Ya Gao
Edit Knowledge, Not Just Facts via Multi-Step Reasoning over Background Stories
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Enabling artificial intelligence systems, particularly large language models, to integrate new knowledge and flexibly apply it during reasoning remains a central challenge. Existing knowledge editing approaches emphasize atomic facts, improving factual recall but often failing to integrate new information into a coherent framework usable across contexts. In this work, we argue that knowledge internalization is fundamentally a reasoning problem rather than a memorization problem. Consequently, a model should be trained in situations where the new information is instrumental to solving a task, combined with pre-existing knowledge, and exercised through multi-step reasoning. Based on this insight, we propose a training strategy based on three principles. First, new knowledge is introduced as a coherent background story that contextualizes novel facts and explains their relation to existing knowledge. Second, models are trained using self-generated multi-hop questions that require multi-step reasoning involving the new information. Third, training is done using knowledge distillation, forcing a student model to internalize the teacher's reasoning behavior without access to the novel information. Experiments show that models trained with this strategy effectively leverage newly acquired knowledge during reasoning and achieve remarkable performance on challenging questions that require combining multiple new facts.
DCG ReID: Disentangling Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle Re-Identification
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal vehicle Re-Identification (ReID) aims to leverage complementary information from RGB, Near Infrared (NIR), and Thermal Infrared (TIR) modalities to retrieve the same vehicle. The challenges of multi-modal vehicle ReID arise from the uncertainty of modality quality distribution induced by inherent discrepancies across modalities, resulting in distinct conflicting fusion requirements for data with balanced and unbalanced quality distributions. Existing methods handle all multi-modal data within a single fusion model, overlooking the different needs of the two data types and making it difficult to decouple the conflict between intra-class consistency and inter-modal heterogeneity. To this end, we propose Disentangle Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle ReID (DCG-ReID). Specifically, to disentangle heterogeneous quality-distributed modal data without mutual interference, we first design the Dynamic Confidence-based Disentangling Weighting (DCDW) mechanism: dynamically reweighting three-modal contributions via interaction-derived modal confidence to build a disentangled fusion framework. Building on DCDW, we develop two scenario-specific fusion strategies: (1) for balanced quality distributions, Collaboration Fusion Module (CFM) mines pairwise consensus features to capture shared discriminative information and boost intra-class consistency; (2) for unbalanced distributions, Guidance Fusion Module (GFM) implements differential amplification of modal discriminative disparities to reinforce dominant modality advantages, guide auxiliary modalities to mine complementary discriminative info, and mitigate inter-modal divergence to boost multi-modal joint decision performance. Extensive experiments on three multi-modal ReID benchmarks (WMVeID863, MSVR310, RGBNT100) validate the effectiveness of our method. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Adaptive Residual-Update Steering for Low-Overhead Hallucination Mitigation in Large Vision Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) often suffer from object hallucination, generating text inconsistent with visual inputs, which can critically undermine their reliability. Existing inference-time interventions to mitigate this issue present a challenging trade-off: while methods that steer internal states or adjust output logits can be effective, they often incur substantial computational overhead, typically requiring extra forward passes. This efficiency bottleneck can limit their practicality for real-world, latency-sensitive deployments. In this work, we aim to address this trade-off with Residual-Update Directed DEcoding Regulation (RUDDER), a low-overhead framework that steers LVLMs towards visually-grounded generation. RUDDER is built on two key innovations: (1) Contextual Activation Residual Direction (CARD) vector, a per-sample visual evidence vector extracted from the residual update of a self-attention layer during a single, standard forward pass. (2) A Bayesian-inspired adaptive gate that performs token-wise injection, applying a corrective signal whose strength is conditioned on the model's deviation from the visual context. Extensive experiments on key hallucination benchmarks, including POPE and CHAIR, indicate that RUDDER achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art methods while introducing negligible computational latency, validating RUDDER as a pragmatic and effective approach for improving LVLMs' reliability without a significant compromise on efficiency.
Memento No More: Coaching AI Agents to Master Multiple Tasks via Hints Internalization
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:As the general capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) agents continue to evolve, their ability to learn to master multiple complex tasks through experience remains a key challenge. Current LLM agents, particularly those based on proprietary language models, typically rely on prompts to incorporate knowledge about the target tasks. This approach does not allow the agent to internalize this information and instead relies on ever-expanding prompts to sustain its functionality in diverse scenarios. This resembles a system of notes used by a person affected by anterograde amnesia, the inability to form new memories. In this paper, we propose a novel method to train AI agents to incorporate knowledge and skills for multiple tasks without the need for either cumbersome note systems or prior high-quality demonstration data. Our approach employs an iterative process where the agent collects new experiences, receives corrective feedback from humans in the form of hints, and integrates this feedback into its weights via a context distillation training procedure. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach by implementing it in a Llama-3-based agent which, after only a few rounds of feedback, outperforms advanced models GPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 in a taskset requiring correct sequencing of information retrieval, tool use, and question answering.
Hypergraph Multi-modal Large Language Model: Exploiting EEG and Eye-tracking Modalities to Evaluate Heterogeneous Responses for Video Understanding
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Understanding of video creativity and content often varies among individuals, with differences in focal points and cognitive levels across different ages, experiences, and genders. There is currently a lack of research in this area, and most existing benchmarks suffer from several drawbacks: 1) a limited number of modalities and answers with restrictive length; 2) the content and scenarios within the videos are excessively monotonous, transmitting allegories and emotions that are overly simplistic. To bridge the gap to real-world applications, we introduce a large-scale \textbf{S}ubjective \textbf{R}esponse \textbf{I}ndicators for \textbf{A}dvertisement \textbf{V}ideos dataset, namely SRI-ADV. Specifically, we collected real changes in Electroencephalographic (EEG) and eye-tracking regions from different demographics while they viewed identical video content. Utilizing this multi-modal dataset, we developed tasks and protocols to analyze and evaluate the extent of cognitive understanding of video content among different users. Along with the dataset, we designed a \textbf{H}ypergraph \textbf{M}ulti-modal \textbf{L}arge \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{M}odel (HMLLM) to explore the associations among different demographics, video elements, EEG and eye-tracking indicators. HMLLM could bridge semantic gaps across rich modalities and integrate information beyond different modalities to perform logical reasoning. Extensive experimental evaluations on SRI-ADV and other additional video-based generative performance benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The codes and dataset will be released at \url{https://github.com/suay1113/HMLLM}.
Query-Guided Self-Supervised Summarization of Nursing Notes
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Nursing notes, an important component of Electronic Health Records (EHRs), keep track of the progression of a patient's health status during a care episode. Distilling the key information in nursing notes through text summarization techniques can improve clinicians' efficiency in understanding patients' conditions when reviewing nursing notes. However, existing abstractive summarization methods in the clinical setting have often overlooked nursing notes and require the creation of reference summaries for supervision signals, which is time-consuming. In this work, we introduce QGSumm, a query-guided self-supervised domain adaptation framework for nursing note summarization. Using patient-related clinical queries as guidance, our approach generates high-quality, patient-centered summaries without relying on reference summaries for training. Through automatic and manual evaluation by an expert clinician, we demonstrate the strengths of our approach compared to the state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) in both zero-shot and few-shot settings. Ultimately, our approach provides a new perspective on conditional text summarization, tailored to the specific interests of clinical personnel.
SynerMix: Synergistic Mixup Solution for Enhanced Intra-Class Cohesion and Inter-Class Separability in Image Classification
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:To address the issues of MixUp and its variants (e.g., Manifold MixUp) in image classification tasks-namely, their neglect of mixing within the same class (intra-class mixup) and their inadequacy in enhancing intra-class cohesion through their mixing operations-we propose a novel mixup method named SynerMix-Intra and, building upon this, introduce a synergistic mixup solution named SynerMix. SynerMix-Intra specifically targets intra-class mixup to bolster intra-class cohesion, a feature not addressed by current mixup methods. For each mini-batch, it leverages feature representations of unaugmented original images from each class to generate a synthesized feature representation through random linear interpolation. All synthesized representations are then fed into the classification and loss layers to calculate an average classification loss that significantly enhances intra-class cohesion. Furthermore, SynerMix combines SynerMix-Intra with an existing mixup approach (e.g., MixUp, Manifold MixUp), which primarily focuses on inter-class mixup and has the benefit of enhancing inter-class separability. In doing so, it integrates both inter- and intra-class mixup in a balanced way while concurrently improving intra-class cohesion and inter-class separability. Experimental results on six datasets show that SynerMix achieves a 0.1% to 3.43% higher accuracy than the best of either MixUp or SynerMix-Intra alone, averaging a 1.16% gain. It also surpasses the top-performer of either Manifold MixUp or SynerMix-Intra by 0.12% to 5.16%, with an average gain of 1.11%. Given that SynerMix is model-agnostic, it holds significant potential for application in other domains where mixup methods have shown promise, such as speech and text classification. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/wxitxy/synermix.git.
GCOF: Self-iterative Text Generation for Copywriting Using Large Language Model
Feb 21, 2024
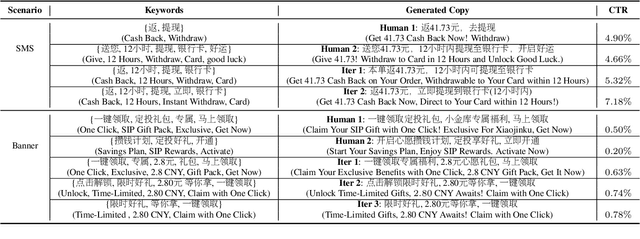
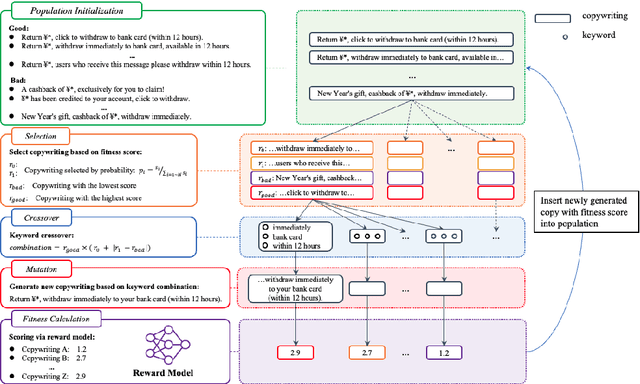
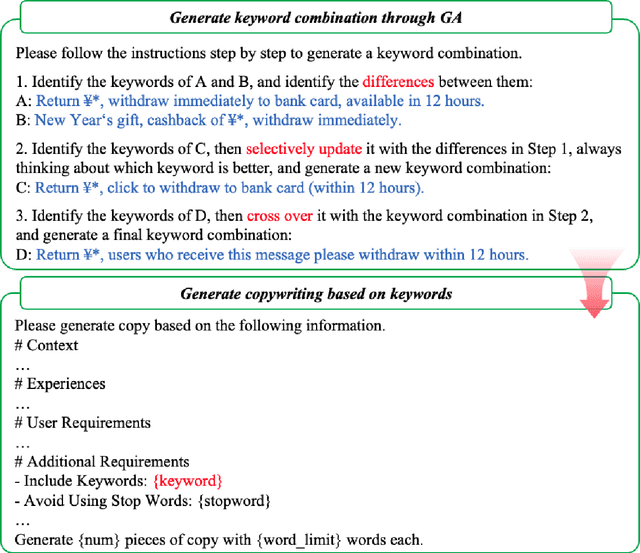
Abstract:Large language models(LLM) such as ChatGPT have substantially simplified the generation of marketing copy, yet producing content satisfying domain specific requirements, such as effectively engaging customers, remains a significant challenge. In this work, we introduce the Genetic Copy Optimization Framework (GCOF) designed to enhance both efficiency and engagememnt of marketing copy creation. We conduct explicit feature engineering within the prompts of LLM. Additionally, we modify the crossover operator in Genetic Algorithm (GA), integrating it into the GCOF to enable automatic feature engineering. This integration facilitates a self-iterative refinement of the marketing copy. Compared to human curated copy, Online results indicate that copy produced by our framework achieves an average increase in click-through rate (CTR) of over $50\%$.
Knowledge-augmented Graph Neural Networks with Concept-aware Attention for Adverse Drug Event Detection
Jan 25, 2023
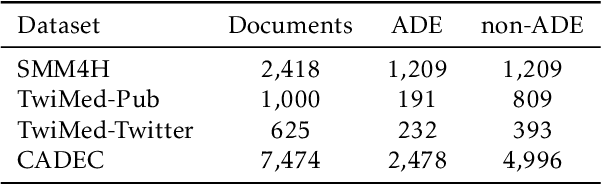
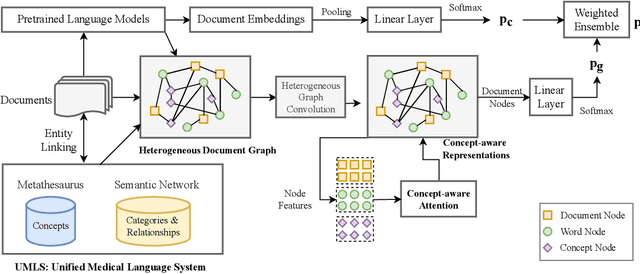
Abstract:Adverse drug events (ADEs) are an important aspect of drug safety. Various texts such as biomedical literature, drug reviews, and user posts on social media and medical forums contain a wealth of information about ADEs. Recent studies have applied word embedding and deep learning -based natural language processing to automate ADE detection from text. However, they did not explore incorporating explicit medical knowledge about drugs and adverse reactions or the corresponding feature learning. This paper adopts the heterogenous text graph which describes relationships between documents, words and concepts, augments it with medical knowledge from the Unified Medical Language System, and proposes a concept-aware attention mechanism which learns features differently for the different types of nodes in the graph. We further utilize contextualized embeddings from pretrained language models and convolutional graph neural networks for effective feature representation and relational learning. Experiments on four public datasets show that our model achieves performance competitive to the recent advances and the concept-aware attention consistently outperforms other attention mechanisms.
Network-Scale Traffic Modeling and Forecasting with Graphical Lasso and Neural Networks
Dec 25, 2017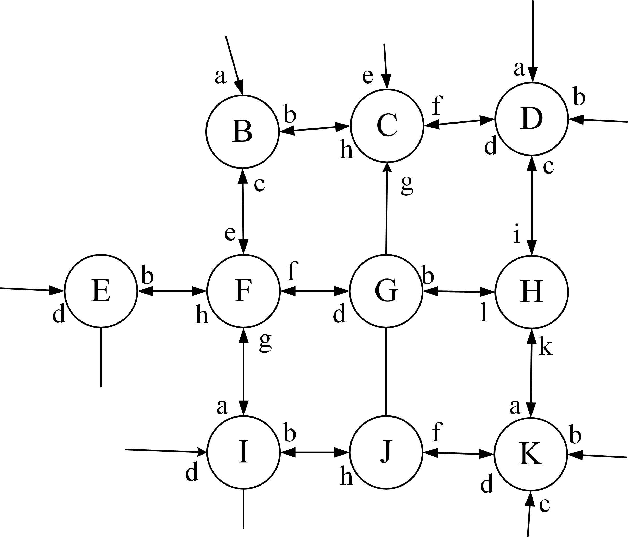
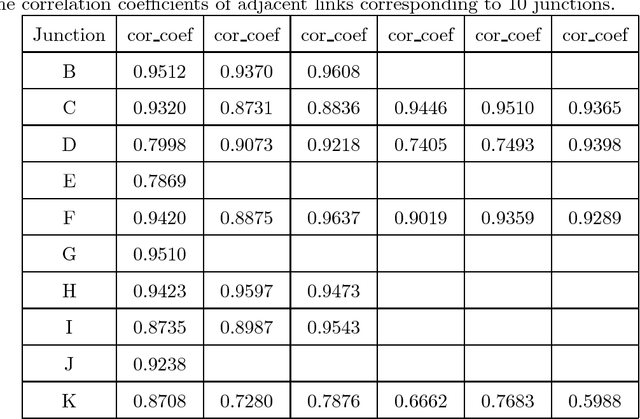
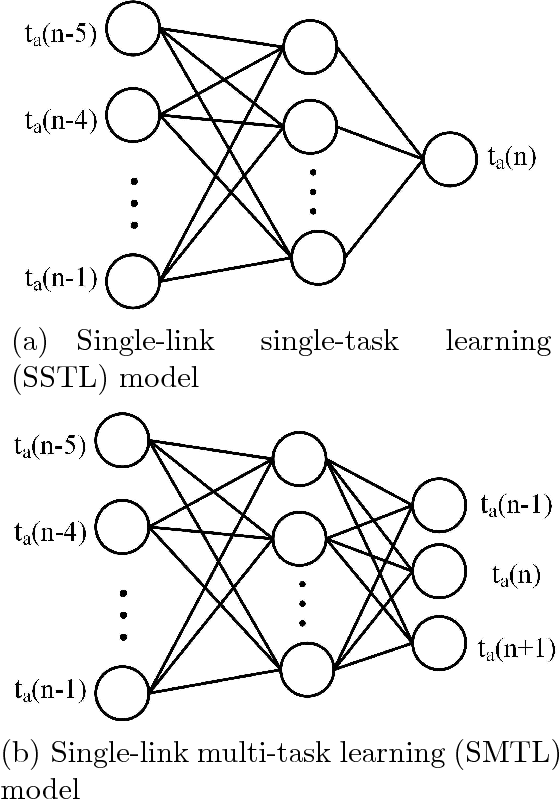
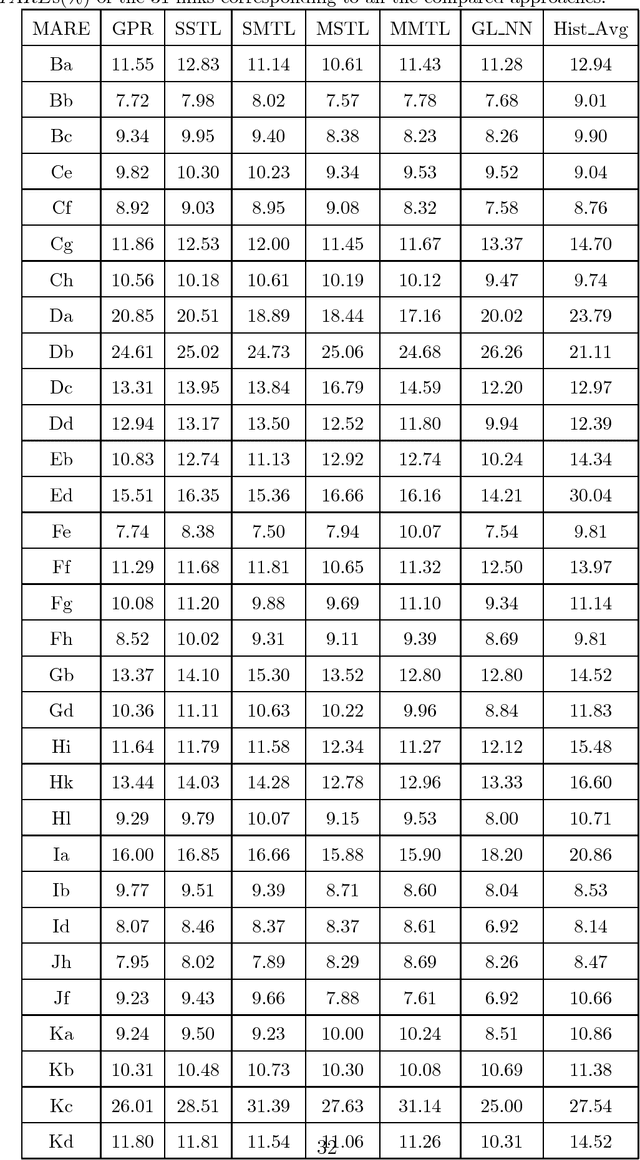
Abstract:Traffic flow forecasting, especially the short-term case, is an important topic in intelligent transportation systems (ITS). This paper does a lot of research on network-scale modeling and forecasting of short-term traffic flows. Firstly, we propose the concepts of single-link and multi-link models of traffic flow forecasting. Secondly, we construct four prediction models by combining the two models with single-task learning and multi-task learning. The combination of the multi-link model and multi-task learning not only improves the experimental efficiency but also the prediction accuracy. Moreover, a new multi-link single-task approach that combines graphical lasso (GL) with neural network (NN) is proposed. GL provides a general methodology for solving problems involving lots of variables. Using L1 regularization, GL builds a sparse graphical model making use of the sparse inverse covariance matrix. In addition, Gaussian process regression (GPR) is a classic regression algorithm in Bayesian machine learning. Although there is wide research on GPR, there are few applications of GPR in traffic flow forecasting. In this paper, we apply GPR to traffic flow forecasting and show its potential. Through sufficient experiments, we compare all of the proposed approaches and make an overall assessment at last.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge