sampling to the Green and Yellow sets. At detection time, we replay the same partitions, compute Green-enrichment and Red-depletion statistics, convert them to one-sided z-scores, and aggregate their p-values via Fisher's method to decide whether a passage is watermarked. We implement generation, detection, and testing on Llama 2 7B, and evaluate true-positive rate, false-positive rate, and text quality. Results show that the triple-partition scheme achieves high detection accuracy at fixed FPR while preserving readability.
* Camera-ready version of the paper accepted for oral presentation at the 11th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC 2025)
Towards Benchmarking Privacy Vulnerabilities in Selective Forgetting with Large Language Models
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have primarily focused on the process of learning from data to acquire knowledgeable learning systems. As these systems are increasingly deployed in critical areas, ensuring their privacy and alignment with human values is paramount. Recently, selective forgetting (also known as machine unlearning) has shown promise for privacy and data removal tasks, and has emerged as a transformative paradigm shift in the field of AI. It refers to the ability of a model to selectively erase the influence of previously seen data, which is especially important for compliance with modern data protection regulations and for aligning models with human values. Despite its promise, selective forgetting raises significant privacy concerns, especially when the data involved come from sensitive domains. While new unlearning-induced privacy attacks are continuously proposed, each is shown to outperform its predecessors using different experimental settings, which can lead to overly optimistic and potentially unfair assessments that may disproportionately favor one particular attack over the others. In this work, we present the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating privacy vulnerabilities in selective forgetting. We extensively investigate privacy vulnerabilities of machine unlearning techniques and benchmark privacy leakage across a wide range of victim data, state-of-the-art unlearning privacy attacks, unlearning methods, and model architectures. We systematically evaluate and identify critical factors related to unlearning-induced privacy leakage. With our novel insights, we aim to provide a standardized tool for practitioners seeking to deploy customized unlearning applications with faithful privacy assessments.
Towards Unveiling Predictive Uncertainty Vulnerabilities in the Context of the Right to Be Forgotten
Aug 10, 2025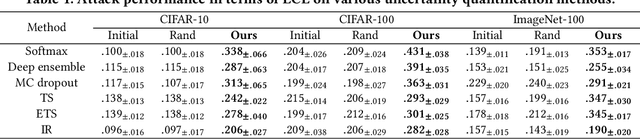
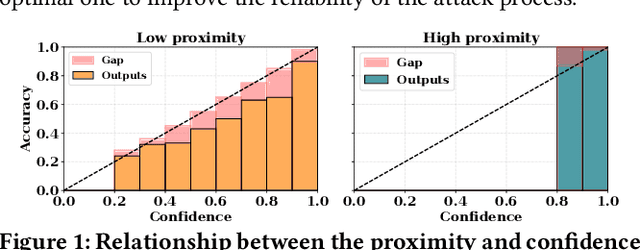
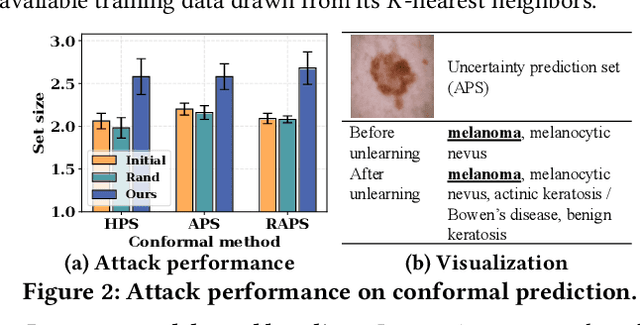
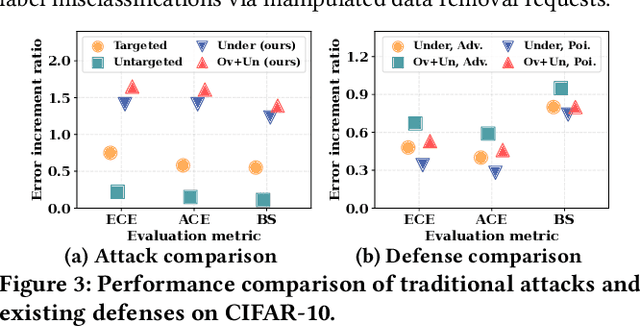
Abstract:Currently, various uncertainty quantification methods have been proposed to provide certainty and probability estimates for deep learning models' label predictions. Meanwhile, with the growing demand for the right to be forgotten, machine unlearning has been extensively studied as a means to remove the impact of requested sensitive data from a pre-trained model without retraining the model from scratch. However, the vulnerabilities of such generated predictive uncertainties with regard to dedicated malicious unlearning attacks remain unexplored. To bridge this gap, for the first time, we propose a new class of malicious unlearning attacks against predictive uncertainties, where the adversary aims to cause the desired manipulations of specific predictive uncertainty results. We also design novel optimization frameworks for our attacks and conduct extensive experiments, including black-box scenarios. Notably, our extensive experiments show that our attacks are more effective in manipulating predictive uncertainties than traditional attacks that focus on label misclassifications, and existing defenses against conventional attacks are ineffective against our attacks.
Membership Inference Attacks with False Discovery Rate Control
Aug 09, 2025
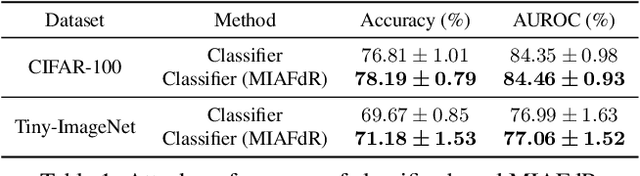


Abstract:Recent studies have shown that deep learning models are vulnerable to membership inference attacks (MIAs), which aim to infer whether a data record was used to train a target model or not. To analyze and study these vulnerabilities, various MIA methods have been proposed. Despite the significance and popularity of MIAs, existing works on MIAs are limited in providing guarantees on the false discovery rate (FDR), which refers to the expected proportion of false discoveries among the identified positive discoveries. However, it is very challenging to ensure the false discovery rate guarantees, because the underlying distribution is usually unknown, and the estimated non-member probabilities often exhibit interdependence. To tackle the above challenges, in this paper, we design a novel membership inference attack method, which can provide the guarantees on the false discovery rate. Additionally, we show that our method can also provide the marginal probability guarantee on labeling true non-member data as member data. Notably, our method can work as a wrapper that can be seamlessly integrated with existing MIA methods in a post-hoc manner, while also providing the FDR control. We perform the theoretical analysis for our method. Extensive experiments in various settings (e.g., the black-box setting and the lifelong learning setting) are also conducted to verify the desirable performance of our method.
Hypergraph Multi-modal Large Language Model: Exploiting EEG and Eye-tracking Modalities to Evaluate Heterogeneous Responses for Video Understanding
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Understanding of video creativity and content often varies among individuals, with differences in focal points and cognitive levels across different ages, experiences, and genders. There is currently a lack of research in this area, and most existing benchmarks suffer from several drawbacks: 1) a limited number of modalities and answers with restrictive length; 2) the content and scenarios within the videos are excessively monotonous, transmitting allegories and emotions that are overly simplistic. To bridge the gap to real-world applications, we introduce a large-scale \textbf{S}ubjective \textbf{R}esponse \textbf{I}ndicators for \textbf{A}dvertisement \textbf{V}ideos dataset, namely SRI-ADV. Specifically, we collected real changes in Electroencephalographic (EEG) and eye-tracking regions from different demographics while they viewed identical video content. Utilizing this multi-modal dataset, we developed tasks and protocols to analyze and evaluate the extent of cognitive understanding of video content among different users. Along with the dataset, we designed a \textbf{H}ypergraph \textbf{M}ulti-modal \textbf{L}arge \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{M}odel (HMLLM) to explore the associations among different demographics, video elements, EEG and eye-tracking indicators. HMLLM could bridge semantic gaps across rich modalities and integrate information beyond different modalities to perform logical reasoning. Extensive experimental evaluations on SRI-ADV and other additional video-based generative performance benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The codes and dataset will be released at \url{https://github.com/suay1113/HMLLM}.
Exploring Fairness in Educational Data Mining in the Context of the Right to be Forgotten
May 29, 2024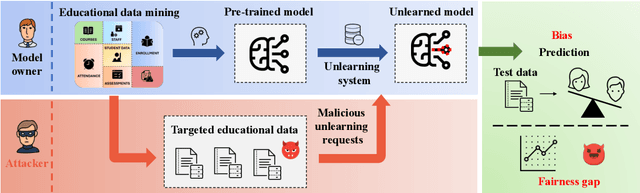



Abstract:In education data mining (EDM) communities, machine learning has achieved remarkable success in discovering patterns and structures to tackle educational challenges. Notably, fairness and algorithmic bias have gained attention in learning analytics of EDM. With the increasing demand for the right to be forgotten, there is a growing need for machine learning models to forget sensitive data and its impact, particularly within the realm of EDM. The paradigm of selective forgetting, also known as machine unlearning, has been extensively studied to address this need by eliminating the influence of specific data from a pre-trained model without complete retraining. However, existing research assumes that interactive data removal operations are conducted in secure and reliable environments, neglecting potential malicious unlearning requests to undermine the fairness of machine learning systems. In this paper, we introduce a novel class of selective forgetting attacks designed to compromise the fairness of learning models while maintaining their predictive accuracy, thereby preventing the model owner from detecting the degradation in model performance. Additionally, we propose an innovative optimization framework for selective forgetting attacks, capable of generating malicious unlearning requests across various attack scenarios. We validate the effectiveness of our proposed selective forgetting attacks on fairness through extensive experiments using diverse EDM datasets.
Towards Modeling Uncertainties of Self-explaining Neural Networks via Conformal Prediction
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:Despite the recent progress in deep neural networks (DNNs), it remains challenging to explain the predictions made by DNNs. Existing explanation methods for DNNs mainly focus on post-hoc explanations where another explanatory model is employed to provide explanations. The fact that post-hoc methods can fail to reveal the actual original reasoning process of DNNs raises the need to build DNNs with built-in interpretability. Motivated by this, many self-explaining neural networks have been proposed to generate not only accurate predictions but also clear and intuitive insights into why a particular decision was made. However, existing self-explaining networks are limited in providing distribution-free uncertainty quantification for the two simultaneously generated prediction outcomes (i.e., a sample's final prediction and its corresponding explanations for interpreting that prediction). Importantly, they also fail to establish a connection between the confidence values assigned to the generated explanations in the interpretation layer and those allocated to the final predictions in the ultimate prediction layer. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, in this paper, we design a novel uncertainty modeling framework for self-explaining networks, which not only demonstrates strong distribution-free uncertainty modeling performance for the generated explanations in the interpretation layer but also excels in producing efficient and effective prediction sets for the final predictions based on the informative high-level basis explanations. We perform the theoretical analysis for the proposed framework. Extensive experimental evaluation demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed uncertainty framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge